Chapter 18, Lesson 4: Leukocytes
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards from Chapter 18, Lesson 4 of McGraw Hill Anatomy and Physiology, Ninth Edition, by Kenneth S. Saladin.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Leukocytes
Another name for white blood cells, they are the least abundant and protect against disease and infection
Granulocytes
White blood cells with specific granules; these include neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils
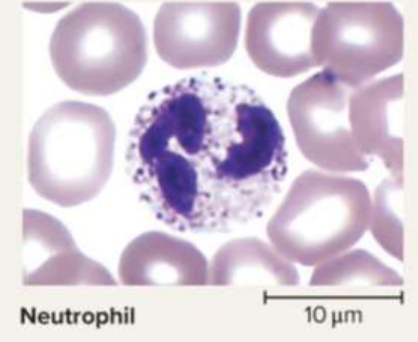
Neutrophils
A type of granulocyte making up 60% to 70% of leukocytes with anti-bacterial and antimicrobial properties
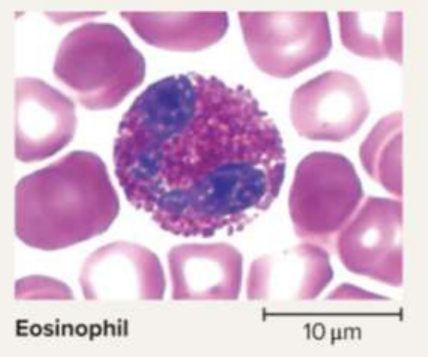
Eosinophils
A type of granulocyte with daily, seasonal, and menstrual fluctuations to counter abnormal conditions
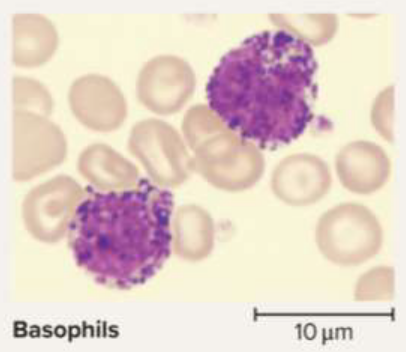
Basophils
A type of granulocyte that aids in clotting with histamine (speeds flow of blood) and heparin (anticoagulant)
Agranulocytes
White blood cells that lack specific granules; these include lymphocytes and monocytes
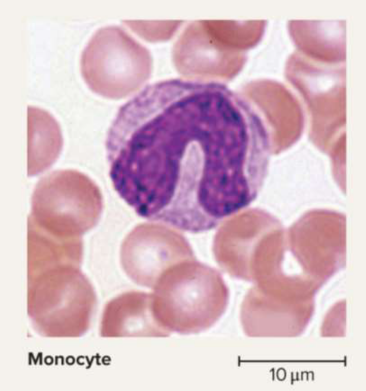
Monocytes
A type of agranulocyte; is the largest type of leukocyte with kidney or horseshoe-shaped nucleus with phagocytization abilities for infections
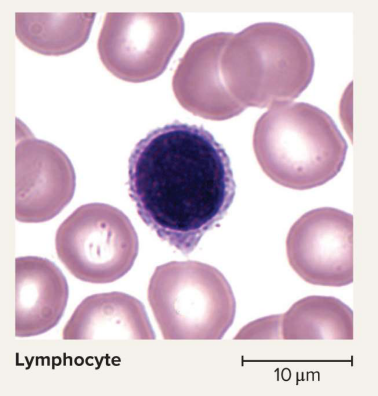
Lymphocytes
A type of agranulocyte with a dark violet nucleus; destroys infections or responds to cancer and infected cells with antigens
Leukopoiesis
The production of white blood cells starting with stem cells in the red bone marrow
Granulocyte life span
Leave after 4-8 hours and live 4-5 days
Monocyte life span
Leave after 20 hours and live a few years
Lymphocyte life span
Live for decades with continuous reclamation
Leukopenia
Low leukocyte count (<5000 per microliter) caused by radiation, disease, or poison, causing higher infection rates
Leukocytosis
High leukocyte count (>10000 per microliter) caused by infection, allergies, or disease
Differential WBC count
Identifies percentage of each type of leukocyte

Leukemia
Cancer of blood-producing tissue causing many leukocytes; can disrupt cell balances and clotting
Myeloid leukemia
Uncontrolled granulocyte production
Lymphoid leukemia
Uncontrolled lymphocyte and monocyte production
Acute leukemia
Sudden appearance with rapid production, death within months
Chronic leukemia
Undetected for months with 3 year survival time
Complete blood count
Profile of data on hematocrit, hemoglobin, WBC data, and RBC data