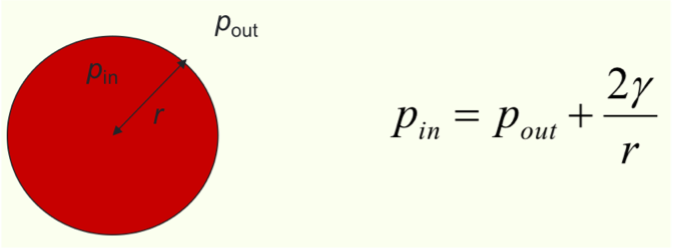ideal gas law and IMF
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What 2 things does the ideal gas law assume?
particles are point masses with no volume
there are no forces between molecules
How does the ideal gas law not account for volume of gas particles?
behaviour deviates at small volumes, high pressures
real gases have finite volume, reduces the space available for compression
Problems caused by IMF for ideal gas law
at short intermolecular separation there will be repulsion between particles (Pauli exclusion)
IMF forces slow down molecules which reduces the frequency of collisions with the container = reduces pressure
What is Van der Waals equation?
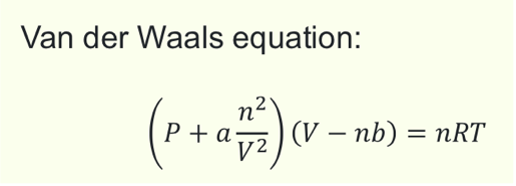
What 3 things affect the values of a in Van der Waals equation?
dipole moment
polarisability
ionisation energy
What does dipole moment mean?
how big the dipole is, the difference in electronegativity
What does polarisability mean?
how easy for induced dipole to form
What is the Lennard Jones potential graph?
potential energy of interaction vs separation
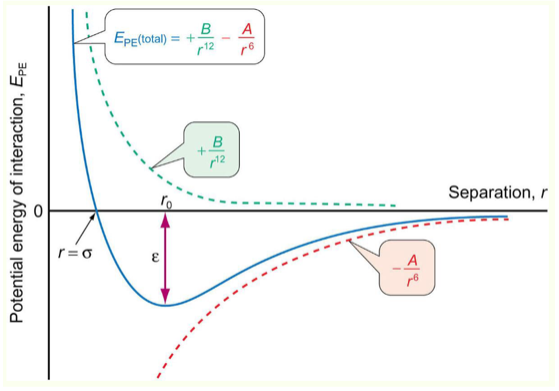
Why does Lennard Jones potential graph never cross the y axis?
can’t put two atoms directly touching
limit to how close atoms can be
What does ε represent in Lennard Jones Potential graph?
What does minimum represent?
ε represents how strong interactions are between molecules (how deep graph is)
most attraction, most potential energy
What does σ represent in Lennard Jones Potential graph?
as close as they can be, above that they are being forced together
x intercept
How to calculate force from Lennard Jones Potential graph?
gradient using F = - dE / dr
steeper gradient = stronger force
What is r0 in Lennard Jones Potential graph?
equilibrium point where attraction = repulsion
At what temperatures does the ideal gas equation break down?
low temperatures, particularly at high pressures
What happens at lower temperatures (energy)?
less translational energy (energy used to move) = slower molecules = stronger attractive forces (have more time to move past each other)
What happens at higher temperatures (speed)?
a gas has a higher average speed and broader distribution of speeds
How do phases change at
low temp
high pressure
low temp = strong interactions between molecules form condense phase
high pressure = gas turns into liquid as molecules are held so closely together
What does enthalpy change mean?
The amount of heat transferred at constant pressure
What is an isotherm?
A graph plotted at constant temperature
Why is ice less dense than water?
Hydrogen bonds hold water molecules apart in a lattice when solid
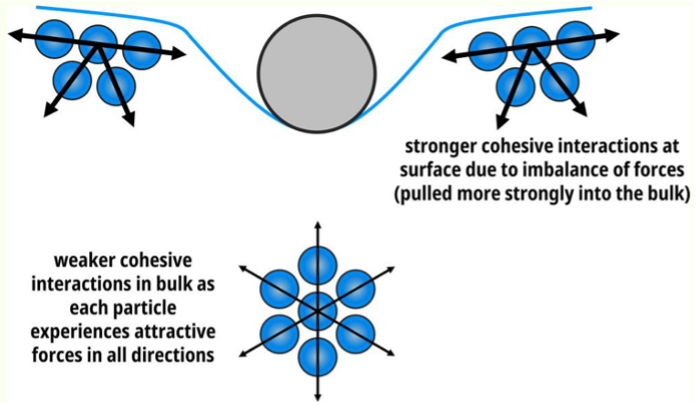
Why are there stronger interactions at the surface of a liquid?
Why weaker interactions in the bulk of liquid?
imbalance of forces = pulled more strongly into middle
weaker interactions in the bulk as each particle experiences attractive forces in all directions
Why does water form larger meniscus than other liquids?
larger surface tension = hydrogen bonding means larger force of attraction at surface
What is capillary action?
some liquids rise up thin tubes against gravity
Why does the meniscus appear concave?
H bonds between water and SiO2 (in glass) are stronger than surface tension
How does surface tension contribute to droplet size?
Equation?
liquids with stronger IMF form larger droplets
𝛾 = surface tension