Second Urinary Exam
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
How will the body compensate when water loss is greater than water gain, such as excessive vomiting or diarrhea? Select all that apply.
increased antidiuretic hormone release to increase blood pressure
Aquaporin-2 channels embed into the apical membrane to increase facultative water resorption
Increased sodium reabsorption, so that water follows
In normal, healthy kidneys ____ are not filtered, however if they were to get past the filtration membrane, this would ______ filtration.
plasma proteins; increase
Which portion of the nephron does NOT have aquaporin channels?
Ascending loop of Henle
Which of the following allows for the process of filtration? Select all that apply.
Fenestrations in the endothelial cells causing them to be leakier than systemic capillaries
The afferent arteriole is wider in diameter than the efferent arteriole
Slits between podocytes allow material from the blood plasma to enter Bowman’s space
Which of the following is true regarding the male and female urethrae? Select all that apply.
The female urethra has one function, but the male urethra serves two functions
Stratified squamous epithelium will be found where it meets the external environment to protect against abrasion
Which of the following statements are true for BOTH the myogenic mechanism and tubuloglomerular feedback?
increased mean arterial pressure will ultimately lead to vasoconstriction of the afferent arteriole
True or False: The segmental veins drain blood from the interlobar veins into the renal veins.
False
True or False: Urea is both reabsorbed and secreted along the renal tubule.
True
You are an investigator measuring the effect of a new drug (Nephrotox) on renal function. Given the following rates, what must be true?
Filtered: 65 mg/hour
Excreted: 100 mg/hour
Nephrotox is secreted at a rate of 35 mg/hour
True or False: The renal corpuscle is comprised of the glomerulus and the proximal convoluted tubule.
False
Which of the following transports urine from the renal pelvis to the urinary bladder?
ureter
Which of the following is located most inferiorly?
internal urethral sphincter
What will result in vasodilation of the afferent glomerular arterioles?
nitric oxide release from the JGA
The glomerular capillaries differ from most other capillary networks in the body because they:
empty into an efferent arteriole instead of a venule
Which of the following sets of transport mechanisms are used for glucose movement in the proximal convoluted tubule?
secondary active transport via a symporter with sodium & facilitated diffusion
Which parameter of the blood is NOT regulated by the kidneys?
Leukocyte production
Match each part of the micturition reflex with the appropriate description.
→ Stimulus
increased stretch of the urinary bladder
Match each part of the micturition reflex with the appropriate description. → Central integration
spinal cord
Match each part of the micturition reflex with the appropriate description.→ Autonomic efferent
Relaxation of the internal urethral sphincter
Match each part of the micturition reflex with the appropriate description. → somatic efferent
relaxation of the external urethral sphincter
Using the values in the image below, calculate net filtration pressure:
15 mmHg
Out of the three pressures depicted in the image, which one is directly affected by mean arterial pressure? (provide the name, not the number, and do not abbreviate)
glomerular hydrostatic pressure
Are you favoring or opposing filtration in this example?
favoring
An increase in blood volume and mean arterial pressure will cause the superior chambers of the heart to stretch stimulating the secretion of __________ . This will decrease _______ and water reabsorption at the ____________ resulting in diuresis. Subsequently, blood volume _________returning mean arterial pressure to a normal range.
atrial natriuretic peptide
sodium
PCT and Loop of Henle
decreases
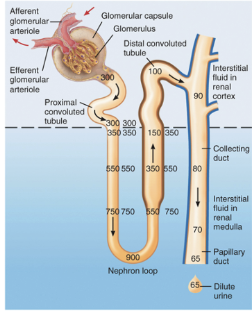
What type of nephron is shown for "A" and how do you know?
Cortical nephron, due to the shorter Loop of Henle within the renal medulla
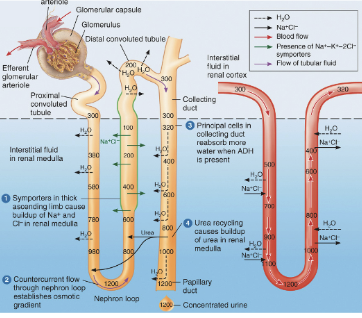
Which nephron contains aquaporin-2 channels on the apical membrane and where would these be located specifically?
Nephron B, proximal convoluted tubule & collecting ducts
Someone celebrates their 21st birthday by taking 21 successive shots of plain, good old-fashioned water, because they aren't interested in drinking alcohol. Which of the following will best describe their urine?
Low osmolarity
Match the substance with where it is produced and secreted from. → Renin
Juxaglomerular cells
Match the substance with where it is produced and secreted from. → Antidiuretic hormone
pituitary gland
Match the substance with where it is produced and secreted from. → Aldosterone
Adrenal gland
Match the substance with where it is produced and secreted from. → Angiotensinogen
Liver
You are working as a research scientist in a molecular genetics lab. You accidentally discovered a new mutation in apical aquaporin-1 channels, which causes them to work improperly. What effect would this have on renal function?
________ will not be possible at the ________, _______-urine output and forming _______ urine.
obligatory water reabsorption
descending limb of the loop of Henle
increasing
dilute
Match the parameter with the best description.
The result of subtracting pressures that oppose filtration from the pressures that favor filtration
Net filtration pressure
Match the parameter with the best description.
Volume of plasma filtered by all renal corpuscles over a period of time
glomerular filtration rate
Match the parameter with the best description.
When this parameter is between 80-180 mmHg, filtration will remain relatively constant due to tightly controlled homeostatic mechanisms
mean arterial pressure
Match the parameter with the best description.
This parameter is the result of plasma proteins present within the glomerular capillary
blood colloid osmotic pressure
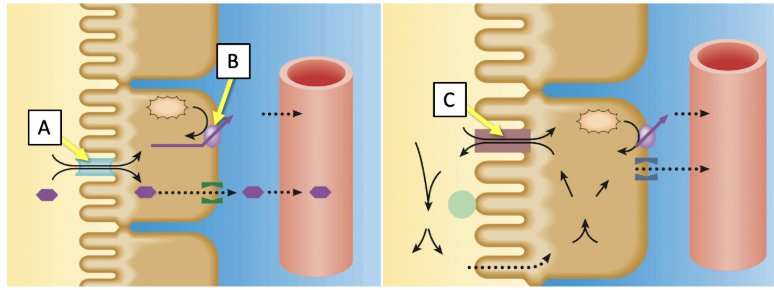
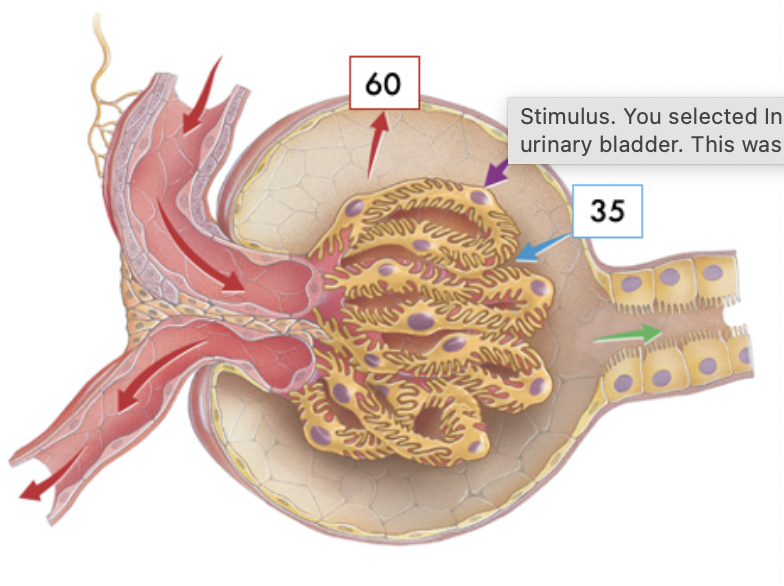
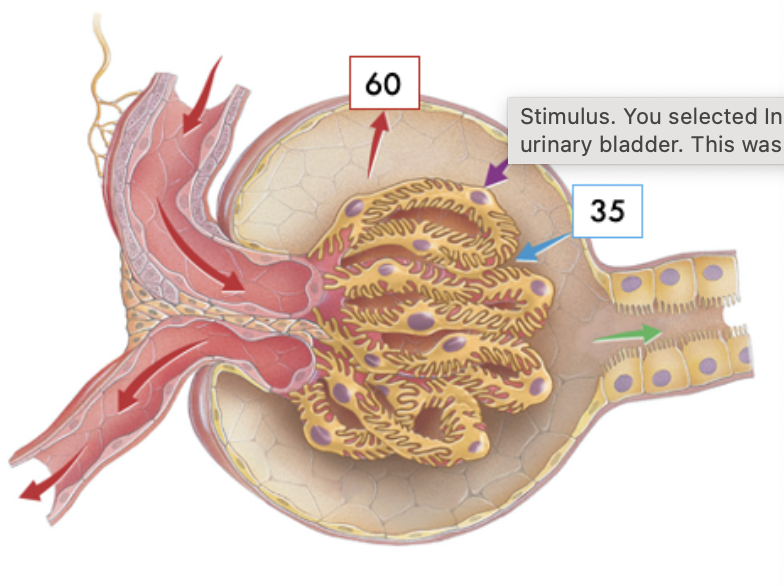
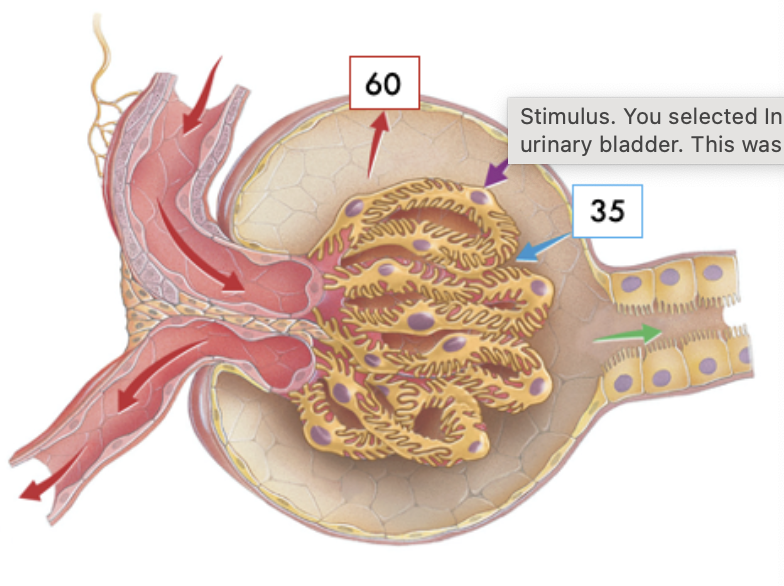
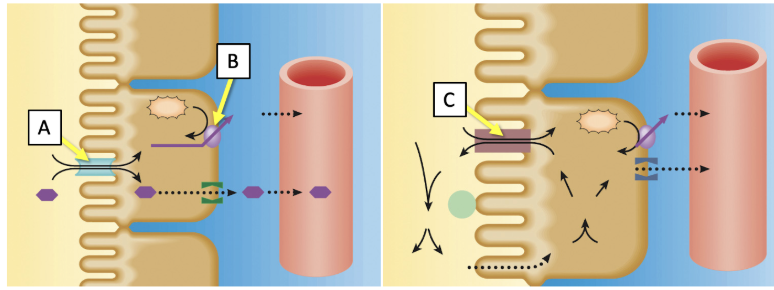
Match the transporters indicated in the image with the best description. (Answers may be used more than once.)
Located on the apical surface of the tubular epithelial cell
A and C only
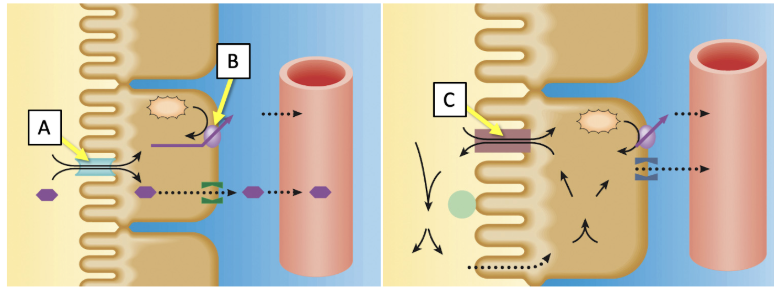
Match the transporters indicated in the image with the best description. (Answers may be used more than once.)
Reabsorption of two substances via a symporter
A only
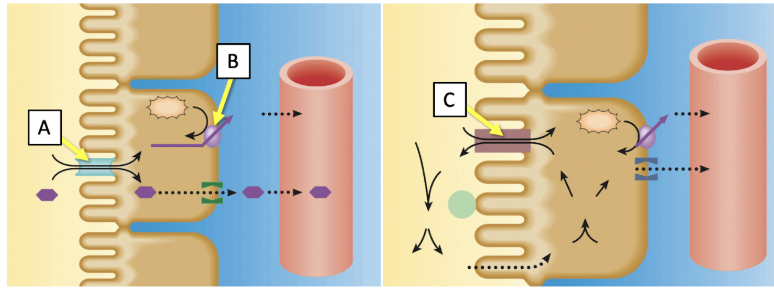
Match the transporters indicated in the image with the best description. (Answers may be used more than once.)
Primary active transport driven by the hydrolysis of ATP
B only
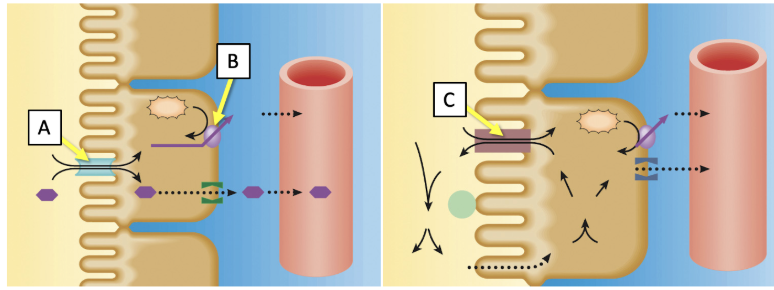
Match the transporters indicated in the image with the best description. (Answers may be used more than once.)
Transcellular route where movement is occurring actively across tubular epithelial cells
A,B and C
Match the transporters indicated in the image with the best description. (Answers may be used more than once.)
Paracellular route where movement is occurring passively between tubular epithelial cells
Neither A,B, or C
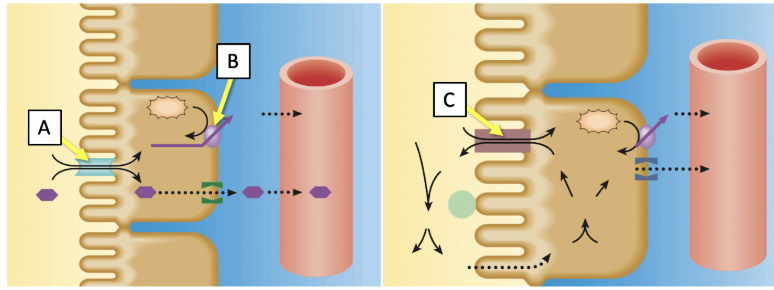
Match the transporters indicated in the image with the best description. (Answers may be used more than once.)
Located on the basolateral membrane of the tubular epithelial cells
B only
You are dissecting the kidneys in the cadaver lab, having the time of your life. The [ Select ] cavity is already exposed, and you move the gastrointestinal organs to better visualize the posterior wall.
Moving superficial to deep: you use your best tools (your hands) to remove the [ Select ] lining the inside of this cavity. Next, you remove the [ Select ], a layer of dense irregular connective tissue that is anchoring the kidneys in place, and then the [ Select ], the adipose tissue providing a great amount of cushion and protection to the vulnerable kidneys.
You then expose the kidneys and want to make a section to view internal anatomy. Your scalpel will move through the following layers:[ Select ] [ Select ], [ Select ]
You want to keep the structures at the hilum of the kidney intact, which is where the [ Select ] emerge.
abdominal
parietal peritoneum
renal fascia
peritoneal fat capsule
fibrous capsule
renal cortex
renal medulla
renal artery, renal vein and ureter
Read the following scenario and answer the associated questions. Do not abbreviate your answers and be as specific as possible.
You are a firefighter/paramedic called to a scene of an accidental amputation. The patient was working late in his woodshop and severed his right hand, causing him to hemorrhage severe amounts of blood. Describe the homeostatic mechanisms that were triggered by this unfortunate accident.
A dramatic loss of blood volume leads to a(n) ______in blood pressure, and activates the ______ nervous system.
decrease
sympathetic
Read the following scenario and answer the associated questions. Do not abbreviate your answers and be as specific as possible.
You are a firefighter/paramedic called to a scene of an accidental amputation. The patient was working late in his woodshop and severed his right hand, causing him to hemorrhage severe amounts of blood. Describe the homeostatic mechanisms that were triggered by this unfortunate accident.
This nervous system activation results in vasoconstriction of the _______ arteriole, which will decrease _______ and urine output to restore blood volume and blood pressure.
afferent
glomerular filtration rate
Read the following scenario and answer the associated questions. Do not abbreviate your answers and be as specific as possible.
You are a firefighter/paramedic called to a scene of an accidental amputation. The patient was working late in his woodshop and severed his right hand, causing him to hemorrhage severe amounts of blood. Describe the homeostatic mechanisms that were triggered by this unfortunate accident.
In addition, ______will be released from the kidney, leading to the conversion of angiotensinogen to angiotensin I, which will be activated to angiotensin II by ______ from the lungs. Angiotensin II will act on the nephron to increase the reabsorption of solutes, so water follows to restore blood volume and blood pressure.
renin
angiotensin converting enzyme
Read the following scenario and answer the associated questions. Do not abbreviate your answers and be as specific as possible.
You are a firefighter/paramedic called to a scene of an accidental amputation. The patient was working late in his woodshop and severed his right hand, causing him to hemorrhage severe amounts of blood. Describe the homeostatic mechanisms that were triggered by this unfortunate accident.
After stabilizing the patient, you learn that the reason behind his accident was indulging in one too many yellow beers before turning on the bandsaw. Alcohol inhibits the release of _____ , and this inhibition will affect the DCT & CD by decreasing ______ water reabsorption to ultimately decrease urine output.
antidiuretic hormone
facultative