Ch. 2 Weak acids (Biochemistry)
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
water has a small degree of __ (reversible)
ionization
ionization of water is crucial for
cellular functions
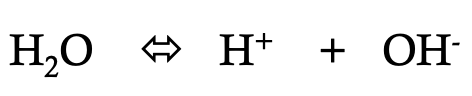
what is depicted on this image
ionization of water
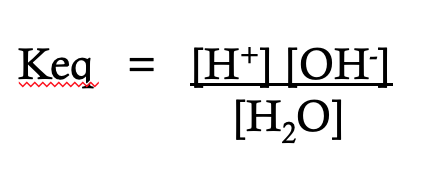
what is depicted on this image
the equilibrium constant of water
the equilibrium constant formula is __ over __
reactants; products
at room temperature (25C), what is the molality of H2O
Keq = 55.5M
what is the Kw (ion-product constant) of water
1 × 10-14
When [H+] = [OH-] = 1 X 10-7 , pH is
7, neutral
the ion production of water is the bases for
the pH scale
the pH formula is
pH= -log [H+]
pOH + pH =
14
pH affects the __ and __ of macromulecules
structure; activity
the more H there is in a solution, the less __ is in a solution
OH
the more OH there is in a solution, the less __ is in a solution
H
HCl and HNO3 are examples of
strong acids
strong acids __ ionize in a solution
completely
weak acids __ ionize in a solution
partially
KOH, NaOH are examples of
strong bases
bronsted acids are proton __
donor
bronsted bases are proton __
acceptors

what is depicted here
a bronsted acid and a brosnted base

HA represents
the conjugated acid

A- represents
a conjugated base
HA and A- are only different by _ proton
1
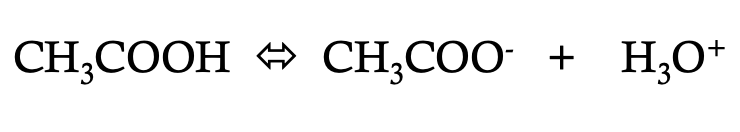
how would you write the Ka of
Ka = [CH3COO-] [H3O+]
[CH3COOH]
Ka is
dissociation (ionization) constant for a given acid when temperature is constant
The greater the Ka, the __ the acid
stronger
The smaller the Ka, the __ the acid
weaker (ka)
pKa formula, pKa=
-log(Ka)
the smaller the pKa, the __ the acid
stronger (pka)
the higher the pKa, the __ the acid
weaker
The pH of a solution is solely dependent on the __ of the conjugate acid and base
equilibrium concentrations
The__ of a solution is solely dependent on the equilibrium concentrations of the conjugate acid and base
pH
Henderson-Hasselback equation
pH = pKa + log [conj base]
[conj acid]
In the Henderson-Hasselback equation the pH is equal to the pKa + the log of the __ over the __
conjugated base; conjugated acid
when a base=acid
the pH=pKa
when the pKa=pH
a base=an acid
maximum buffering capacity is when
pH = pKa then a base=an acid
Henderson/Hasselback equation only applies to __ acids and bases
weak
the pKa of an acid is the pH at which and acid is__ ionized
half
since pKa of an acid is at a given temperature constant, the pH changes require changes in
base/acid
when pH less than pKa, the __ predominates
acid
when pH greater than pKa, the __ predominates
base
when the acid predominates
H+ is on
when the base predominates
H+ is off