Chapter 12 End of Chapter Questions (copy)
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Knowledge and Comprehension
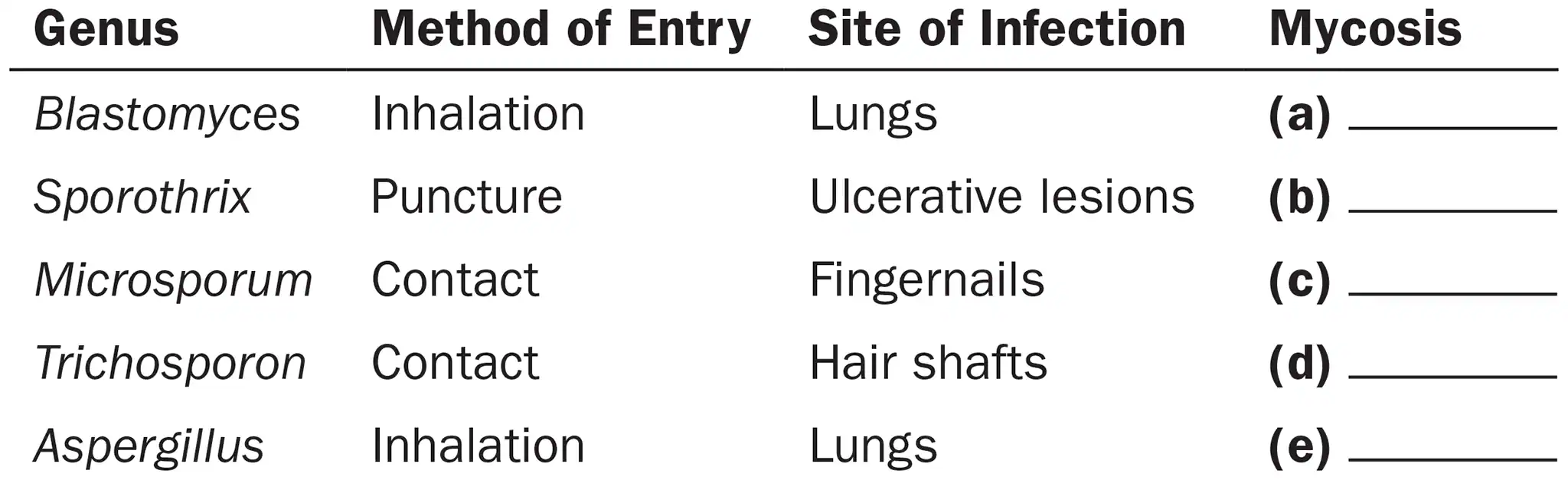
Following is a list of fungi, their methods of entry into the body, and sites of infections they cause. Categorize each type of mycosis as cutaneous, opportunistic, subcutaneous, superficial, or systemic.
Blastomyces
Systemic
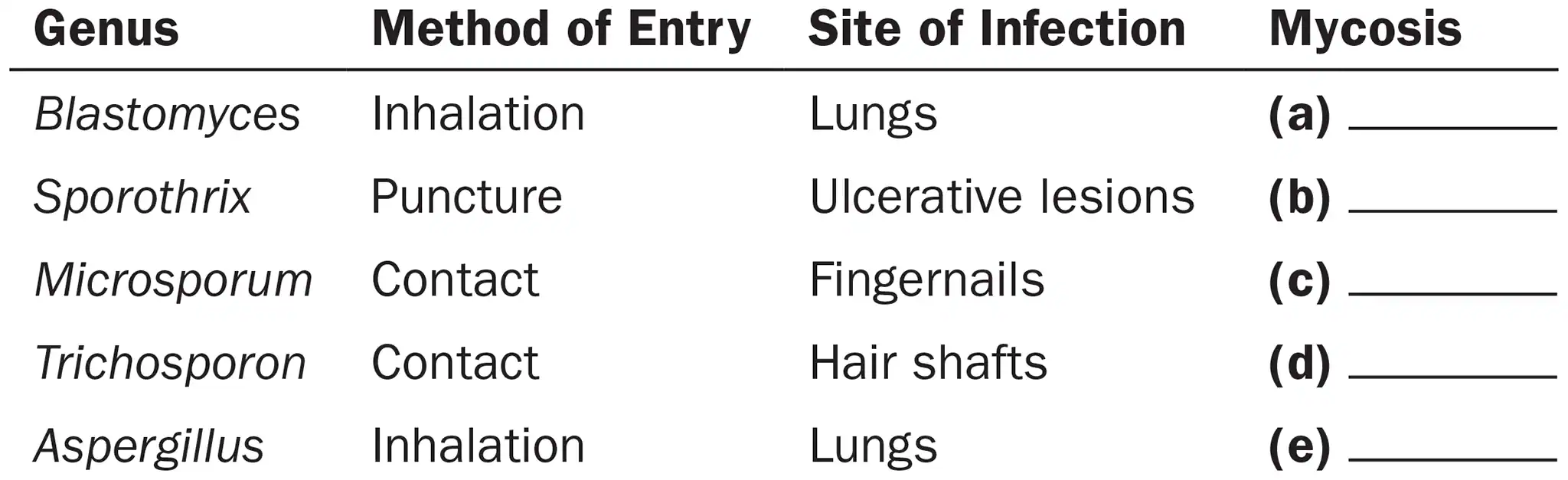
Following is a list of fungi, their methods of entry into the body, and sites of infections they cause. Categorize each type of mycosis as cutaneous, opportunistic, subcutaneous, superficial, or systemic.
Sporothrix
Subcutaneous
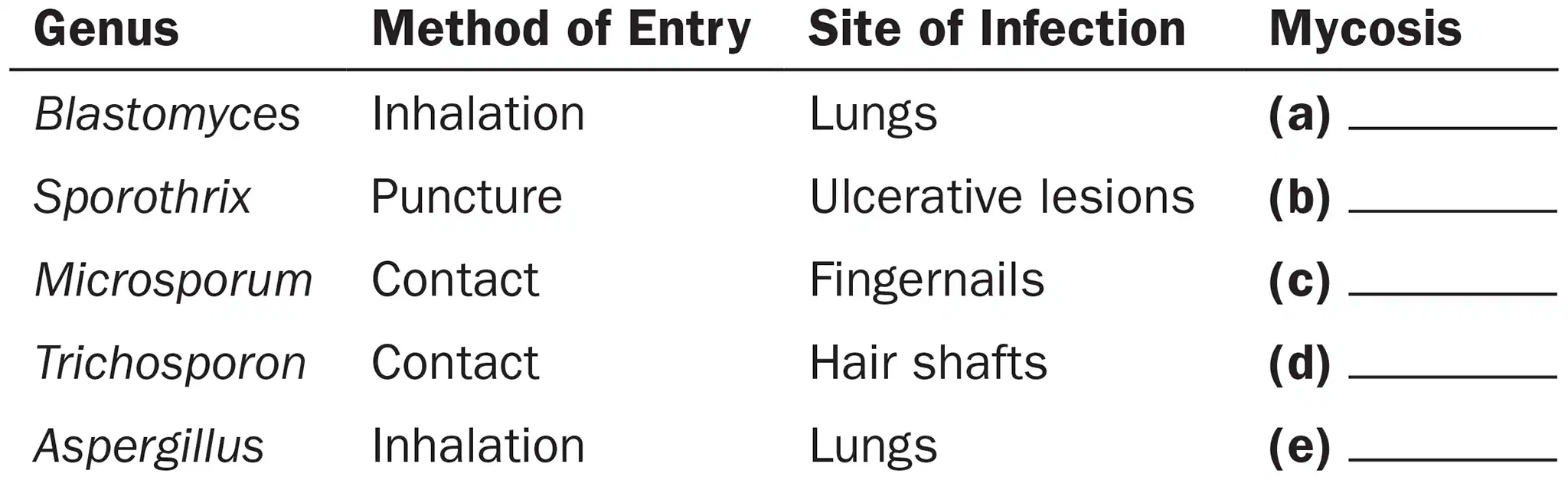
Following is a list of fungi, their methods of entry into the body, and sites of infections they cause. Categorize each type of mycosis as cutaneous, opportunistic, subcutaneous, superficial, or systemic.
Microsporum
Cutaneous
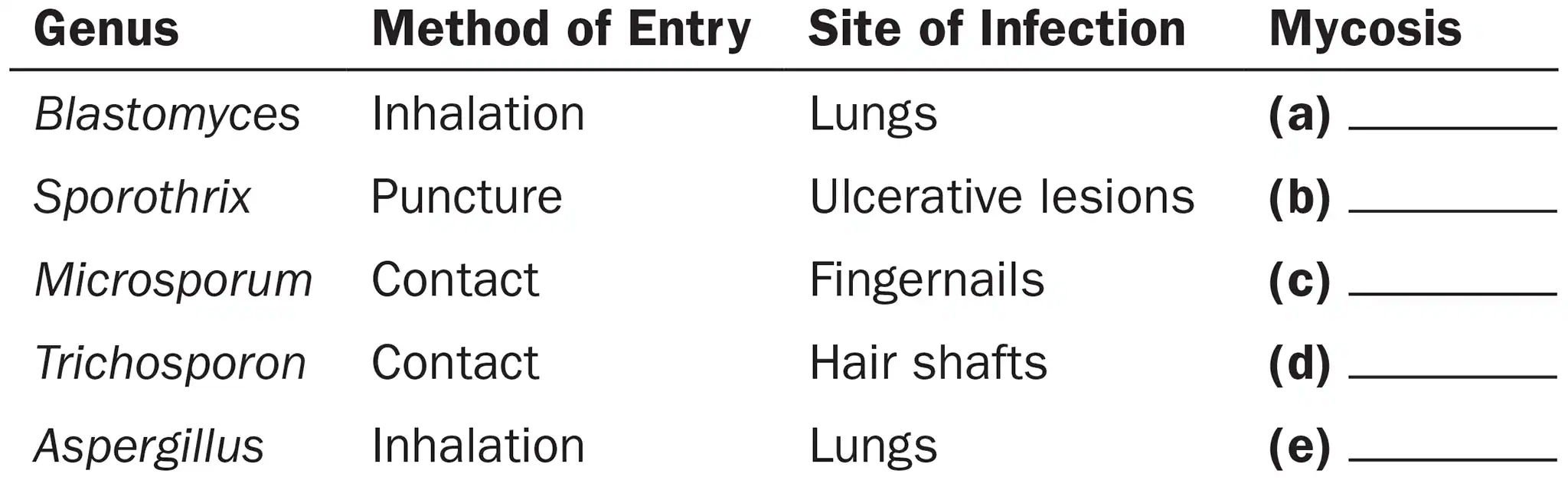
Following is a list of fungi, their methods of entry into the body, and sites of infections they cause. Categorize each type of mycosis as cutaneous, opportunistic, subcutaneous, superficial, or systemic.
Trichosporon
Superficial
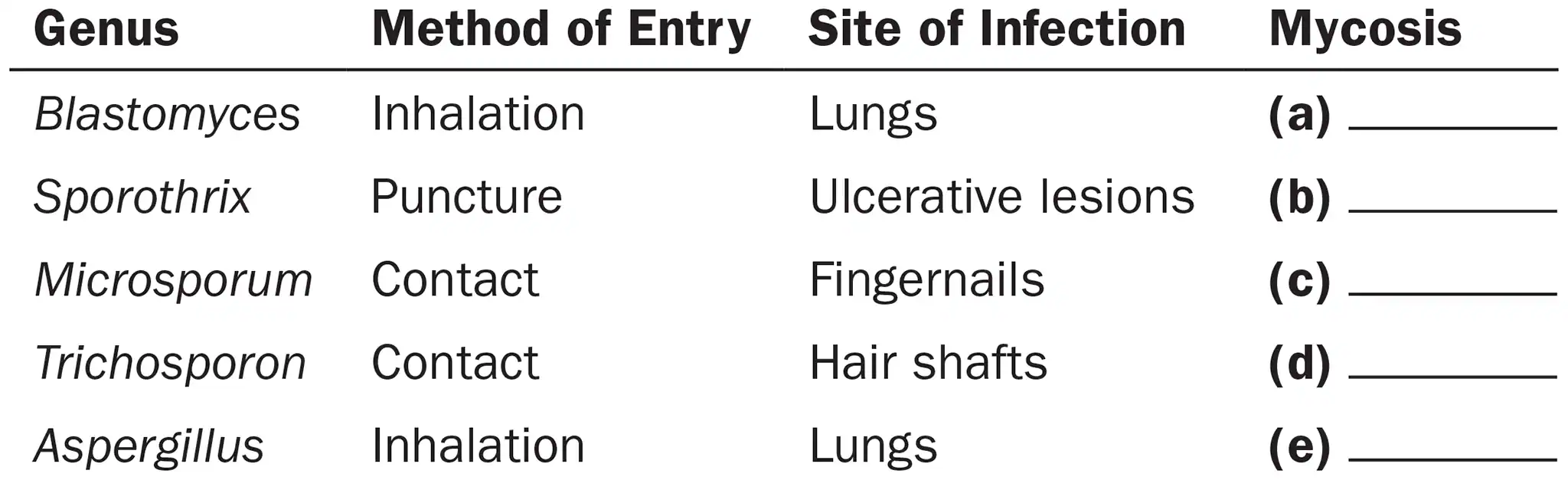
Following is a list of fungi, their methods of entry into the body, and sites of infections they cause. Categorize each type of mycosis as cutaneous, opportunistic, subcutaneous, superficial, or systemic.
Aspergillus
Systemic
A mixed culture of Escherichia coli and Penicillium chrysogenum is inoculated onto the following culture media. On which medium would you expect each to grow? Why?
0.5 % peptone in tap water
10% glucose in tap water
E. coli, E. coli can utilize peptone as a nitrogen and carbon source but fungi prefer carbohydrates for growth
P. chrysogenum, no nitrogen for E. coli growth while fungi thrive in high sugar + low nitrogen environments
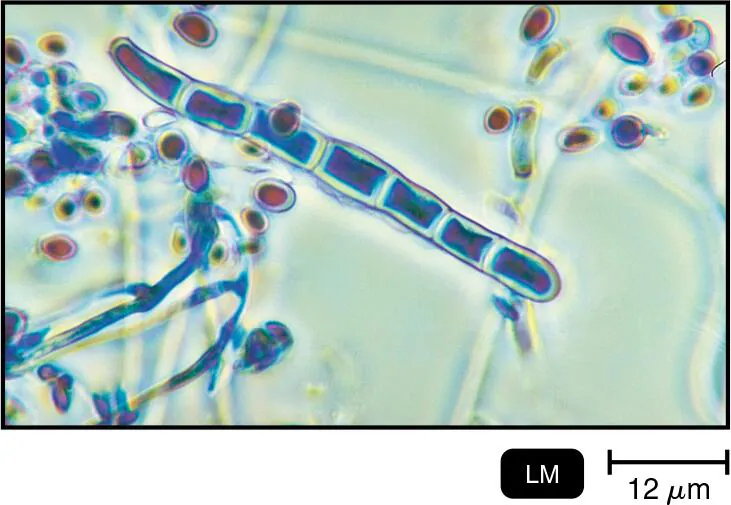
NAME IT Identify the structures of this eukaryote, which has an affinity for keratin.
Arthroconidia (Trichophyton)
Briefly discuss the importance of lichens in nature.
First colonizers on newly exposed rock or soil, chemically weather large inorganic particles into soil
Briefly discuss the importance of algae in nature.
primary producers in aquatic food chains, important oxygen-producers.
Differentiate cellular and plasmodial slime molds.
How does each survive adverse environmental conditions?
Cellular slime molds exist as single ameboid cells. Plasmodial slime molds are multinucleate masses of protoplasm.
Both survive adverse environmental conditions by forming spores.
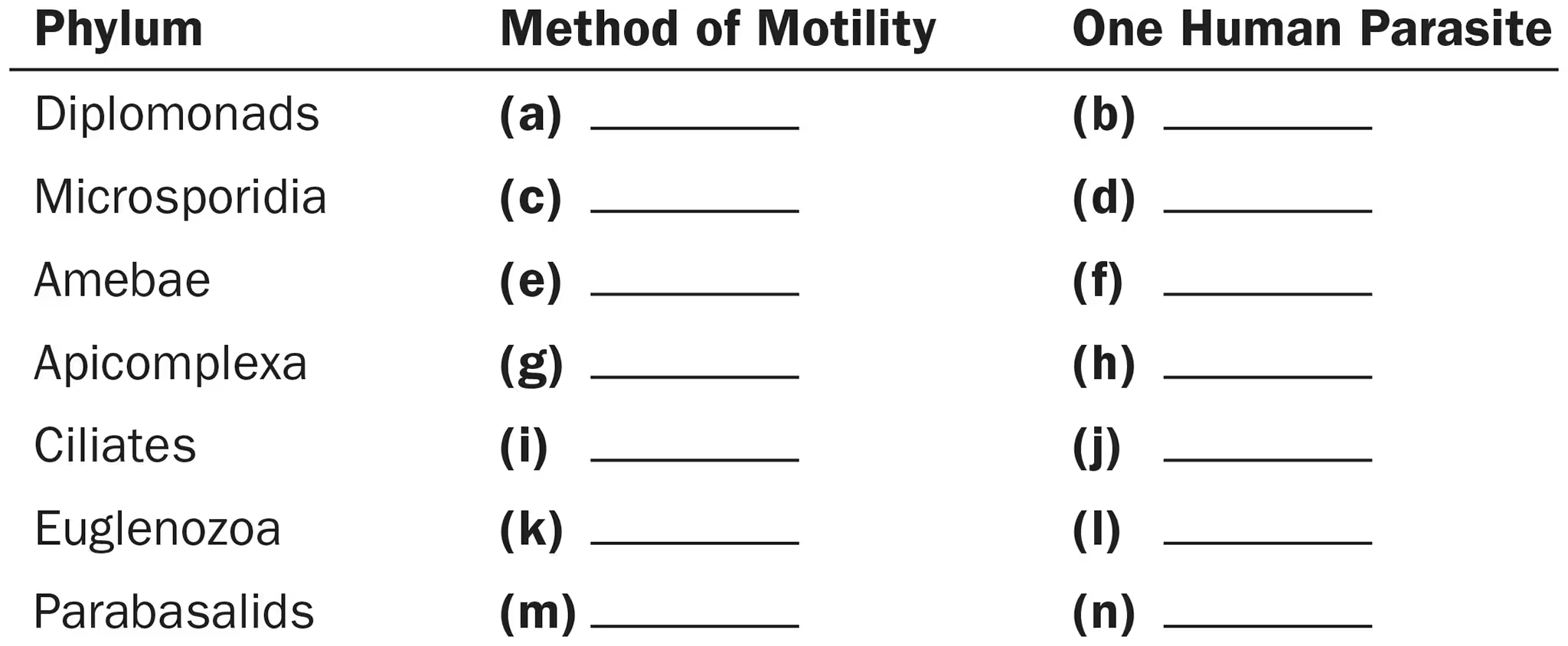
For the phylum Diplomonads, name
Method of motility
1 human parasite
Flagella
Giardia
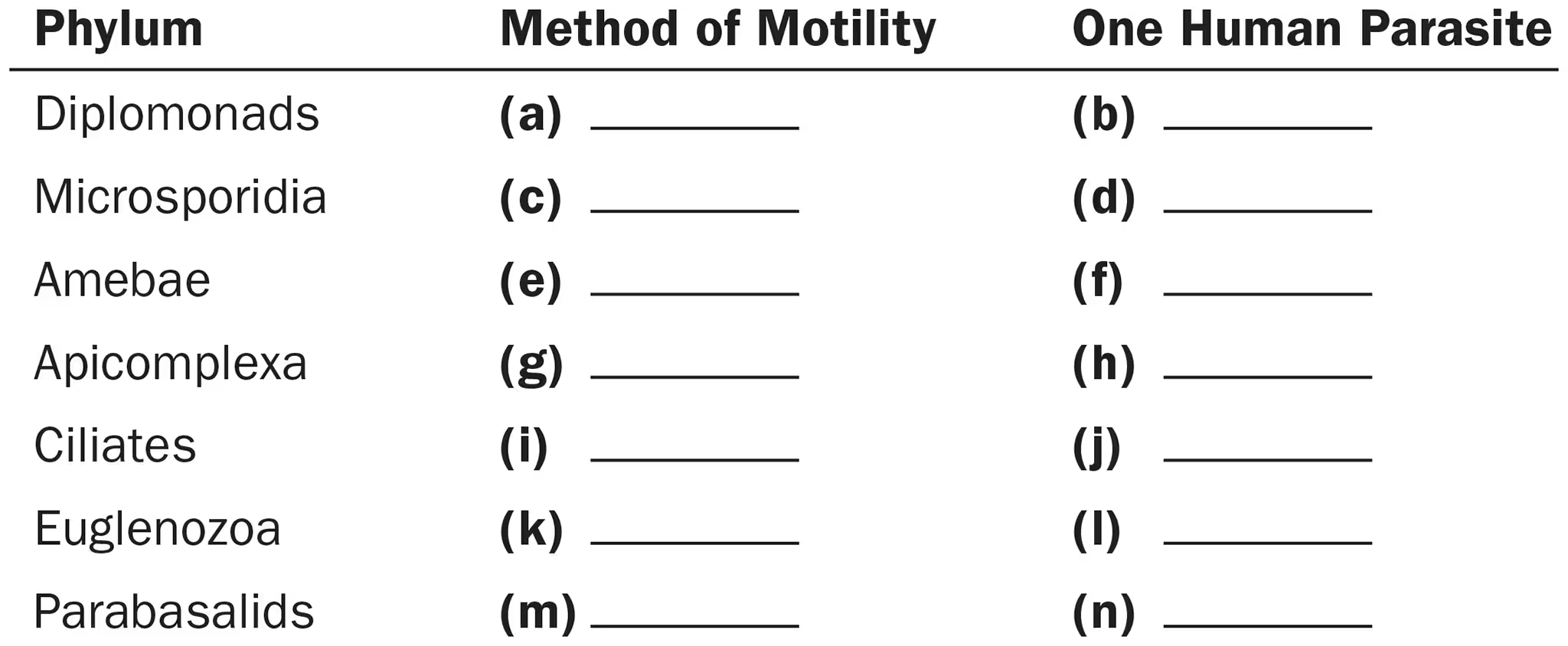
For the phylum Microsporidia, name
Method of motility
1 human parasite
None
Nosema
For the phylum Amebae, name
Method of motility
1 human parasite
Pseudopods
Entamoeba
For the phylum Apicomplexa, name
Method of motility
1 human parasite
None
Plasmodium
For the phylum Ciliates, name
Method of motility
1 human parasite
Cilia
Balantidium
For the phylum Euglenozoa, name
Method of motility
1 human parasite
Flagella
Trypanosoma
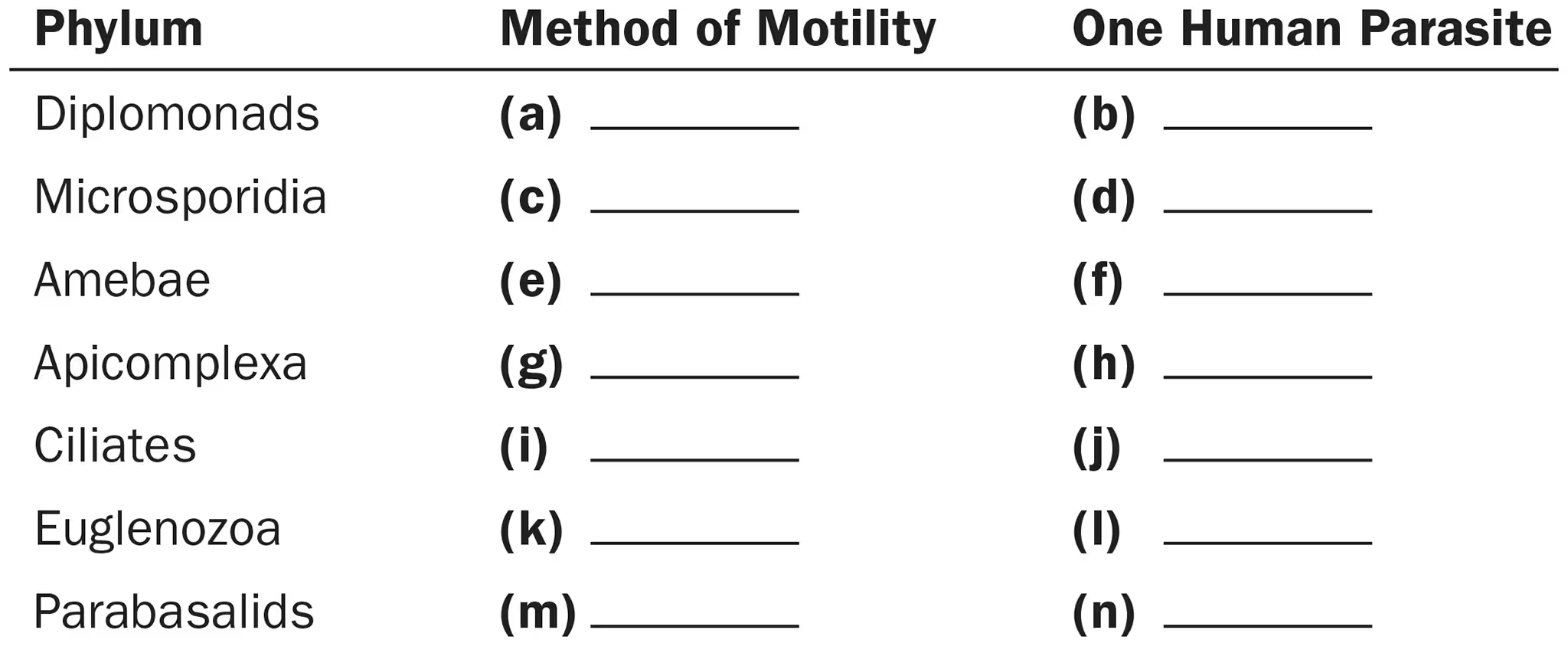
For the phylum Parabasalids, name
Method of motility
1 human parasite
Flagella
Trichomonas
Why is it significant that Trichomonas does not have a cyst stage?
No protective cyst —> can’t survive long outside a host, must be transferred from host to host quickly.
Name a protozoan parasite that does have a cyst stage.
Entamoeba histolytica
Cryptosporidium parvum
Toxoplasma gondii
By what means are helminthic parasites transmitted to humans?
Ingestion
Most roundworms are dioecious. What does this term mean?
Male and female reproductive organs are in separate individuals (biological males vs biological females)
To what phylum do roundworms belong?
Phylum Nematoda
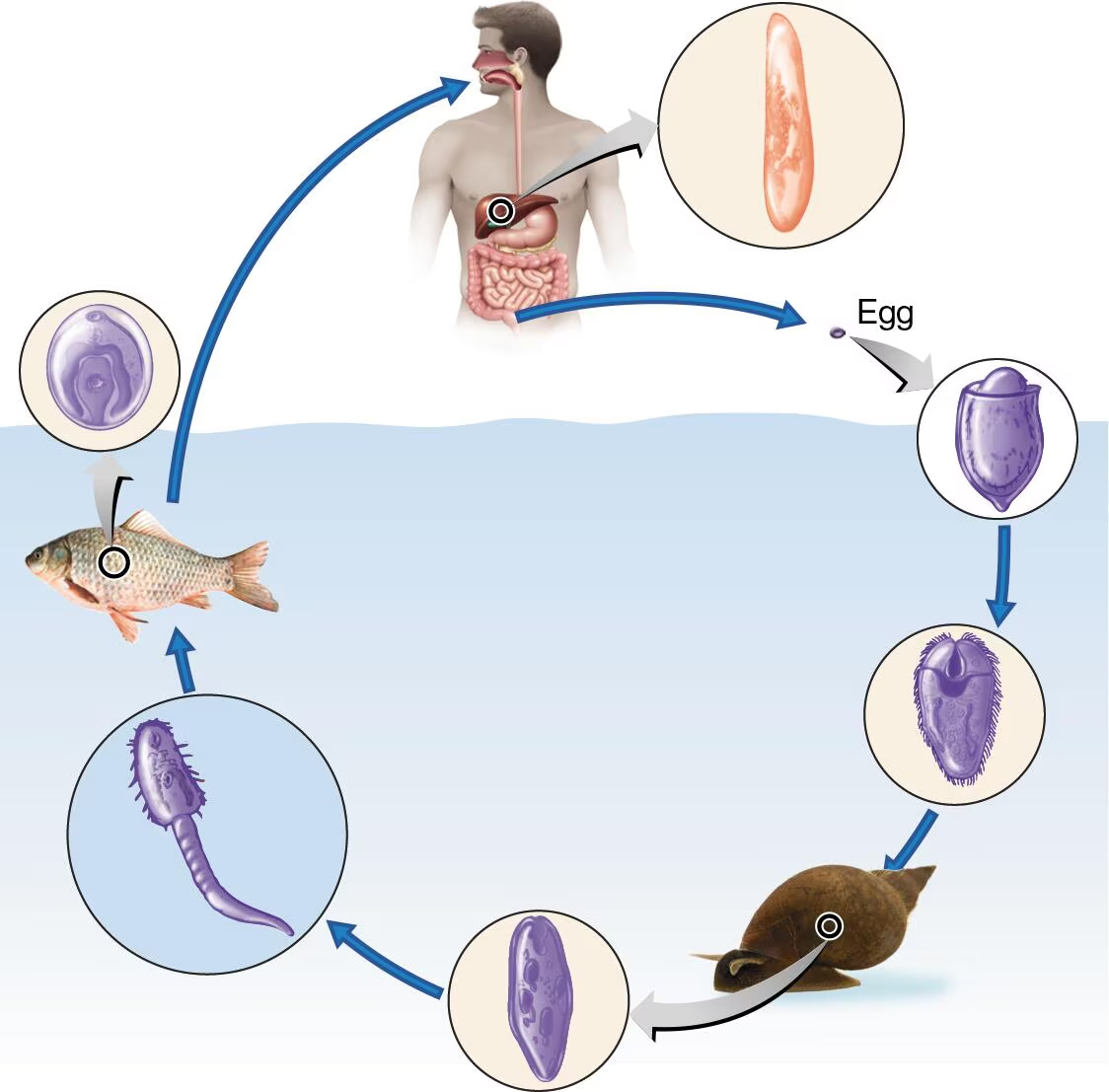
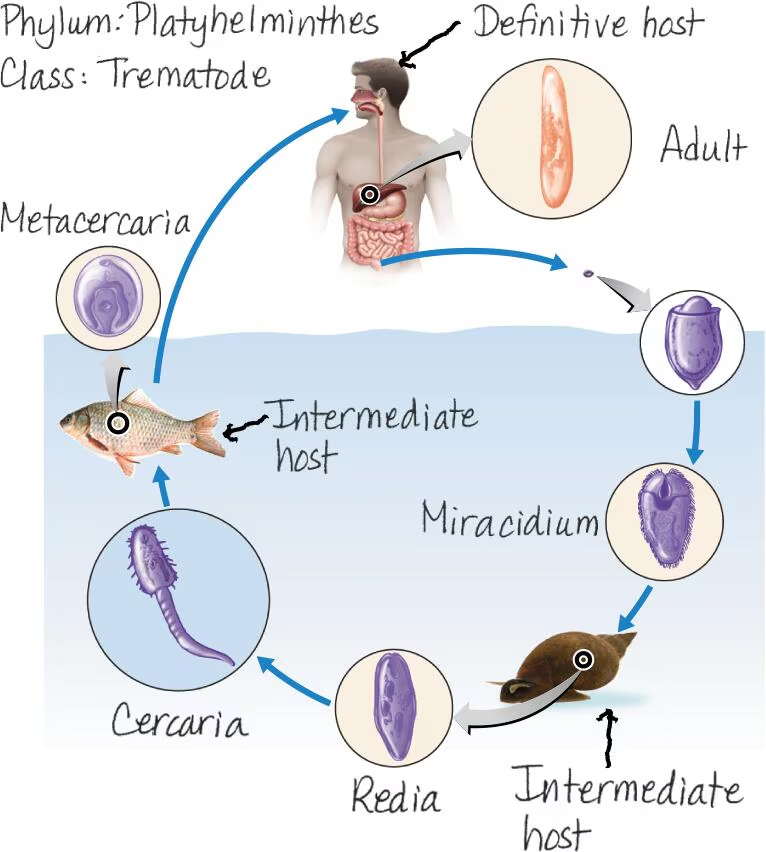
DRAW IT A generalized life cycle of the liver fluke Clonorchis sinensis is shown here.
Label the fluke’s stages.
Identify the intermediate host(s).
Identify the definitive host(s).
To what phylum and class does this animal belong?
view image
snail, fish
human/mammals
Phylum: Platyhelminthes, Class: Trematode
Multiple Choice
How many phyla are represented in the following list of organisms: Echinococcus, Cyclospora, Aspergillus, Taenia, Toxoplasma, Trichinella?
1
2
3
4
5
4

Put the preceding stages in order of development, beginning with the egg.
5, 4, 1, 2, 3
4, 2, 5, 1, 3
2, 5, 4, 3, 1
3, 4, 5, 1, 2
2, 4, 5, 1, 3
2

If a snail is the first intermediate host of a parasite with these stages, which stage would be found in the snail?
1
2
3
4
5
2
Fleas are the intermediate host for Dipylidium caninum tapeworm, and dogs are the definitive host. Which stage of the parasite could be found in the flea?
cysticercus larva
proglottids
scolex
adult
1
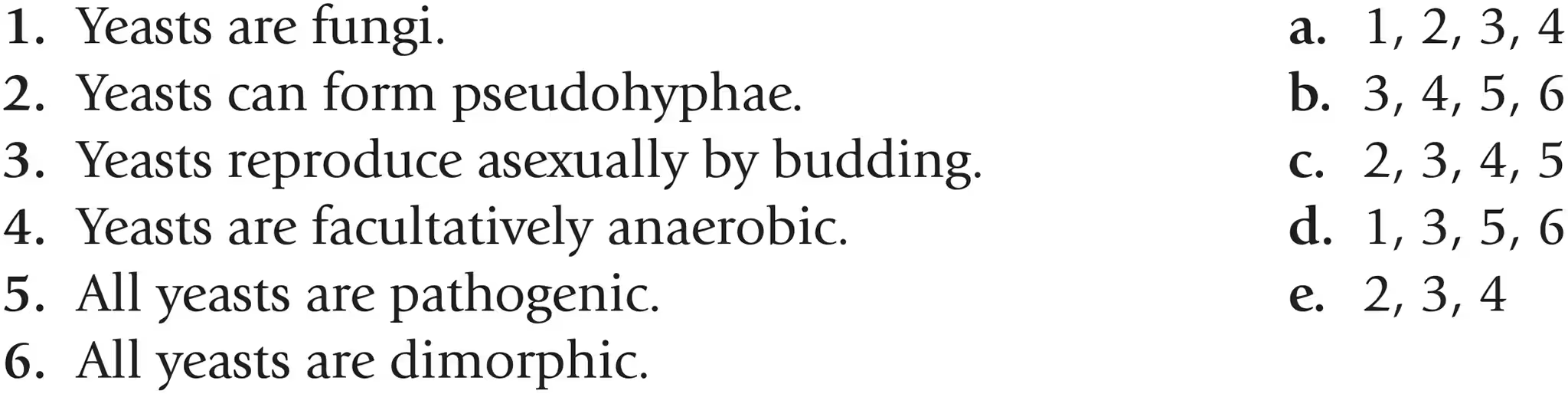
Which of the following statements about yeasts are true?
a
Which of the following events follows cell fusion in an ascomycete?
conidiophore formation
conidiospore germination
ascus opening
ascospore formation
conidiospore release
4
The definitive host for Plasmodium vivax is
human.
Anopheles.
a sporocyte.
a gametocyte.
2

These are obligate intracellular parasites that lack mitochondria.
4

These are nonmotile parasites with special organelles for penetrating host tissue.
1

These photosynthetic organisms can produce neurotoxins.
3
Analysis
Alexandrium (red tide) has been called a plant, protist, protozoan, and alga in the past. Now it’s in the SAR clade, along with Plasmodium and Paramecium.
Are all SAR members photosynthetic? Are any?
Not all Chromalveolata are photosynthetic. Dinoflagellates, diatoms, green algae, brown algae, phytoplankton, seaweed, are photosynthetic.
Alexandrium (red tide) has been called a plant, protist, protozoan, and alga in the past. Now it’s in the SAR clade, along with Plasmodium and Paramecium.
Explain why it has been so difficult to accurately classify Alexandrium.
Because it changes colors depending on depth of water, and it can also live on land.
The life cycle of the fish tapeworm Diphyllobothrium is similar to that of Taenia saginata, except that the intermediate host is fish.
Describe the life cycle and method of transmission to humans.
Immature eggs-->oncosphere-->coracidia-->proceroid larvae (crustacean, first immediate host)-->pleroceroid larvae (sparganum) (infective agent for humans) (freshwater fish, secondary immediate host)-->predator fish ingests freshwater fish-->human ingests undercooked predator fish-->immature adult tapeworms-->mature adult tapeworms-->immature eggs released by the proglottids
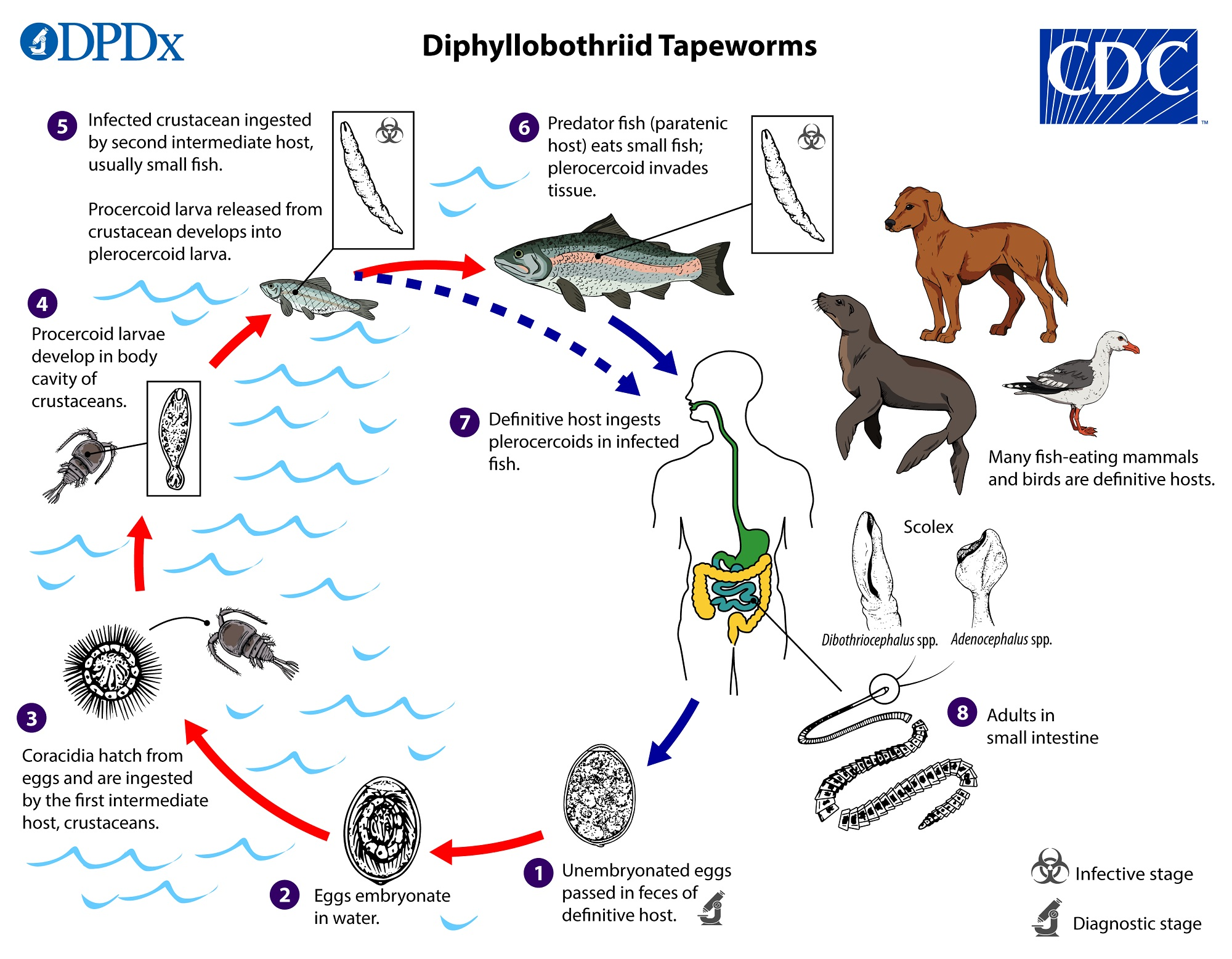
The life cycle of the fish tapeworm Diphyllobothrium is similar to that of Taenia saginata, except that the intermediate host is fish.
Why are freshwater fish more likely to be a source of tapeworm infection than marine fish?
Tapeworms survive better in freshwater than saltwater
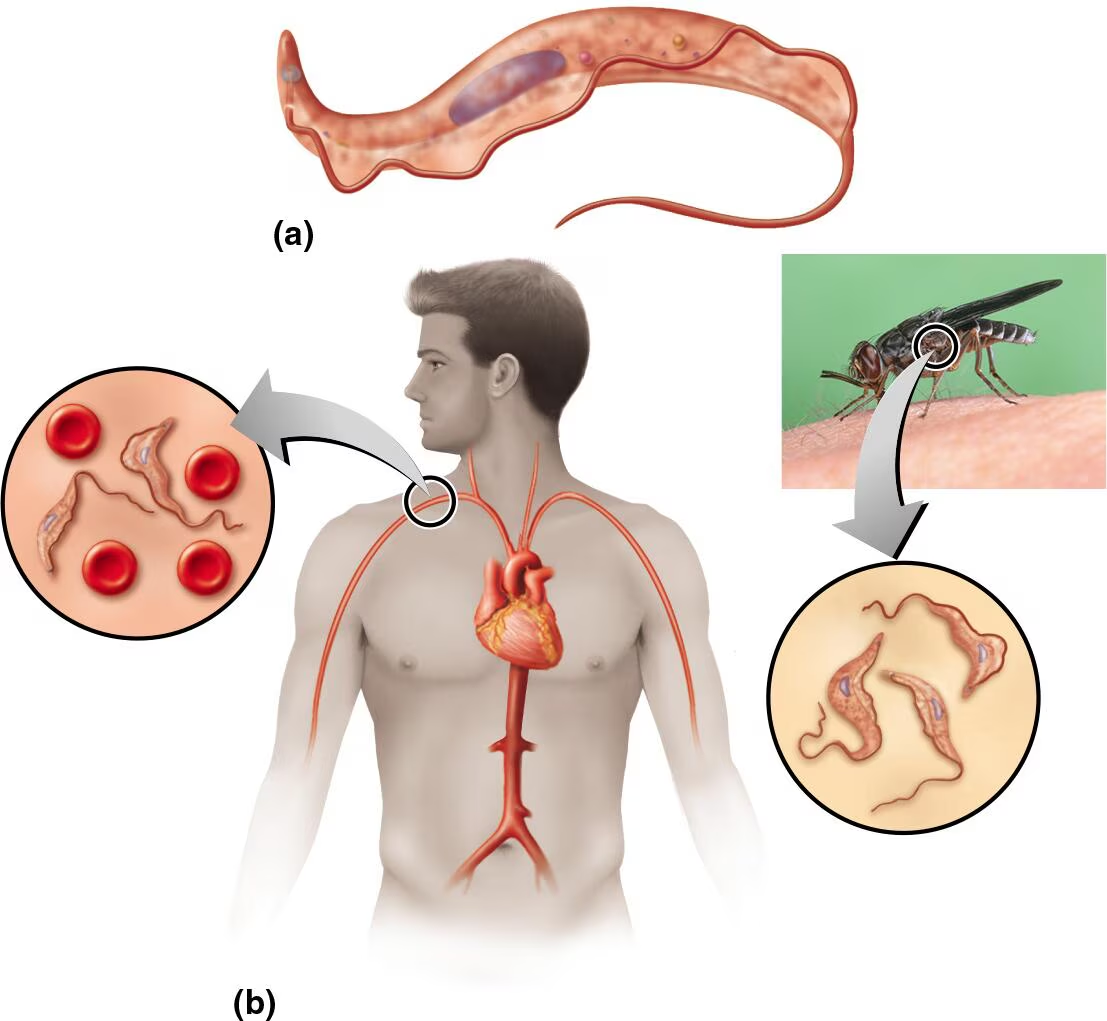
Trypanosoma brucei gambiense—part (a) in the figure—is the causative agent of African sleeping sickness. To what phylum does it belong? Part (b) shows a simplified life cycle for T. b. gambiense. Identify the host and vector of this parasite.
Phylum: Sarcomastigophora
Host: Mammals
Vector: Tsetse fly
Clinical Applications and Evaluation
A child developed generalized seizures. A CT scan revealed a single brain lesion consistent with a tumor. Biopsy of the lesion showed a cysticercus. The patient lived in South Carolina and had never traveled outside the state.
What parasite caused this disease?
How is this disease transmitted?
How might it be prevented?
Taenia solium
Ingestion of undercooked meat or dirty water.
By cooking meat thoroughly and avoiding contaminated water.
A California farmer developed a low-grade fever, myalgia, and cough. A chest X-ray exam revealed an infiltrate in the lung. Microscopic examination of the sputum revealed round, budding cells. A sputum culture grew mycelia and arthroconidia.
What organism is most likely the cause of the symptoms?
How is this disease transmitted?
How might it be prevented?
Coccidiodes fungus, causes Coccidioidomycosis (valley fever)
Inhaling spores
By limiting exposure to spores
An adolescent in California complained of remittent fever, chills, and headaches. A blood smear revealed ring-shaped cells in the teen’s red blood cells. The infection was successfully treated with primaquine and chloroquine. The patient lives near the San Luis Rey River and has no history of foreign travel, blood transfusion, or intravenous drug use.
What is the disease?
How was it acquired?
Malaria
Anopheles mosquito bite (carries infective stage of the Plasmodium, the sporozoite)