machine elements quiz 1
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
aa
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Machine Elements
are the fundamental building blocks of any mechanical system. They are standardized components designed to perform specific functions within a machine. These parts, also known as machine components, are crucial for the machine's overall operation and integrity
Shafts
Rotating members that transmit power/torque between components.
Bearings (rolling-element)
Support a shaft and reduce friction via balls/rollers between inner/outer races.
Gears
Toothed wheels that transmit motion and change speed/torque by meshing.
Belts and Pulleys
Flexible drive using a belt around pulleys to transmit power between shafts.
Couplings (rigid, flexible, fluid)
Connect two shafts to transmit power while accommodating misalignment or damping vibration.
Flywheels
Rotating masses that store kinetic energy and smooth speed fluctuations.
Chains & Sprockets
Positive (no slip) flexible drive using a roller chain over toothed wheels.
Cams & Followers
Convert rotary to prescribed reciprocating motion via a profiled cam and follower.
Linkages
Assemblies of links/joints that generate desired motion paths and force transmission.
Levers
Simple machine elements that amplify force or motion about a fulcrum.
Linear guides / Ways
Precisely finished guide surfaces or rails that provide accurate linear motion.
Springs (coil, leaf, torsion)
Store and release energy, provide force, or absorb shock/deflection
Keys & Keyways / Splines
Positive drive features that lock hubs to shafts to transmit torque without slip.
Fasteners (bolts, screws, nuts, rivets)
Detachable or permanent joints that hold components together.
Welds & Pins
Permanent or semi-permanent structural joining of parts.
Clutches & Brakes
Engage/disengage power flow (clutch) or dissipate energy to stop/hold (brake).
Seals (mechanical seals, lip seals) & Gaskets
Contain fluids and exclude contaminants at rotating or static interfaces
Lubrication elements
Oils/greases and channels that reduce wear & heat in contacts like bearings/gears.
Housings/Frames
Structural supports that hold elements in alignment and carry loads.
Importance of Machine Elements
Every machine is an assembly of these elements
Every machine is an assembly of these elements
WHY ARE MACHINE ELEMENTS IMPORTANT? 1
Proper design ensures reliability, efficiency, and safety
WHY ARE MACHINE ELEMENTS IMPORTANT? 2
Foundation for understanding complex mechanical systems
WHY ARE MACHINE ELEMENTS IMPORTANT? 3
position, velocity, and acceleration of a particle as it moves along a curved line in two or three dimensions
the ____ of an object is the rate of change of its position with respect to a frame of reference
a vector quantity that is defined as the rate at which an object changes its velocity
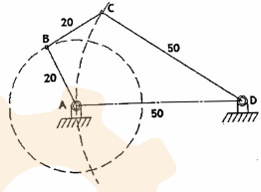
is a rigid body having two or more paring elements which connect it to other bodies for the purpose of transmitting force or motion
Four Bar Chain
are mechanisms composed only of lower pairs
Four Bar Chain
these mechanisms are popular because of its simplicity and flexibility
frame
every mechanism has a fixed link called the ___
grashof’s criterion
is useful in determining if one link in a four bar mechanism can complete one revolution
Grashof’s Law
states that for a planar four-bar linkage, if the sum of the shortest and longest links is not greater than the sum of the remaining two links, at least one of them will be revolving
grashof’s chain
a four bar mechanism is considered ____ if it satisfies:
Lmin + Lmax < L’ + L”
kinematic inversion
is the process of fixing one link in a kinematic chain and allowing other links to move relative about the fixed linkThis method results in different mechanisms depending on which link is chosen as fixed. c
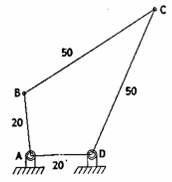
crank and rocker mechanism
the shortest link AB is adjacent with the frame can complete full rotation and link CD will oscillates less than 180 degrees
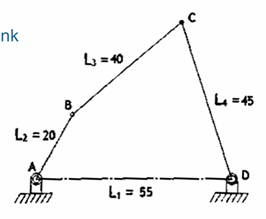
double crank mechanism
if the shortest link AD is held fix then links AB and DC will have complete rotation
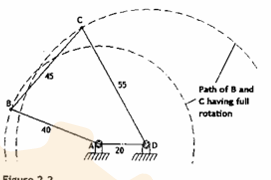
double rocker mechanism
if the shortest link BC is the coupler or assigned to be the floating link then both other links AB and DC will oscillate. in this assembly, the shortest link BC can still make a full roation
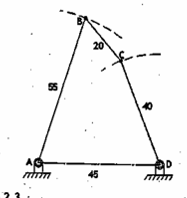
non-grashof’s chain
a four-bar mechanism is considered as a non-grashof’s chain if it satisfies
Lmin + Lmax > L’ + L”
in a _____, there is no link capable of rotating in full rotation, therefore it is not useful for motor driven application
inversion of non-grashof’s chain
depends on the location of the longest link in the mechanism. all inversions are double rocker mechanism which means two links can oscillate more than 180 degrees and cross the frame line to make a mirror image configuration
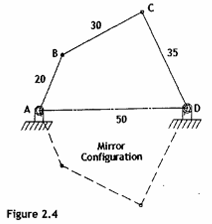
inward inward mechanism
the longest link AD is held fix or assigned to be the frame, then link AB and link DC will cross the fram line AD both in inward oscillation, respectively
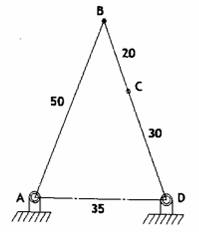
inward outward mechanism
the longest link AB is adjacent to the frame, then link AB and link DC will cross the frame line AD in inward and outward oscillation, respectively.
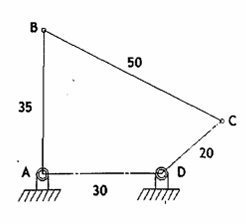
outward outward mechanism
the longest link BC is coupler, all other links can cross the frame line AD both oscillating in outward manner
transition chain
Lmin + Lmax = L’ + L”
uncertainty configuration
a transition chain is similar with grashof’s chain, except that in some configurations all links become collinear. this particular form is known as
parallelogram mechanism
both link AB and CD moves in the same direction
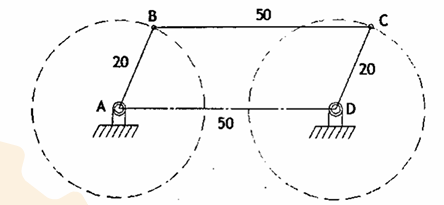
deltoid or kite mechanism
when the equal lengths of the links are adjacent to each other and the longer link length is held fix. the resulting linkage is a crank and rocker mechanism as shown below. similarly, this type of mechanism also has uncertainty configurations
rhombus mechanism
when equal lengths of the links are adjacent to each other and the shortest link length is held fix, the resulting linkage is a double crank mechanism as shown below. again this type of mechanism also has uncertainty configurations