DNA/Biotechnology
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
When does DNA replication occur?
before cell division
What is semiconservative replication?
when a DNA molecule contains one original strand and a newly synthesized compliment
Where is the 5-prime end?
phosphate terminus
Where is the 3-prime end?
hydroxyl terminus
What direction are nucleotides added to a growing strand?
5’ to 3’ direction
What is the leading strand?
the strand being synthesized continuously
What is the lagging strand?
the strand being synthesized discontinuously in fragments
What does helicase do?
unwinds DNA strands
What does topoisomerase do?
relaxes the supercoil at the replication fork
What is the replication fork?
the location where the two strands are separated
What does DNA polymerase do?
synthesizes new strands by attaching things to the 3’ end of the template strand
What does ligase do?
joins DNA fragments on the lagging strand
What occurs in DNA Transcription?
DNA —> Non-template strand —> Template strand
DNA matches with the Non-template strand. The Non-template strand pairs with the Template strand(ex: A from the non-template strand pairs with a T that goes to the template strand). The Template strand base pairs to create mRNA(ex: A from the template strand pairs with a U to create mRNA)
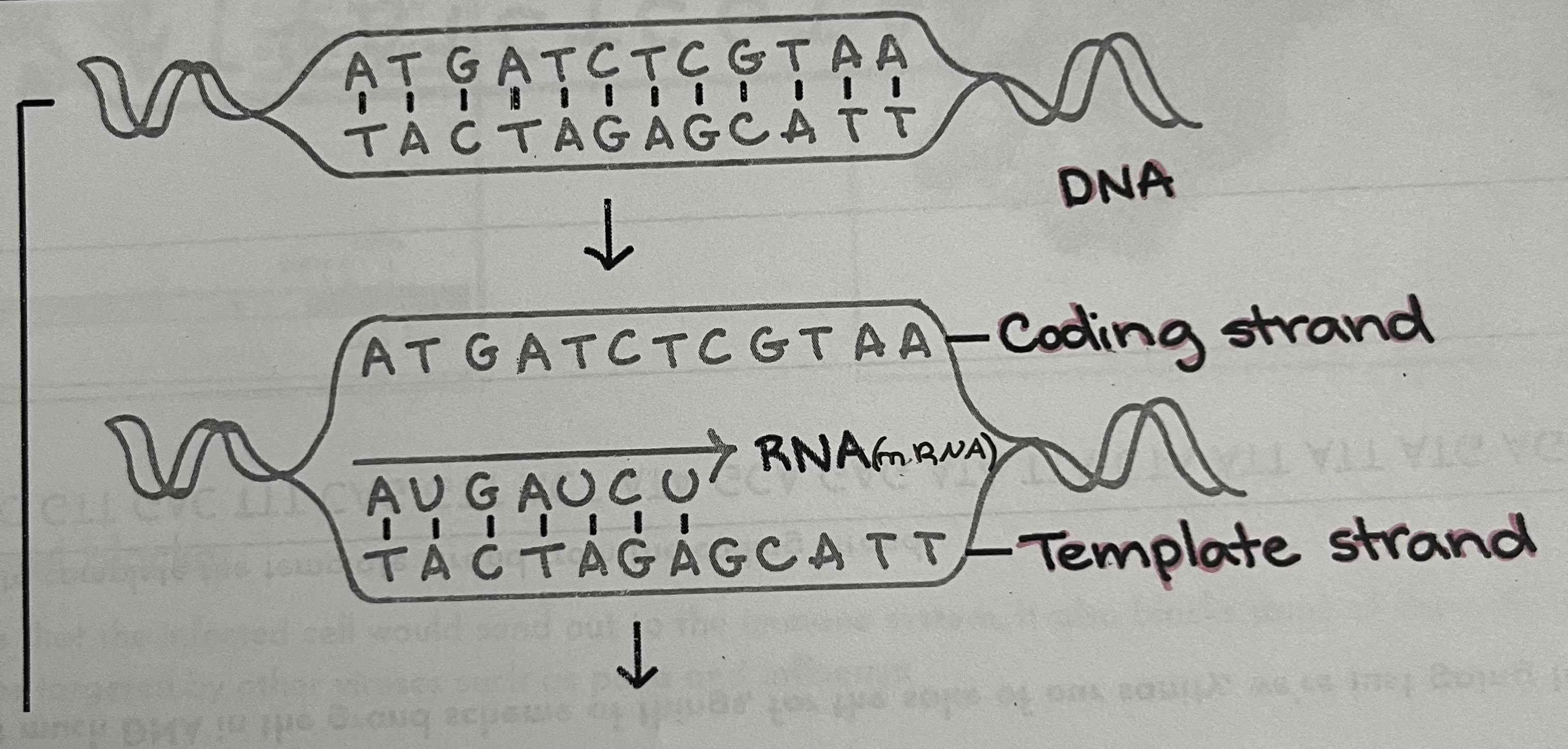
What organelle contains RNA and assembles proteins?
ribosomes
What does the template strand do during DNA transcription?
it is the strand used to produce RNA; it is the strand that pairs with the nucleotides that will become RNA
What are the other names for the template strand?
noncoding strand
minus strand
antisense strand
What are the other names for the non-template strand?
coding strand
sense strand
What does messenger RNA(mRNA) do?
carries genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes
What is a codon?
A 3-base sequence found on messenger RNA(mRNA)
What does transfer RNA(tRNA) do?
recruited to the ribosomes to help create a specific polypeptide sequence as directed by messenger RNA(mRNA)
What is an anti-codon?
a 3-base sequence on transfer RNA(tRNA)
What does ribosomal RNA(rRNA) do?
is a functional unit of ribosomes responsible for protein assembly
What are introns?
sequences of an mRNA transcript that DO NOT code for amino acids; they are taken out during RNA processing and are not included in the mature mRNA transcript
What are exons?
sequences of an mRNA transcript that DO code for amino acids; they are kept during RNA processing and are connected in the mature mRNA transcript
What is alternative splicing?
the process of splicing introns and connecting retained exons in mature mRNA transcript
What is DNA translation?
the process by which an mRNA sequence is used to generate a polypeptide(mRNA into amino acid chain that forms polypeptide)
What organelle is the site of DNA replication occur?
ribosomes
Where does translation occur?
cytoplasm
What is reverse transcriptase?
an enzyme that copies viral RNA into viral DNA
What occurs during the 1st step of translation?
rRNA in the ribosome interacts with the mRNA at the first start codon
mRNA nucleotides are grouped together and read as codons(many amino acids are encoded for by more than one codon)
What occurs during the 2nd step of translation?
newly arrived tRNA brings another amino acid to be added to the growing polypeptide chain
rRNA adds amino acids as tRNA brings them
What occurs during the 3rd step of translation?
amino acids continue to be added the the growing polypeptide chain until a stop codon is reached
translation ends
amino acids are no longer added
newly synthesized polypeptide is released