cell nuclear and cell devision
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
what are the phases in the cell cycle
G1
S
G2
M
are G1/2 growth or gap phases
gap
what happens during the interphase phases ( G1, S, G2 )
G1:
Cell grows in size
Synthesises proteins and organelles needed for S phase
decides whether to go into S phase
2. S:
DNA replicates makeing 2 sister chromotaids
histones and proteins synthesised
3. G2:
cell prepares fro mitosis by growing more
check for error in DNA replication
What is the point at which growth factors re-enter or leave the cell called
Restriction point (R)- where the cell commits to going through cell division
What are the 5 stages of mitosis
Prophase
Prometaphase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
describe the steps in cell division
prophase:
Early prophase : Chromosomes condense,
At late prophase, the chromosome condensation is complete and sister chromatids start to become visible.
Spindle apparatus formed by microtubules
Structure is still in nuclear envelope
prometaphase
Nuclear envelope breaks
Chromosomes attach to kinetochores on spindle
metaphase:
chromosomes line up on the microtubule spindle at the middle of the cell
they are ready to seperate
anaphase:
sister chromotids seperate
Cytokenis begins ( this is see by an actin band formed around the middle of the cell seperating the two daughter cells)
telophase:
chromatid fully seperated
chromatid decondense and form chromosomes
spindle fibres disapear
nuclear envelop ereforms
nucleolus reform
actin band contracts so the 2 cells begin to seperate
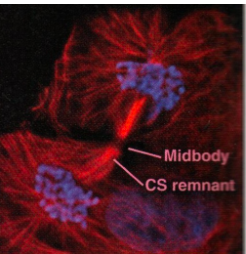
cytokensis :
2 cells seperate making 2 daughter cells
how long does cytokinesis take
1 hr
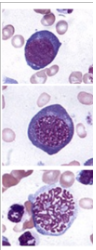
what stage are these cells in - 3 pics
Interphase
Early prophase
Late prophase
what stage is in this image - pic
Metaphase- chromosomes line up in the middle
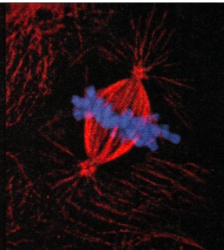
what stage of mitosis is this image in - pic
Telophase- you can see the actin is starting to constrict it an dits not a fully cut so its not cyokenisis
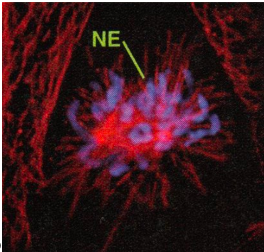
what stage of mitosis is this - pic
Prometaphase- the Nucleas isn’t intact so not prophase and the chromosomes are not in the middle yet so not metaphase
what stage of mitosis is this - pic
Anaphase- the chromosomes are pulled part to opposite poles

what is meiosis
A type of cell division that happens in germ cells (cells in the ovaries and testes) making the haploid gametes( sex cells)
what happens during meiosis 1 and 2
meiosis 1
after dna replication (interphase) each chromosome has 2 sister chromatids
the homologous chromosomes pair up making bivalent pairs ( one chromosome from mum one from dad)
recombination( crossing over) happens when the homologous chromosomes swap pieces at the chismata( this is the point that they cross) this increases variation
in anaphase 1 the homogenous chromosomes separate
at the end there are 2 cells each haploid but the chromosomes are still duplicated
meiosis 2
no DNA replication before this
In anaphase 2 the chromtids split at the centromere
now theres 4 haploid gametes that are all genetically different
steps of meiosis
Meiosis I (reductional division):
Prophase I: homologous chromosomes pair (synapsis) and crossing over at chiasmata
Metaphase I: homologous pairs line up at the equator
Anaphase I: homologues separate to opposite poles
Telophase I & Cytokinesis: two haploid cells formed
Meiosis II (equational division, like mitosis):
Prophase II: chromosomes condense
Metaphase II: chromosomes line up at the equator
Anaphase II: sister chromatids separate
Telophase II & Cytokinesis: four haploid gametes produced
what are chiasmata
points where homologous chromosomes cross over and exchange DNA
Function: hold homologues together until anaphase I, then break to allow separation
What is random assortment of maternal and paternal chromosomes?
During metaphase there is random assortment if their chromosomes which help with genetic variation
How does Genetic variation happen ( meiosis)
crossing over: happens during prophase 1 making new combinations of maternal and paternal genes
random assortment increases genetic variation
this makes there be genetic diversity in offspring
How many different combinations of chromosomes and gametes are there
2^23 - chromosomes
8.4x10^6 - gametes
What are the differences between mitosis and meiosis
pic
What happens to the chromosome pairs during the formation of gametes and fertilisation
Meiosis: gametes get 23 chromosomes each
Fertilization: sperm + egg → 46 chromosomes (diploid)
how is DNA structured and packaged in chromatin
DNA wraps twice around 8 histones making one nucleosome
Histone H1 coils nucleosomes into 30 nm fibre
Fibre forms loops attached to scaffold proteins
Loops condense during mitosis to form visible chromosomes
explain the 2 different tightness of packaging of chromatin
Euchromatin - loosely packed so more active so the genes are expressed
Hetreochromatin - tightly packed so inactive and the genes aren’t expressed
The more condensed the chromotin the less transcriptional active
draw a labeled chromosome, with kinetochore,centromere,chromatid
pic
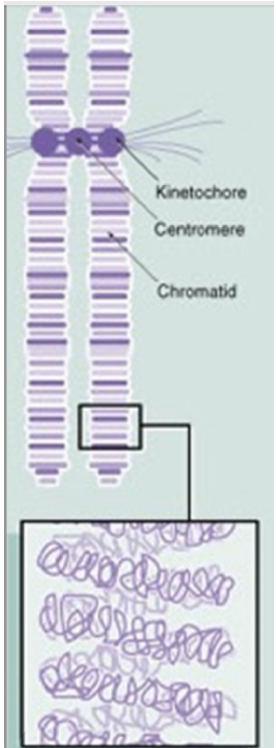
how do you classify mitotic chromosoms
through staining that amkes a banding pattern
through size
what are telomeres
Telomeres: tandem repeats (GGGTTA in humans) at chromosome ends
Functions:
Prevent chromosome fusion
Solve DNA replication end problem → telomerase adds repeats so important DNA isn’t lost during division
Where are telomerase expressed what is its functions
Telomerase: enzyme that rebuilds telomeres
Expressed in: germ cells and cancer cells; normally inactive in somatic cells
Function:
Somatic cells → telomeres shorten → cell senescence
Cancer cells → telomerase active → telomeres maintained → unlimited division
What is a karyotype
Organsisd display of all the chromosomes in a cell
It is arranged by: size, number,shape and banding pattern
Banding pattern is shown using stains
This helps with classification as each species has a differnt karotype
It helps to detect genetic abnormalities
How is the banding pattern in the karyotype useful
Karyotype banding patterns: show characteristic chromosome stripes
Use: detect large-scale chromosome changes (deletions, additions)
Clinical relevance: helps identify diseases and affected chromosome regions
what are autosomes
non sex chromosomes
In somatic cells, where does each chromosome from the pair come from?
one maternal one paternal
what is aneuploid, heteroploid, polyploid cells and where are they found
Aneuploid = 1 chromosome off e.g 45 instead of 46
Heteroploid = total number of chromosmes isnt a multiple of a haploid set ( incuding aneuploid)
Polyploid = extra full sets e.g 3n
abnormal number of chromosomes
cancer cell
what are the layers of the nuclear membrane
The nucleus has double nuclear membrane
Outer nuclear membrane is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum
Inner nuclear membrane is supported by the nuclear lamina - a meshwork of filament protein called lamins
what is the structure and function of nuclear pore
many proteins with aqueous chanel in the middle
used for communication between nucleas and cytoplasm
how does transport through a nucleaas work
Small molecules (under 9nm in diameter) like amino acids, nucleotides, short peptides are able to pass through the pores via passive diffusion
Larger molecules require active transport
Some proteins work in the Nucleas and have nuclear localisation sequences (NLS) which are short of amino acids which are recognised and allows the protein to enter the cell
How do proteins with a Nuclear localisation signal get into the nucleus
NLS is on proteins that need to work in the nucleas and it helps with entery
Cytoplasmic import receptors recognise the nuclear localisation signal and transport the protein into the Nucleas
Inside the Nucleas the receptors release the protein using energy from the hydrolysis of GTP
The removal works the same way with the protein carrying a nuclear export signal
What the nucleolus and what is the role of it
Nucleolus: largest structure in the nucleus, usually central
Role: transcribes rRNA and assembles ribosomal subunits
Ribosomal subunits move to the cytoplasm for protein synthesis
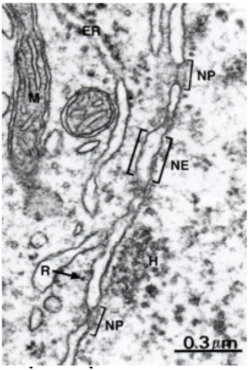
label diagram: pic
pic
