Atomic Structure
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/16
Last updated 11:09 AM on 3/25/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
1
New cards
Define atom.
Smallest particle of every state of matter is called atom
2
New cards
Mass and charge of a proton?
Relative Mass: 1 amu
Actual Mass: 1.673 x 10^-27 kg
Charge: + 1.6 x 10^-19 C
Actual Mass: 1.673 x 10^-27 kg
Charge: + 1.6 x 10^-19 C
3
New cards
Mass and charge of neutron?
Relative Mass: 1 amu
Actual Mass: 1.675 x 10^-27 kg
Charge: zero
Actual Mass: 1.675 x 10^-27 kg
Charge: zero
4
New cards
Mass and charge electron?
Relative Mass: 1/1840 OR 1/1836
Actual Mass: 9.11 x 10^-31
Actual Charge: -1.6x 10^-19
Actual Mass: 9.11 x 10^-31
Actual Charge: -1.6x 10^-19
5
New cards
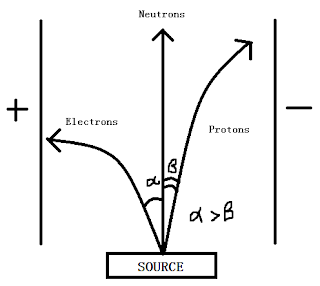
Behaviour of subatomic particles in an electric field:
* protons are +ve charged so attracted to -ve plate (less deflected, due to its larger mass)
* neutron has no charge so unaffected
* electron -ve charged so attracted to +ve plate
* neutron has no charge so unaffected
* electron -ve charged so attracted to +ve plate
6
New cards
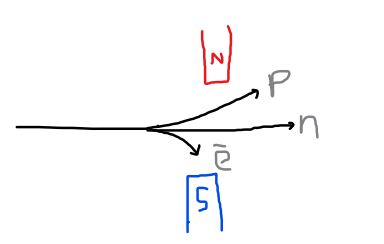
Behaviour of subatomic particles in a magnetic field:
7
New cards
Sequence of general electronic configuration:
1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 4s2, 3d10, 4p6, 5s2, 4d10, 5p6…
8
New cards
Define first ionization energy:
Energy required to ==remove 1 mole of of electron== from a ==gaseous atom== to form ==+1 charged gaseous ion== at ==standard conditions==.
9
New cards
Define enthalpy change of atomization:
Energy required to ==form 1 mol of gaseous atom of any element from its standard state==, at ==standard condition==.
10
New cards
Define second ionization energy:
Energy required to ==remove 1 mole of of electron== from a ==gaseous atom== to form ==+1 charged gaseous ion to form +2 charged gaseous ion== at ==standard conditions==.
11
New cards
Factors affecting Ionization Energy.
1. Atomic radii/distance from nucleus/number of shells: Increase in the number of shells makes the valence electron less firmly held in the valence shell so less IE means less energy is required to remove the electron.
12
New cards
Why is the first ionization energy of phosphorus greater than the first ionization energy of silicon.
A phosphorus atom has one more proton than in its nucleus
13
New cards
Which factor helps to explain why the first ionization energies of the Group I elements decrease from lithium to sodium to potassium to rubidium.
The shielding effect of the inner shells increase.
14
New cards
What factor affects value of activation energy?
1. nature of reactants
2. presence of a catalyst
__**NOTE**__**:** ==Activation energy does not depend upon the temperature, pressure, volume, concentration, or coefficients of reactant.==
15
New cards
Why is the first ionisation energy of oxygen less than that of nitrogen?
the oxygen atom has a pair of electrons in one p orbital that repel each other.
16
New cards
Which statement about the electrons in a ground state carbon is correct?
A. Electrons are present in four different energy levels.
B. There are more electrons in p orbitals than there are in s orbitals.
C. The occupied orbital of highest energy is spherical.
D. The occupied orbital of lowest energy is spherical.
A. Electrons are present in four different energy levels.
B. There are more electrons in p orbitals than there are in s orbitals.
C. The occupied orbital of highest energy is spherical.
D. The occupied orbital of lowest energy is spherical.
Option D. The occupied orbital of lowest energy is spherical.
17
New cards