Unit 3 quiz
1/59
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
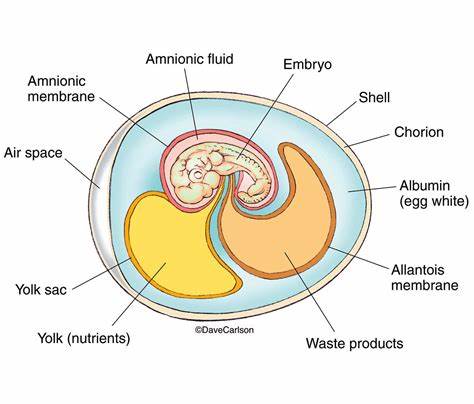
Amniotic egg
allows vertebrates to reproduce on land without relying on water for the development of their offspringIt is a protective, fluid-filled sac that surrounds and cushions the embryo, providing nutrients and facilitating gas exchange
Temporal fenestra
openings in the skull behind the eyes of vertebrates, they serve as attachment points for muscles and can aid in jaw movement and strength
Therapsids
group of synapsid vertebrates that include mammals and their ancestors. They are characterized by features such as differentiated teeth and a more advanced jaw structure, indicating a transition towards mammalian characteristics.
Anapsid
group of amniote vertebrates that are characterized by their skull structure, which lacks temporal fenestrae
Diapsid
amniote vertebrates that have two temporal fenestrae on each side of their skull
Synapsid
group of amniotes characterized by a single temporal fenestra on each side of the skull.
Diaphragm
critical muscle in mammals that play a significant role in respiration. It’s a dome-shaped sheet of muscle and tendon located at the base of the thoracic cavity. The primary function is to facilitate breathing. When it contracts, it flattens and moves downward, increasing the volume of the thoracic cavity and creating a negative pressure that draws air into the lungs (inhalation). When it relaxes, it returns to its dome shape, reducing the thoracic volume and pushing air out of the lungs (exhalation).
Costal ventilation
a method of breathing in reptiles where the rib cage expands and contracts to aid in lung ventilation. Uses intercostal muscles to contract and relax the rib cage's movement helps draw air into the lungs and push it out.
Alveolar lung
a type of lung structure found in mammals, characterized by small air sacs that increase surface area for gas exchange.
Faveolar lung
a type of lung found in some reptiles and amphibians, characterized by a series of small, sac-like structures that increase the surface area for gas exchange.
Turbinates
structures (bony or cartilaginous ridges) within the nasal cavity that help warm, humidify, and filter the air as it is inhaled through mucous membranes
Adipocytes
specialized cells that store fat and play a key role in energy metabolism and regulation of body weight.
Alpha keratin
a fibrous structural protein found in hair, nails, and the outer layer of skin, providing strength and protection.
Beta keratin
a type of fibrous protein found in feathers, scales, and certain types of skin, contributing to their durability and flexibility.
Cryptodira
a suborder of turtles characterized by their ability to retract their heads back into their shells.
Pleurodira
a suborder of turtles characterized by their ability to retract their heads sideways under the edge of their shells, differing from Cryptodira.
Trochlear process
a bony projection in the skull that serves as a point of articulation for muscles and ligaments, particularly involved in the movement of the eye or certain bones.
Carapace
the upper shell of a turtle, tortoise, or crustacean, providing protection and support.
Plastron
the lower shell of a turtle or tortoise, which protects the underside and aids in support.
Horny scutes
the hard, keratinized plates that cover the carapace and plastron of turtles, providing additional protection.
Thermal inertia
the ability to retain heat, affecting temperature regulation in organisms and environments.
Temperature dependent sex determination (TSD)
A phenomenon where the sex of offspring is determined by the temperature at which eggs are incubated, commonly seen in reptiles.
Sphenodon
a genus of reptiles known as tuataras, which exhibit temperature dependent sex determination.
Autotomy
the ability of certain animals to intentionally shed a body part, usually as a defense mechanism.
Pseudoautotomy
a form of autotomy where an animal can shed a body part with some significant injury, often used to escape predators. Non-spontaneous tail break
Hemipenes
paired reproductive organs found in male squamates, which include snakes and lizards, only one is used during mating, used to transfer sperm to the female's cloaca during copulation
Acrodont dentition
type of tooth implantation where the teeth are fused to the summit of the alveolar ridge of the jaw without sockets, means the teeth are attached directly to the bone and do not have roots
Gekkota
infraorder of squamate reptiles that includes all geckos and the limbless "snake-lizards" of the family Pygopodidae.
toe pads
nocturnal activity: many are but not all
tail autotomy
Scincoidea
superfamily within the order Squamata, which includes lizards and snakes, commonly known as skinks and their close relatives, such as plated lizards and spinytail lizards
Lacertoidea
superfamily within the order Squamata, which includes lizards and snakes, This group encompasses several families, including Lacertidae (wall lizards), Teiidae (New World runners), Gymnophthalmidae (spectacled lizards), and Amphisbaenia (worm lizards)
Anguimorpha
suborder of squamate reptiles, which includes lizards and snakes. This group is part of the proposed "venom clade" Toxicofera, which also includes iguanians and snakes
Iguania
is a suborder of lizards within the order Squamata. This group is diverse and includes many familiar lizards like iguanas, chameleons, and agamid lizards
Serpentes
characterized by their elongated, legless bodies and have evolved a wide range of adaptations to thrive in diverse environments
Squamosal
thin, flat bone that forms part of the side of the skull above and behind the ear in mammals, it is a cranial suture between the temporal and parietal bones
Postorbital
one of the bones in vertebrate skulls which forms a portion of the dermal skull roof and, sometimes, a ring about the orbit. Generally, it is located behind the postfrontal and posteriorly to the orbital fenestra.
Temporal bar
a bony structure in the skull, especially in reptiles. It provides stability and places for jaw muscles to attach, helping the animal to bite and chew more effectively.
Inertial feeding
method of prey transport used by some reptiles, particularly lizards, It involves using the inertia of the head and body to move food from the jaws into the oral cavity and down the throat, prey says in place and the lizard tosses and catches it to work its jaws aroundit
Unilateral feeding
feeding mechanism observed in snakes, where the prey is transported through the oral cavity using alternating, unilateral movements of the jaw
Constriction
method used by certain snakes to subdue and kill their prey. This technique involves wrapping the body around the prey and tightening the coils with every exhalation of the prey, ultimately leading to suffocation or circulatory arrest
Opisthoglyphous
type of venomous snake characterized by having rear-fanged dentition
Proteroglyphous
group of venomous snakes characterized by having front-fanged dentition. These snakes have fangs that are positioned at the front of their upper jaw, which are used to deliver venom efficiently into their prey.
Solenoglyphous
group of venomous snakes known for their highly specialized and efficient fangs. These snakes have the most advanced venom delivery system among all snakes.
Pit organs
specialized sensory structures found in some snakes, particularly those in the subfamilies Crotalinae (pit vipers) and Boidae (boas and pythons). These organs enable the snakes to detect infrared radiation, essentially allowing them to "see" heat
Lateral undulation
most common form of locomotion used by snakes to move across various surfaces. This type of movement involves a series of coordinated, wave-like motions that travel down the length of the snake's body
Rectilinear
unique mode of movement used by large-bodied snakes, such as boas and pythons, to move in a straight line. Unlike the more common lateral undulation, involves a series of muscle contractions that allow the snake to move forward smoothly
Concertina
specialized type of movement used by snakes to navigate through narrow passages or confined spaces. This type of locomotion is especially useful for climbing and moving through burrows or tight crevices
Sidewinding
unique and efficient form of locomotion used by some snakes, especially those living in sandy or loose substrates like deserts. This method of movement minimizes contact with the hot surface and allows the snake to move quickly and effectively across loose ground
Draco
genus of gliding lizards found in Southeast Asia
Gular fan
expandable flap of skin found under the throat of some lizards
Display action pattern
specific, ritualized behaviors used by animals to communicate with others, often as part of territorial displays, courtship, or threat displays. These patterns are highly stereotyped and repetitive, making them recognizable and understandable by other members of the species
Femoral glands
specialized glands found in some lizards, located on the inner thighs. These glands play a crucial role in chemical communication, particularly in mate attraction and territorial marking
Mate guarding
behavior observed in many animal species where an individual, usually a male, stays close to a mate to prevent other potential mates from gaining access. This behavior helps ensure that the offspring are sired by the guarding individual
Yolk-sac placenta
structure that plays a crucial role in early pregnancy, particularly in providing nutrients and support to the developing embryo before the placenta is fully formed
Crocodylidae
family of reptiles commonly known as crocodiles, which includes alligators and caimans. They are characterized by their long snouts, powerful jaws, and semi-aquatic habitats.
Alligatoridae
family of reptiles that includes alligators and caimans, characterized by their broad snouts and aquatic habitats.
Gavialidae
family of freshwater reptiles commonly known as gavials or gharials, characterized by their long, narrow snouts and primarily piscivorous diet.
Osteoderms
bony deposits forming scales, plates, or other structures in the skin of reptiles.
Dome pressure receptors
specialized sensory structures found in some reptiles, used to detect changes in pressure and temperature in their environment.
Osmoregulatory pits
specialized sensory structures in some reptiles that help detect changes in water concentration in their environment.
Lingual salt glands
salivary glands in reptiles that aid in digestion and moisture retention.