Ultrasound Physics Ch 1-2 (The Basics & Sound)
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Unrelated
not associated
related/proportional
associated or affiliated but not specific
Directly related/proportional
As one increases so does the other
Inversely related/proportional
As one increases the other decreases
Reciprocal
. ex- 2 and 2/10
.when multiplied together the result is one
. special form of inverse
increase by a factor
multiply
.ex- increase by a factor of 6 is 6x larger
Decrease by a factor
Divide by that number
. ex- decrease by a factor of 3 is 1/3
percent is
unitless
10^9
giga(G)- Billion
10^6
mega(M)- Million
10^3
kilo(k)-thousand
10^2
hecto(h)- hundred
10^1
deca(da)- ten
10^-1
deci(d)- tenth
10^-2
centi(c)- Hundredth
10^-3
milli(m)- Thousandth
10^-6
micro(,u)- Millionth
10^-9
nano(n)- Billionth
Billions/billionths
giga & nano (G & n)
millions/millionths
mega & micro (M & ,u)
thousands/thousandths
kilo and milli (k & m)
hundreds/hundredths
hecto and centi (h & c)
tens/tenths
deca & deci (da & d)
sound is a
mechanical wave
molecules in a medium vibrate
back and forth from a fixed point
Can sound travel through a vacuum?
No, it must travel through a medium
Sound travels
in a straight line
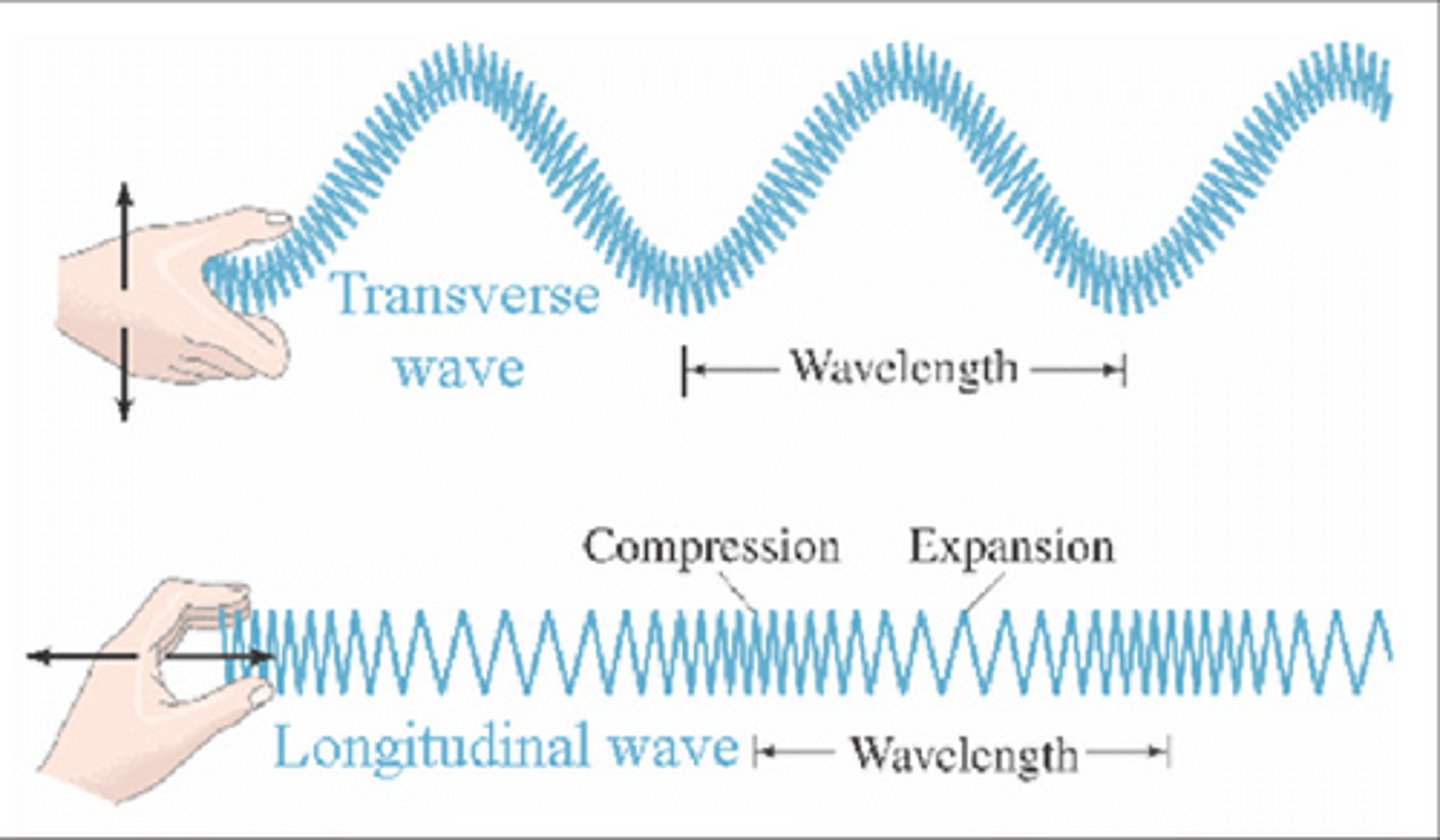
Sound waves are longitudinal or transverse waves
longitudinal waves
compressed means
squeezed together
Rarefied means
stretched apart
The 4 acoustic variables rhythmic oscillations are
pressure, density, distance, temperature
Sound waves are also known as
acoustic waves
Pressure units are
Pascals (Pa)
Density units are
kg/cm^3
Distance units are
cm, mm
Temperature units are
Fahrenheit and Celsius
The acoustic parameters that describe the characteristics of sound waves are
1. period
2. frequency
3. amplitude
4. power
5. intensity
6. wavelength
7. propagation speed
In transverse waves particles move
perpendicular to direction the wave propagates
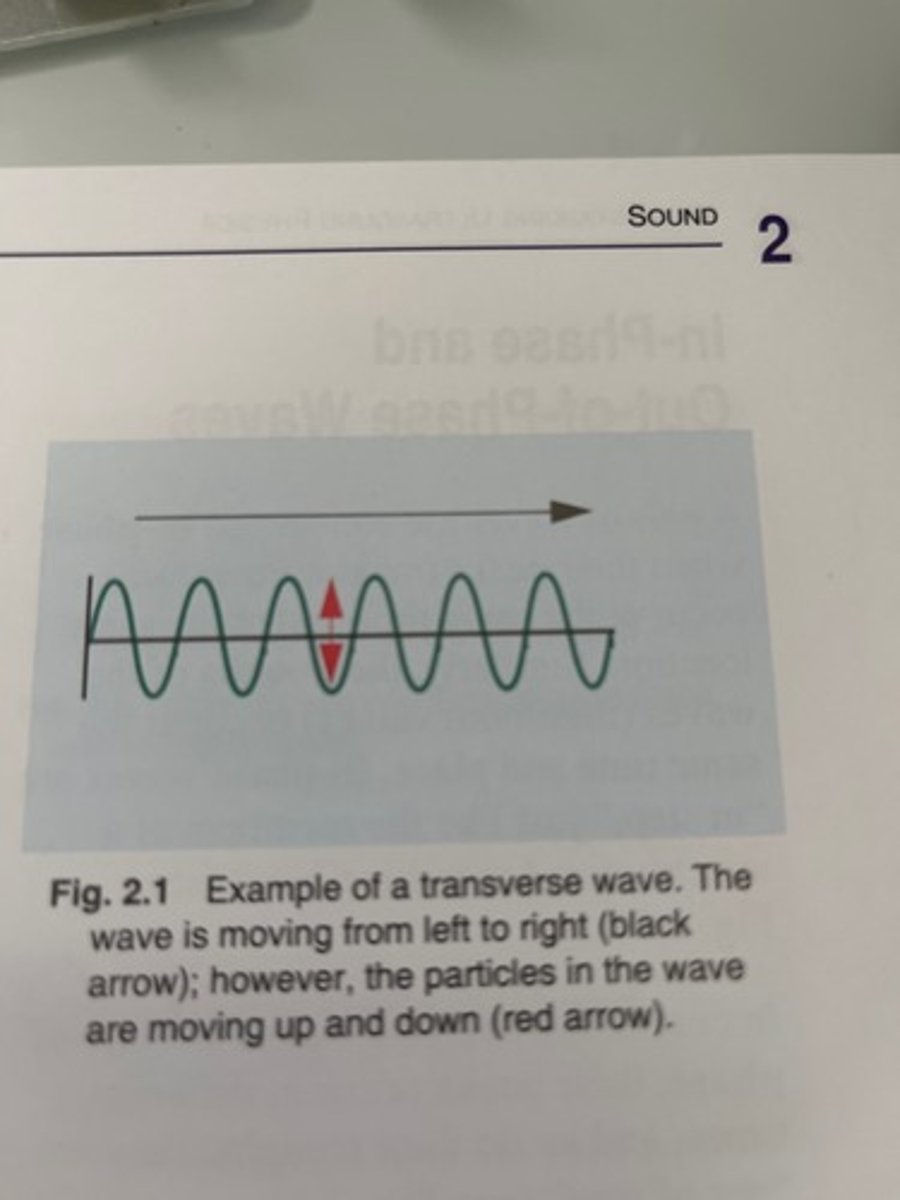
In longitudinal waves particles move
In the same direction that the wave propagates
peaks
max values
troughs
min values
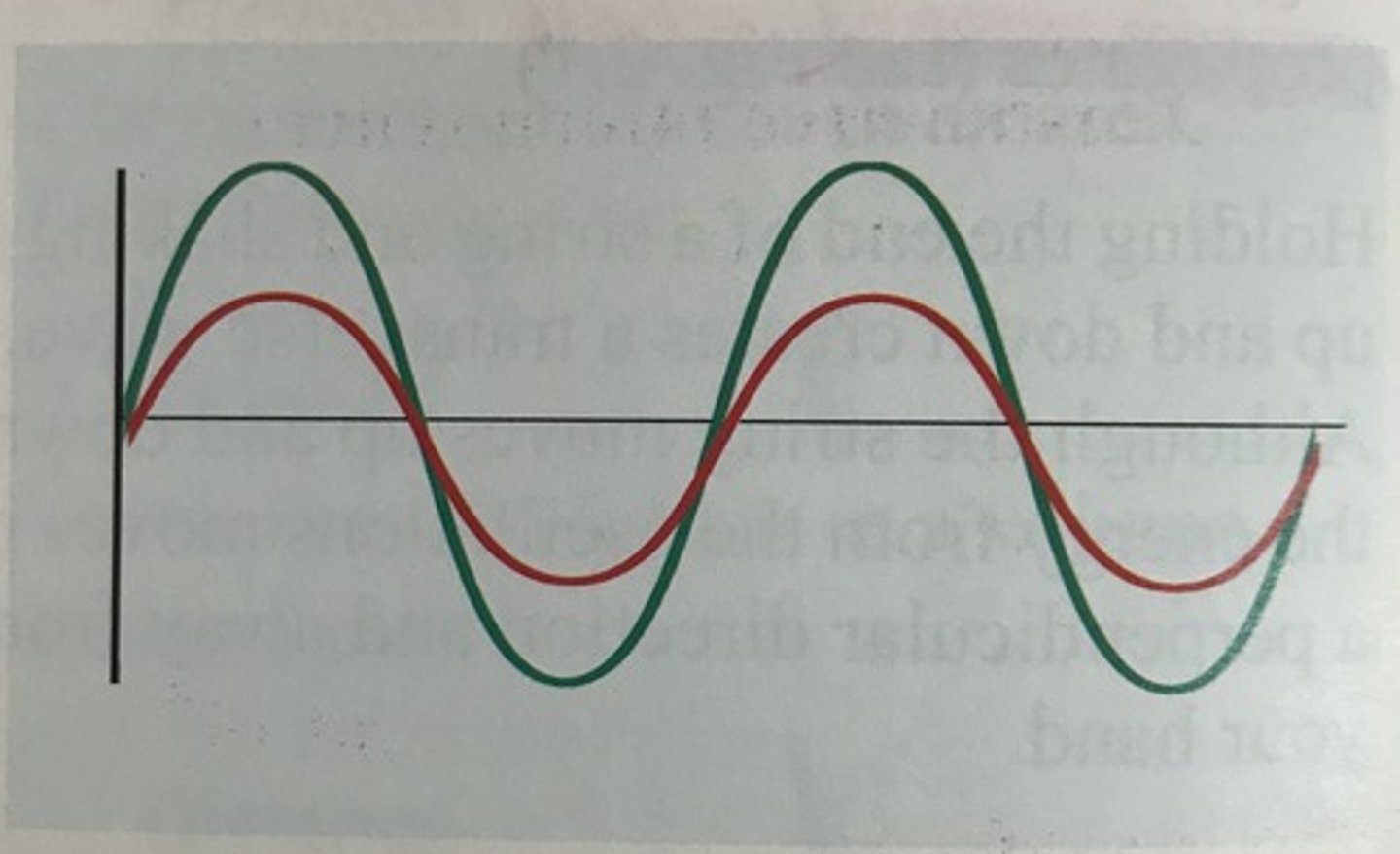
Waves are _________________ when their peaks and troughs occur at the same time and at the same location.
in- phase
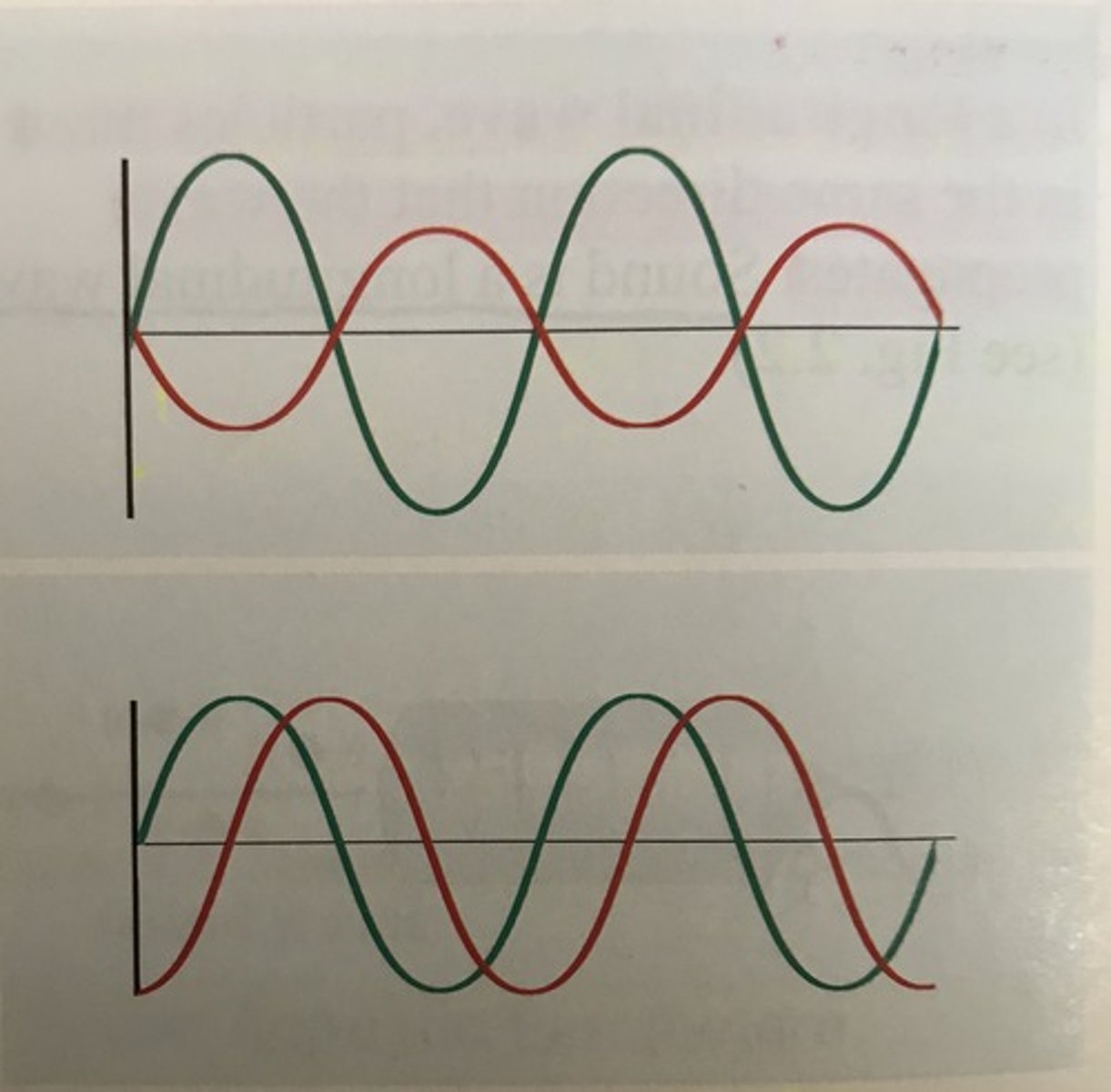
Two waves are ________________ when their peaks and troughs occur at different times.
out-of-phase
The following bullet points are describing:
. multiple sound beams travel in a medium arriving at an identical location @ the same time
. waves lose individual characteristics & combine forming a single wave
interference
both in-phase and out-of-phase wave pairs undergo interference; however,
they combine differently
Constructive interference
. in-phase waves
. forms a single wave of greater amplitude, larger wave
Destructive interference
. out-of-phase waves
. forms lesser amplitude, smaller wave
What happens when 2 out of phase waves are of equal amplitude?
. complete destructive interference, they cancel each other out
What happens when the frequencies of waves differ?
both constructive and destructive interference occur
Sound waves are
pressure waves