Membrane and Transport
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Diffusion
Movement of particles or molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
Osmosis
Diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane
Selectively pemeable membrane
A membrane that allows certain materials to pass through via special protein channels
Semi-permeable membrane
a membrane (as a cell membrane) that allows some molecules that are small enough to pass through but not others
Brownian motion
the chaotic movement of particles, caused by collision with other particles of the fluid in which they are dispersed
Dynamic Equilibrium
condition of continuous, random movement of particles but no overall change in concentration of substances/molecules
Hypertonic
A solution that has a higher concentration of solutes than another.
Hypotonic
A solution that has a lower concentration of solutes than another.
Isotonic
Two solutions that have an equal concentration of solutes.
Solute
substance that is dissolved in a solution
Solvent
the liquid that contains the dissolved solute in a solution.
plasma membrane (cell membrane)
Flexible, selectively permeable (having pores or openings) boundary that helps control what enters and leave the cell.
Facilitated Diffusion
this form of diffusion is regulated by protein channels in the membrane and requires no energy input from the cell
Active Transport
movement of molecules or ion into or out of the cell against its concentration gradient (from low to high) and requires an input of energy.
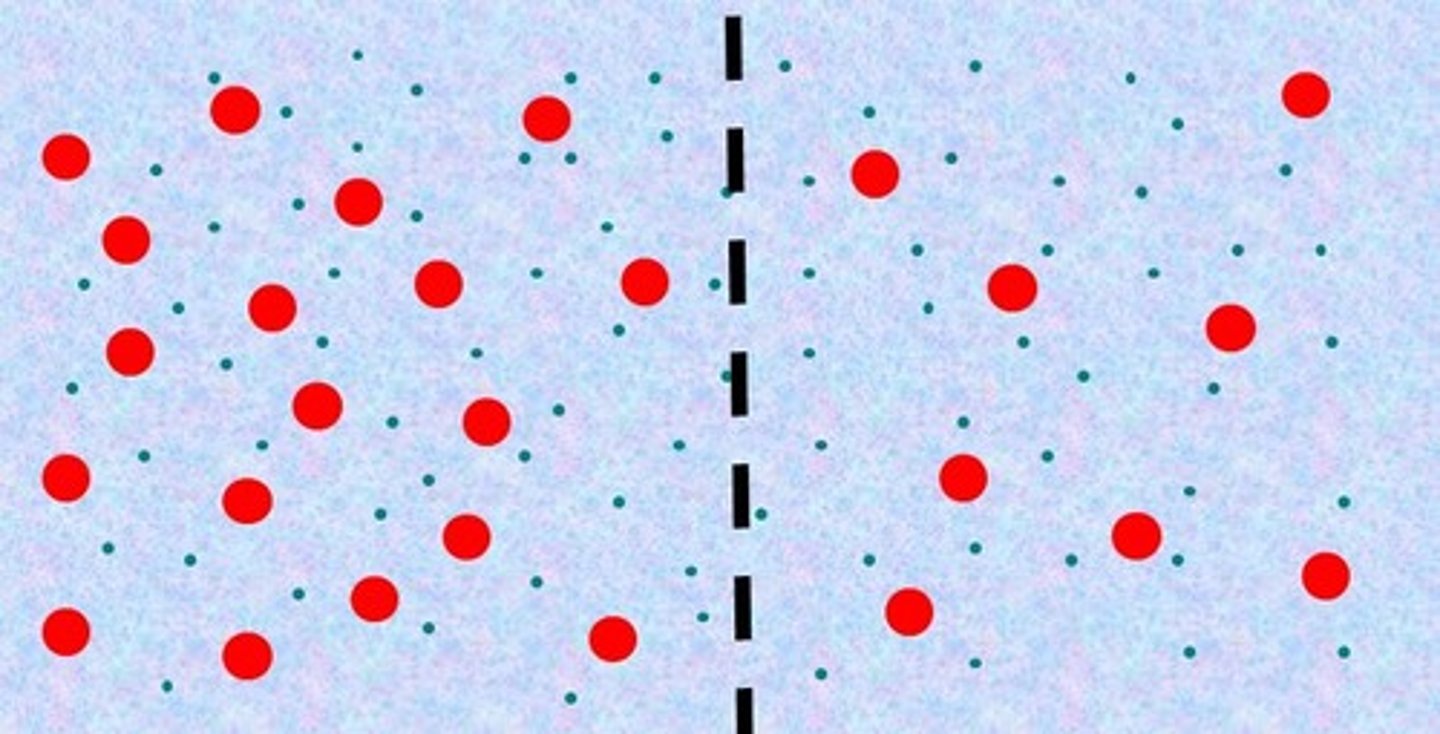
Hypertonic
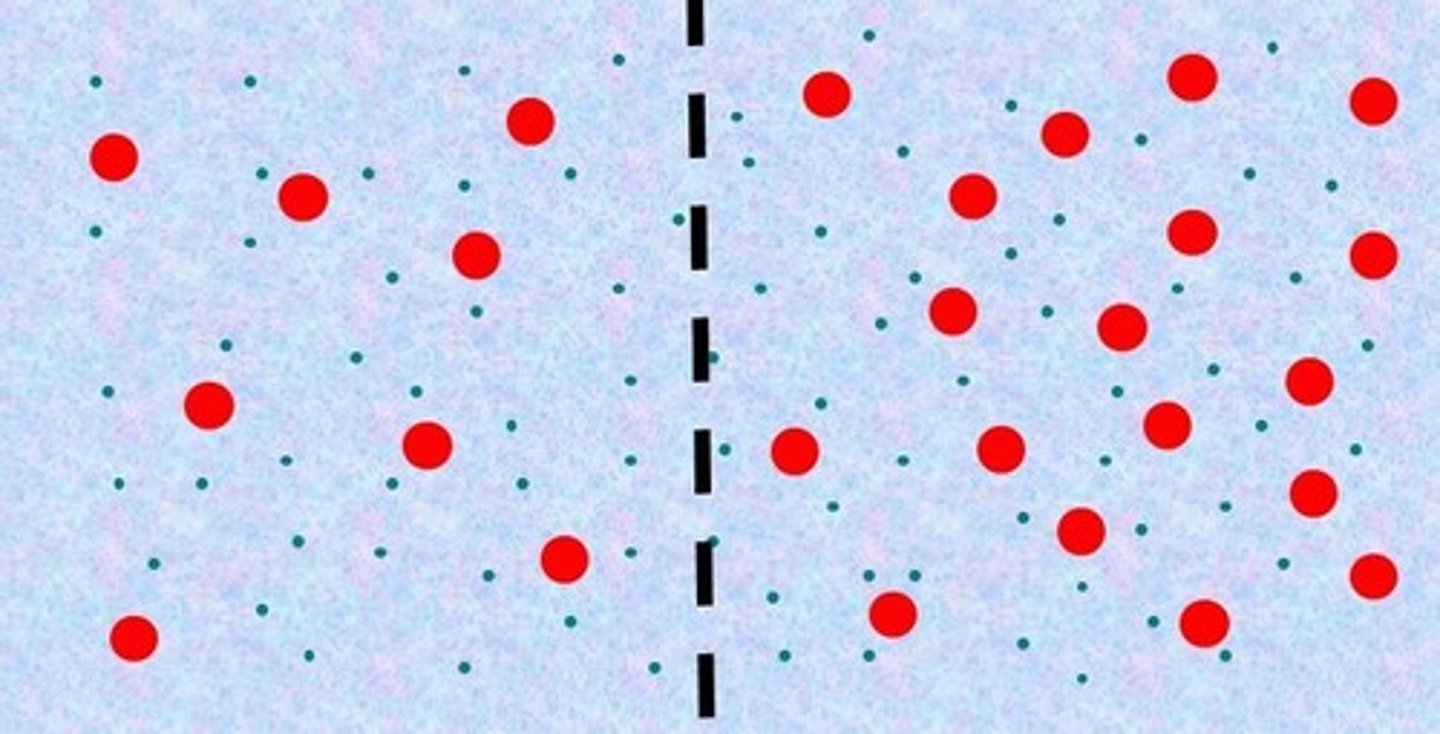
the left side is _____ compared to the right side.
Hypotonic
The right side is _____ compared to the left side.
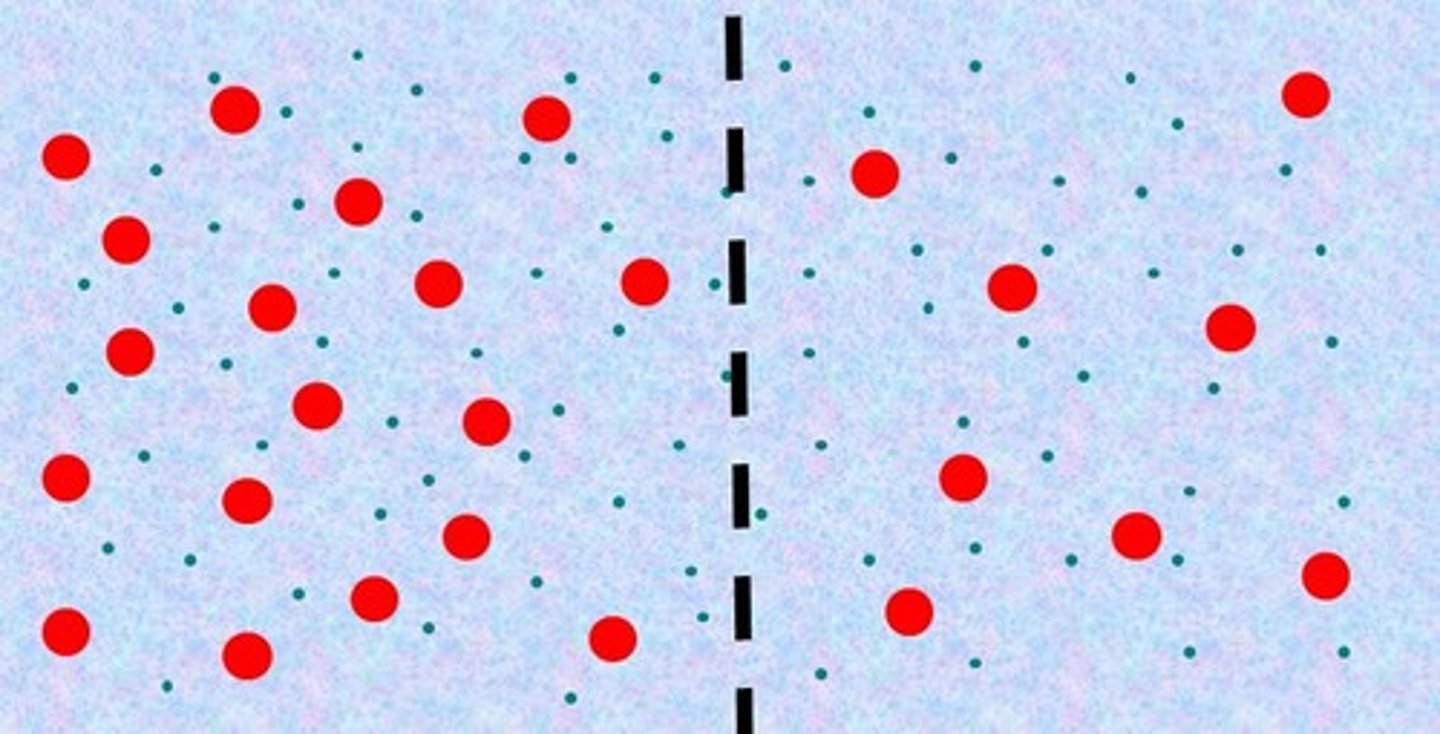
right, left, osmosis
Water will move from the _____ to the _____ by _____.

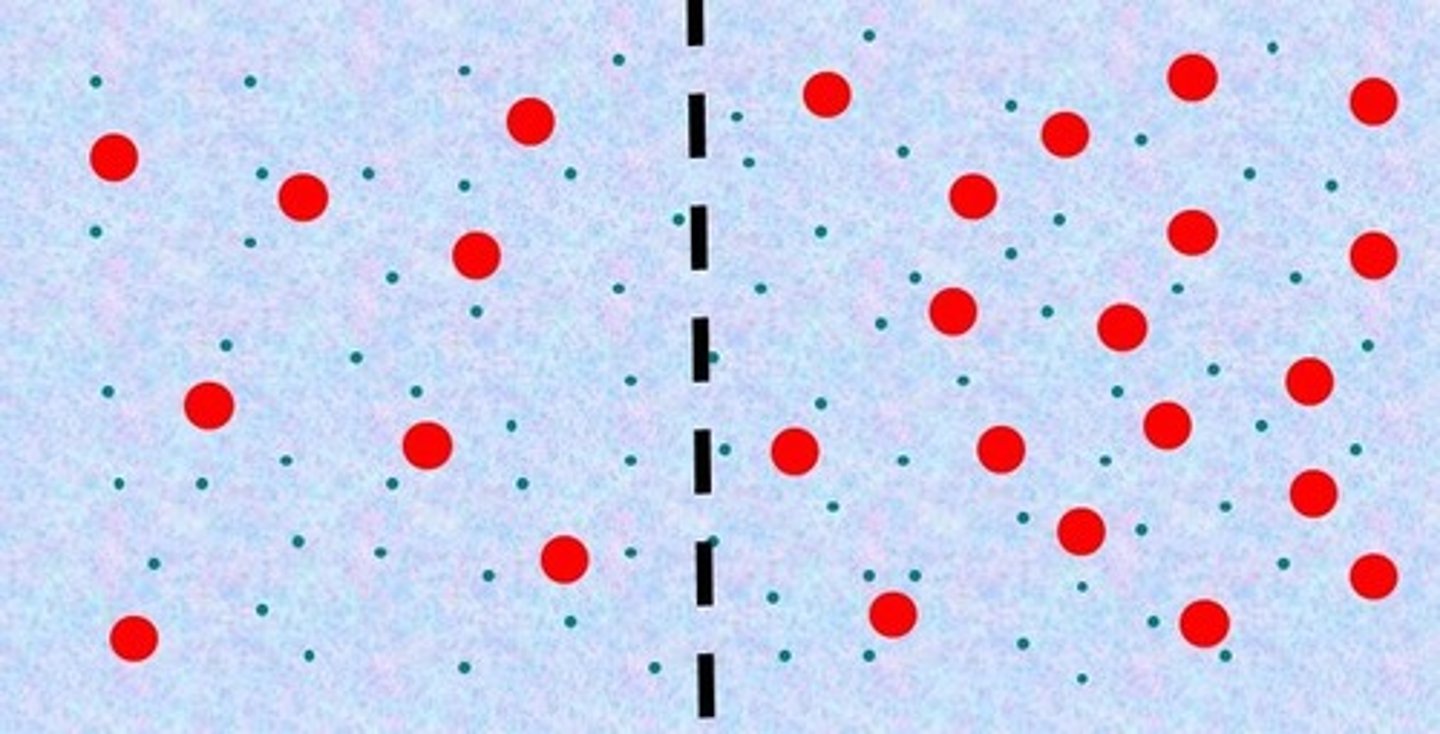
Hypotonic
The left side is _____ compared to the right side.
Hypertonic
The right side is _____ compared to the left side.
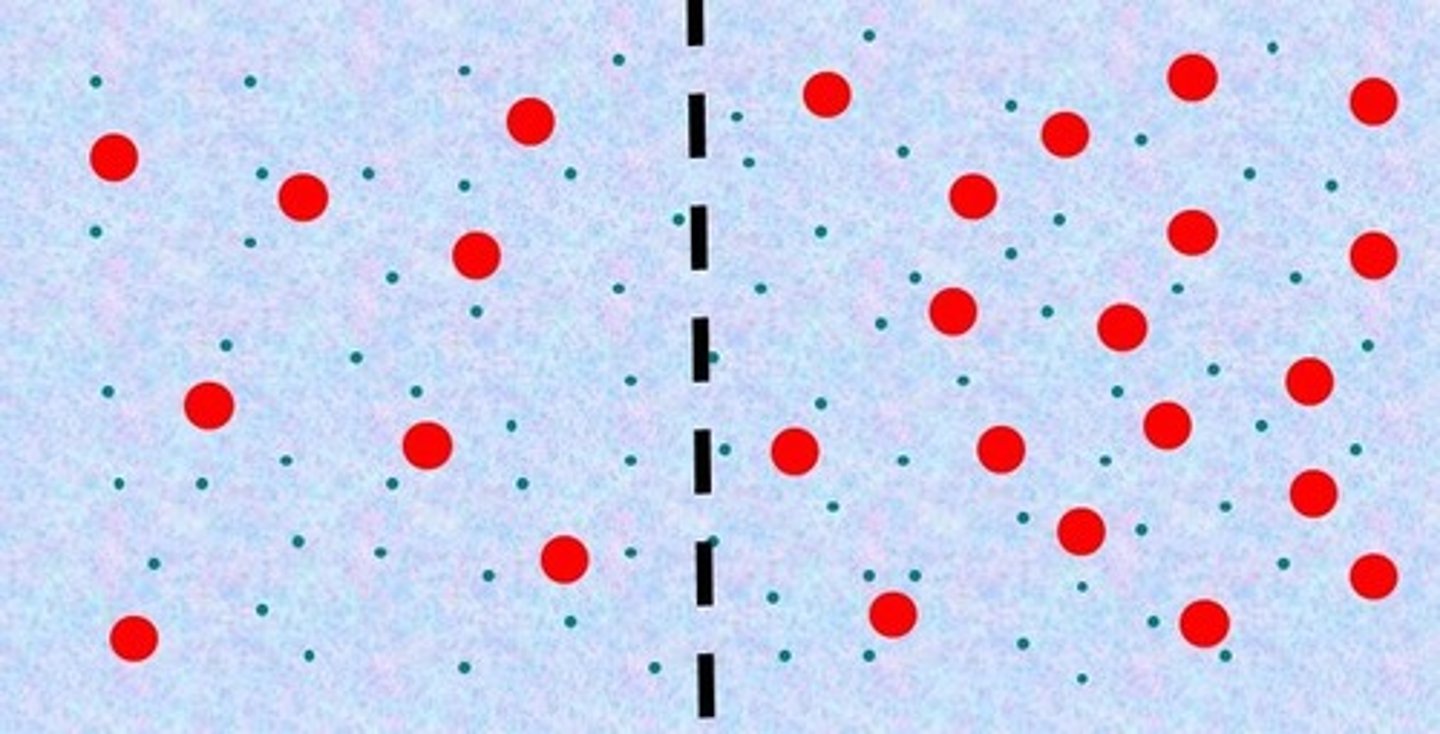
left, right, osmosis
Water will move from the _____ to the _____ by _____.
Phospholipid
molecule that makes up cell membranes. It has a hydrophilic "head" and two hydrophobic "tails".
Hydrophilic
water loving. substances that easily mix with water.
fluid mosaic model
Structural model of the plasma membrane where molecules (phospholipids, proteins, carbohydrates, etc.) are free to move sideways within a lipid bilayer.
Hydrophobic
water hating. substances that will not mix with water.
carrier proteins (transporters)
binds to specific chemical, changes shape, moves the specific chemical across the membrane
Active transport that requires energy (ATP)
intracellular
Located inside a cell.
extracellular
Located outside a cell.
concentration gradient
difference in the concentration of a substance from one location to another (like from outside the cell to inside the cell)
Transport Protein
Proteins within the cell membrane that function to move substances into or out of the cell.