NPB: Controlling Skeletal Muscle
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
T/F: With contraction of skeletal muscle we do not intend the contraction
False, with contraction of skeletal msucle we do intend these contractions, (i.e. using apple pencil on ipad)
The skeletal muscle is ___(uncontrolled/controlled)
controlled → very well
Hierarchy of Control
High - Cerebral Cortex
- Brain Stem Subcortical/ Cerebellar
Low - Spinal Cord
Cerebral Cortex
Highest level of control
decided what you want to do with the contraction
also for the future (i.e. want to run two miles)
Spinal Cord
Reflexive
Myostatic Reflux
muscle spindle
basic
Controls the CPU
Control motor activities
specific patterned motor activities
chew → central pattern generator
swim → central pattern generator
CPU
located: gray matter of spinal cord
Alpha Motor Neuron
Comes from: ventral gray matter
cell bodies & neuron are there
Crosstalk occurs with
low levels all the way to the top → cortical control
control really well → coordinated
Upper Motor Neuron
associated with the brain → spinal cord → lower motor neuron (alpha motor neuron) → skeletal muscle
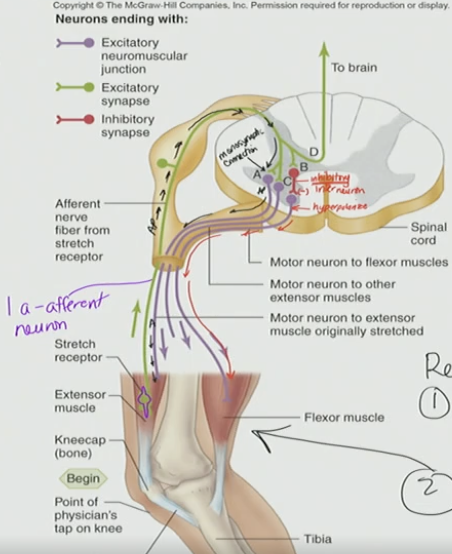
Muscle Spindle
stretch when the muscle is stretch → activates the 1-a-afferent neuron → info sent to spinal cord
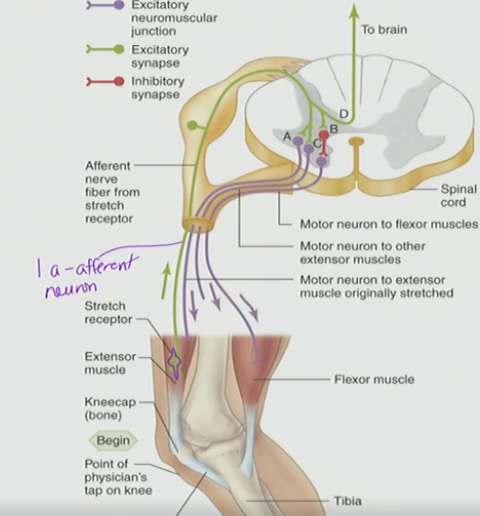
T/F: The muscle spindle sends stretch information to the spinal cord by activating the 1a afferent neuron.
True
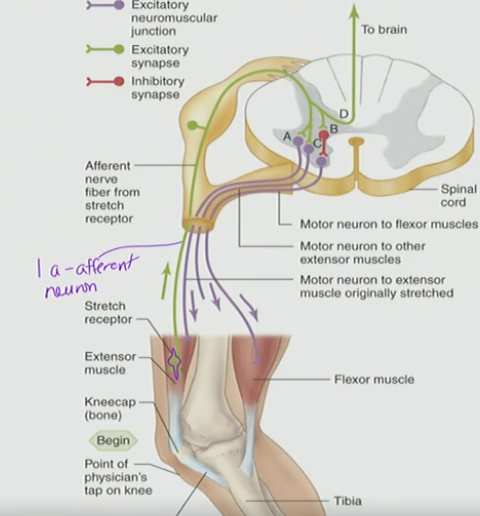
What is the role of the muscle spindle in skeletal muscle?
A) It generates contraction by releasing neurotransmitters
B) It detects stretch and sends signals via 1a afferent neurons
C) It prevents overstretch by relaxing the tendon
D) It stores calcium for muscle activation
B) It detects stretch and sends signals via 1a afferent neurons
When a muscle is stretched, the __________ is also stretched, activating the __________ neuron, which sends information to the spinal cord.
muscle spindle, 1-a-afferent
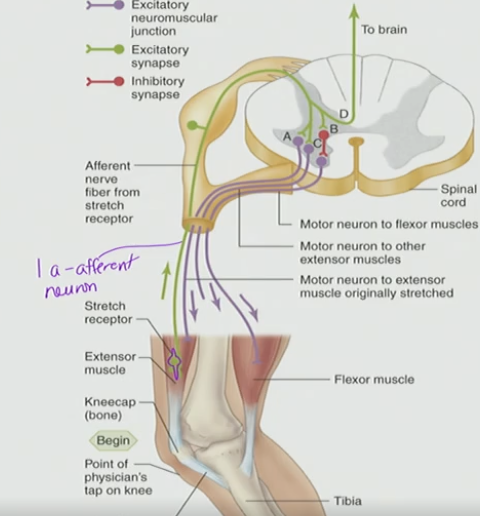
Monosynaptic Connection
AP travel all the way down on same muscle
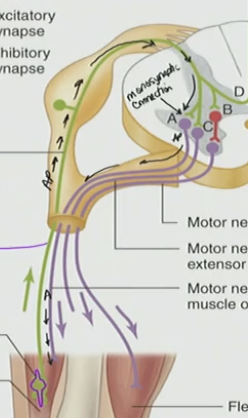
Inhibitory Interneuron
The neurotransmitter it releases is an inhibitory neurotransmitter (GABA, glycine)
Causes alpha motor neuron to hyperpolarize → no AP fired → goes to opposite muscle (antagonistic muscle)
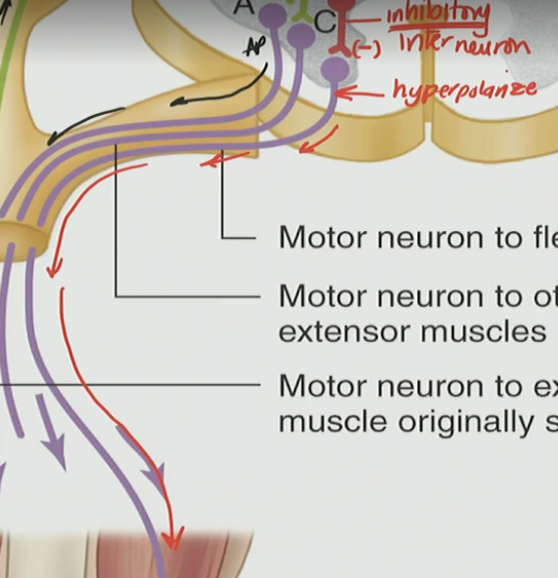
Interneuron
helps makes decisions
process lots of things
What is this process called?
Myotatic reflex
Stretch reflex
Knee-jerk reflex
What occurs in myotatic reflex/knee-jerk reflex?
The muscle spindle will stretch when the muscle is stretched
This activate the 1a afferent
The information will be sent to the spinal cord
The result response will appear
Stretched muscle will contract. This is the extensor.
Flexor will not contract
Activate 1a afferent → info to spinal cord → Result/Response
Stretched muscle will contract (Extensor)
Knee-jerk: wack knee → stretched quadriceps → leg kick out → contraction
Flexor (antagonistic muscle) will not contract bc we inhibit the motor neuron that goes to it at the level of spinal cord
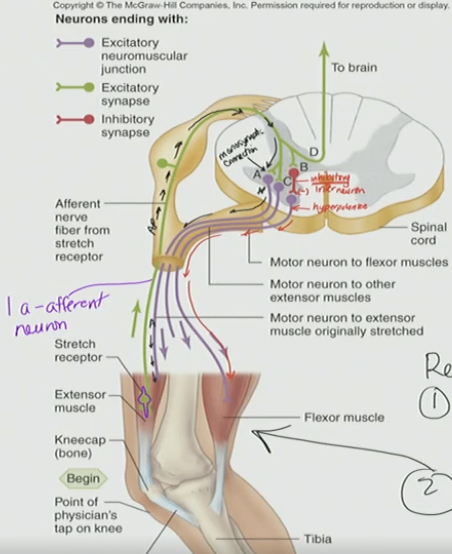
Spinal Cord: Pain Withdrawal Reflex
Step on tack with right leg
withdrawal right leg form painful stimulus
contract the flexor NOT extensor → this allows you to pull leg away from the painful stimulus
opposite leg is extended (extensor muscles) NOT flexor
Nociceptor Afferent Neuron
pain sensitive neuron
sent to spinal cord
interneurons immediate response
T/F: In a reflex, you have to activate the hamstrings, which allows them to contract.
True, you need to contract it as in flexor to withdrawal from the pain
The foot for posture activates the ___(flexor/extensor)
extensor → quad
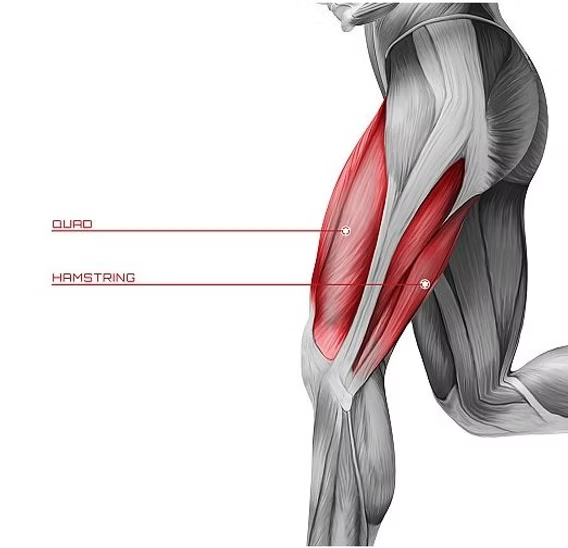
T/F: The hamstring on the side of the injured leg contracts to lift the foot during a withdrawal reflex.
True, The hamstring is a flexor that contracts to bend the knee and lift the foot away from pain.
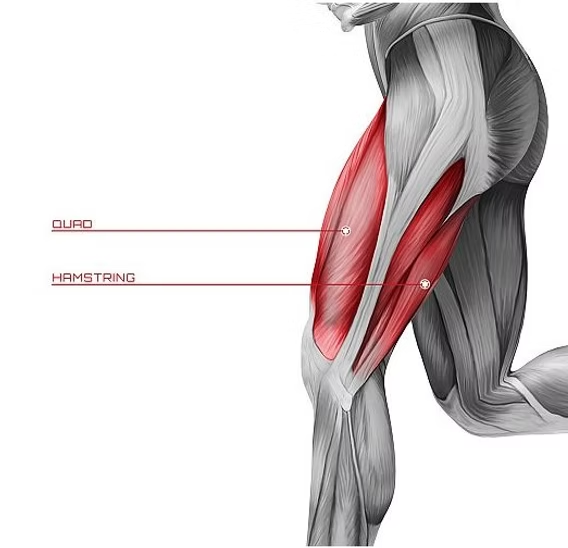
T/F: The quadriceps on the injured leg contract to stabilize posture.
False, that would be the opposite leg quad extensor
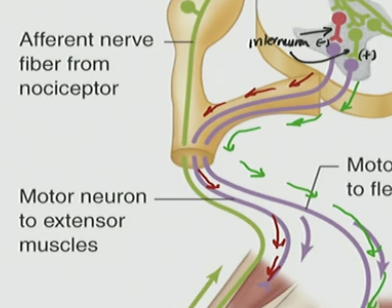
Excitatory interneuron (green)
talks downstream → flexor (hamstring)
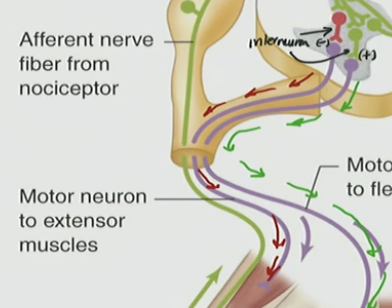
Inhibitory interneuron (red)
inhibit extensor (quad), but activate flexor (hamstring)
T/F: You cannot override the pain withdrawal reflex
False, you actually can override the pain withdrawal reflex bc there are so many synaptic connections (descending pathway)
T/F: You cannot override the knee-jerk reflex
True, you cannot override the knee-jerk reflex because there is a lack of synaptic connections
T/F: The spinal cord mediates reflex responses without input from the brain.
True, Reflexes like the withdrawal or stretch reflex are handled at the level of the spinal cord.