Understanding Bone Pathologies and Their Radiographic Appearances
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Normal bone appearances
Bone diseases can affect bone composition, hence altering their radiographic appearance.
Epiphyseal plate
Formed from cartilage and therefore radiolucent.
Joint cavity
Contains articular hyaline cartilage and synovial fluid, therefore radiolucent.
Cortex
Solid white line around bone.
Medullary cavity
Less dense than cortex and so brighter on x-ray.
Bone density
The bones of the skull and face vary in density - eg the dense occiput and less dense temporal bones.
Metabolic bone disease
An umbrella term for a broad range of clinically different bone abnormalities, usually caused by mineral abnormalities / deficiencies (eg calcium, phosphorous, vitamin D).
Osteoporosis
The most common metabolic bone disease that can result in bone pain, fracture, and loss of height.
Decreased bone density
Osteoporosis leads to decreased amount of calcium, therefore decreased bone density, resulting in weakened bones more susceptible to fractures.
Risk factors for osteoporosis
Diet/weight, family history, medications, hormone levels, smoking.
Osteoporotic fractures
Weakened bones are more likely to break, with the incidence of spinal wedge fractures being common.
DEXA scanning
Bone density (risk of osteoporosis) can be measured by DEXA scanning, which stands for Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry.
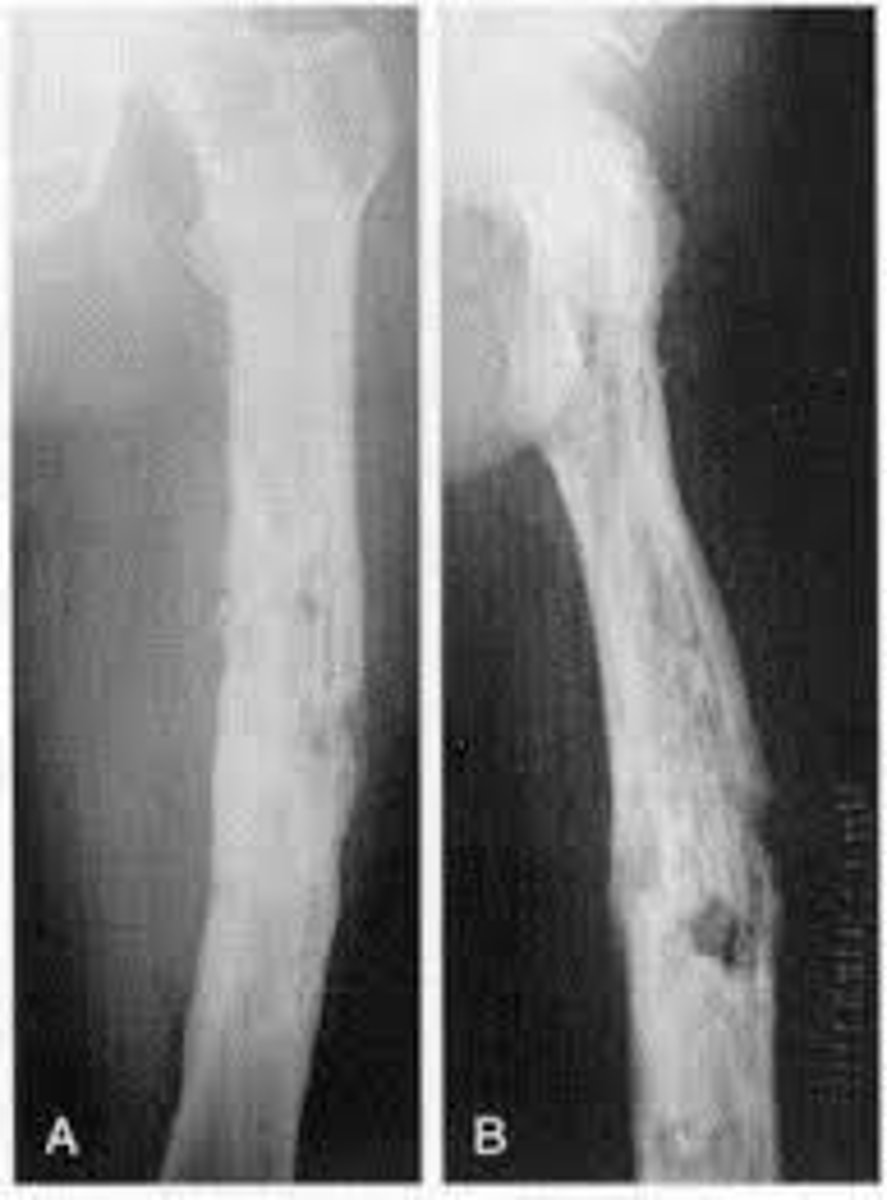
Colles fracture
Colles fractures are the most common type of distal radial fracture, particularly common in patients with osteoporosis.
Osteoporotic wedge fracture
A common site for fractures in patients with osteoporosis.
Bone pain
Can result from osteoporosis and other metabolic bone diseases.
Fracture
A break in bone that can occur due to weakened bone structure.
Loss of height
Can occur due to wedge fractures associated with osteoporosis.
Annual cost of osteoporotic fractures
Osteoporotic fractures cost the NHS around £4 billion annually (UK Parliament, 2020).
Colles fracture
A Colles fracture in an elderly patient generally leads to an assessment for osteoporosis.
Neck of femur (NOF) fracture
Neck of femur fractures in the elderly are common and associated with high mortality rates (up to 30% within 1 year).
Neck of femur fractures
Also known as 'broken hip', the neck is the weakest part of the femur and can lead to disruption of femoral blood supply (avascular necrosis).
Prognosis of neck of femur fractures
Prognosis is varied but is complicated by advanced age.
Surgical treatment for neck of femur fractures
Dynamic hip screw (DHS) is used, guided by radiographers in theatre using an Image Intensifier (II).
Insufficiency fractures
Arise from normal stresses on abnormal bone.
Osteoporotic fracture
A fracture that occurs due to weakened bones from osteoporosis.
increased risk based on diet, weight hormone levels and smoking
no symptoms till the bone is broken.
Pathological fracture
A fracture that occurs in a bone that is weakened by disease.
Fibrous dysplasia
A bone disorder where scar-like tissue develops in place of normal bone.
Paget's disease of bone
A condition where osteoclast cells absorb bone at a faster rate than usual, leading to larger but weaker new bone.
Causes of Paget's disease
Although the cause is unknown, there is a linked genetic predisposition and environmental factors like diet lacking in calcium, and exercise can lead to the development of this disease
Radiographic appearances of Paget's disease
Osteolytic lesions, bone enlargement, deformities, thickened cortex, coarse trabeculae.
Osteomyelitis
An infection of the bone which can be treated with antibiotics and can cause serious long-term problems if untreated.
Causes of osteomyelitis
Usually arises as a result of infection traveling through the bloodstream or from a nearby infected tissue.
Radiographic appearances of osteomyelitis
Soft tissue swelling, periosteal reaction, cortical irregularity, Brodie abscess, thickened and irregular bone, sclerosis, elevated periosteum.
Osteomalacia
Softening of the bones, referred to as rickets in children, often due to vitamin D deficiency.
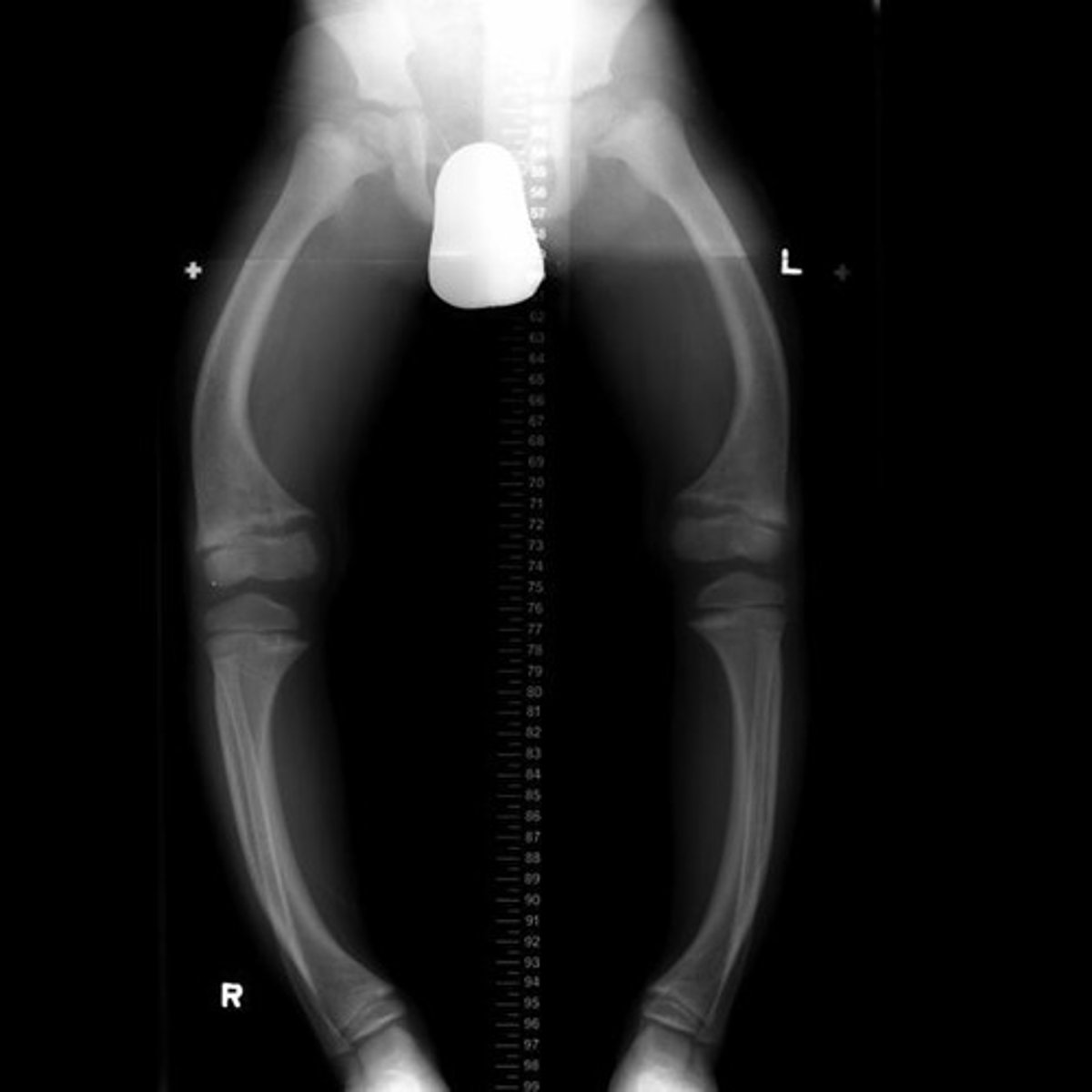
Radiographic appearances of osteomalacia
Pseudofractures, low bone density, blurred trabeculae, lower limb bowing.
Osteogenesis imperfecta
An inherited bone disorder present at birth characterized by absent or low levels of collagen, leading to soft bones and minimal impact fractures.
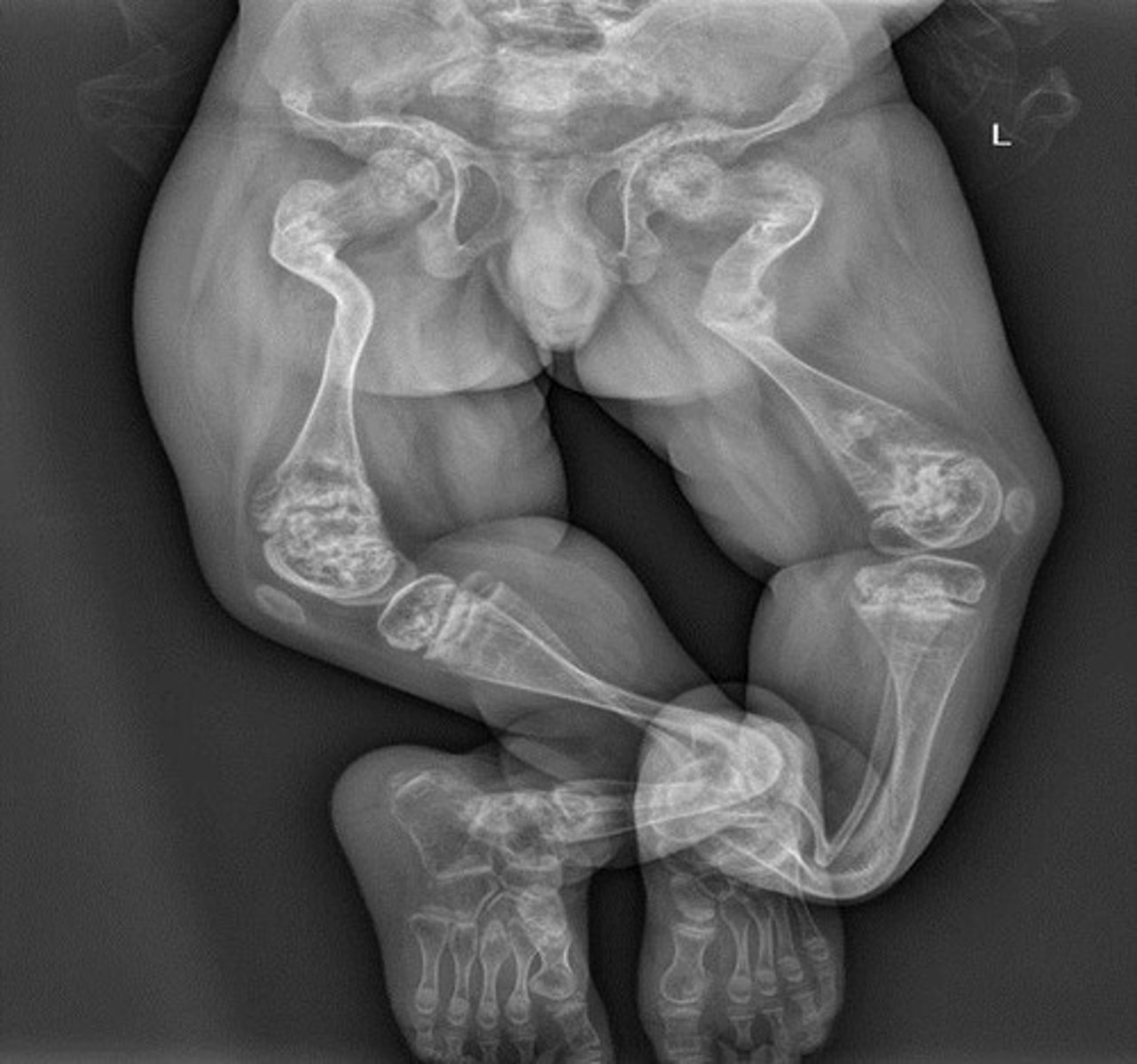
Signs of osteogenesis imperfecta
Range of signs and symptoms from mild to severe, including irregular shaped bones, hypermobile joints, problems with teeth formation, short stature, bone or joint pain, and fatigue.
Osteo
Prefix meaning bone.
Chondro
Prefix meaning cartilage.
Arthro
Prefix meaning joint.
itis
Suffix meaning inflammation of.
blast
Suffix meaning developing cell.
clast
Suffix meaning break down.
oma
Suffix meaning tumour.
physis
Suffix meaning growth.
ectomy
Suffix meaning removal of.
gensis
Suffix meaning development.