Design unit 3 terms
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
Design elements (7)
Basic components that are used to construct a design composition
i.e., line, shape, tone, form, space, colour, texture
Design principles (12)
Describe how elements are applied to a composition
i.e., balance, contrast, emphasis, repetition, movement, scale, unity, variety, pattern, harmony, alignment, hierarchy
Gestalt principles
Describes how people group and interpret visual info
Explains how this affects perception and behaviour
Helps optimise design for audience impact
Semiotics
Study of symbols, signs and images
Explores how they create meaning
Used to influence, connect and communicate with audiences
Sign
Conveys meaning through signs
Combination of the signifier and signified
Symbol
No obvious resemblance between the signifier and signified
e.g., letters and numbers, red octagon = ‘stop’
Index
Shows evidence of what’s being represented
e.g., paw print = animal
Icon
Has an obvious physical resemblance to what is being signified
e.g., male and female pictograms to indicate toilets
Signifier
The form the sign takes
Signified
The message or concept that the signifier communicates
Design lifecycle
The total environmental cost or impact of a design over its useful life
Stages of design lifecycle (6)
Pre-production, testing and use of prototypes
Acquisition of raw materials
Manufacturing, processing and formulation
Distribution and transportation
Use, re-use and maintenance
Recycling and waste management
Strategies for reducing environmental impact (DREAMS MD)
designing for reliability and durability
reducing resource consumption
extending the lifespan of materials or products
adaptable, multi-functional or modular designs
making repair or maintenance easier
selecting low-impact resources and processes
making items easy to disassemble or break down
designing for eco-efficiency if power is required
Copyright
A legal right created by the law of a country that grants the creator of an original work exclusive rights for its use and distribution
Gaining copyright
Automatic and free in Australia once documented
Copyright duration
70 years after creator’s death for literary, dramatic, musical and artistic works
70 years after creation for sound recording and films
Trademark
Protects a company's unique brand, products or services
Gaining trademark
Min cost of $250
Min registration time of 7 months
Lasts for up to 10 years before renewal
Benefits of trademark
Business asset (more successful the business, more valuable the trademark)
Legal right to place ® next to it
Exclusive rights
Ability to deter others from using it
Ability to sell or license it to others to use
Patent
Protects any device, substance, method or process that's new, inventive and useful
Gaining a patent
Min registration cost of $110 for a provisional patent (up to several thousand for full protection)
Min registration time of 6 months (up to several years)
Lasts for up to 20 (standard) to 25 years (pharmaceutical)
Benefits of a patent
Receive commercial rights (can monopolise the market)
Freedom to license others to manufacture item without risking them stealing the idea
Right to take legal action that stops others from manufacturing/using/selling invention without permission
Design rights
Protects the overall visual appearance of new and distinctive products
Gaining design rights
Min registration cost of $250 ($420 for certification)
Min registration time of 2 months (4 months to certify)
Lasts up to 10 years (can renew at 5 years)
Benefits of design rights
Exclusive right to use design and authorise others to do so
Right can grow in value and be sold and licensed
Able to apply for same design right overseas
Right to take legal action against someone who uses design without permission
Gestalt principles (5)
Figure-ground
Similarity
Continuity
Proximity
Closure
Figure-ground
The perception of visual elements as either the main object or background
Creates emphasis, establishes clear distinction, draw attention to important elements
Similarity
The tendency of the brain to group together elements that share similar visual characteristics
Establish consistency and unity, cohesive and harmonious, reinforces overall message
Continuity
The human eye's preference for smooth and continuous lines or patterns
Guide viewer's eyes and create visual flow, establish clear visual path and organisation, no abrupt changes in direction
Proximity
The tendency to perceive objects that are close together as belonging together
Organise info, create visual hierarchy
Closure
The mind's tendency to perceive incomplete or fragmented elements as a complete whole or pattern
Engage viewers' imagination, creates visual interest, viewer encouraged to actively complete image
Typeface
The overall design of a set of characters (century gothic, comic sans, times new roman)
Font
Specific variations/styles within a typeface (bold, italic, regular)
Serif
More traditional style, have feet
Sans serif
More modern style, don't have feet
Script
Cursive, more decorative
Display
Decorative, good as design focal point
Hue
Name of colour
Saturation
Intensity/purity of colour
Value
Lightness/darkness of colour
Tonal range
Levels between image's lightest and darkest points
Linear design process
Comprises of defined steps in a specific sequence, proceeding through each step, to develop a single solution
Linear process limitations
Narrow focus
Limited options
Inflexible and static
Problems can't be found
Problems can't be fixed
Redo and repeat
Iterative design process
Involves repeated cycle of prototyping, testing and refining ideas based on stakeholder feedback
Iterative process features
Open ended
Endless variations possible
Flexible and adaptable
Problems identified early
Problems resolved
Define, test and refine
Convergent thinking
Process of finding concrete and familiar solutions to problems
Uses logic and multiple facts to converge onto an answer
Divergent thinking
Creative process of generating original ideas and possibilities
Process of exploring an issue more widely or deeply
Uses imagination to diverge from a question and come up with multiple ideas
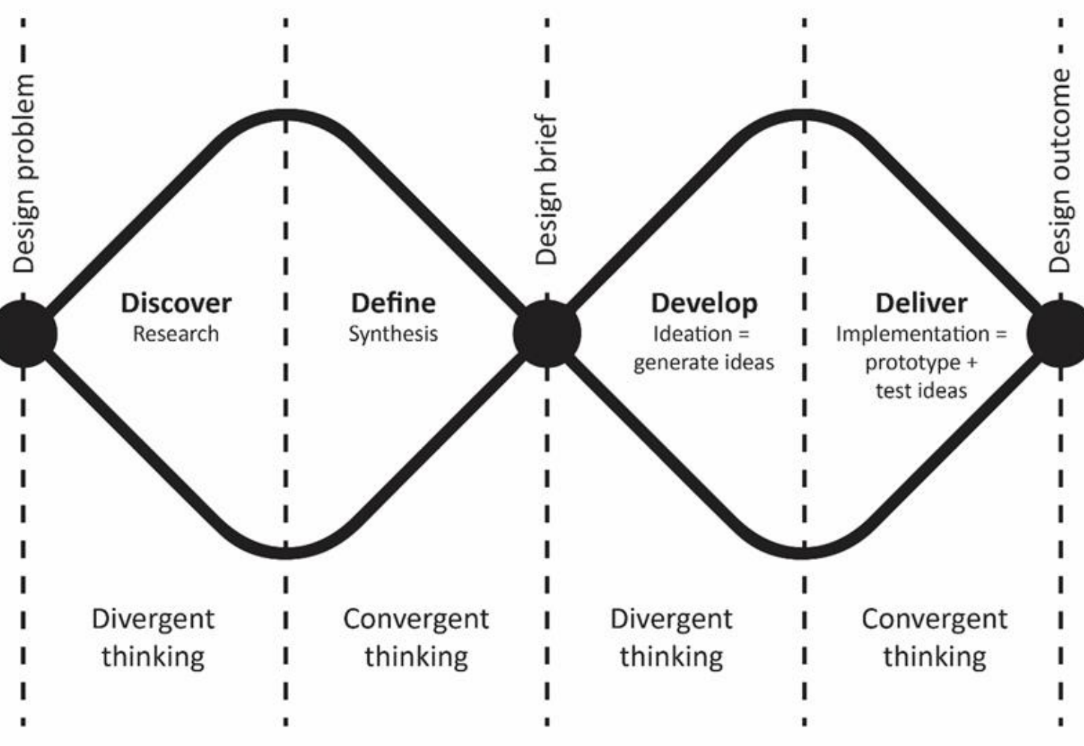
Discover
Helps people understand the problem
Involves speaking to and spending time with people affected by the issues
Define
Insight gathered from the discovery phase can help define the challenge in a different way
Develop
Encourages people to give different answers to the clearly defined problem
Seek inspiration from elsewhere and co-designing with a range of different people
Deliver
Involves testing different solutions at a small-scale
Those that don't work are rejected and those that do are improved
Communication strategies
Strategies/devices strategically used to engage/persuade the audience (shock, humour, emotion, metaphor)
Target audience
Specific group of people that a product, service, marketing campaign is intended to reach
OSH
Occupational Safety and Health
The legal responsibility of all workplaces to protect the safety, health and welfare of employees, customers and the general public
Ergonomics
Ensures designs are compatible with the needs, abilities and limitations of the user
Safe design
Consider hazard identification and risk assessment to eliminate the risk of injury throughout the life of the design
Safe design considerations
Equipment, materials, working conditions, distribution and marketing and use and maintenance
Sustainable design
An approach to design that consists of a variety of sustainable design principles, centered around extending product lifespans and avoiding the depletion of natural resources
Product life cycle
The period of time from when the product is introduced to the market to when it's taken off shelves and no longer available to consumers
Circular economy
Prioritises the reuse of products and materials and the overall reduction of waste
Greenwashing
Any unsubstantiated claims about a product being produced sustainably or other eco-conscious practices
Standardisation
The practice of using universal parts in products' designs
Benefits of sustainable design
Less waste/emissions/energy used
Connect with eco-conscious consumers
Potentially receive gov subsidies/tax incentives
Drawbacks of sustainable design
Higher material costs
Sustainable materials are often recycled or sourced in sustainable ways -> more specialised equipment, source from different regions, less materials sourced, different packing and shipping
Linear design process steps
Design brief, research, ideate, develop, refine, produce
Double diamond
hello
Line
Directional - lead the eye through artwork and draw attention to certain parts or focus points
Organic - appear natural and imperfect
Implied - created when the eye connects a composition’s elements to suggest a perceived line
Shape
2D - can only be measured by height and width
Geometric - enclosed figures formed by joining a certain number of points lines or curves and are usually simple and symmetrical
Abstract - symbols that might represent abstract ideas or simplified versions of more complex ones
Tone
Tonal scale - the range of lightness or darkness in the composition
High key - limited range of dark values
Low key - limited range of light values
Form
3D - can only be measured by height, width and depth
Proportion
Space
Positive - subject or areas of interest in a composition
Negative - area of the composition that’s left empty
Organised
Colour
Psychological effects - can affect the emotions and moods of people
Additive (RGB) - created by mixing different amounts of light colours, begin as black and become more white as colours are added
Subtractive (CMYK) - created by completely or partially absorbing some light wavelengths and reflecting others
Texture
Visual - illusion of physical texture
Tactile - how the composition surface physically feels
Design thinking
Approach for identifying, redefining and solving problems
Way of thinking and working that includes a set of strategies and methods for testing concepts and ideas
i.e., design mindset, empathy map, needfinding
Empathy mapping
Visual representation of the attitudes and behaviours of a user
Captures and represents a user’s emotions and thoughts based on first-hand data
Demographic characteristics
Used to identify and develop a complete target audience or end-user profile
Statistical info used to influence and support design decisions to ensure their designs meet the needs of the end user
Psychographic segmentation
Used to identify and develop a complete target audience or end-user profile
Internal psychological characteristics used to influence and support design decisions
Discover methods
Empathy mapping
Needfinding
Collaborative brainstorm
Define methods
Design brief
Develop methods
Concept maps
Visual brainstorm
6 thinking hats
SCAMPER
Synectic triggers
Deliver methods
PMI
SWOT analysis
Compare and contrast
6 thinking hats