Chemistry AC1 and AC2
1/122
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
"C1 - States of Matter Particle model"
"C1 - States of Matter Particle model"
"Solids, Liquids and Gases - How are they arranged"
"Solids are tightly packed in a regular arrangement liquids are in a random arrangement close together gases are randomly arranged and are very far apart"
"Solids, Liquids and Gases - Can they be compressed"
"Solids cannot liquids cannot gases can"
"Solids, Liquids and Gases - What is their motion"
"solids vibrate liquids slide over each other gases move freely in random speeds and directions"
"Solids, Liquids and Gases - What is their shape and volume"
"Solids have a definite shape and volume liquids have a indefinite shape but definite volume gases have a indefinite shape and volume"
"Name all the changes between states of matter [Solid <-> Liquid <-> Gas]"
"Solid to Liquid: melting Liquid to Solid: freezing Liquid to Gas: boiling / evaporating Gas to Liquid: condensation Solid to Gas: sublimation Gas to Solid: deposition"
"Melting and boiling"
"Melting and boiling"
"What is melting point"
"the temp at which a substance melts or freezes"
"What is boiling point"
"the temp at which a substance boils or condenses"
"What is required and How does the change of state [Solid <-> Liquid <-> Gas] happen"
"Requires heat energy that is transferred to kinetic energy in the particles. The particles will move more and move and overcome bonds to become the next state"
"What is required and How does the change of state [Gas <-> Liquid <-> Solid] happen"
"Particles lose heat energy and therefore kinetic energy. This makes the particles move less and the bonds reform"
"Describe a heating curve example"

"Gas pressure"
"Gas pressure"
"What causes gas pressure"
"gas pressure is caused by force exerted by gas particles as they collide with the walls of their container"
"Why does gas pressure increase when temp rises"
"The heat energy is transferred into kinetic energy in the particles. They move faster and collide with the walls more often. This leads to increase force therefore increased pressure"
"What is the formula for pressure"
"force/area = pressure"
"What things affect gas pressure"
"temperature size of container amount of particles"
"Diffusion"
"Diffusion"
"What is diffusion"
"The net movement of particles from an area of high to low concentration randomly"
"What four things (and why) affect diffusion"
"Temperature - higher kinetic energy to move Surface area - large surface area is faster diffusion Concentration gradient - higher gradient is faster diffusion Molecular mass - bigger molecule will diffuse slowly"
"C12 - Experimental techniques"
"C12 - Experimental techniques"
"Chromatography"
"Chromatography"
"What is a Solvent"
"substance solute dissolves in (usually liquid)"
"What is a Solute"
"substance that dissolves into solvent"
"What is a Solution"
"mixture of solute and solvent"
"What is Solubility"
"how easily the solute dissolves"
"What is Dissolving"
"when a solute mixes into a solvent without chemically bonding or disappearing (cant be seen but still there)"
"What are the 5 seperation methods"
"Chromatography fractional distillation simple distillation Filtration evaporation/crystallisation"
"What is a mixture"
"Two or more combined substances that are not chemically bonded together"
"What are the two "phases" in chromatography"
"Stationary phase - doesn't move - Paper / solute mobile phase - moves - water / solvent"
"What is chromatography and how does it work"
"lets us separate inks and dyes according to size and solubility of particles as the solvent (water) rises through the paper it dissolves the sample mixture which will then travel up the paper The smaller and more soluble particles travel further"
"What is retention factor"
"to measure how far a compound travels relative to the solvent front"
"What is the formula"
"Distance from baseline to spot centre/Distance from base line to solvent front"
"Any spots at the same height are…"
"the same substance"
"Filtration"
"Filtration"
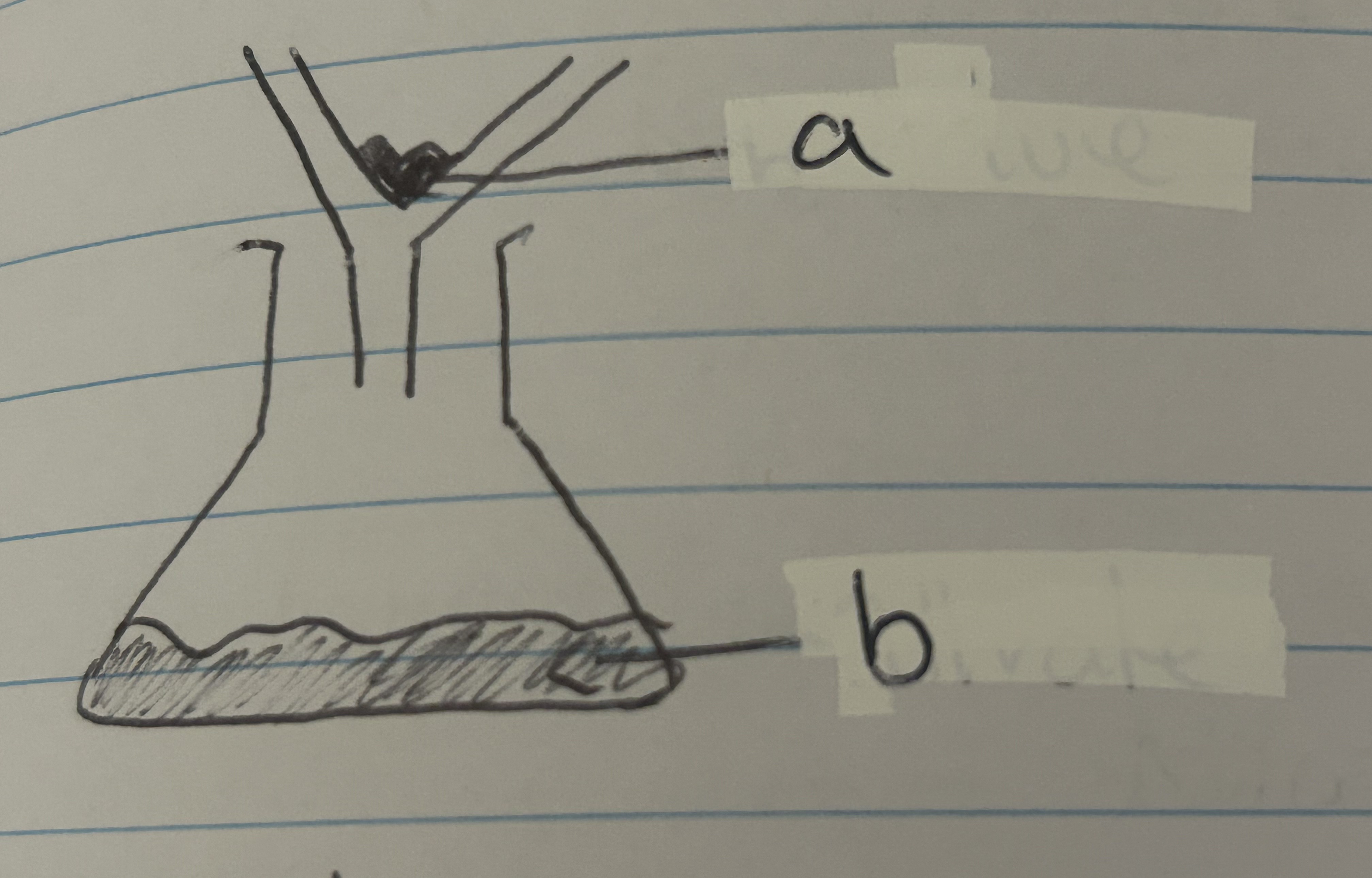
"Label the parts"
"a - residue b - filtrate"
"Fill in the gaps Filtration separates a (a) from a (b) solid or a (c) from a solid that is mixed with it. Filter paper contains tiny (d). Some particles will be small enough to pass through, this is the (e). Particles that cannot pass through are (f)."
"Fill in the gaps Filtration separates a solute (a) from a insoluble (b) solid or a solvent (c) from a solid that is mixed with it. Filter paper contains tiny holes (d). Some particles will be small enough to pass through, this is the filtrate (e). Particles that cannot pass through are residue (f)."
"Evaporation and distillation"
"Evaporation and distillation"
"What is evaporation"
"A liquid turning to gas leaving behind the solid, used for separating a soluble solid and liquid"
"What is distillation"
"Separate and collect the liquid when separating it from a soluble liquid or solid"
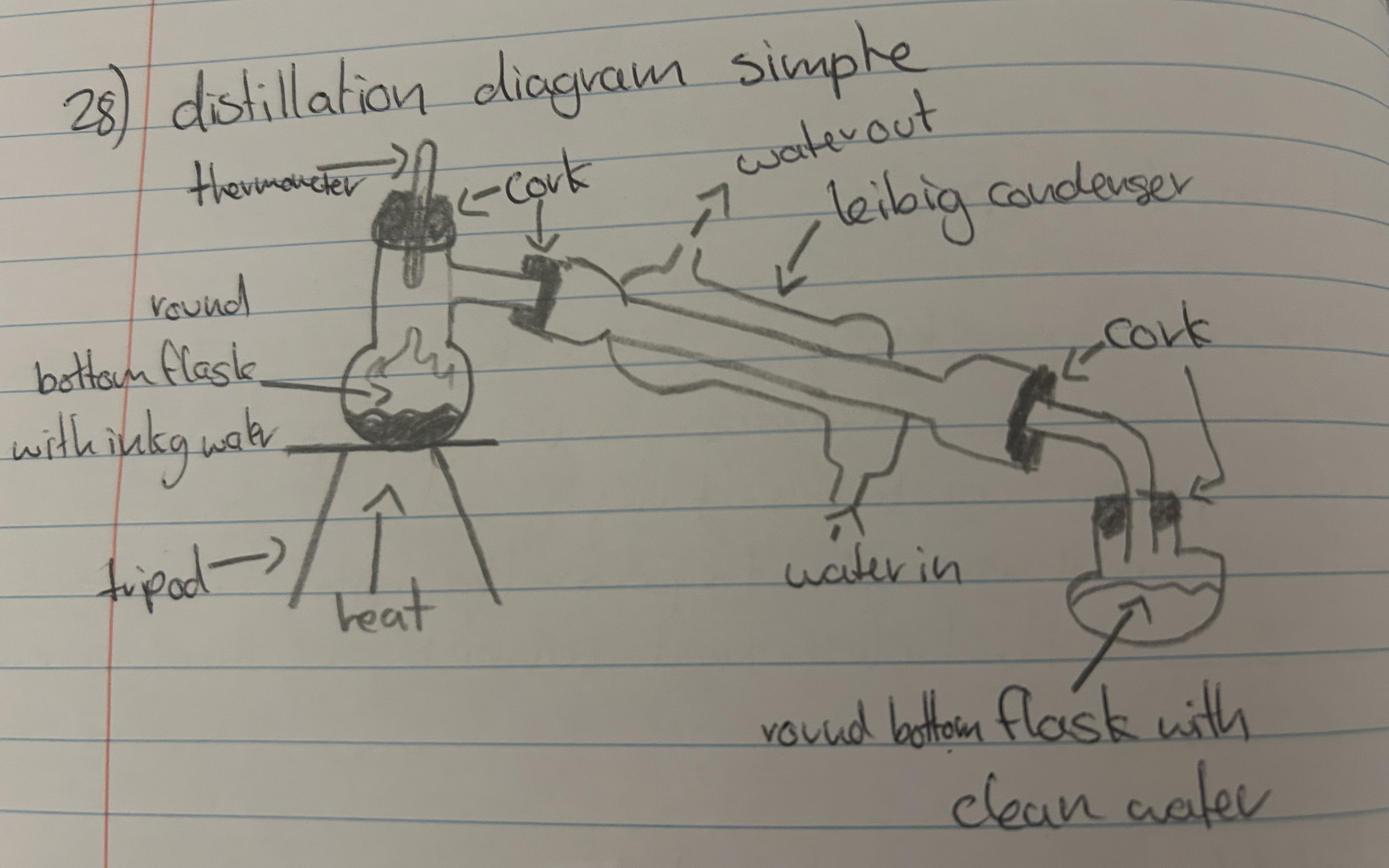
"explain a distillation diagram (simple)"
"explain a distillation diagram (fractional)"
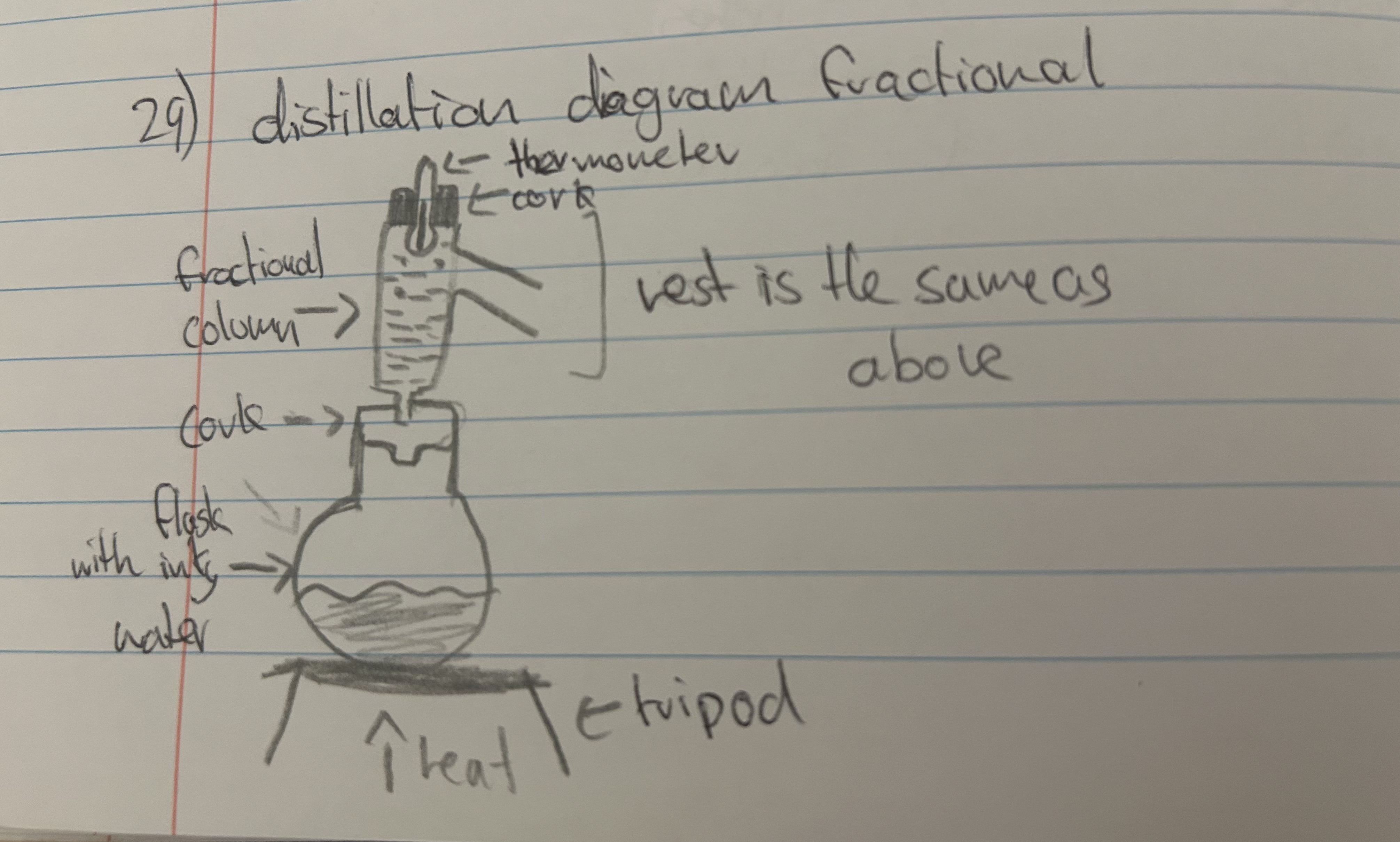
"What is the difference between fractional and simple distillation"
"simple - separating a soluble solid with a liquid while being able to collect both
fractional - separating two miscible liquids and being able to keep both"
"Purity and separation techniques"
"Purity and separation techniques"
"Definition of pure in chemistry with example"
"Contains only one type of substance - e.g. water only contains H2O molecules"
"How to know if a substance is pure"
"pure substances have sharp boiling points impurities will have an effect on the melting and boiling point (not sharp)"
"C2 - Atoms, elements and compounds"
"C2 - Atoms, elements and compounds"
"structure of an atom"
"structure of an atom"
"What are atoms"
"the smallest amount of a substance you can possibly have"
"What is an element"
"a substance made of just one type of atom"
"What is atomic mass"
"protons + neutrons in an atom"
"Relative atomic mass"
"the weighted average mass of an element's atoms"
"What is atomic number"
"number of protons in a regular atom"
"What are the limits on each shell"
"2, 8, 8, 2"
"What are isotopes"
"atoms with the same number protons and electrons but different number of neutrons"
"What are ions"
"same number of protons and neutrons but different number of electrons"
"Explain an example of an ionic diagram"
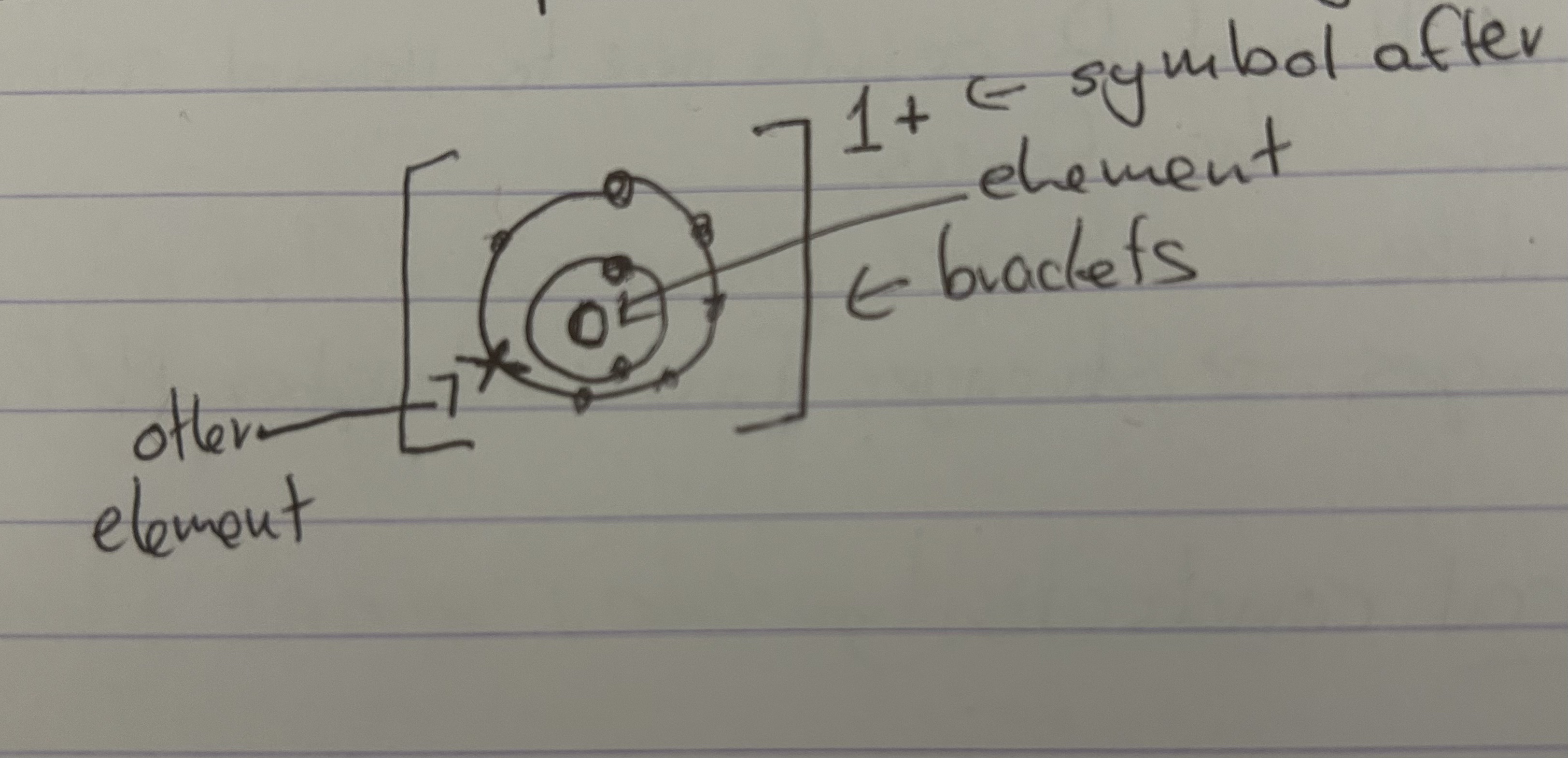
"Ions and ionic bonding"
"Ions and ionic bonding"
"Ionic Bonds form through the transfer of electrons between…."
"metals and non-metals"
"What type of ions do metals form"
"Cations (positive)"
"What type of ions do non-metals form"
"Anions (negative)"
"What are the opposing ions held together by"
"strong electrostatic forces of attraction acting in all directions"
"What is a lattice"
"when ions form a regular arrangement of alternating positive and negative ions. It is a massive 3D structure. It has no individual bonds, the forces act across the millions of ions."
"What are the properties of ionic compounds"
"Very high M and B points due to thermal energy it takes to overcome the forces
very brittle
higher charges → stronger forces → higher M/B points"
"Electrical conductivity"
"Electrical conductivity"
"What is required for electrical conductivity"
"free moving particles that are charged”
"Only as which states of matter can ions conduct"
"liquids and gases"
"C2.5 Covalent bonding"
"C2.5 Covalent bonding"
"What is a covalent bond"
"a bond of a shared pair of electrons between the atoms"
"Between only what do covalent bonds occur"
"Non-metals"
"Are the bonds in covalent bonds strong or weak"
"very strong"
"how do covalent bonds occur"
"when both atoms need to gain electrons"
"What are the two types of covalent structures - with examples"
"simple molecular (small molecules like water) Giant covalent (diamond, graphite)"
"True or False - Some atoms can form multiple covalent bonds"
"True"
"How to tell how many bonds an element can form"
"8 - its group number ----- Tip: only draw valence shell"
"C2.6 Simple Covalent Structures vs Giant Covalent"
"C2.6 Simple Covalent Structures vs Giant Covalent"
"For each statement write if its simple or giant - low melting points"
"simple"
"For each statement write if its simple or giant - high melting points"
"giant"
"For each statement write if its simple or giant - always solid at room temp"
"giant"
"For each statement write if its simple or giant - gases and liquids at room temp"
"simple"
"For each statement write if its simple or giant - Doesn't conduct electricity except graphite"
"giant"
"For each statement write if its simple or giant - doesn't conduct any electricity"
"simple"
"For each statement write if its simple or giant - isolated molecules with weak forces between molecules"
"simple"
"For each statement write if its simple or giant - Repeating 3D structures with strong bonds but no forces at all except graphite"
"giant"
"For each statement write if its simple or giant - conduct heat"
"giant"
"For each statement write if its simple or giant - regular crystal arrangement"
"giant"
"For each statement write if its simple or giant - strong bonds between atoms"
"both"
"What are intermolecular forces"
"forces between molecules"
"Why does simple covalent have low M/B points"
"they have weak intermolecular forces that are easy to overcome"
"Up to how many molecules can a simple covalent structure have"
"up to 10"
"How can you tell if intermolecular forces have been overcome"
"a change in state Solid <-> liquid <-> gas"
"Why can't simple covalent structures conduct electricity"
"they are not charged or free moving"
"Why can graphite conduct"
"it has delocalised electrons because each carbon atom is bonded to 3 not 4 ------------ Tip: only need to know about diamond and graphite in GCSE"
"C2.6 Graphite and Diamond"
"C2.6 Graphite and Diamond"
"is it true that both diamond and graphite have no intermolecular forces"
"no, graphite has weak ones and diamond has none"
"What element makes them both"
"carbon"
"How many are bonds are in graphite and diamond"
"in diamond there are four other carbon atoms bonded to one but in graphite there are 3"
"How is graphite able to conduct electricity"
"it has delocalised electrons"
"What is the structure of a diamond"
"it is a lattice structure in a tetrahedral arrangement"
"What is the structure of a graphite"
"lattice in a hexagonal (honeycomb) pattern"