Systems Path Lungs
1/176
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
177 Terms
collapsed lung
atelectasis
lung collapse due to airway obstruction and resorption of air in alveoli
resorption atelectasis
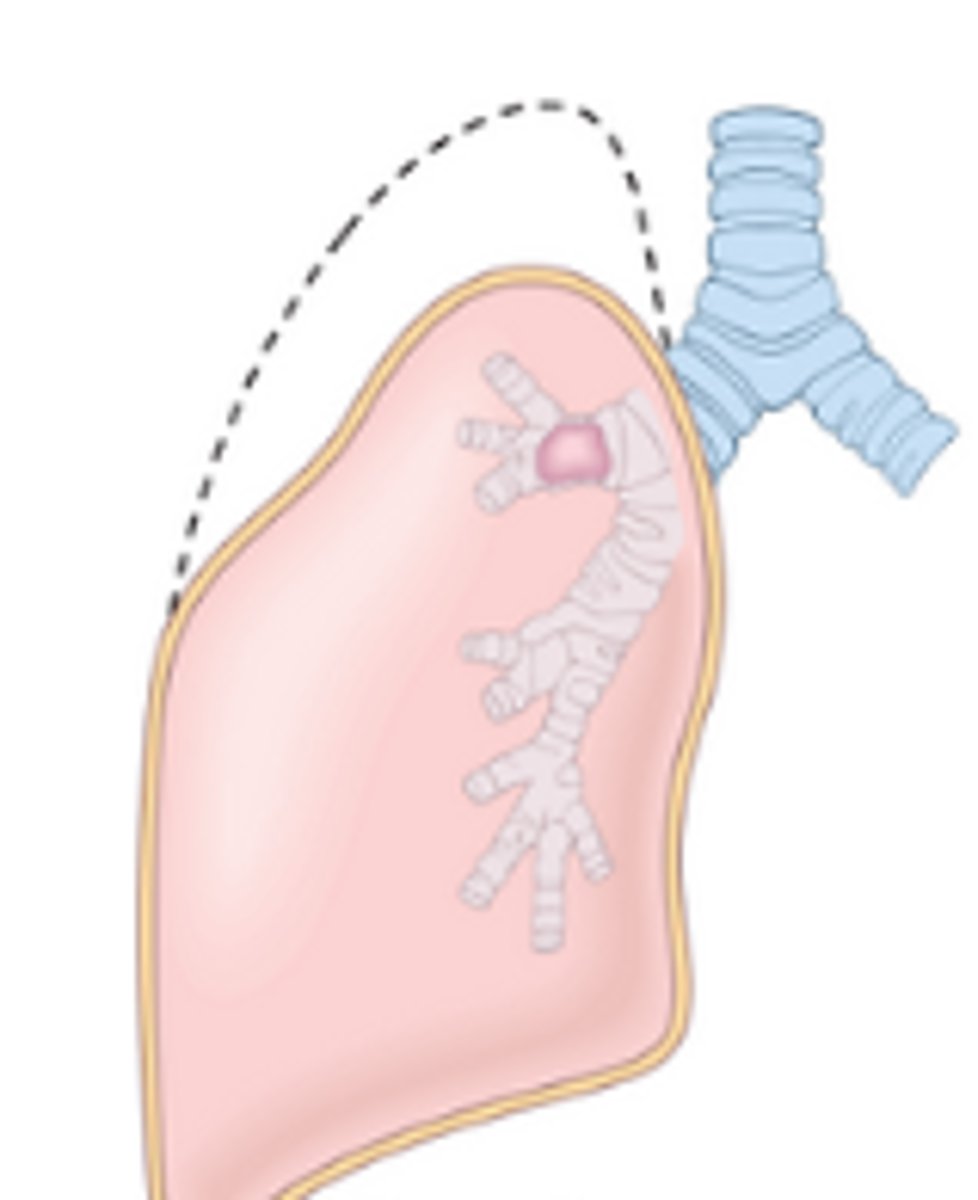
Features of resorption atelectasis
dyspnea and cyanosis
risks associated with resorption atelectasis
CF, chronic bronchitis, tumor, foreign body
form of lung collapse where pleural space fills with fluid/air and compresses lungs causing collapse
compression (passive) atelectasis
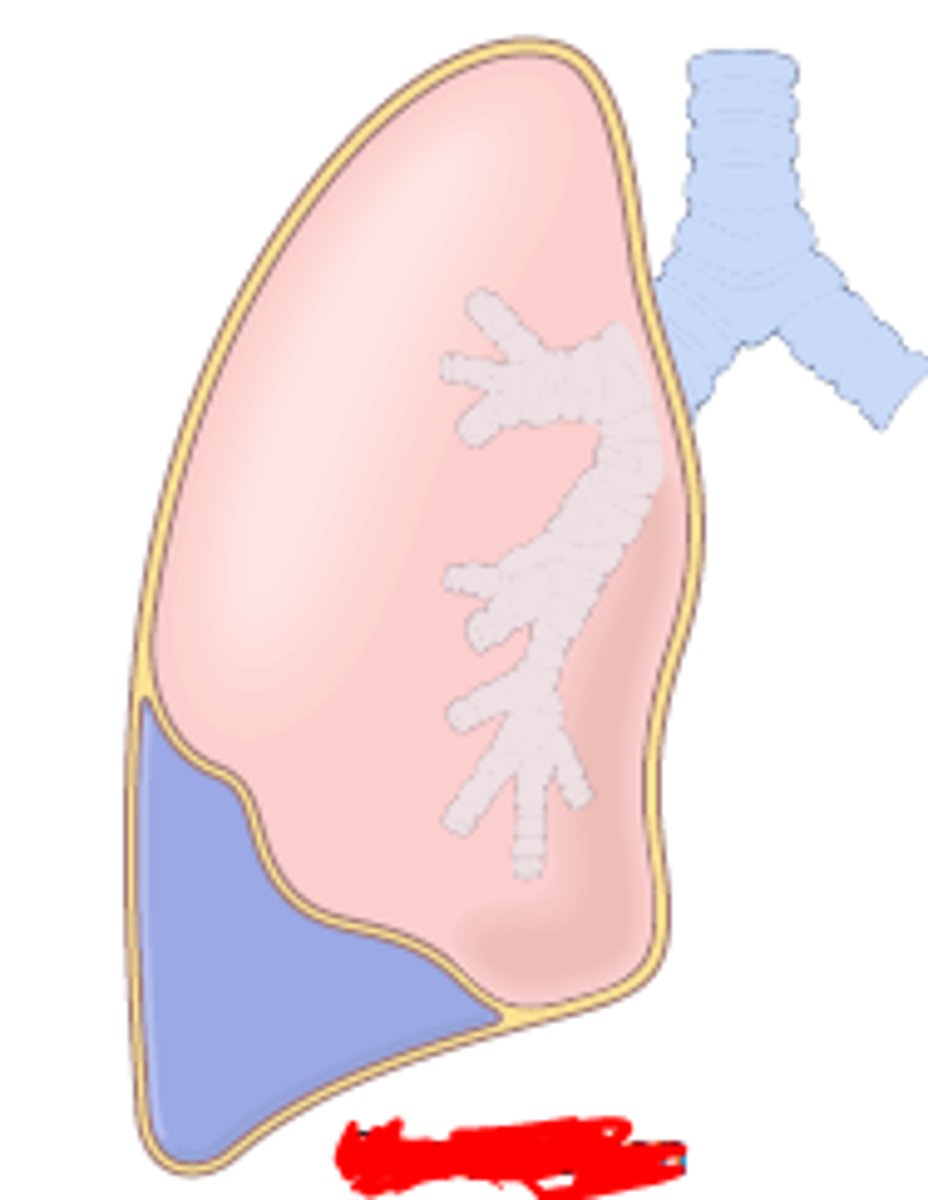
features of compression atelectasis
dyspnea and cyanosis
risks for developing compression atelectasis?
heart failure and trauma
form of lung collapse due to decreased lung expansion; chronic inflammation leads to fibrosis
contraction atelectasis
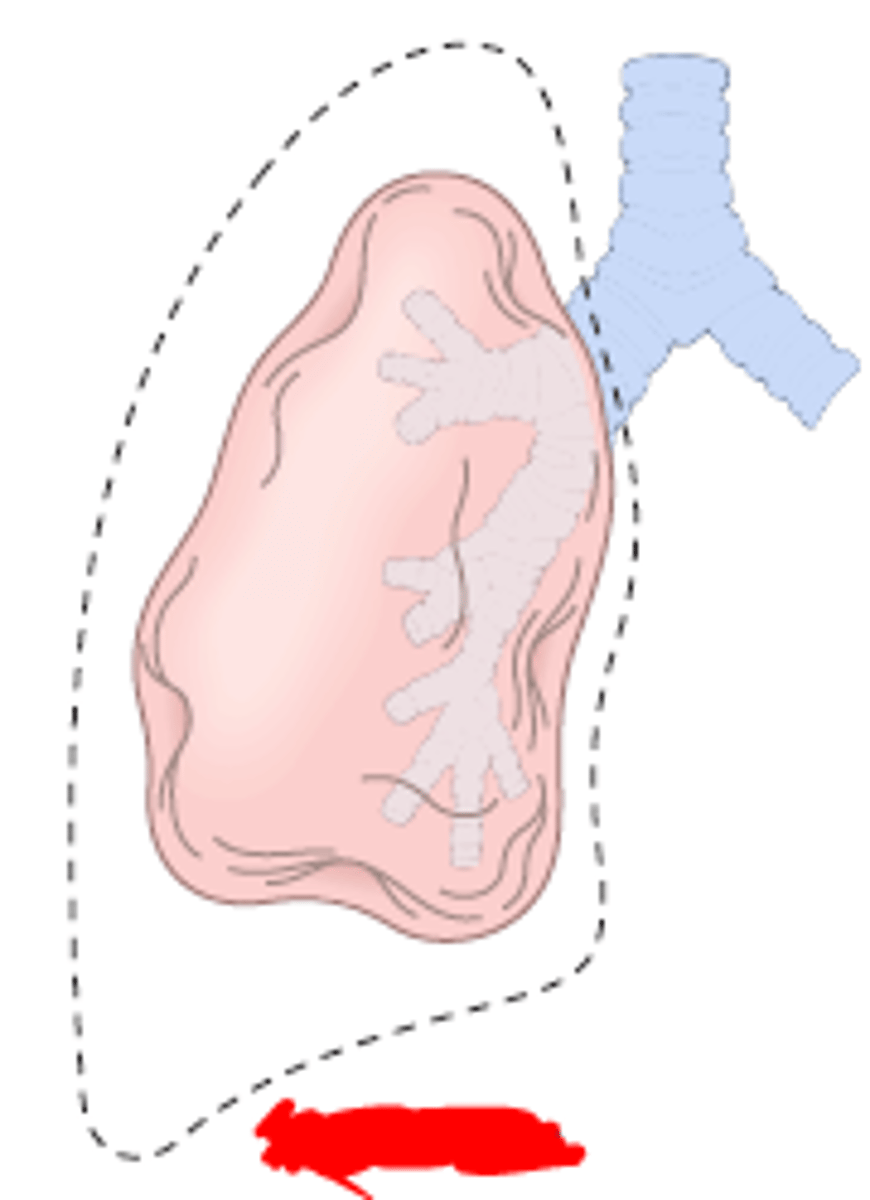
risk associated with developing contraction atelectasis
history of pulmonary fibrosis
features of contraction atelectasis
dyspnea and cyanosis ; poor prognosis
severe lung injury that leads to alveolar damage and massive inflammation characterized by severe dyspnea, cyanosis, and hyaline membranes
acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
why may someone develop ARDS?
history of pneumonia or trauma
signs/symptoms of ARDS
diffuse alveolar damage, bilateral pulmonary infiltrates, acute dyspnea, hypoxemia, organ failure
acute/subacute respiratory illness defined by e-cig / vaping use, pulmonary infiltrates, or absence of other lung disease
vaping associated lung injury (VALI)
viral causes of common cold
rhinovirus, coronavirus, RSV, influenza
bacterial causes of common cold
group A b-hemolytic strep or H. influenzae
locations of acute respiratory infections
nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, epiglottis
widespread viral infection called the "kissing disease" characterized by pharyngitis, lymphadenopathy, exudative pharyngitis, and splenomegaly
EBV (mono)
Cause of acute laryngitis
inhalation of irritating agent
acute laryngitis symptoms
pharyngitis, hoarseness, cough, dysphagia
alternative forms of laryngitis
tuberculosis, diphtheritic
hallmark of diphtheria
"dirty gray" pseudomembranes
Diphtheria causative agent
Corynebacterium diphtheriae
self-limited viral URTI caused by parainfluenza (MC) or RSV
laryngotracheobronchitis (Croup)
hallmarks of croup
prominent stridor, "seal-like" bark
croup increases risk for
secondary bacterial infection (staph MC, strep, H. influenzae)
small, round nodules on vocal cords
vocal cord polyp
raspberry-like growth on vocal cords
laryngeal papilloma
who are carcinomas of larynx MC in?
>40 years, males
what are carcinomas of larynx caused by?
smoking, alcohol, irradiation, asbestos
malignancy of larynx, early sign = hoarseness
laryngeal carcinoma
MC laryngeal carcinoma (60-70% of cases)
glottic
20-40% of laryngeal cancers
supraglottic
very rare laryngeal carcinoma
subglottic
what is the most common site of metastasis?
lungs
MC lung tumor which is benign and characterized by a single solitary pulmonary nodule called a "coin lesion"
hamartoma
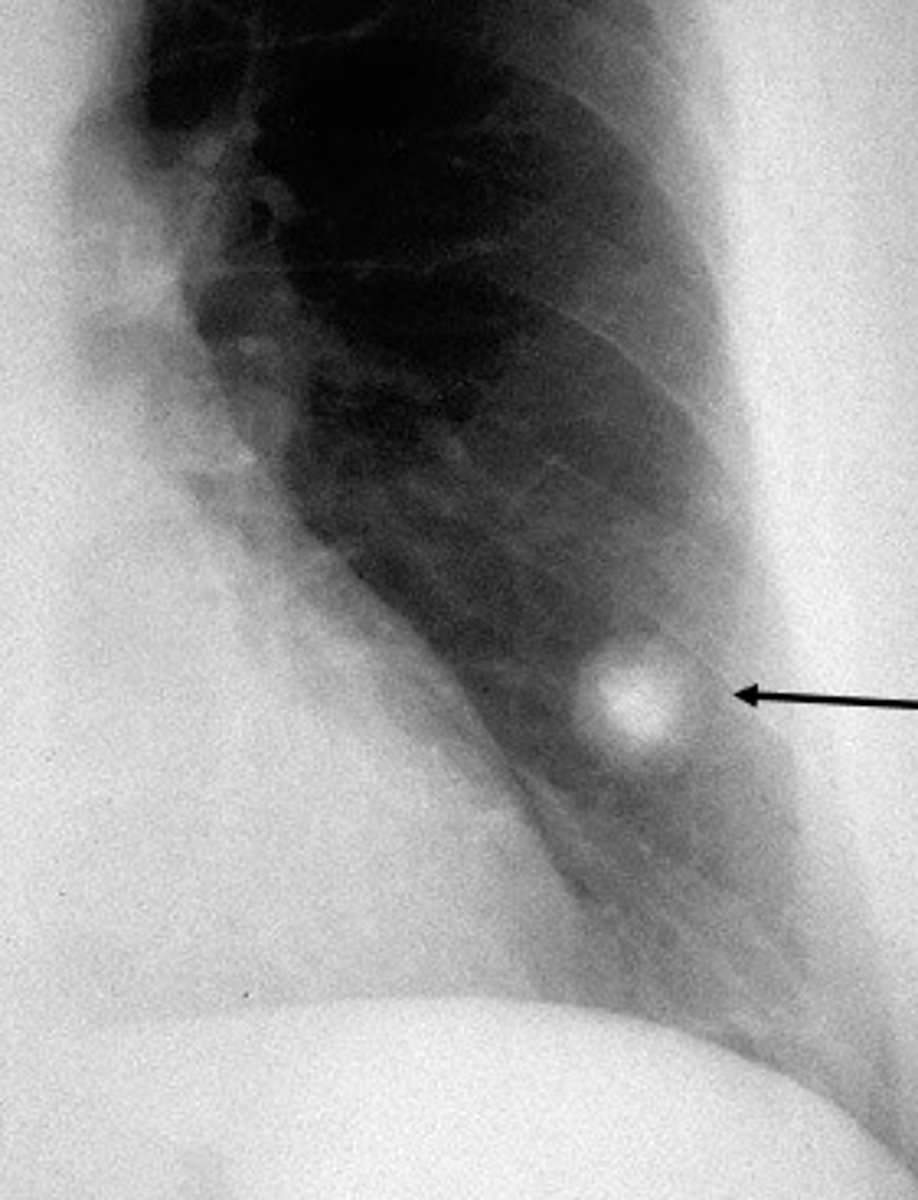
lung tumor which arises from bronchial epithelia
bronchogenic carcinoma
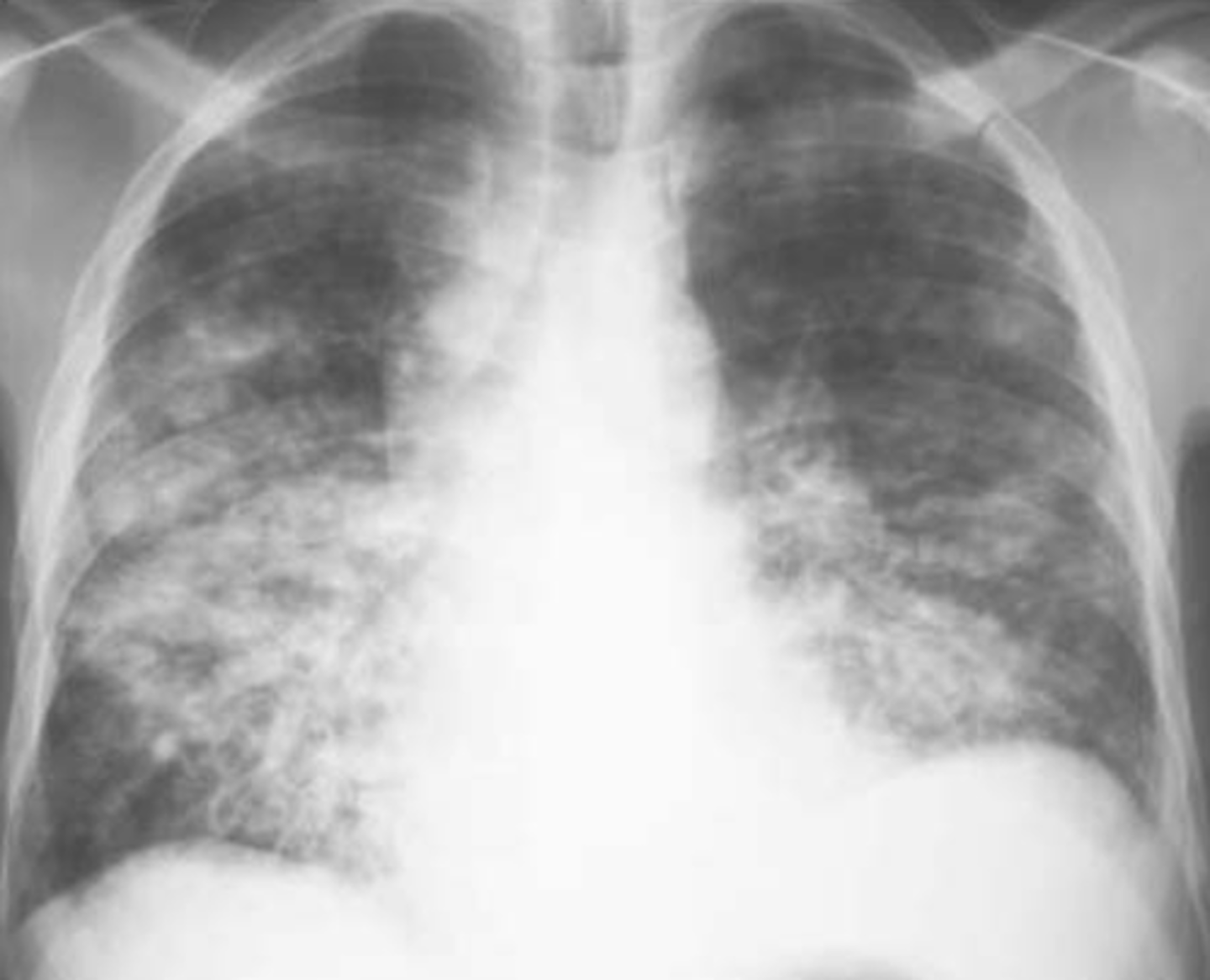
malignancy of bronchial glandular cells which is usually found in non-smokers
adenocarcinoma
who is an adenocarcinoma MC in?
ages 50-70
malignancy of bronchial epithelial cells common in smokers
squamous cell carcinoma
malignant of bronchial epithelial cells which is the worst prognosis of all lung cancers due to increased odds of metastasis at time of diagnosis
small-cell carcinoma
who is small cell carcinomas common in?
smokers age 50-70
malignancy of bronchial epithelial cells common in smokers and non-smokers
large cell carcinoma
what causes 90% of lung cancers?
smoking
sites of mets from lung cancer?
brain, liver, bones, adrenals
most aggressive lung cancer
small cell carcinoma
MC non-small cell lung cancer located in pulmonary apex which leads to damage and symptoms with vertebrae, upper ribs, brachial plexus and sympathetics
pancoast tumor
who is pancoast tumors common in?
smokers age 50-70
signs and symptoms of pancoast tumor
pancoast syndrome and Horner syndrome
shoulder pain/C8-T2 radicular pain
pancoast syndrome
ptosis, miosis, anhindrosis
Horner syndrome
fluid in pleural cavity
pleural effusion
protein poor pleural effusion caused by heart failure
transudate (hydrothorax)
MC cause of pleural effusion
heart failure
protein rich pulmonary effusion caused by inflammatory conditions
exudate (pleuritis)
pus in pleural space
empyema
causes of pleural exudate
bacterial/viral infections, tumors, pulmary infarction
air within pleural cavity
pneumothorax
a type of pneumothorax in which air that enters the chest cavity is prevented from escaping and shifts mediastinum
tension pneumothorax
blood in pleural cavity
hemothorax
lymphatic fluid in pleural cavity
chylothorax
malignancy of mesothelium (pleura) associated almost exclusively with asbestos exposure
mesothelioma
How does mesothelioma develop?
chronic inflammation and failed phagocytosis due to asbestos
alveolar inflammation from infection causing fever and lung consolidation
pneumonia
what type of acute bacterial pneumonia affects multiple lobes?
bronchopneumonia
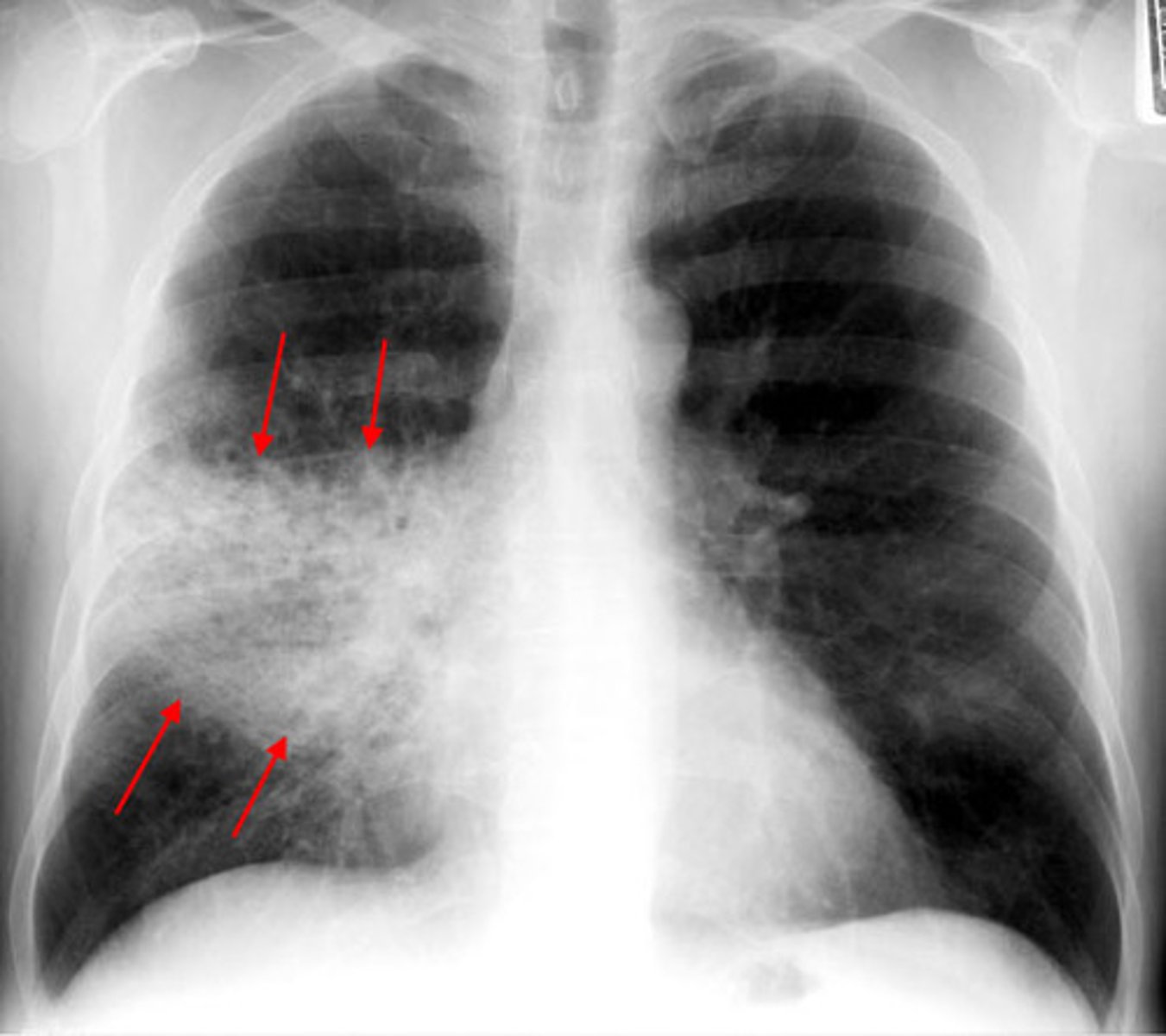
90% of lobar pneumonia is from what?
strep. pneumoniae
what type of pneumonia affects a single lobe, has homogenous consolidation and an abrupt line of radiopacity?
lobar pneumonia
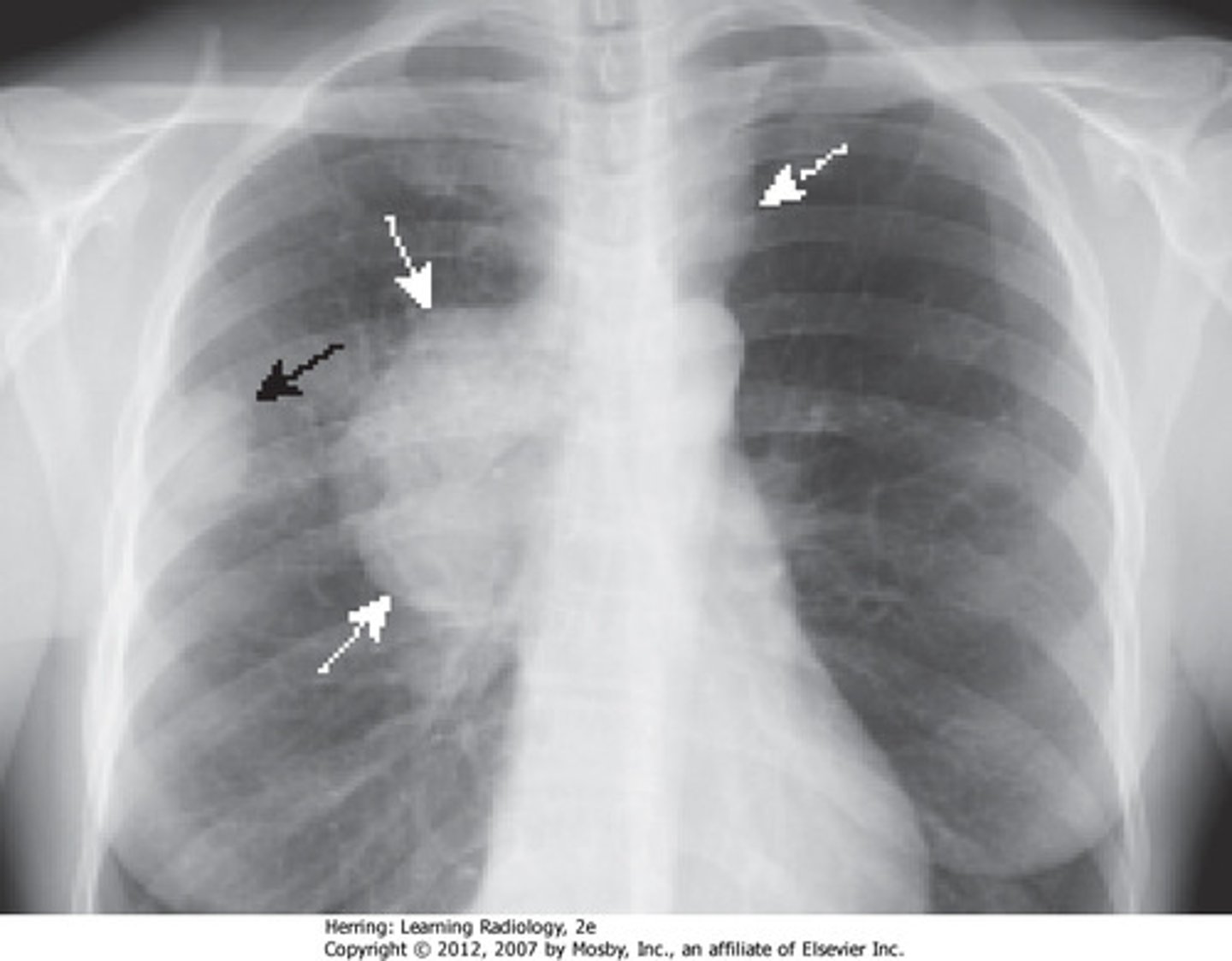
acute lung infection from strep pneumonia, commonly follows a viral URTI, causing productive cough, fever and dyspnea
community-acquired acute pneumonia (able to be seen on X-ray)
how does community-acquired acute pneumonia develop?
local inflammation -> consolidation
risks factors associated with developing community-acquired acute pneumonia
diabetes, CHF, COPD, immunosuppression, reduced splenic function
a lobar pneumonia caused by the bacterium Legionella pneumophila which causes dyspnea, fever and aches
legionnaire disease
pathology caused by legionella pneumophila causing a mild URTI
pontiac fever
"self limited" acute lung infection from common cold virus/mycoplasma pneumonia ; causes non-productive cough and mild dyspnea
community-acquired atypical pneumonia
how does community-acquired atypical pneumonia develop?
local inflammation of alveolar septa ( no consolidation on X-ray)
what is different about community-acquired atypical pneumonia?
edema is confined to alveolar septa
community-acquired atypical pneumonia causative agent
mycoplasma pneumoniae
what type of pneumonia is caused by staph aureus (MC) or E.coli and acquired after being in a hospital setting for 48+ hours?
hospital-acquired (nosocomial)
Symptoms of hospital acquired pneumonia
productive cough, dyspnea, fever
how does hospital acquired pneumonia develop?
local inflammation = consolidation (able to be seen on xray)
pneumonia caused by inhalation of foreign material such as gastric contents
aspiration pneumonia
aspiration pneumonie causative agents
strep pneumoniae, staph aureus, H. influenze
areas of suppurative necrosis due to bacterial infection causing foul/purulent septum, cavitation (right-side), fever, cough, etc.
lung abscess
causes of a lung abscess
aspiration, bronchial obstruction, hematogenous spread
chronic infection of mycobacterium tuberculosis which is the MC cause of infectious disease worldwide
tuberculosis
What type of tuberculosis simply means infected, not symptomatic or contagious?
primary
what type of tuberculosis is symptomatic with hemoptysis, productive cough, fever and malaise and the infection is no longer dormant
secondary
what is TB diagnosed by?
tuberculin test
how does primary TB develop?
sensitization and walling off in granulomas
how does secondary TB develop?
re-emergence of T-cell hypersensitivity resulting in destructive cavitations
How is TB transmitted?
respiratory droplets
who is most likely to get TB?
80% in endemic areas of Africa and Asia
subpleural caseous granulomas
ghon focus
sub pleural and lymph node regions have granulomas (tuberculoma)
ghon complex
calcification and fibrosis of hisar nodes
ranke complex
systemic tuberculosis infection caused by pulmonary lymphatic and hematogenous spread
military tuberculosis
who can develop military TB?
anyone with secondary TB
MC form of extrapulmonary TB
lymphadenitis
TB in the spine
Pott's disease
what poses as a risk for developing pneumonia?
immunosuppression (AIDS, transplant recipients, elderly, radiation)
opportunistic viral pathogen causing fever and respiratory infection
cytomegalovirus (HHV-5)