earth's materials: minerals & rocks (#2)
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
🍂
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
1. naturally occurring
2. inorganic
3. homogeneous solid
4. has definite chemical composition
5. ordered crystalline structure
5 characteristics of minerals
color
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF MINERALS:
Wavelength of light reflected by the mineral;
Most noticeable physical property;
greatly affected by impurities
can be idiochromatic, allochromatic, or pseudochromatic
streak
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF MINERALS:
color of a mineral in its powdered form;
more reliable in mineral identification than color
luster
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF MINERALS:
quality of reflected light of a mineral’s surface;
can be metallic or non-metallic
hardness
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF MINERALS:
measure of resistance of a mineral to abrasion;
measured by scratching mineral with another object of known hardness
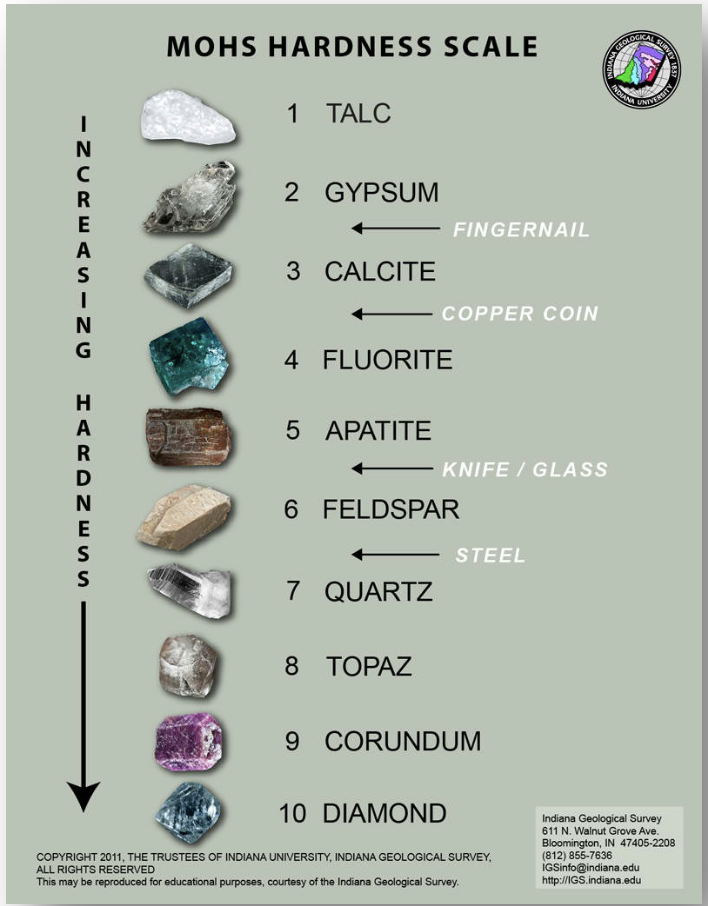
Mohs scale of hardness
Mohs scale
this is used to measure a mineral’s hardness;
this is composed of 10 minerals, numbered from 1 to 10 (1 as the softest and 10 as the hardest);
a relative and not qualitative measure of the mineral's hardness
True
TRUE OR FALSE:
The scale does not mean that calcite is not thrice as hard as talc. The Mohs scale just indicates that calcite is harder than talc.
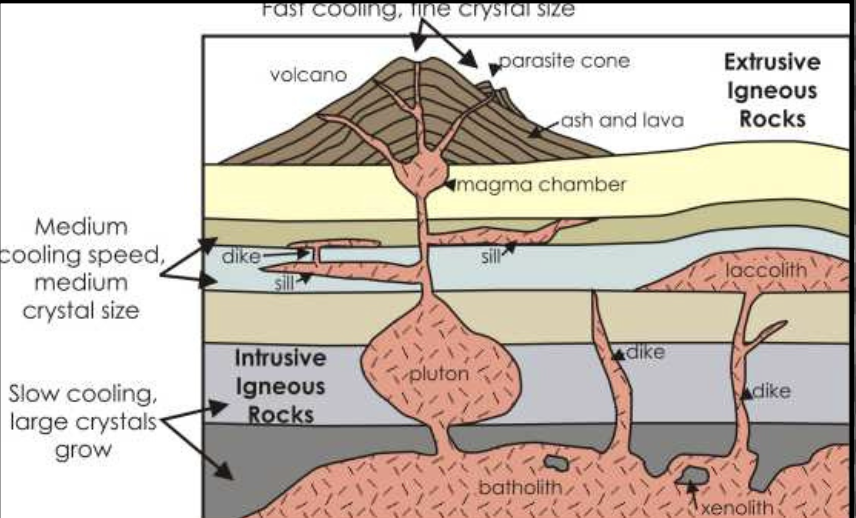
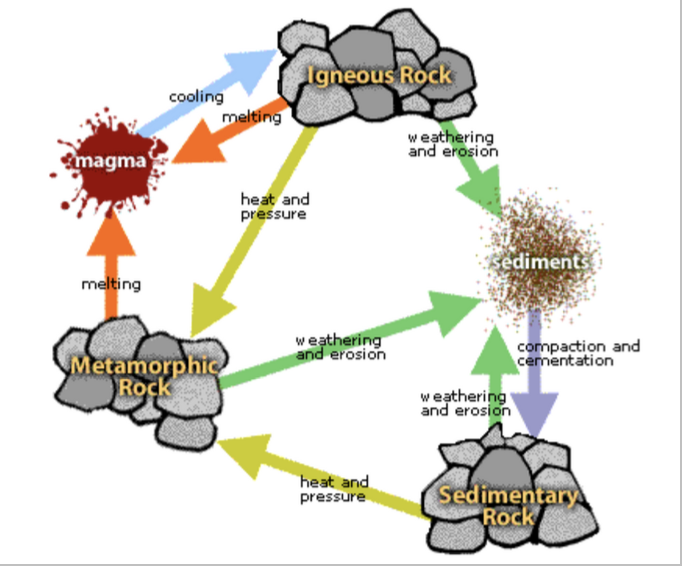
cooling & crystallization
ROCK CYCLES:
rocks that are deep under the earth’s surface have a chance to melt into magma and cool (called ______), and when these crystals form from magma, this process happens;
forms igneous rocks
(should have 2 answers)
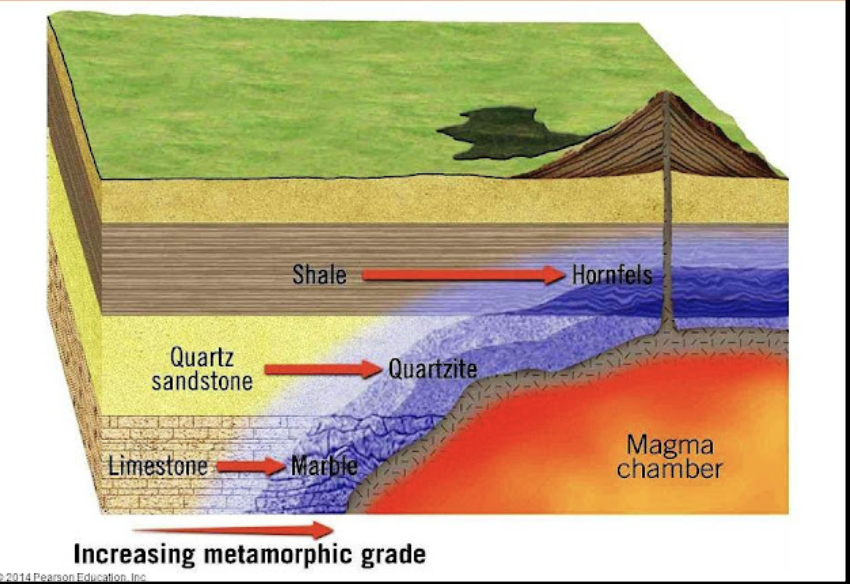
metamorphism
ROCK CYCLES:
What process happens when rocks that are exposed to high temperatures and pressures within the crust form a metamorphic rock?
4 types: contact, burial, regional, and dynamic
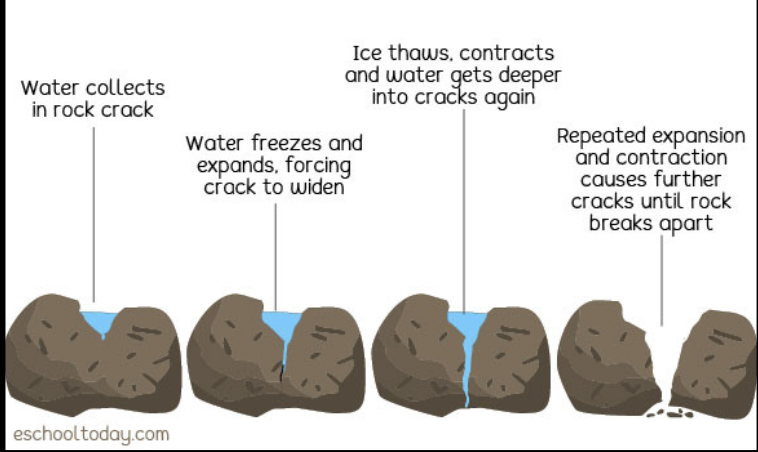
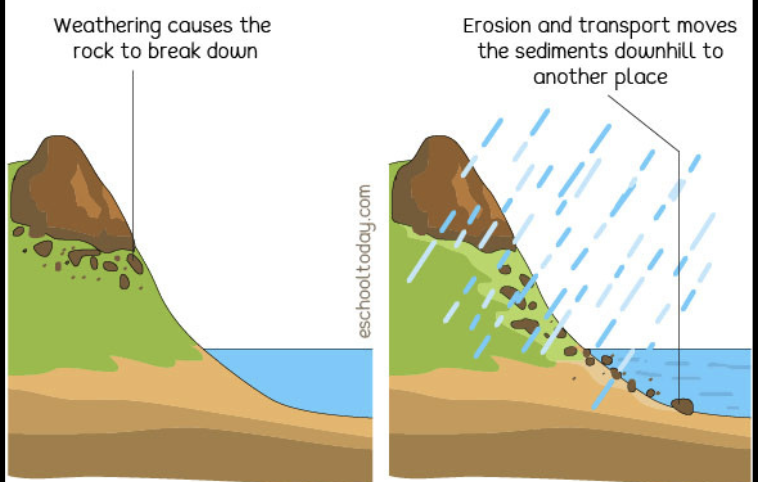
weathering
ROCK CYCLE:
this process is related to the breaking of rocks which depends on the parent material and the environmental conditions;
this can break down large rocks into smaller rocks called sediments
mechanical, chemical, & biological
erosion
ROCK CYCLES:
this happens when moving water and wind carry these rocks to one place or another, basically the displacement of these rocks
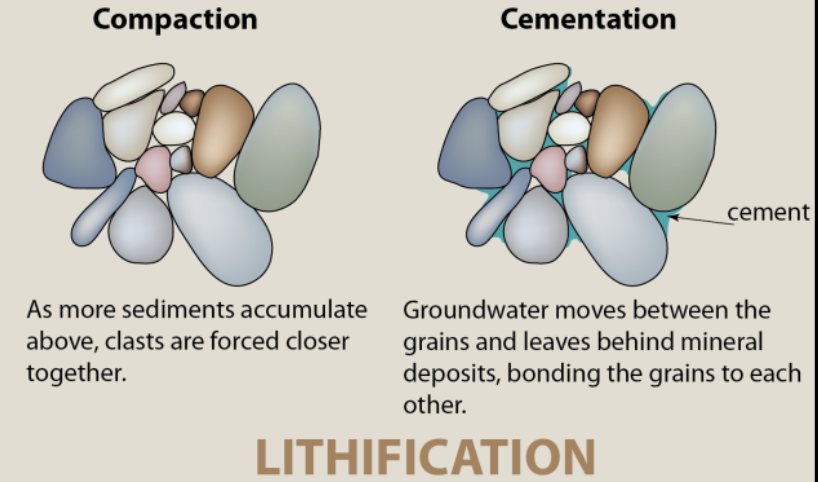
lithification
ROCK CYCLES:
process where these sediments harden to become sedimentary rocks
igneous rocks
TYPES OF ROCKS:
these are deep under the earth’s surface and have a chance to melt into magma and cool;
formed by cooling & crystallization
2 class. based on location: intrusive/plutonic & extrusive/volcanic
intrusive/plutonic - granite, diorite
IGNEOUS ROCKS (LOCATION):
these are those that solidify below earth’s surface
(give examples)
extrusive/volcanic - basalt, andesite, obsidian
IGNEOUS ROCKS (LOCATION):
these are those that solidify above earth’s surface
(give examples)
sedimentary
TYPES OF ROCK:
these are rocks formed from lithification and where fossils are typically found;
2 ways to classify: clastic/detrital & chemical rocks
clastic rocks - sandstone, shale, mudstone
2 WAYS TO CLASSIFY SEDIMENTARY ROCKS:
this differentiates rocks in terms of size;
formed from fragments or "clasts" of pre-existing minerals and rocks, broken down by weathering and erosion, and then cemented together
(give example)
chemical rocks - dolomite, limestone
2 WAYS TO CLASSIFY SEDIMENTARY ROCKS:
these are formed from dissolved compounds and ions in solution which happen during chemical weathering
shale
this is the most abundant sedimentary rock on earth and formed from clay & silt
depositional environment
an accumulation of chemical, biological, and physical properties and processes associated with the deposition of sediments that lead to a distinctive suite of sedimentary rocks;
where sediments are deposited;
most commonly seen in areas with sources of water
metamorphic
TYPES OF ROCK:
these are rocks that have been altered, changed, or transformed in the solid-state due to changes in pressure, temperature conditions, and chemical actions of hot fluids;
2 types: foliated & nonfoliated
foliation
UNDER METAMORPHIC ROCKS:
this is caused by extreme forces of heat and pressure pressing parallel layers of minerals into denser, distinguishable layers;
pervasive layering caused by compositional layering or by the parallel orientation of platy (e.g, mica) or elongate (e.g., amphibole) mineral grains
foliated - slate, schist
2 TYPES OF METAMORPHIC ROCKS:
these rocks produce evident lines or bands at the surface
(give example)

non-foliated metamorphic rock - marble
2 TYPES OF METAMORPHIC ROCKS:
these rocks have no layers and lack a banded appearance
(give example)

igneous, sedimentary, & metamorphic rocks
3 rock types
4 TYPES OF METAMORPHISM:
due to lithostatic pressure
4 TYPES OF METAMORPHISM:
magmatic heat and fluids act to produce change
4 TYPES OF METAMORPHISM:
result of high differential pressures associated with intense deformation along faults
4 TYPES OF METAMORPHISM:
occurs within a large area and caused primarily by mountain-building forces
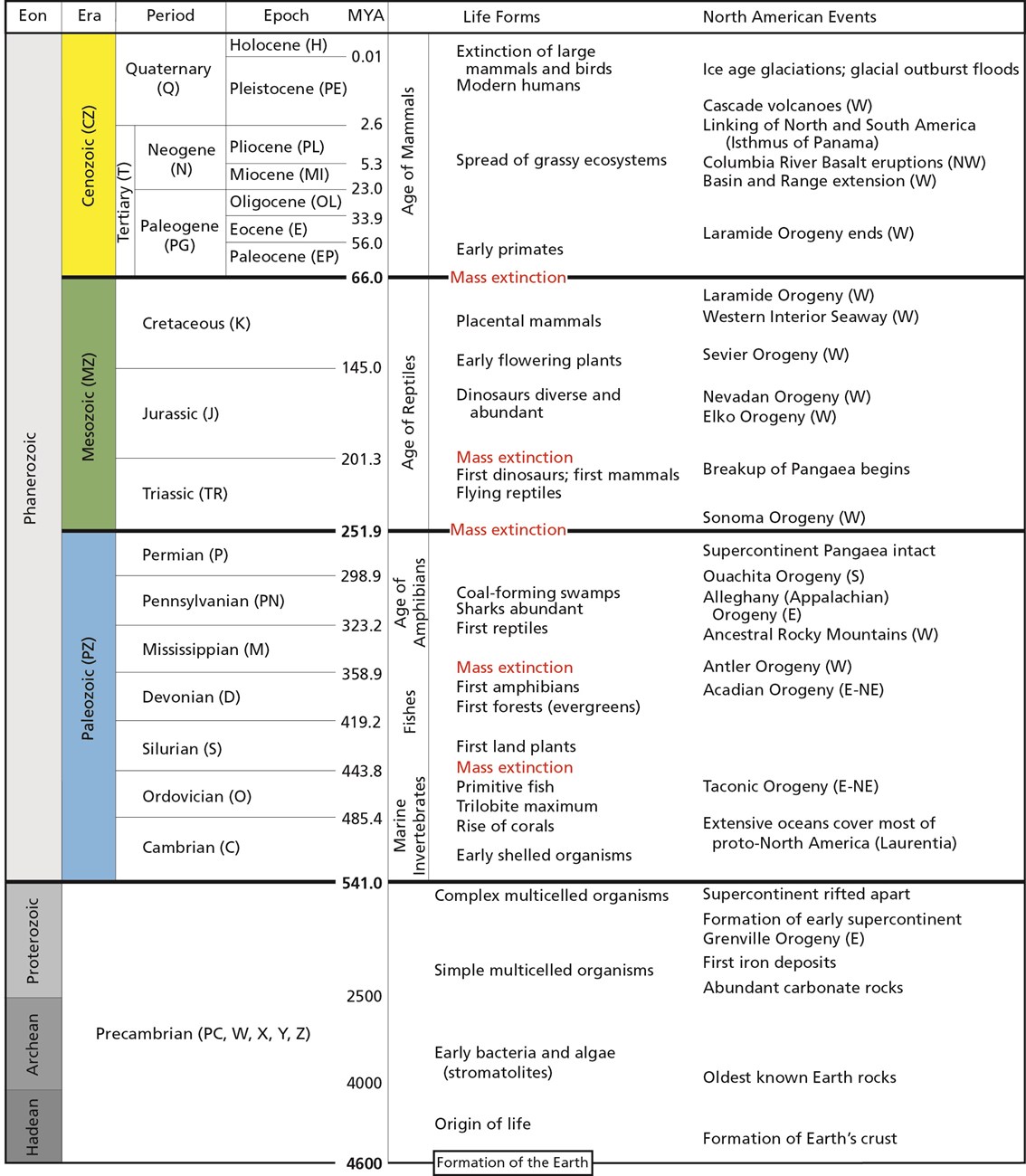
geological time scale
system of chronological dating that relates geological strata to time
UNDER GTS:
this is the period covering the physical formation and development of the Earth before any recorded human history
UNDER GTS:
determines which rock, fossil, or event happens first
UNDER GTS:
study of rock strata or layers; strata means layers of rock or sediment
UNDER GTS:
determines the actual age of a rock by radiometric dating
UNDER GTS:
method used to date rocks and other objects based on the known decay rate of radioactive isotopes
UNDER GTS:
process by which the nucleus of an unstable atom loses energy by emitting high-energy particles
precrambrian
TIME DIVISIONS:
covers around 88% of the GTS;
informal unit of time;
3 eons: Hadean, Archean, Proterozoic
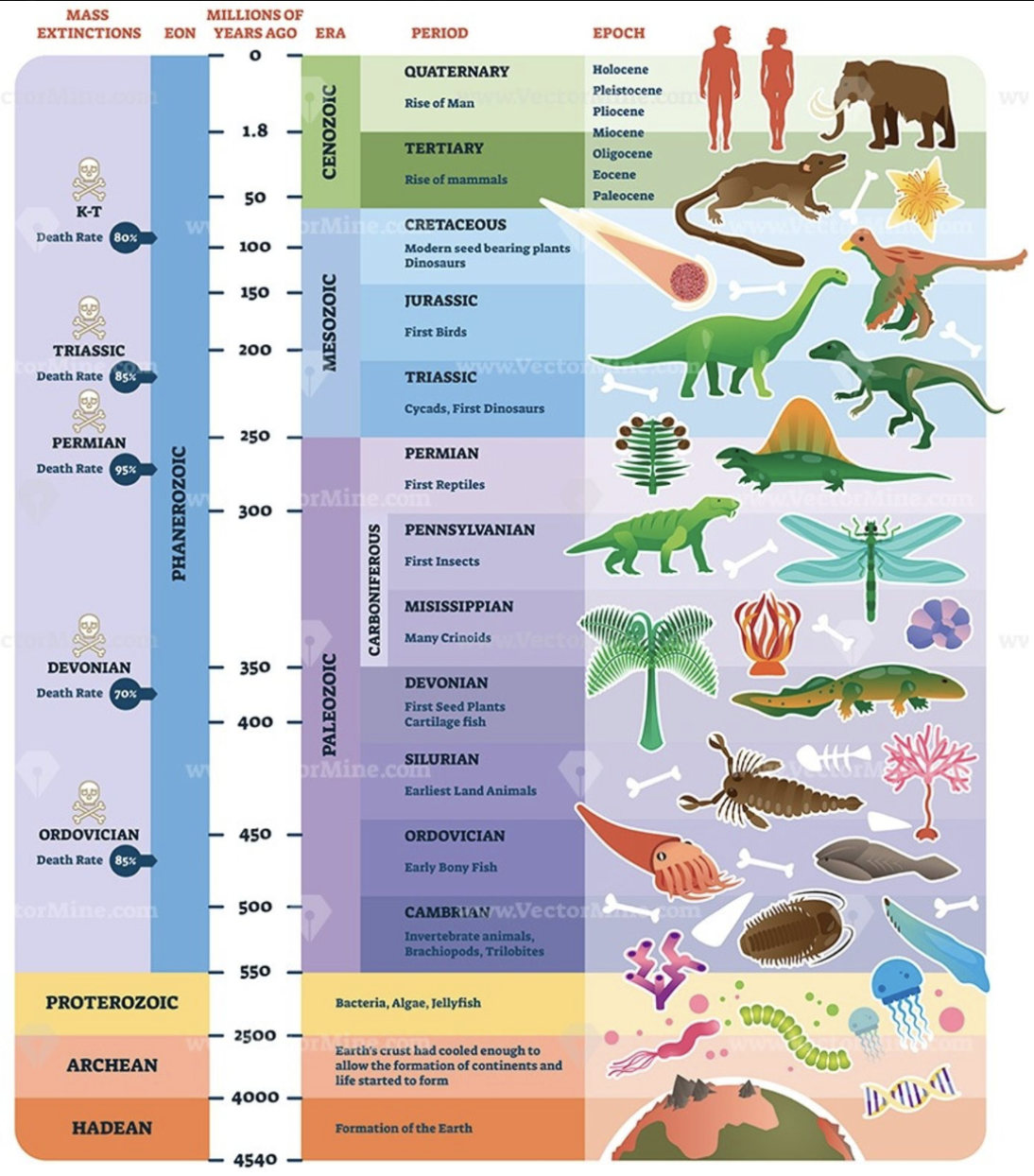
Paleozoic, Mesozoic, Cenozoic
3 eras of the Phanerozoic eon wherein visible life has been observed
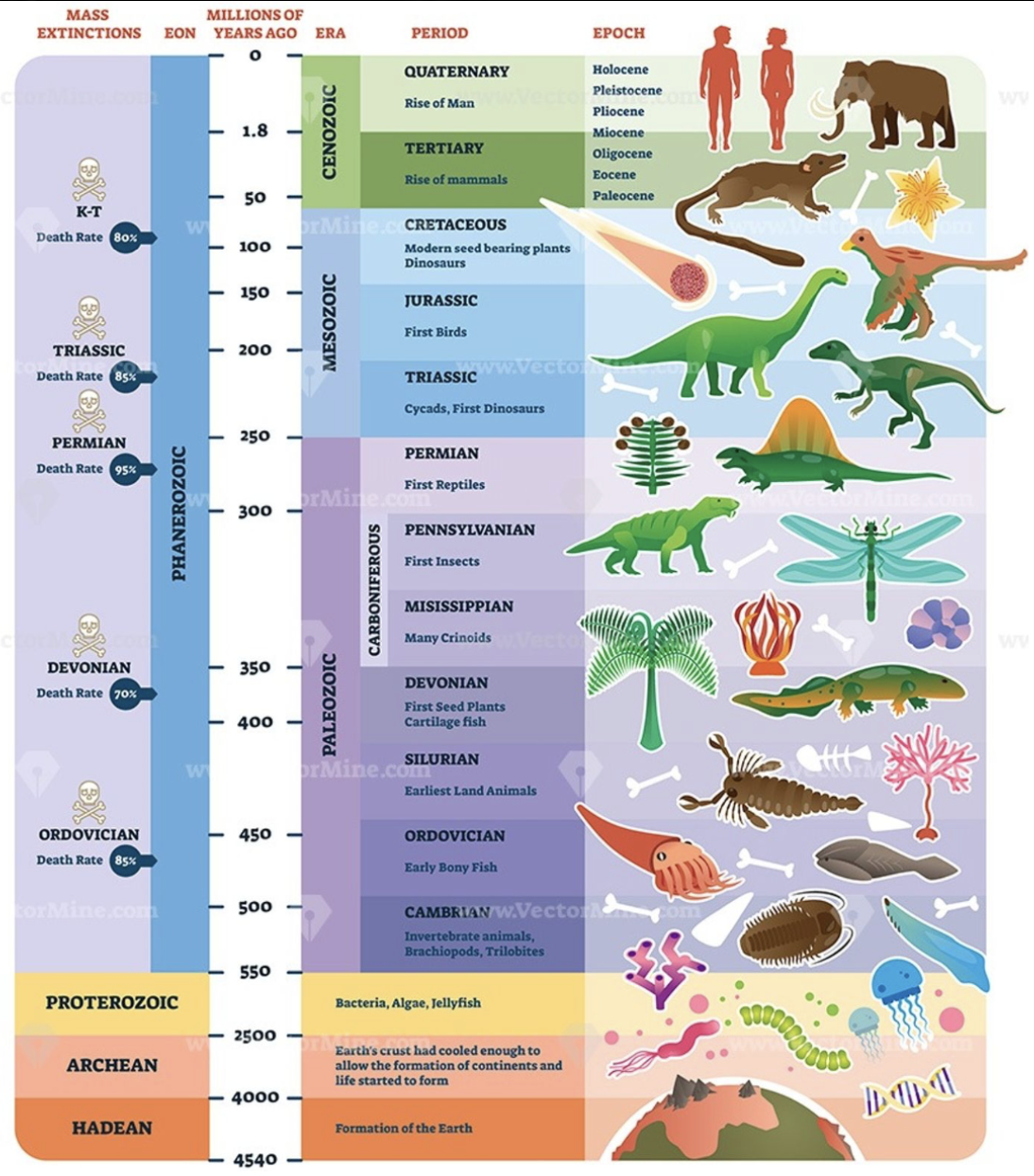
Paleozoic era
3 PHANEROZOIC ERAS:
life in the early period of this era was dominated by marine organisms but by the middle of the era plants and animals evolved to live and reproduce on land;
first air-breathing tetrapods & amphibians evolved reptiles with the amniotic egg;
includes Carboniferous period;
Pangaea began to form near the end of this
Mesozoic era
3 PHANEROZOIC ERAS:
best known as the age of reptiles, most notably, the dinosaurs;
follows the Permian Mass Extinction;
first appearance of frogs, turtles, icthyosaurs & pleiosaurs, birds;
angiosperms (flowering & seed-bearing) originated during the Cretaceous;
ended with the K-PG Mass Extinction
Cenozoic era
3 PHANEROZOIC ERAS:
a.k.a. age of mammals because they came to be dominant and large after giant reptiles’ extinction & includes the rise of man;
began 66 million years ago;
subdivided into epochs;
North America's characteristic landscapes began to develop
dissolution
process by which soluble rocks such as limestone (predominantly calcium carbonate), chalk (also calcium carbonate), dolomite (magnesium calcium carbonate), gypsum (hydrated calcium sulfate), and halite/“rock-salt” (sodium chloride) are dissolved by the passage of water or weakly acidic water either over the rock surfaces or through fractures and pores in the rock