chemistry unit 2 aos 1
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
characteristics of solutions
an aqueous solution consists of a solid, liquid or gas dissolved in a liquid, the substance that is being dissolved is called the solute, the solvent is the liquid, homogenous solutions have the dissolved solute evenly distributed in the solvent
dissolution
the process of dissolving a solute into a solvent is called dissolution, for a substance to dissolve the attractive forces between the solute and the solvent must be similar to or greater than the forces between the solute particles and the forces between the solvent molecules
what dissolution involves
solute particles attracted to some of the solvent particles, solute particles are separating from one another, some of the solvent particles separating from one another to allow the solute particles to disperse throughout the liquid, if not attached to solute particles the solvent particles are attracted to other solvent particles
forces between h2o molecules
water is known as the universal solvent, the forces between water molecules are hydrogen bonds and dispersion forces
polar and non-polar substances
water is a polar molecule and will dissolve other polar molecules like ethanol, ethanol is miscible in water, non-polar molecules like hexane and petrol dont dissolve in water and are immiscible because the dispersion forces are weak and arent strong enough to disrupt the hydrogen bonds between water molecules
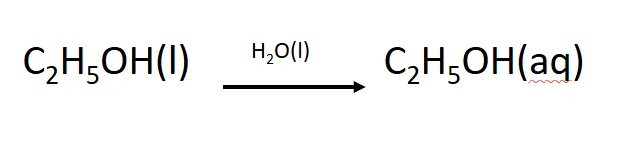
why does ethanol dissolve in water
ethanol can hydrogen bond with h2o molecules, the hydrogen bonds between ethanol and h2o are similar/greater than the hydrogen bonds between h2o molecules
what happens when ethanol dissolves in water
hydrogen bonds between h2o molecules break, hydrogen bonds between ethanol molecules break, new hydrogen bonds form between ethanol and h2o molecules, sugars have an -OH group which hydrogen bonds with water
ionisation
Hydrochloric acid, HCl, nitric acid, HNO3, and sulfuric acid, H2SO4 form hydrogen ions, H+ or H3O+ in water, the ions, H3O+ (aq) and Cl-(aq) form ion-dipole attractions with the polar H2O molecules, since the ion-dipole forces > hydrogen bonding between H2O molecules, then HCl dissolves readily in water
