6.2 The Blood System
5.0(1)Studied by 23 people
Card Sorting
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:20 AM on 5/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
1
New cards
Describe Galen’s beliefs of the blood system
* arteries and veins were separate blood networks connected via invisible pores
* veins thought to pump natural blood that was produced by the liver
* arteries thought to pump heat produced by the heart via the lungs
* veins thought to pump natural blood that was produced by the liver
* arteries thought to pump heat produced by the heart via the lungs
2
New cards
Describe Harvey’s blood system proposal
* arteries and veins were part of a single connected blood network
* arteries pumped blood from the heart
* veins returned blood to the heart
* arteries pumped blood from the heart
* veins returned blood to the heart
3
New cards
Describe the function of the atria
blood returning to the heart is collected via veins, atria acts as reservoirs
4
New cards
Describe the function of the ventricles
act as pumps, expel blood from the heart at high pressure via arteries
5
New cards
Distinguish between the functions of the left and right side of the heart
left side pumps oxygenated blood around the body (systematic circulation) whereas the right side pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs (pulmonary circulation)
6
New cards
Distinguish between the structures of the left and right side of the heart
left side of the heart has a thicker muscular wall (myocardium) as it has to pump blood faster
7
New cards
Describe the function of the arteries
convey blood at high pressure from the heart ventricles to the tissues of the body and lungs
8
New cards
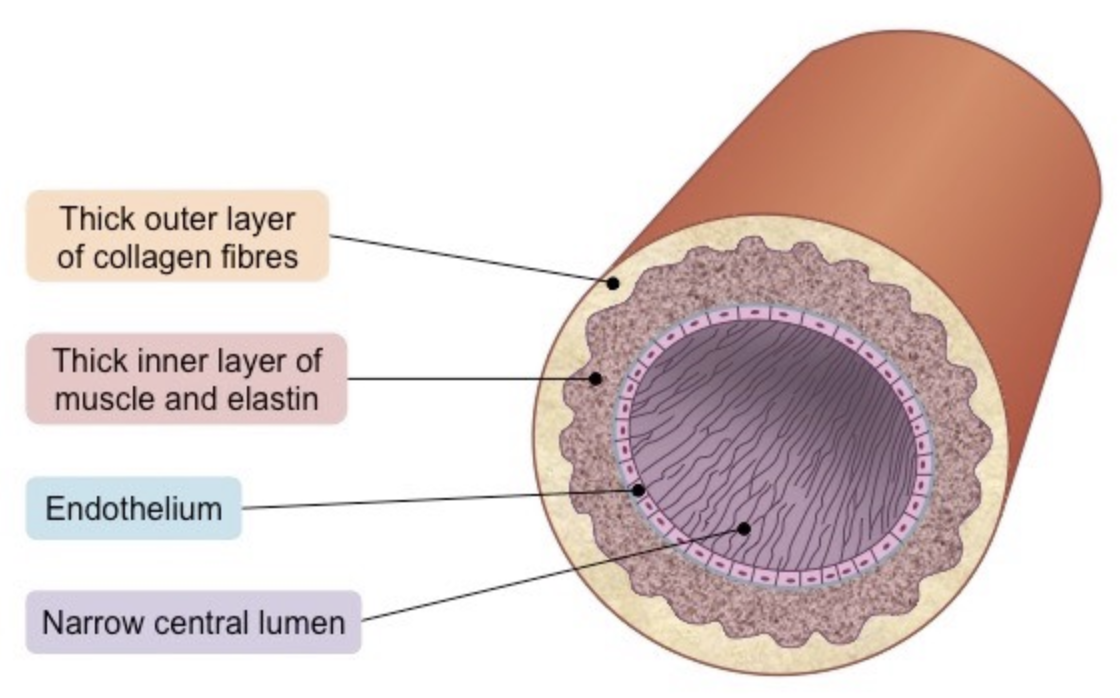
Describe the structure of the arteries that enable them to do their function
* narrow lumen (relative to wall thickness) to maintain high blood pressure
* thick wall containing an outer layer of collagen to prevent artery from rupturing under high pressure
* the arterial wall contains an inner layer of muscle and elastic fibers to maintain pulse flow (allows it to contract and stretch)
* thick wall containing an outer layer of collagen to prevent artery from rupturing under high pressure
* the arterial wall contains an inner layer of muscle and elastic fibers to maintain pulse flow (allows it to contract and stretch)
9
New cards
Describe how the muscle fibers help with blood flow
* form a rigid arterial wall that can withstand high blood pressure without rupturing
* can also contract and narrow the lumen to increase blood pressure
* can also contract and narrow the lumen to increase blood pressure
10
New cards
Describe how arterial elastic fibers aid in blood flow
* allow the arterial wall to stretch and expand during a pulse
* elastic recoil: pressure exerted on the arterial wall is returned to the blood when the artery returns to its original size
* helps push the blood forward through the body and maintain pressure
* elastic recoil: pressure exerted on the arterial wall is returned to the blood when the artery returns to its original size
* helps push the blood forward through the body and maintain pressure
11
New cards
Describe the function of the capillaries
used to exchange materials between the cells in tissue and blood at a low pressure
12
New cards
Describe the process of blood exchange between the arteries and capillaries
1. arteries split into arterioles
2. arterioles split into capillaries
1. this decreases arterial pressure as volume is increased, ensures blood is moving slowly, and that all cells are located near a blood supply
3. after the material exchange, capillaries pool into venules which collate into larger veins
13
New cards
Describe the structure of capillaries
* small diameter allows for passage of only one red blood cell at a time
* capillary wall of single layer of cells minimizes diffusion distance
* surrounded by basement membrane that is permeable to certain materials
* pores aid in the transport of material between fluid and blood
* capillary wall of single layer of cells minimizes diffusion distance
* surrounded by basement membrane that is permeable to certain materials
* pores aid in the transport of material between fluid and blood
14
New cards
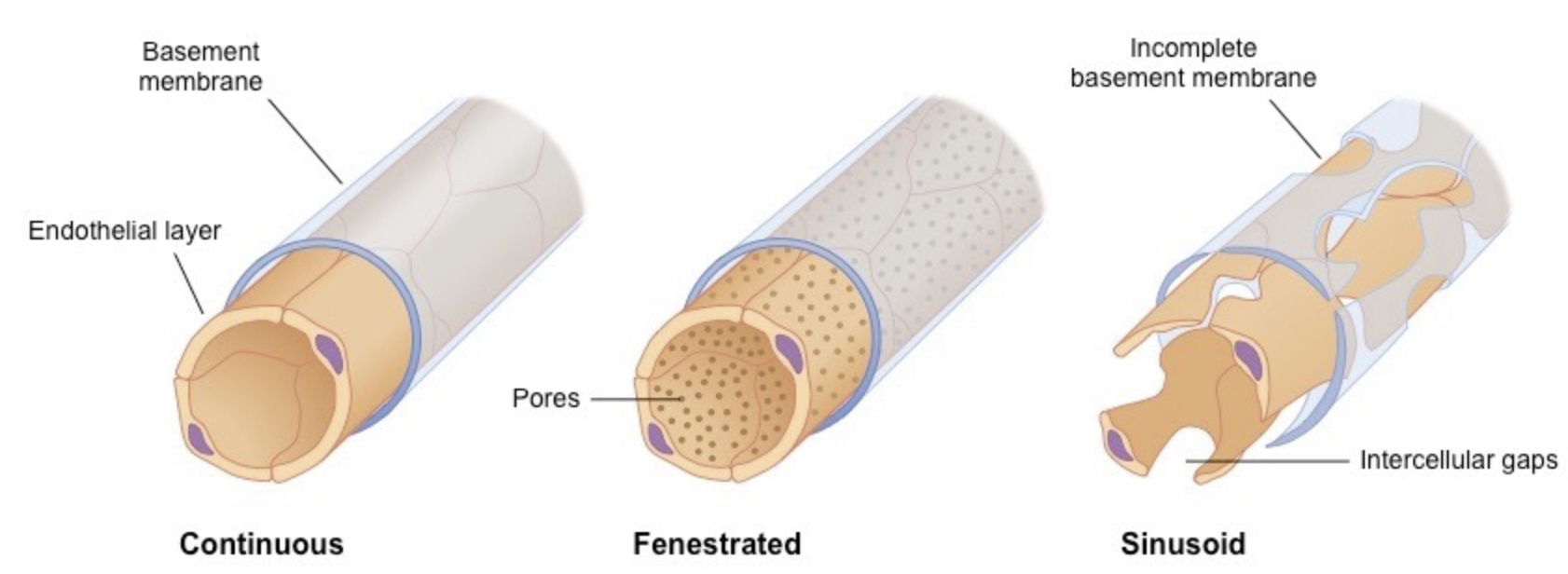
Describe how capillary structure can vary depending on its location
__Continuous capillary structure__
* endothelial cells held together by tight junctions to limit permeability of large molecules
__Fenestrated capillary structure__
* pores help with absorption
* located in tissues specialized for absorption (intestines, kidneys)
__Sinusoidal__
* open spaces between cells make cells permeable to large molecules and cells
* ex) in liver
* endothelial cells held together by tight junctions to limit permeability of large molecules
__Fenestrated capillary structure__
* pores help with absorption
* located in tissues specialized for absorption (intestines, kidneys)
__Sinusoidal__
* open spaces between cells make cells permeable to large molecules and cells
* ex) in liver
15
New cards
Describe the flow of blood in capillaries
low pressure allows for max material exchange
\
higher hydrostatic pressure in the arteriole end of the capillary forces material from the bloodstream into the tissue (oxygen and nutrients)
\
lower hydrostatic pressure at the venule end of the capillary allows material to enter the bloodstream (carbon dioxide and urea)
\
higher hydrostatic pressure in the arteriole end of the capillary forces material from the bloodstream into the tissue (oxygen and nutrients)
\
lower hydrostatic pressure at the venule end of the capillary allows material to enter the bloodstream (carbon dioxide and urea)
16
New cards
Describe the function of the veins
to collect blood from the tissues and convey it at low pressure to the atria of the heart
17
New cards
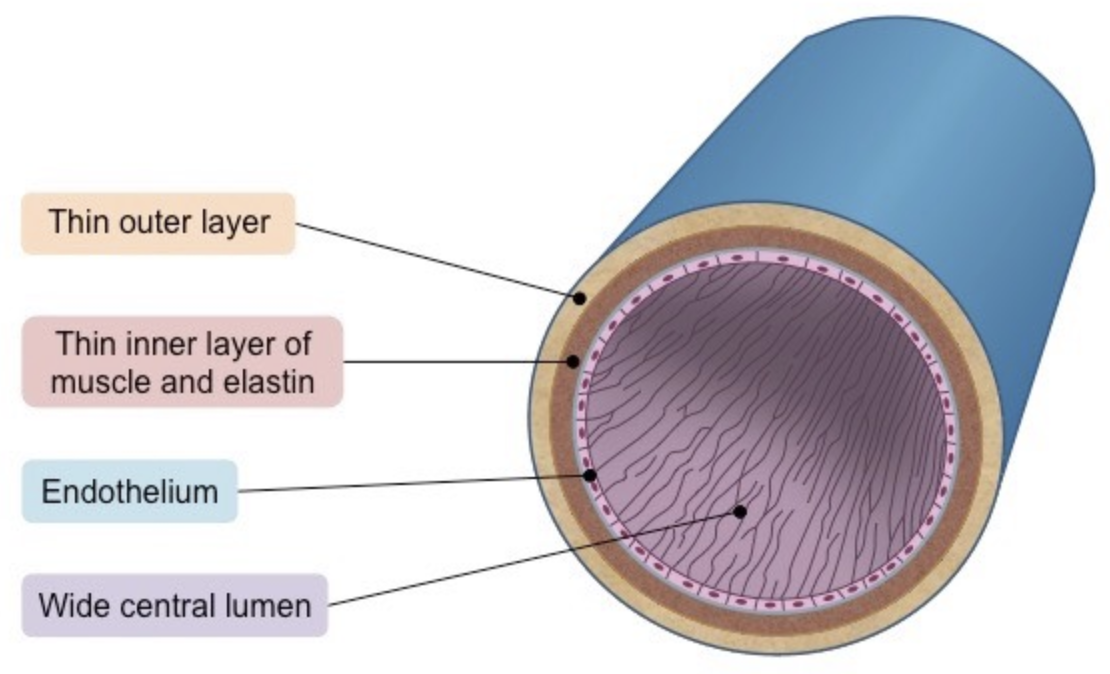
Describe the structure of the veins
* very wide lumen relative to wall thickness to maximize blood flow for effective return
* thin wall with less muscle and elastic fibers because blood is at low temperature
* valves to prevent backflow and stop the blood from pooling at lowest extremities
* thin wall with less muscle and elastic fibers because blood is at low temperature
* valves to prevent backflow and stop the blood from pooling at lowest extremities
18
New cards
Describe the flow of blood in the veins
* low pressure makes it difficult for the blood to move against gravity
* valves help maintain circulation of blood
* veins passing between skeletal muscle groups facilitate venous flow via periodic contractions
* when skeletal muscles contract, they squeeze the vein causing blood to flow out of site of compression
* veins usually run parallel to arteries so the arterial bulge can cause the same effect
* valves help maintain circulation of blood
* veins passing between skeletal muscle groups facilitate venous flow via periodic contractions
* when skeletal muscles contract, they squeeze the vein causing blood to flow out of site of compression
* veins usually run parallel to arteries so the arterial bulge can cause the same effect
19
New cards
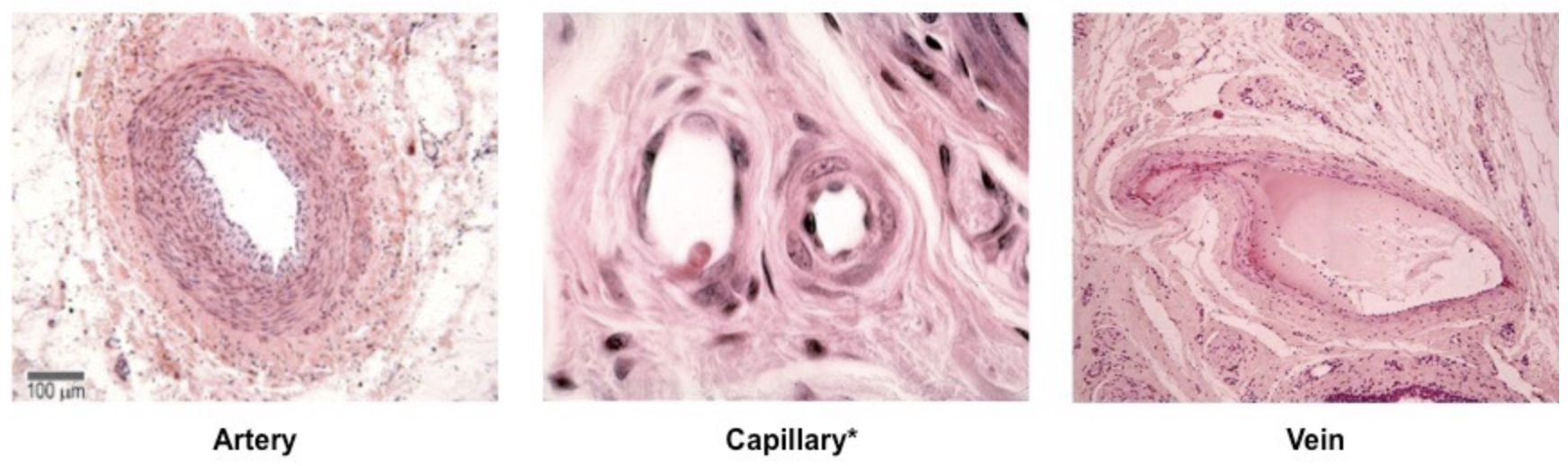
Describe the difference in structure between arteries, capillaries, and veins
arteries: thick walls (three distinct layers), narrow lumens, high blood pressure
capillaries: single cell thick wall for rapid exchange, extremely narrow lumen, low pressure
veins: thin walls, wide lumens, valves present, low blood pressure
capillaries: single cell thick wall for rapid exchange, extremely narrow lumen, low pressure
veins: thin walls, wide lumens, valves present, low blood pressure
20
New cards
Describe the location & function of the atria
smaller chambers near the top of the heart that collect blood from the body and lungs
21
New cards
Describe the location & function of the ventricles
larger chambers near the bottom of the heart that pump blood to the body and the lungs
22
New cards
Describe the location of the atrioventricular valves and name them
located between the atria and the ventricles, bicuspid valve on the left side (mitral), tricuspid valve on the right side
23
New cards
Describe the location of the semilunar valves and name them
located between the ventricles and arteries, aortic valve on the left side and the pulmonary valve on the right side
24
New cards
Describe the function of the vena cava
feeds into the right atrium and returns deoxygenated blood from the body
25
New cards
Describe the function of the pulmonary artery
connects to the right ventricle and sends deoxygenated blood to the lungs
26
New cards
Describe the function of the pulmonary vein
feeds into the left atrium and returns oxygenated blood from the lungs
27
New cards
Describe the function of the aorta
extends from the left ventricle, sends oxygenated blood around the body
28
New cards
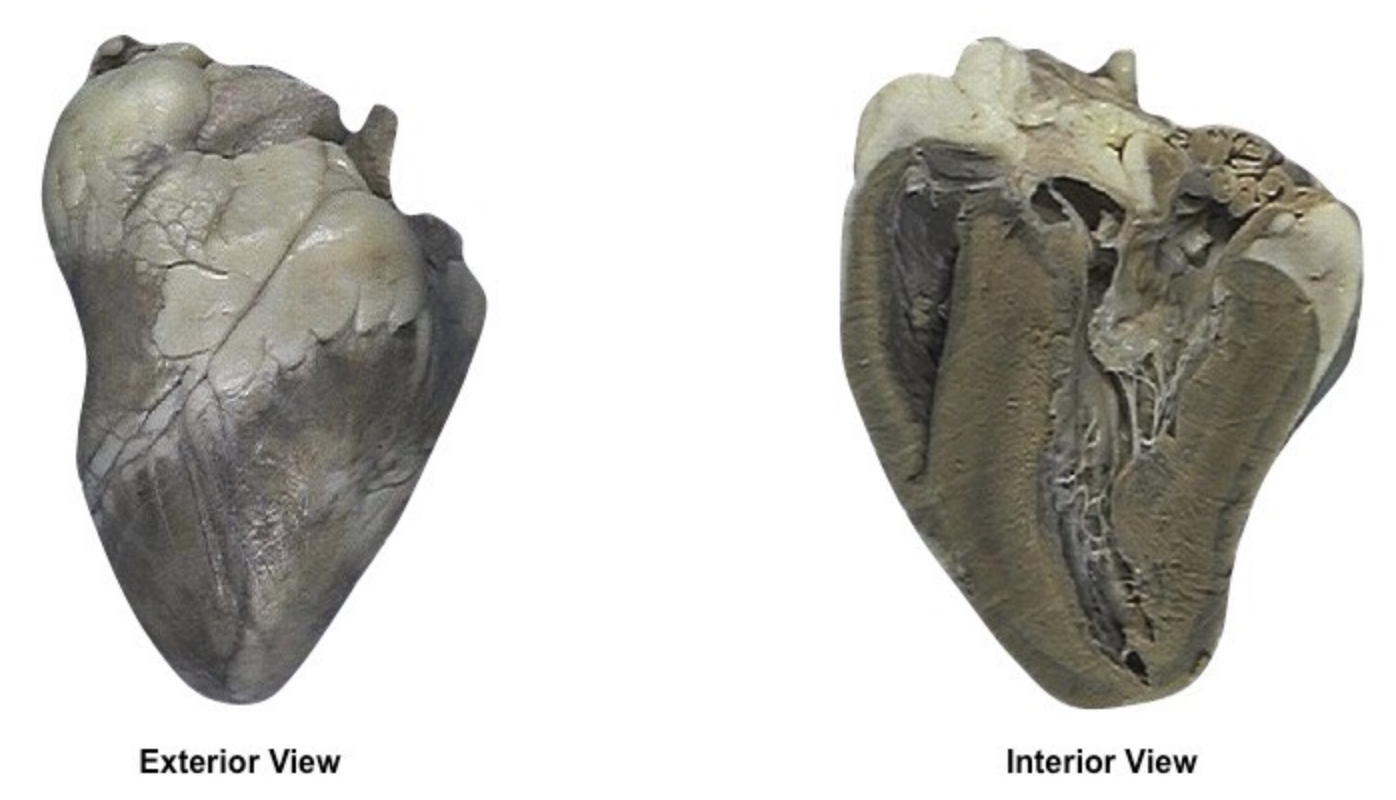
Label the left and right side, the opening to the aorta, the left and right atrium/ventricle, and the septum
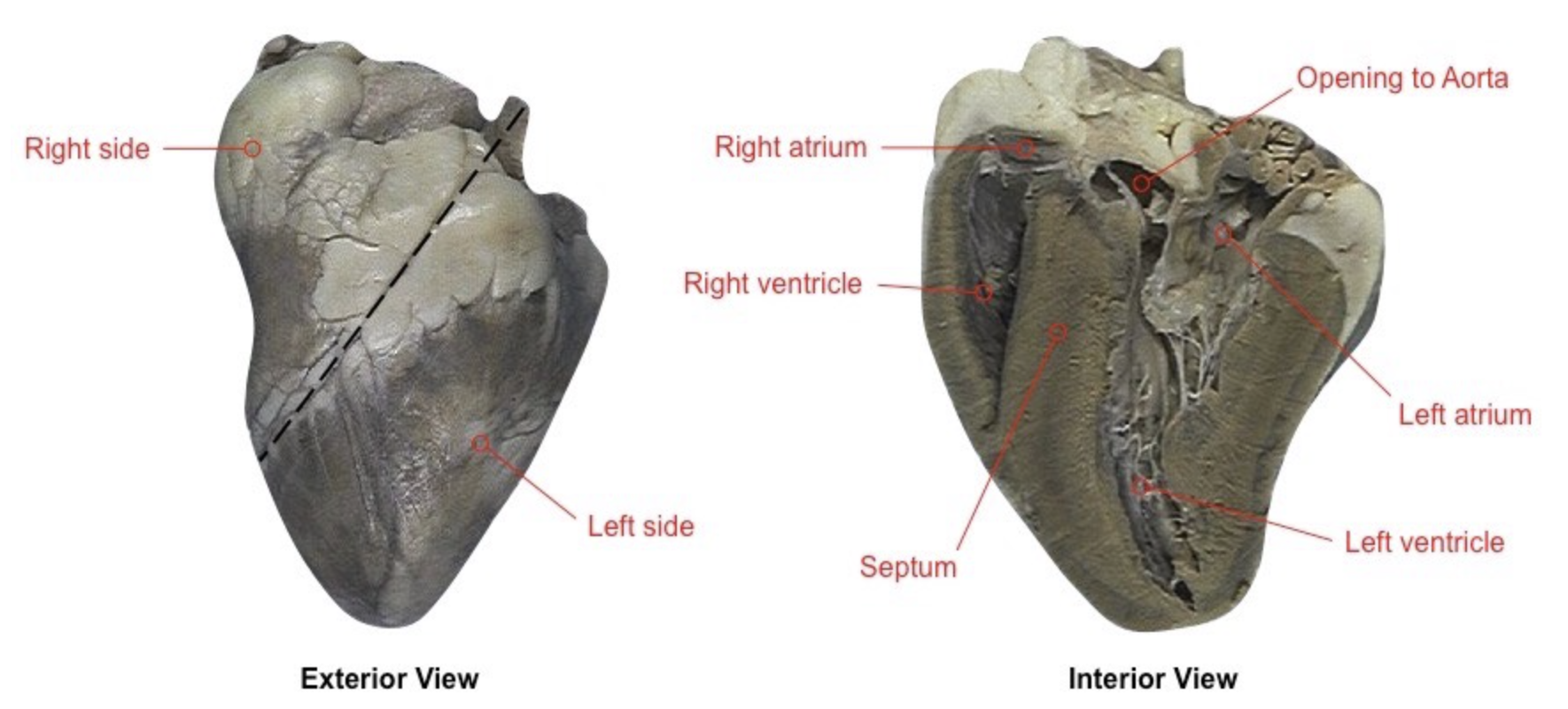
29
New cards
Describe why the heart is myogenic
the signals for cardiac compression derive from the heart (signaled by the heart muscle cells called the cardiomycoytes) itself rather than brain signals
30
New cards
Describe the primary pacemaker of the heart
* cluster of cardiomyocytes within the wall of the right atrium direct the contraction of heart muscle tissue
* this is called the sinoatrial node (SA node)
* this is called the sinoatrial node (SA node)
31
New cards
Describe the secondary pacemaker of the heart
\
\
If the SA node fails, the AV node can maintain contractions at a lower rate
32
New cards
Describe the tertiary pacemaker
the bundle of His can coordinate contractions at an even lower rate than the AV node
33
New cards
Describe what occurs when the interference of pacemakers occurs
irregular and uncoordinated contraction of heart muscle will occur
* this is called fibrillation
* normal rhythm can be re-established with a defibrillator (controlled electrical current)
* this is called fibrillation
* normal rhythm can be re-established with a defibrillator (controlled electrical current)
34
New cards
Describe the electrical conduction of the heart beat
* sinoatrial node sends electrical impulse
* contraction of the myocardium is stimulated
* causes atria to contract
* stimulates node called the AV node at the junction between the atrium and ventricle
* AV node sends signals down the septum to the Bundle of His (a nerve bundle)
* Bundle of His innervates nerve fibers called Purkinje fibers in the ventricular wall to cause ventricular contraction
* contraction of the myocardium is stimulated
* causes atria to contract
* stimulates node called the AV node at the junction between the atrium and ventricle
* AV node sends signals down the septum to the Bundle of His (a nerve bundle)
* Bundle of His innervates nerve fibers called Purkinje fibers in the ventricular wall to cause ventricular contraction
35
New cards
State what is responsible for the two heart sounds
first heart sound: AV valve closing after blood enters the ventricle
\
second heart sound: aortic valve closing to prevent back flow
\
second heart sound: aortic valve closing to prevent back flow
36
New cards
Describe how nerve signaling can increase or decrease heart rate
* the sympathetic nerve releases the neurotransmitter noradrenaline aka norepinephrine to increase heart rate
* the parasympathetic nerve (vagus nerve) releases the neurotransmitter acetylcholine to decrease heart rate
* the parasympathetic nerve (vagus nerve) releases the neurotransmitter acetylcholine to decrease heart rate
37
New cards
Describe how hormonal signaling can regulate heart rate
* the hormone adrenaline aka epinephrine is released from the adrenal glands to increase heart rate by activating the same pathways as the neurotransmitter noradrenaline
38
New cards
Describe what happens during systole
1. blood returning to the heart flows into the atria and ventricles as pressure is lower due to low volume of blood
2. when ventricles reach 70% capacity, atria contract, this increases pressure in the atria and forces blood into ventricles
1. this is called atrial systole
3. ventricles contract, ventricular pressure exceeds atrial pressure
4. AV valve closes to prevent backflow (first heart sound)
5. pressure builds in contracting ventricles
1. this is called isovolumetric contraction
6. ventricular pressure exceeds blood pressure in the aorta
7. aortic valve opens, blood released into aorta
39
New cards
Describe what happens during diastole
1. blood exits ventricle and travels down aorta
2. ventricular pressure decreases
3. when ventricular pressure drops below aortic pressure, aortic valve closes to prevent backflow (second sound)
4. when ventricular pressure drops below atrial pressure, AV valve opens to allow blood to flow from atria to ventricle
5. aortic pressure remains high throughout as muscle and elastic fibers in arterial wall maintain blood pressure
40
New cards
Draw the graph of the pressure changes during systole and diastole
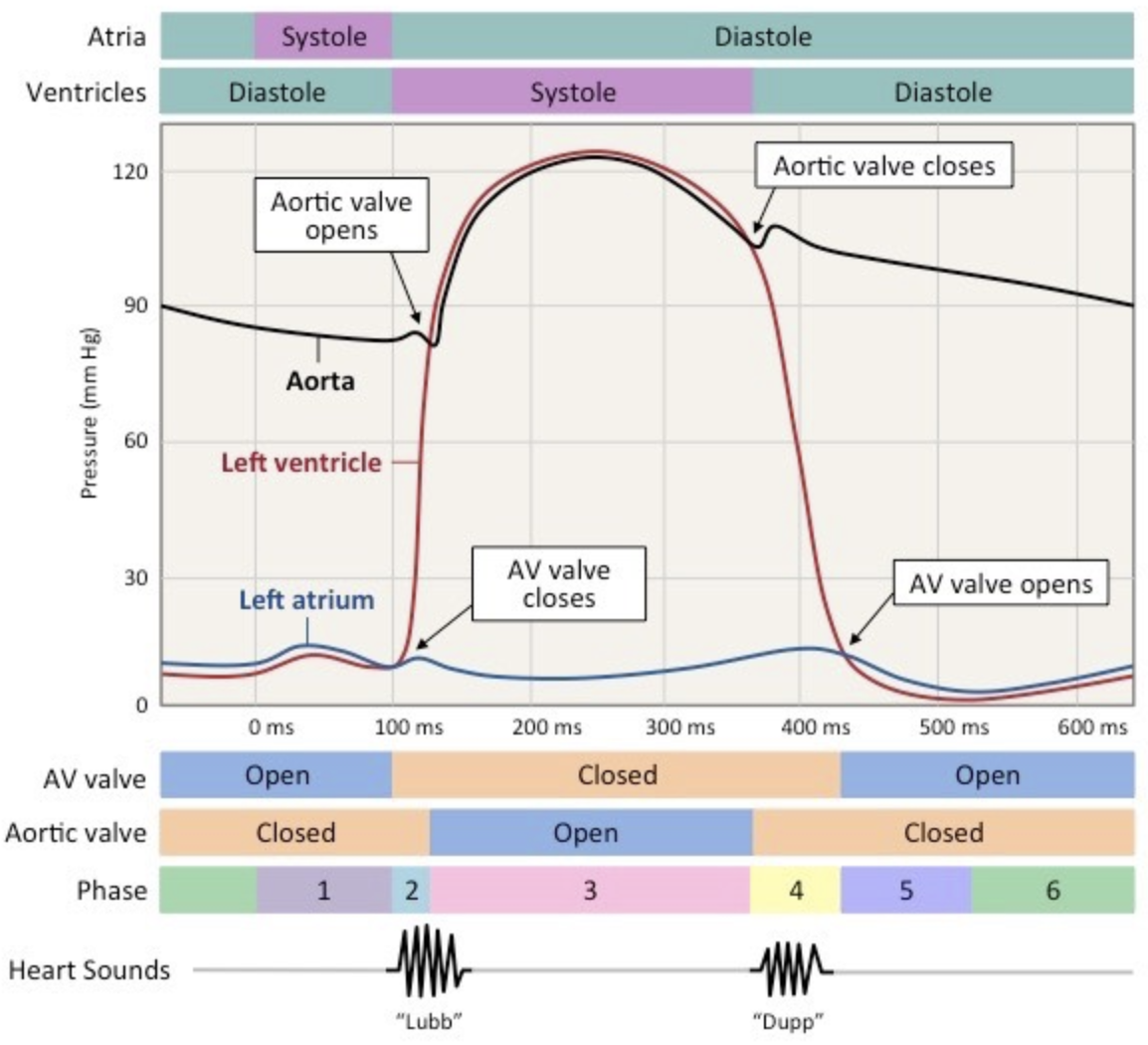
41
New cards
Describe the function of coronary arteries
the blood vessels that surround the heart and nourish the cardiac tissue to keep the heart working
42
New cards
State the definition of atherosclerosis
hardening and narrowing of the arteries due to the deposition of cholesterol
43
New cards
Describe how atherosclerosis causes coronary occlusion
1. atheromas (fatty deposits) develop in the arteries which reduce the lumen diameter (stenosis)
2. restricted blood flow increases pressure
3. causes stress on arterial wall which damages the wall
4. damaged region is repaired with fibrous tissue which reduces the elasticity of the wall
5. smooth lining of the artery is degraded over time
6. lesions form called atherosclerotic plaques
7. if the plaque ruptures, blood clotting is triggered
8. this forms a thrombus which reduces blood flow
9. if the thrombus is dislodged, it can become an embolus and cause a blockage of a smaller ateriole
44
New cards
Describe the consequences of coronary occlusion
myocardial tissue needs oxygen and nutrients from the coronary arteries to function, so a coronary occlusion would result in the myocardial tissue not functioning
* can lead to an acute myocardial infarction (heart attack)
* can lead to an acute myocardial infarction (heart attack)
45
New cards
Describe how coronary artery blockage is treated
by-pass surgery or creating a stent
46
New cards
What are risk factors for coronary heart disease
A GODDESS
\
Age
* blood vessels become less flexible with age
Genetics
* hypertension predisposes individuals to heart disease
Obesity
* places additional strain on heart
Diseases
* ex) diabetes increases risk of CHD
Diet
* saturated fats, salts, alcohol increase risk
Exercise
* lack of exercise increases risk
Sex
* males at greater risk due to lower estrogen levels
Smoking
* nicotine causes vasoconstriction which raises blood pressure
\
Age
* blood vessels become less flexible with age
Genetics
* hypertension predisposes individuals to heart disease
Obesity
* places additional strain on heart
Diseases
* ex) diabetes increases risk of CHD
Diet
* saturated fats, salts, alcohol increase risk
Exercise
* lack of exercise increases risk
Sex
* males at greater risk due to lower estrogen levels
Smoking
* nicotine causes vasoconstriction which raises blood pressure