Nucleotides
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
What does a nucleotide consist of?
Sugar
Phosphate group
A base (A, T , C or G)
What is DNA?
Polymer made of repeating units of nucleotides
Has deoxyribose sugar
What bond is between the complementary bases?
Hydrogen bonds
What are the two nuclei acids?
DNA and RNA are polymers - individual nucleotides are the monomers that build up the polynucleotides
DNA = deoxyribonucleic acid
DNA = ribonucleico acid
Bases in RNA
A = U
C = G
What is a purine
Contains 2 carbon - nitrogen rings
A and G
What is a pyrimidine?
Contains one carbon - nitrogen ring
T C and U
How may strands does DNA have compared to RNA
DNA has double strands
RNA is single strand
How many hydrogen bonds between AT and CG?
A - T = 2
C - G = 3
Where is the hydroxyl and Pentose groups in DNA?
Hydroxyl group on carbon 3 of pentose sugar and phosphate group on carbon 5 of nucleotide
What is bonded to carbon 2 on DNA and RNA?
DNA = H group
RNA = hydroxyl group, more susceptible to hydrolysis
How do phosphodiester bonds form?
Condensation reactions occurs between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the pentose sugar of the other via condensation reactions
Make a sugar phosphate backbone
Describe how 2 single polynucleotide strands join to make a double helix
Hydrogen bonding between base pairs
2 hydrogen bonds between at and 3 between cg
Complementary base parking
Antiparallel strands twist to make double helix
What is ATP consisted of?
Adenine, Ribose, 3 phosphate groups
AMP = 1 phosphate group
ADP = 2 phosphate groups
ATP = 3 phosphate groups
What is ATP?
Chemical energy needed to fuel biological activities
Is produced continuously
What is the role of ATP?
Stores most of the energy in the third bond of the molecule
Energy is release when the bond is broken to release the third inorganic phosphate
What is phosphorylation
Adding a phosphate group
How is ATP formed
Using ATP synthase,
ADP bonds to a third norganic phosphate group using energy from glucose
What does anti parallel mean?
Parallel but with chains running in oppose directions
3 to 5 direction
5 to 3 direction
Explain the steps of purification of DNA
Prepare your equipment - kiwi, pineapple juice, salt , detergent and cold alchohol
Make the extraction solution - water, salt and detergent
Prepare fruit mush using pestle and mortar
Add extraction solution and leave for 20 min - detergent breaks down cell membrane so DNA can be released
Filter the solution - gets rid of pulp
Purify DNA by removing proteins bound to DNA using pineapple juice
Precipitating the DNA - DNA mixes with alcohol and produced white clump of DNA
Purpose of detergent
Breaks down cell membrane
Processs of precipitating DNA from cells
Cell surface membrane and nuclear envelope are physically broken down by detergent
Mixture is filtered
DNA is precipitated using ethanol
Why does DNA need to replicate
Before a cell divided, it needs to copy itself so each new cell has a copy of DNA
Explain Semi conservative replication (1)
DNA helicase causes 2 strands to seperate as it breaks the hydrogen bonds between the bases
Forms 2 strands
Semi conservative replication (2)
Each original strand is a template
Free nucleotides are attracted to exposed complementary bases
Semi conservative replication (3)
DNA polymerase joins free nucleotide to the original strand (phosphodiester bond)
Forms sugar phosphate backbone
Hydrogen bonds form between bases
Semi conservative replication (4)
2 identical strands forme
Nucleotides joined to from a polynucleotide
Each strand has half the oriental DNA
Evidence for the semi conservative replication - theory
Matthew Meselsohn and Franklin Stahl used E. coli
Grown in a medium containing heavy isotope nitrogen 15
This bacteria used the 15N to make the purine and pyrimidine bases in its DNA
Explanation of results - Semi conservative replication
Parental generation - both strands made with 14N
First generation - DNA made of one strand 15N and one strand 14N
Second generation - some DNA made of 2 strands of 14N and some with mix
Explain what genes are
each gene has a different sequence of bases
Gene code for a specific polypeptide
Each gene is on a fixed position on a chromosome
sequence of three bases code for..
Amino acid
The order of the bases are important - why?
They control the order the amino acids are assembled to produce a protein
Structure of amino acid
Amino group - NH2
Carboxyl group - COOH
r group
What is a codon
Sequence of 3 nucleotide bases that code for an amino acid
Degenerate code:
More than one codon codes for each amino acid
Non - overlapping code
Only read once
Universal code
The same codon codes for the same amino acids in all organisms
How does DNA control all activities in cell?
Chemical reactions are controlled by enzymes, which are proteins
DNA codes for proteins
Why may 2 different species of Actium have different percentages of guanine?
Different proteins
Different base sequence
Different genes
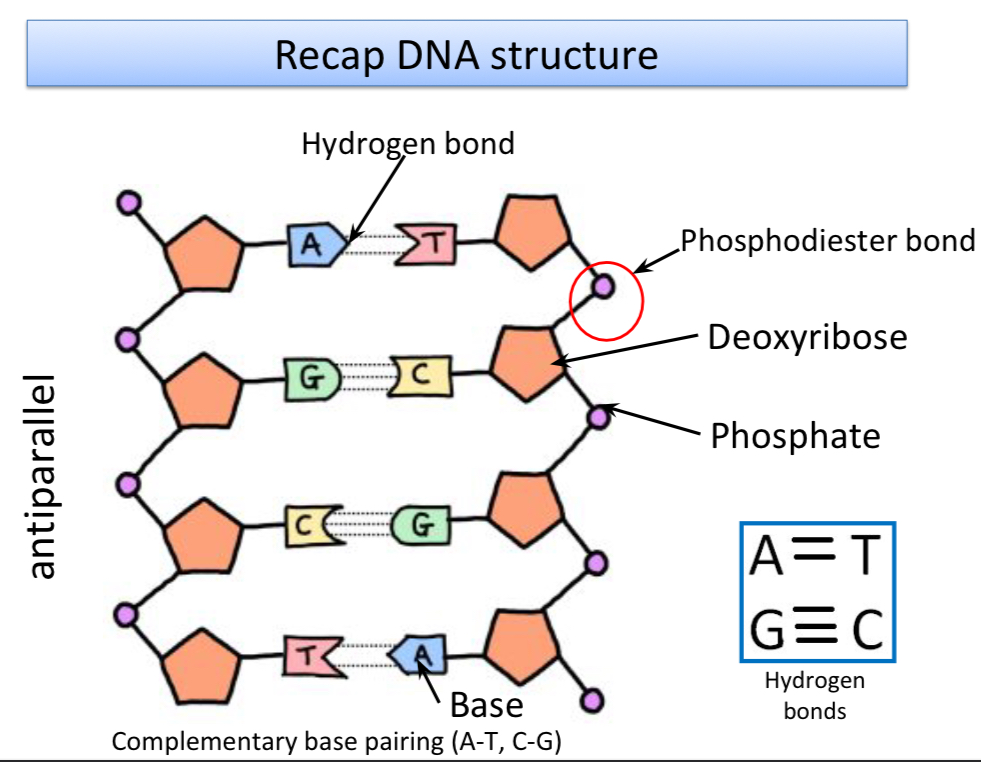
Name the DNA structure
Explain mRNA:
Made in the nucleus, small enoug to pass through nuclear pores
Carries copy of genetic code for a protein to the ribosome in cytoplasm
Uses Uracil instead of thymine
Describe tRNA
One strand folded in on itself
Amino acid determined by anticodon at top
Anticodon is complementary to the codon on mRNA
Transcription process
DNA helicase seperate the 2 trends pf DA by breaking the H bonds
RNA polymerase = moves along one strand of DNA, causing RNA nucleotides to align with complementary bases and join together using a phosphodiester bond
As it moves along, DNA strands rejoin behind it
Describe how mRNA is formed by transcription in eukaryotes
Hydrogen bonds break - DNA helicase
One DNA strand is a template, RNA snucleotides align by complementary bases
Uracil pairs with adenine instead of thymine
RNA polymerase joins nucleotides with phosphodiester bonds
Explain process of translation (1) until next codon
One end of the mRNA attaches to the ribosome
TRNA molecule with complementary anticodon attaches to ribosome
Second tRNA molecule binds to next codon
Exaplin process of translation (2)
Ribosomes move along mRNA and join 2 amino acids together by a peptide bond
Continues until stop codon is reached