Basic Microeconomics (lesson 2)
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Is the process by which resources are transformed into useful forms
Refer to anything provided by nature or previous generations that can be used directly or indirectly to satisfy human wants.
What are the three resources?
What are the three basic questions?
He developed the theory of comparative advantage to explain the benefits of specialization and free trade.
According to this theory specialization and free trade will benefit all trading parties, even those that maybe absolutely more efficient producers.
Is the process of using resources to produce new capital. Capital is the accumulation of the previous investment.
Are goods produced for present consumption.
Are goods used to produce other goods or services over time.
Is a graph that shows all of the combinations of goods and services that can be produced if all of societies resources are user efficiency.
it has a negative slope that indicates the trade-off that a society faces between two goods.
The slope of the ppf is also called?
Resources are either unemployed, or are used inefficiently.
Is desirable because it yields more of both goods, but it is not attainable given the amount of resources available in the economy.
Is one of the possible combinations of goods produced when resources are fully and efficiently employed.
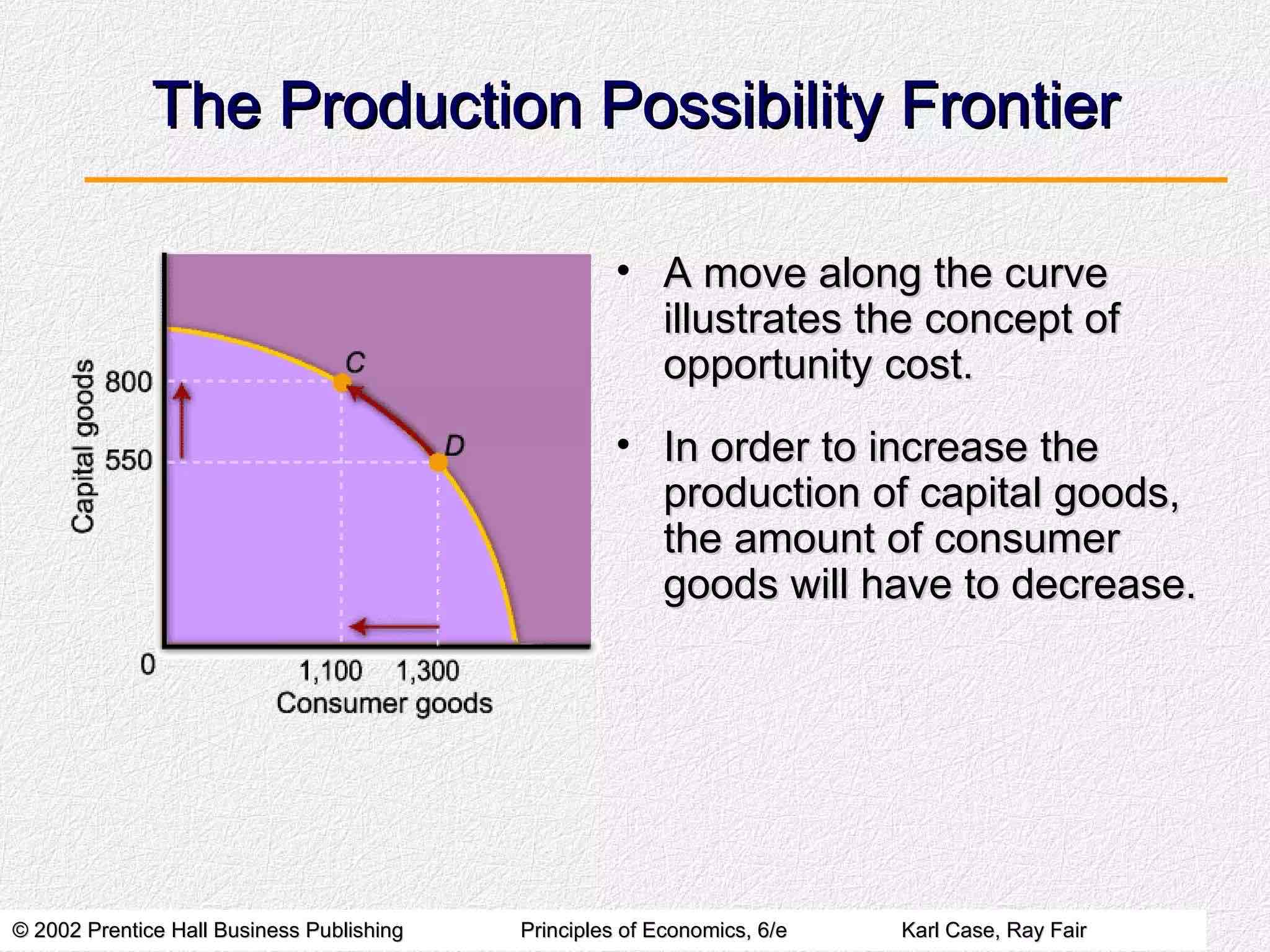
A move along the curve illustrates the concept of opportunity cost.
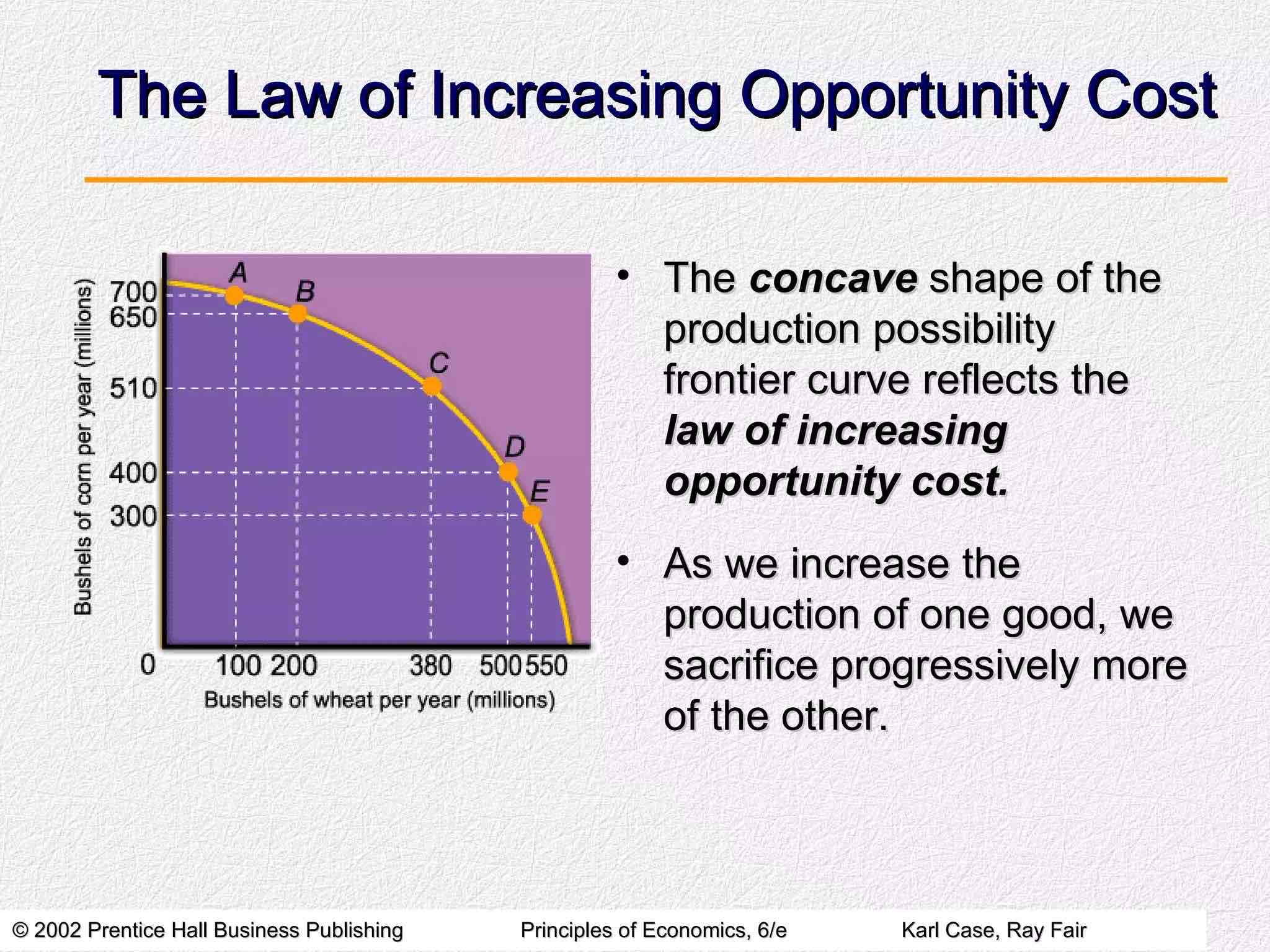
The concave shape of the production possibility frontier curve reflects the low of increasing opportunity costs.
Is an increase in the total output of the economy. It occurs when a society acquires new resources, or when it learns to produce more using existing resources.
Outward shifts of the curve represents?
To increase the production of one good without decreasing the production of the other, the ppf must shift?
Given scarce resources, how, exactly, do large complex societies go about answering three basic economic questions.
_____ Are the basic arrangements made by the societies to solve the economic programs.
They include:
A central government either directly or indirectly sets output targets, incomes and prices.
Literary from the french: “allow (them) to do.” Individual people and firms pursue their own self interest without any central direction or regulation.
Is the institutions through which buyers and sellers interact and engage in exchange
Under a free market system, individual producers must figure out how to plan, organize, and coordinate the production of products and services.
Is also determined in a decentralized way. The amount that any one household gets depends on its income and wealth.
Is the amount that a product sells for per unit
Markets are not perfect, and government plays a major role in all economic systems in order to: