Lab 1: Light Microscopy and Examination of Natural Microbes
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary-style flashcards covering key terms from Lab 1 on light microscopy and observation of pond water and hay infusion organisms.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Antoni van Leeuwenhoek
Pioneer of microbiology; first to observe bacteria, algae, fungi, and protozoa using a simple single-lens microscope; often called the father of microbiology.
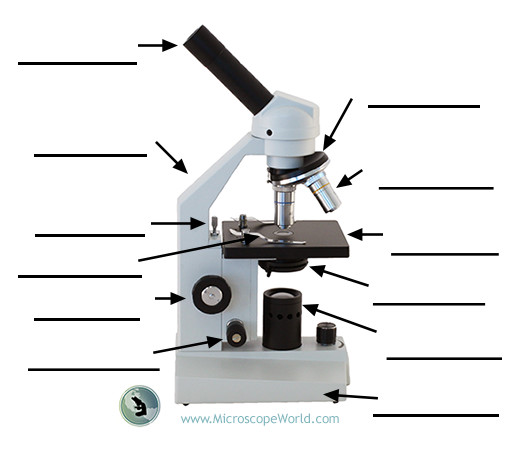
Light microscope
Instrument that uses visible light and lenses to magnify small specimens; the lab uses a compound-type microscope.
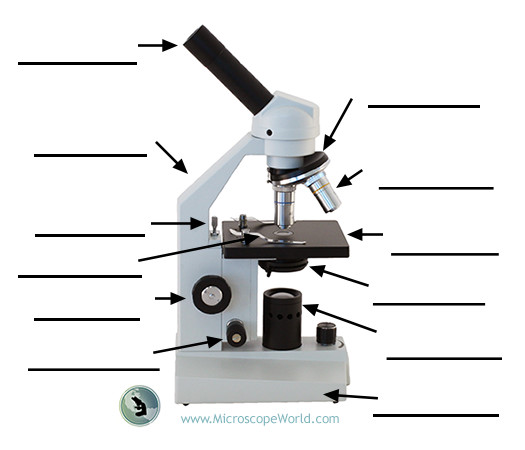
Ocular (eyepiece) lens
The lens at the top you look through; typically 10X or 15X magnification.

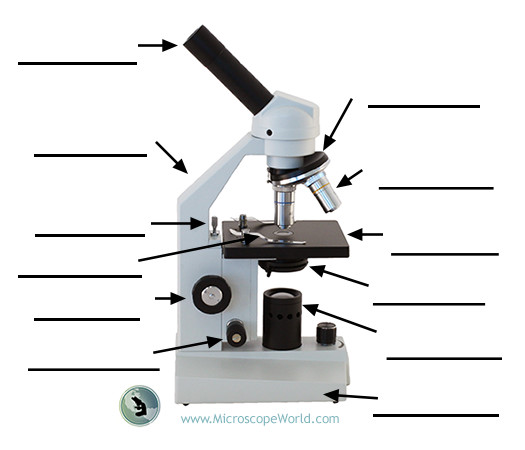
Illuminator
The steady light source that illuminates the specimen; mirrors may reflect external light in some setups.

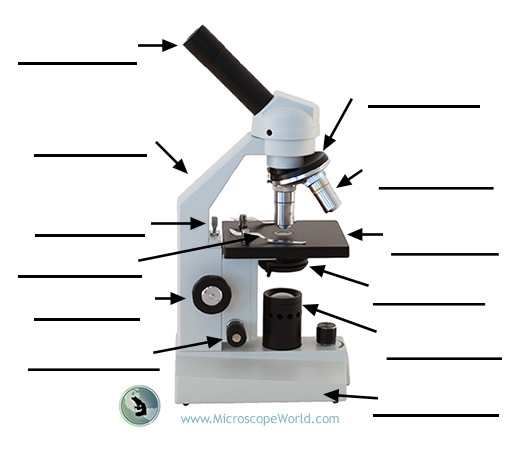
Stage
Flat platform where slides are placed; moves horizontally and vertically to position the specimen.

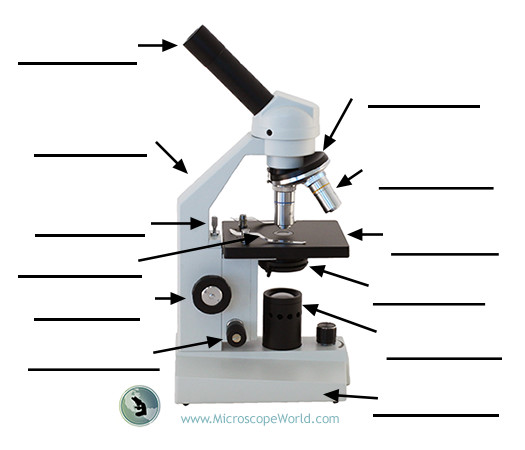
Objective lenses
Lenses closest to the specimen; common magnifications include 4X, 10X, 40X, and 100X.

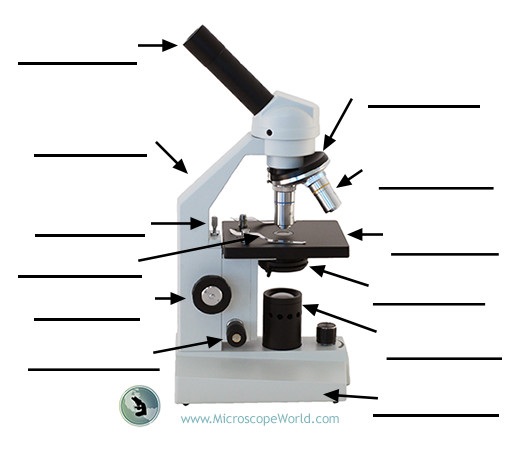
4X objective
Lowest-power objective used to locate and roughly focus on the specimen.

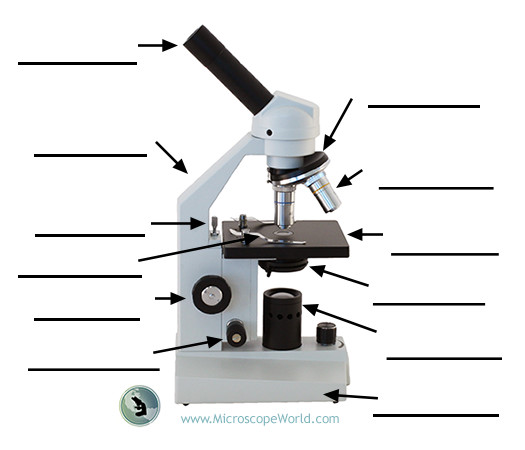
10X objective
Medium-power objective used to center and begin focusing on the specimen.

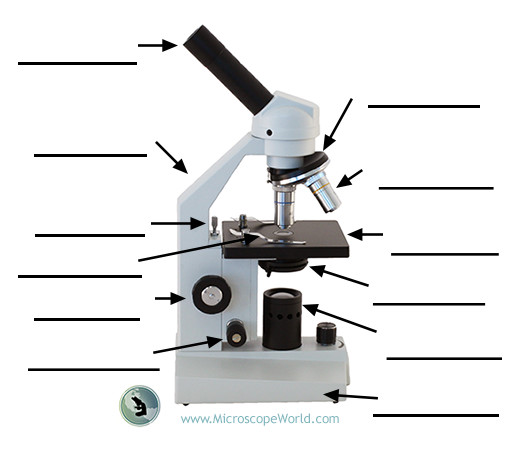
40X objective
High-power objective used for detailed viewing; requires careful focusing with the fine adjustment.

100X objective (oil immersion)
Immersion objective that requires a layer of mineral oil between the lens and slide for higher resolution.

Immersion oil
Mineral oil used with the 100X objective to improve clarity and numerical aperture.
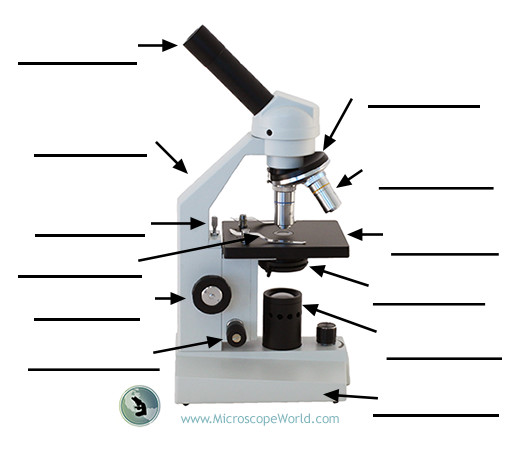
Condenser lens
Lens system that focuses light onto the specimen and helps control light intensity.

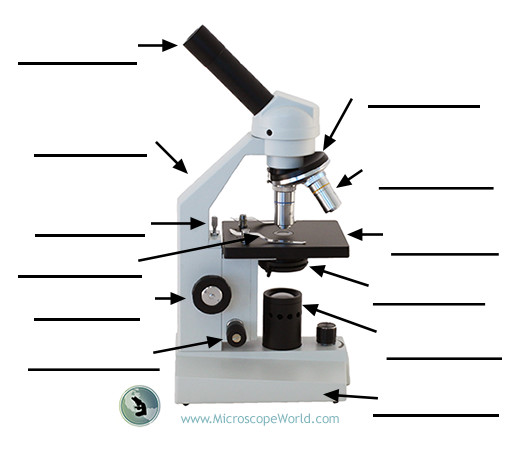
Coarse adjustment knob
Large knob used for initial focusing with low magnifications (up to 10X) by moving the stage a larger distance.

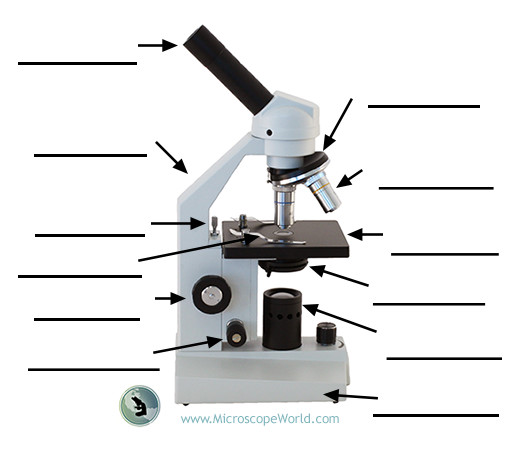
Fine adjustment knob
Small knob used for precise focusing, especially with 40X and 100X objectives.

Coverslip
Thin glass piece placed over the specimen on a slide to flatten and protect the sample.
Wet mount
Slide preparation where living or preserved material is placed in liquid and viewed under a coverslip.
Hanging drop
Slide technique where a drop of sample is suspended between a coverslip and slide to observe true motility in three dimensions.
Brownian motion
Random, jittery movement of particles in a fluid due to molecular collisions; not true motility.
True motility
Directional movement of organisms indicating active life (as opposed to Brownian motion).
Pond water
Water collected from ponds containing algae, bacteria, protozoa, etc., used for observation in this lab.
Hay infusion
Grass clippings soaked in water for 24–48 hours to create a nutrient-rich sample for observing pond life.
Algae
Photosynthetic eukaryotes often appearing as green clumps in pond samples.
Bacteria
Microscopic prokaryotes lacking a nucleus; come in various shapes and can be observed in pond samples.
Cyanobacteria
Photosynthetic bacteria formerly called blue-green algae; common in pond water.
Protozoa
Single-celled eukaryotes; often motile and observed in pond water and hay infusion.
Fungi
Eukaryotic organisms (molds, yeasts) that may appear in natural water samples; have cell walls.
Prokaryote vs Eukaryote
Prokaryotes lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles; eukaryotes have a nucleus and organelles.
Cell wall
Rigid layer found in some organisms (e.g., bacteria, plants, fungi); not all microbes have one.
Vacuole
Storage organelle within cells; involved in storage and transport.
Chloroplast
Organelle in photosynthetic cells (like algae) where photosynthesis occurs.
Nucleus
Membrane-bound organelle containing genetic material in eukaryotic cells.
Flagella
Whip-like appendages used for locomotion in some bacteria and protozoa.