Roman Art and Archaeology: Week 9
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
1
New cards
Campania
the region of Italy, specifically the Bay of Naples, where Pompeii is located
2
New cards
Herculaneum
a city destroyed by the flow of mud and gas from the eruption of mount Vesuvius; considered a better single preserved moment than Pompeii
3
New cards
Pompeii
the famous city preserved in the ash from the eruption of mount Vesuvius
4
New cards
Pliny the Younger
son of the famous writer, Pliny the Elder, and writer of the only first-person account of the eruption of Mount Vesuvius
5
New cards
orthogonal plan
a map of streets at right angles
6
New cards
basilica
a public space used for some court matters and business
7
New cards
hypocaust heating system
really boiling hot furnace creates steam and hot water: air is sent under the floor and water creates HOT bath
8
New cards
Riot with Nuceria
(59 CE) Riot at the Pompeii Amphitheater between Pompeians and Nucerians
9
New cards
earthquakes of Pompeii
62 CE
10
New cards
Eruption of Mount Vesuvius
79 CE
11
New cards
Four Pompeian Styles
not distinct periods of style (they overlap) but “trends” in art and architecture that were popular in Pompeii
12
New cards
First Style
(200-60 BCE) imitates opulancy of different architectural forms such as ashlar masonry (smooth marble blocks) and different colored marble
13
New cards
Second Style
(1st c BCE) “opening” of vistas into imaginary landscapes; inntended to be “voyages of the mind” in nature; less interesting stuff on the floor
14
New cards
Third Style
(20 BCE--20 CE) minimalist color fields and framed floating landscapes; reduction and attenuation of form
15
New cards
Fourth Style
(20-54 CE and beyond) features greek mythological scenes at the “pregnant moment”; intended to interest but not tell the whole story; perspectival architecture
16
New cards
xenia
still life scenes, usually of food
17
New cards
Villa of the Papyri
Villa with preserved texts from the eruption
18
New cards
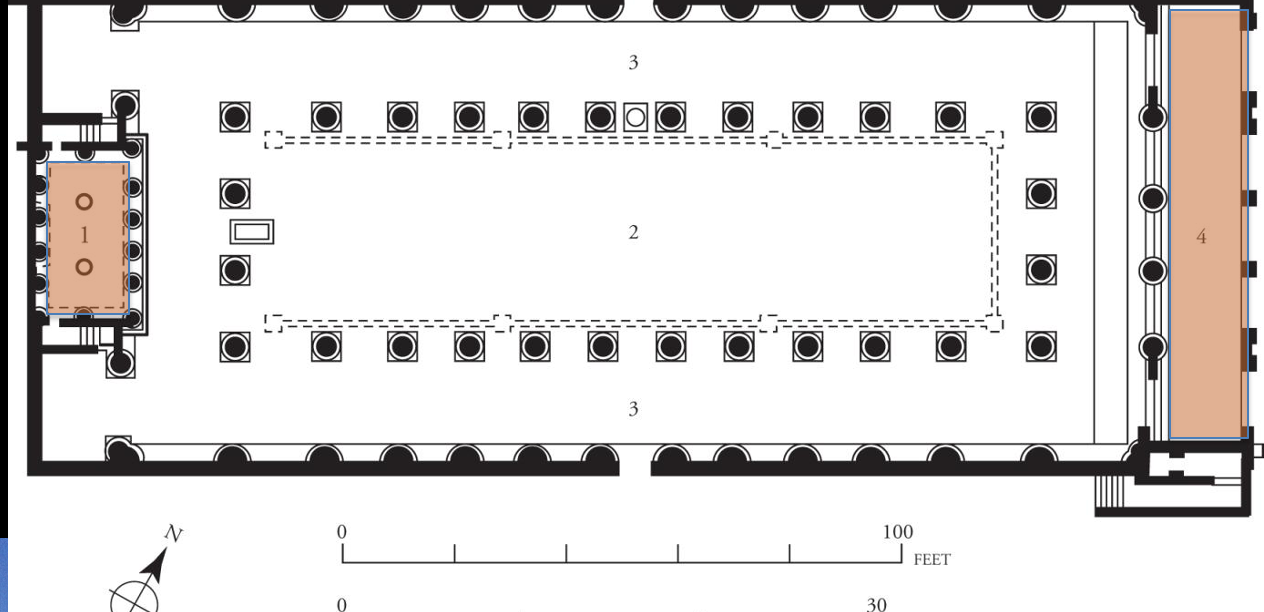
Fig. 3-10A Plan of the basilica, Pompeii, ca. 80–70 BCE. (1) tribunal, (2) nave, (3) aisle, \n (4) chalcidicum
19
New cards
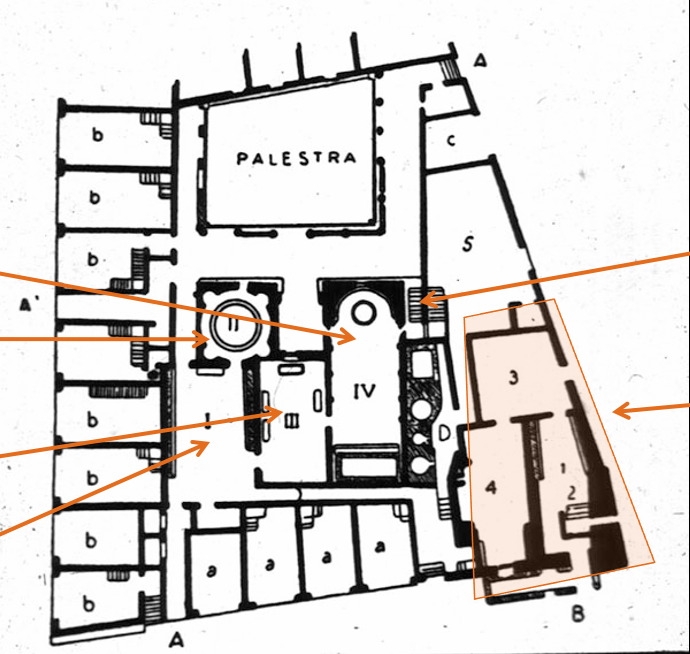
Fig. 3-11 Plan of the Forum Baths, Pompeii, ca. 80–70 BCE and Augustan
20
New cards
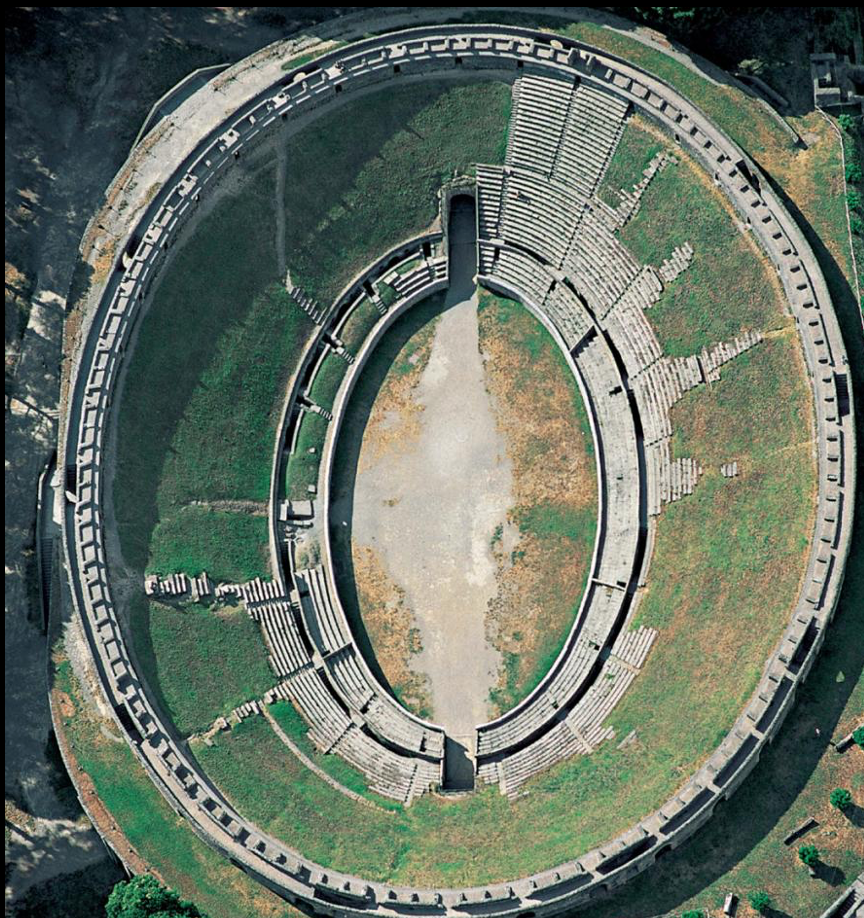

Fig. 3-15 Aerial view of the amphitheater (looking northwest), Pompeii, ca. 80–70 BCE
21
New cards
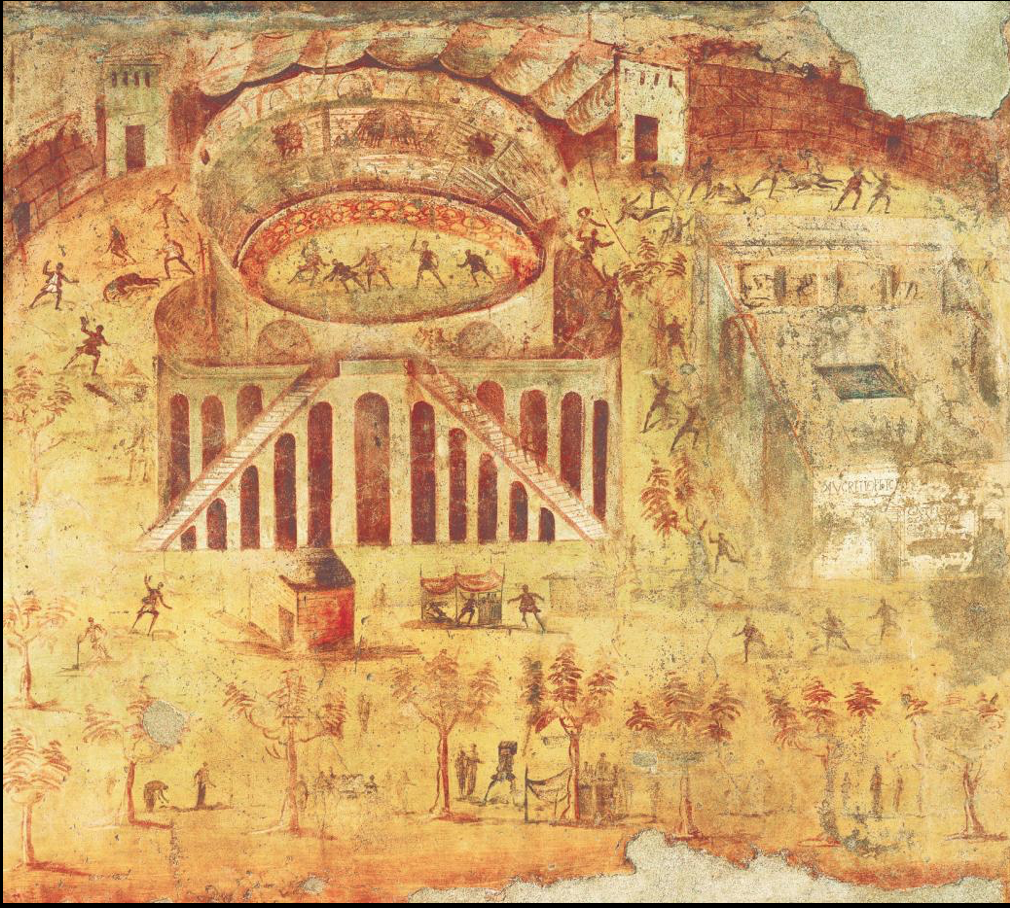

Fig. 3-18 Brawl in the Pompeii amphitheater, from House I,3,23, Pompeii, ca. 60–79 CE
22
New cards

Fig. 3-7 Capitolium and western arch, forum, Pompeii, during the earthquake of 62 CE, as represented in a relief at House of L. Caecilius Iucundus, Pompeii, ca. 62-70
23
New cards
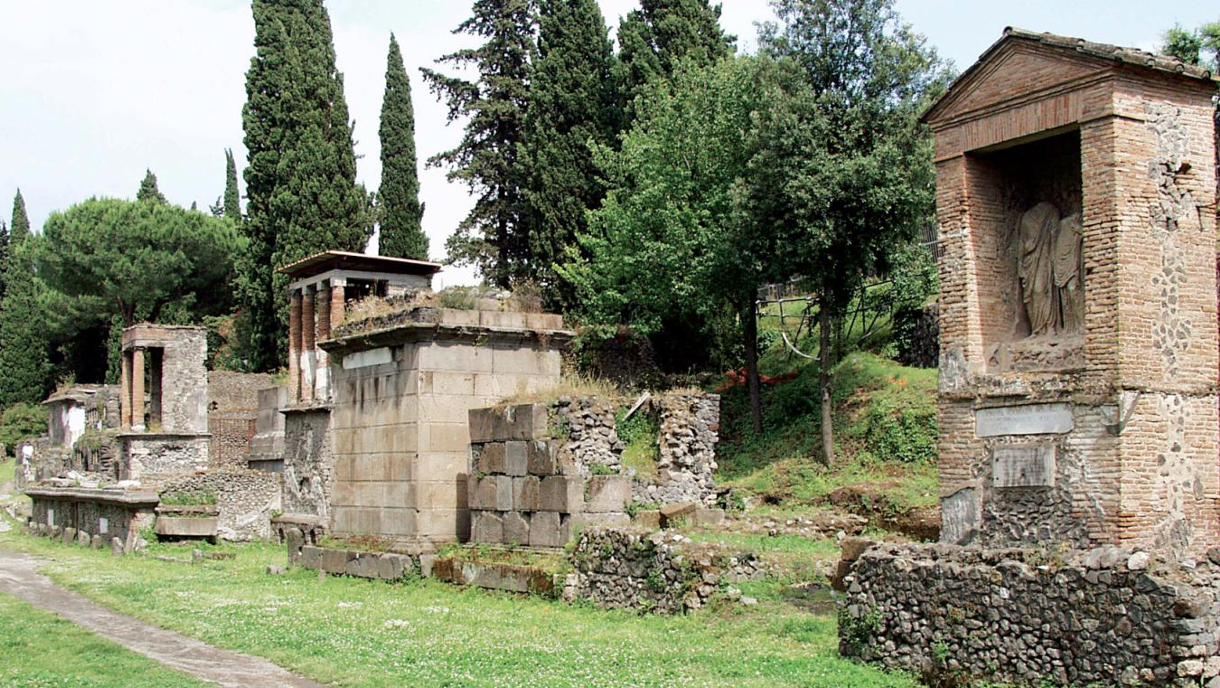

Fig. 3-19 Tombs on the south side of the road outside the Nuceria gate, Pompeii
24
New cards
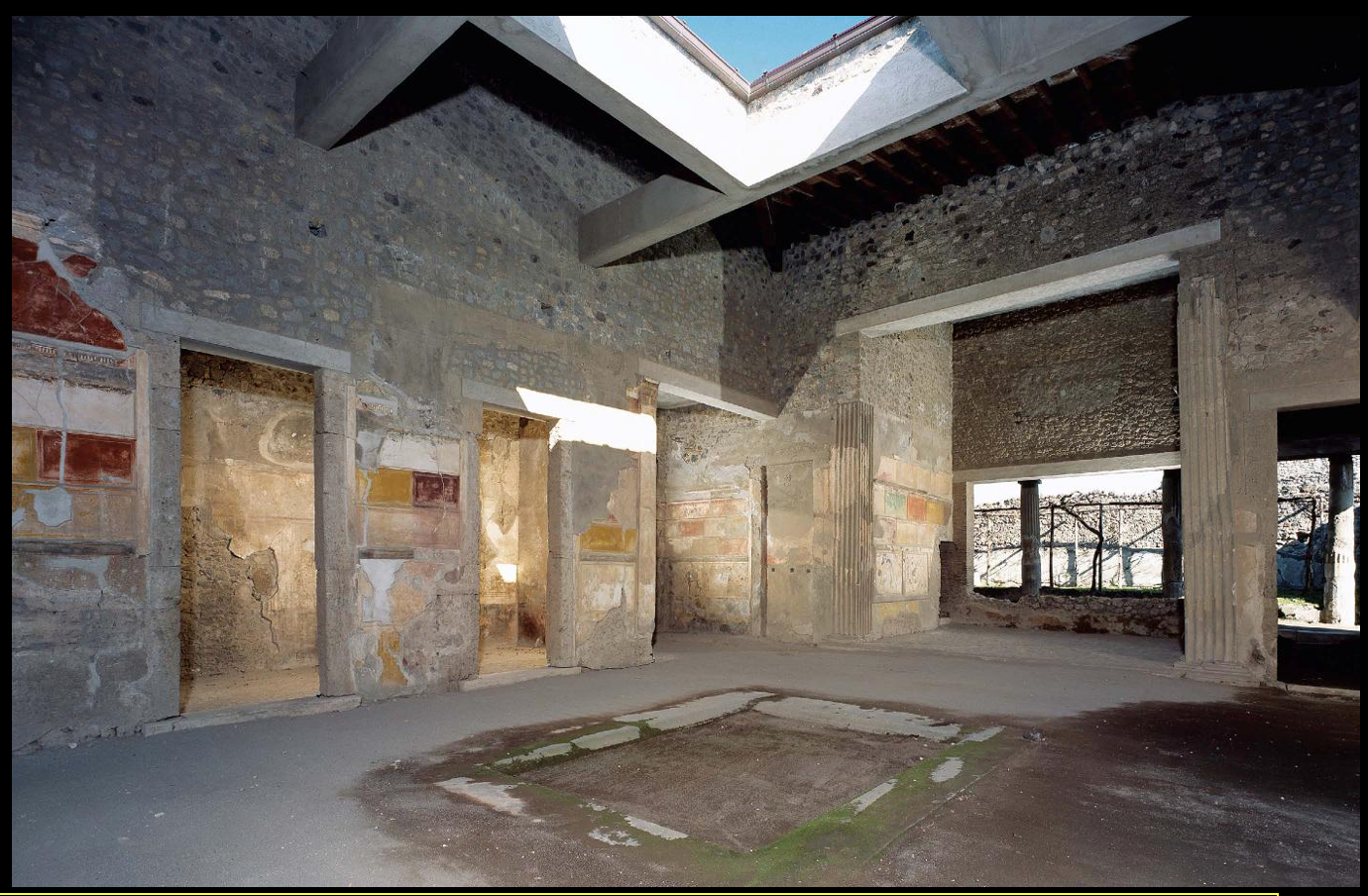

Fig. 4-3 Atrium of the House of Sallust looking toward the hortus, Pompeii, mid-second century BCE
25
New cards
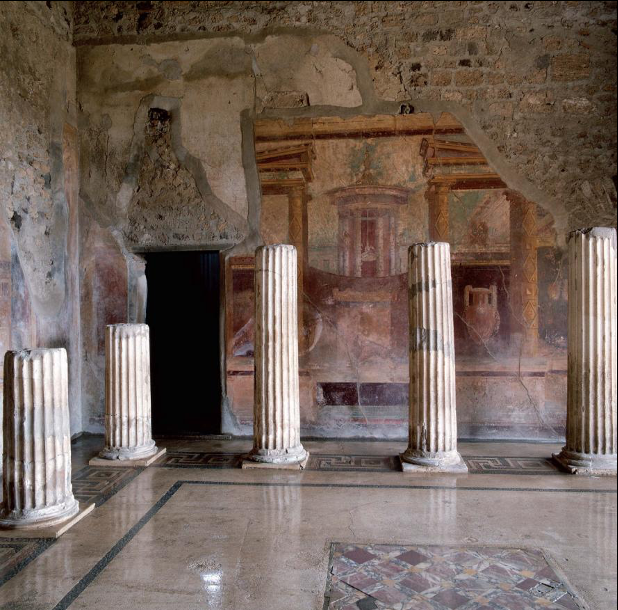

Fig. 4-13 Corinthian oecus of the House of the Labyrinth, Pompeii, mid-first century BCE
26
New cards
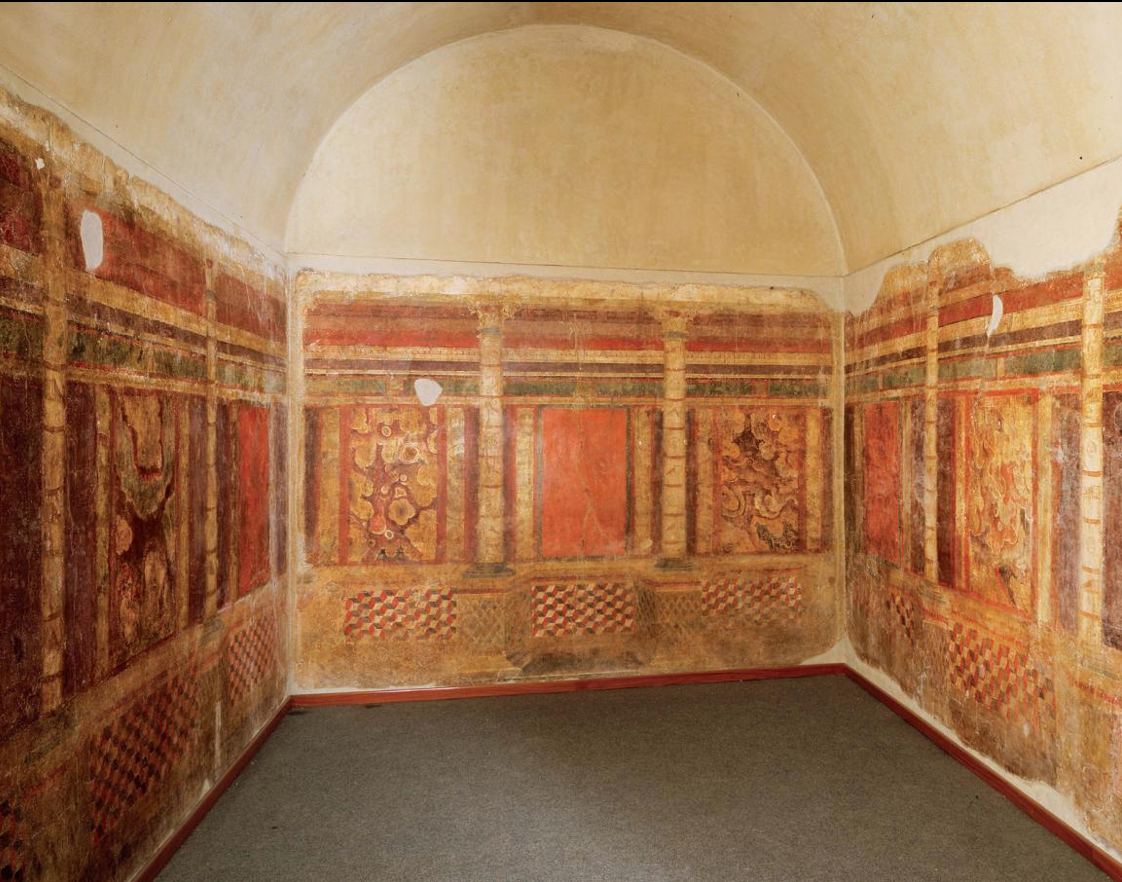

Fig. 4-17 Second Style mural paintings in room 2 of the House of the Griffins, Palatine Hill, Rome, ca. 80 BCE
27
New cards
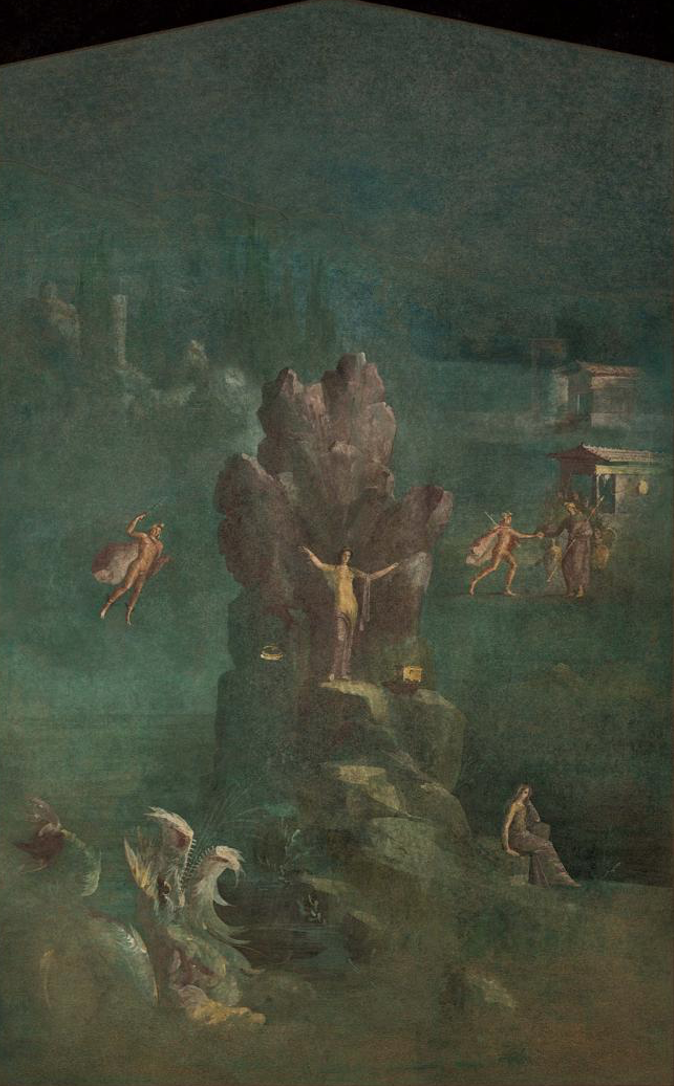
Fig. 6-25 Perseus and Andromeda, detail of a Third Style mural painting, Villa of Agrippa Postumus, Boscotrecase, ca. 10 BCE
28
New cards

Fig. 11-17 *Perseus and Andromeda*, mural painting from the House of the Dioscuri, Pompeii, ca. 62–79 CE
29
New cards
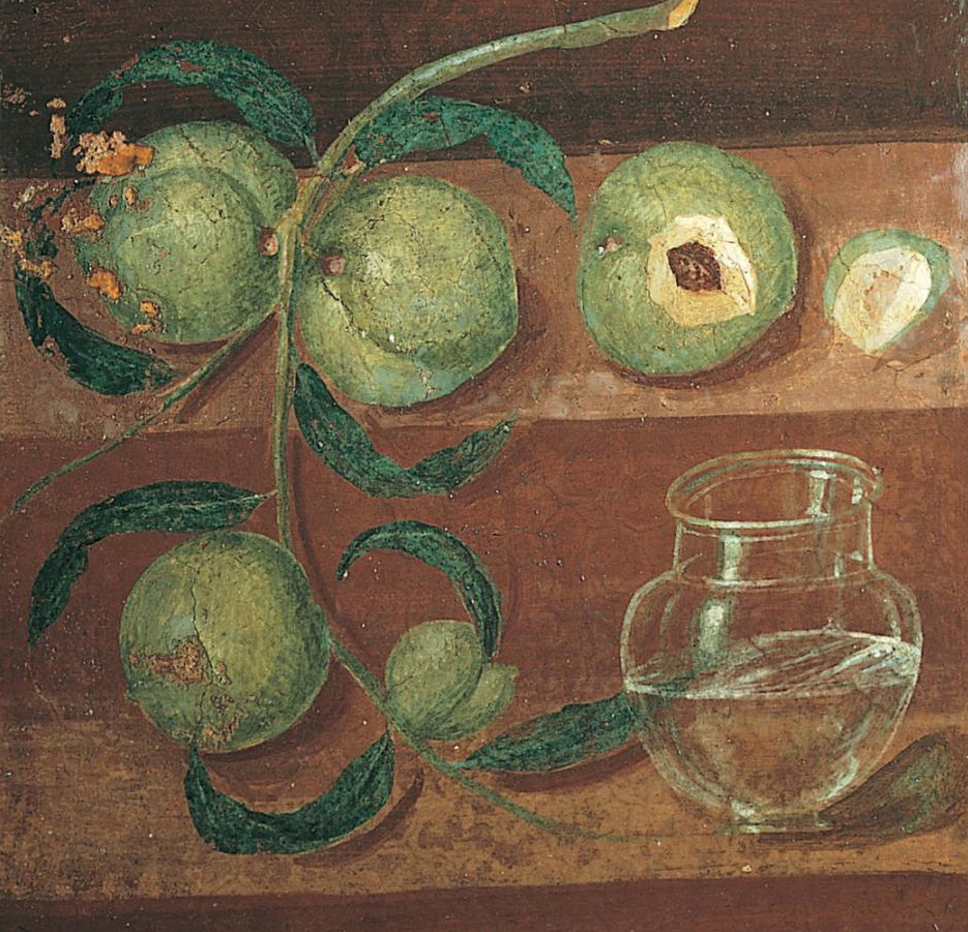

Fig. 11-18 Still life with peaches, detail of a Fourth Style mural painting, from the House of the Stags, Herculaneum, ca. 70–79. Fresco
30
New cards

Fig. 11-19 The baker Terentius Neo and his wife, mural painting from house VII,2,6, Pompeii, ca. 70–79. Fresco
31
New cards

Fig. 11-21 The old farmer of Corycus, folio 7 verso of the *Vatican Vergil,* ca. 400–420. Tempera on parchment