insect final
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
What is meant when we say insects are “inside out and upside down”?
Exoskeleton is on the outside of the body. Circulatory system is located dorsally and central nervous system is located ventrally
What is the ventral nerve cord composed of
bundles of nerve cells called ganglia

Tracheole
where oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange in tissues occurs; cells all nearby; gas movement is by simple diffusion and some pumping
spermatheca
stores sperm
What are the four layers of the exoskeleton in order from the inside to the outside of the insect?
Epicuticle (non-living)
exocuticle (non-living)
endocuticle (non-living)
living cells, epidermis
What are the 3 parts of the alimentary canal and which part(s) are made of cuticle
Foregut, midgut, hindgut; foregut and hindgut made of cuticle
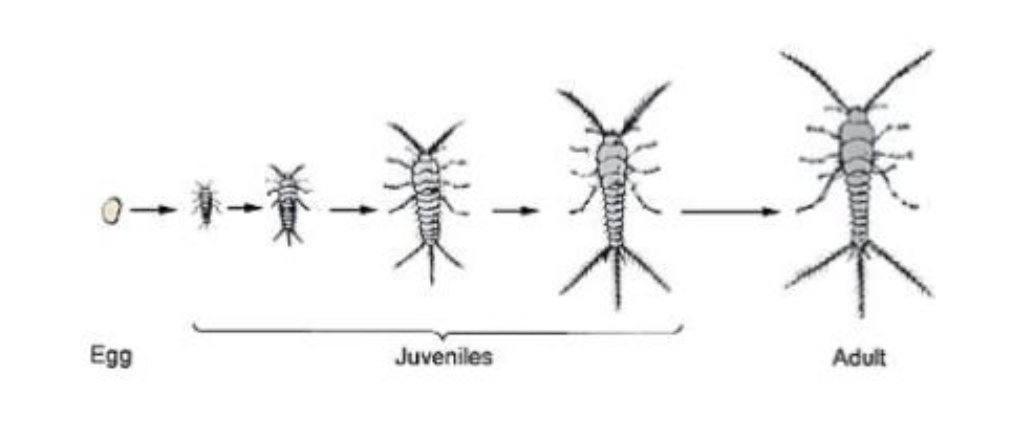
what type of metamorphosis is this
none
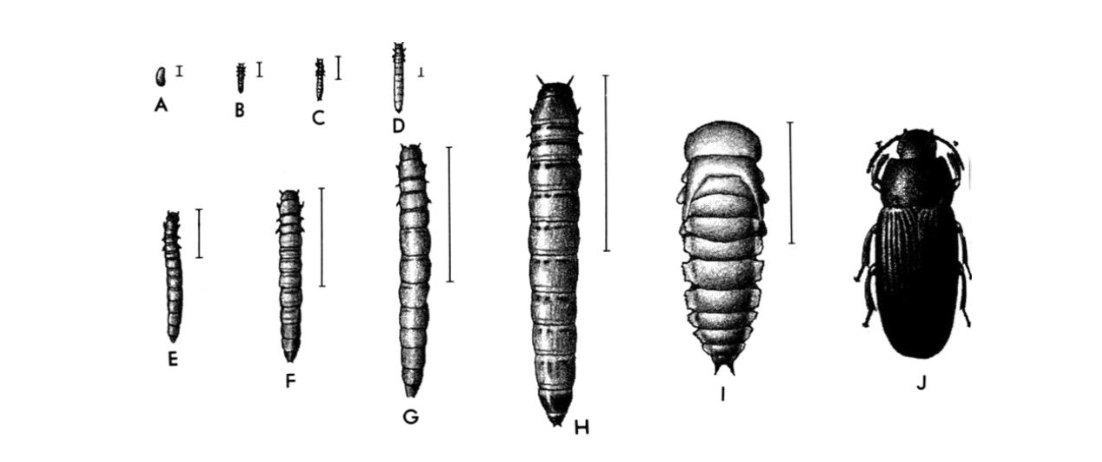
what type of metamorphosis is this
complete
what are the 4 life stages of complete metamorphosis?
egg, juvenile, pupal, adult
what are the life stages of incomplete metamorphosis
egg, juvenile, adult
How do you tell incomplete metamorphosis apart from no metamorphosis and complete metamorphosis?
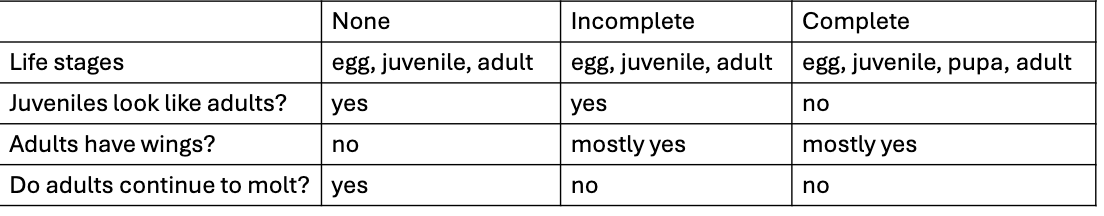
What types of metamorphosis do these have:
hemiptera
fleas
caddisflies
praying mantis
incomplete
complete
complete
incomplete

what order does this insect belong to?
coleoptera (coleo=sheath, ptera=wing)

name the order that this insect belongs to
diptera (di=two, ptera=wing)

name the order this insect belongs to
lepidoptera (lepido=scale, ptera=wing)

name the order of the insect
hymenoptera (hymeno=membranous, ptera=wing)

name the order
ephemeroptera (ephemero=short lived, adults only live a few days)
name the taxonomic rank:
Cyloneda polita
Coccinella
Coccinellidae
species
genus
family
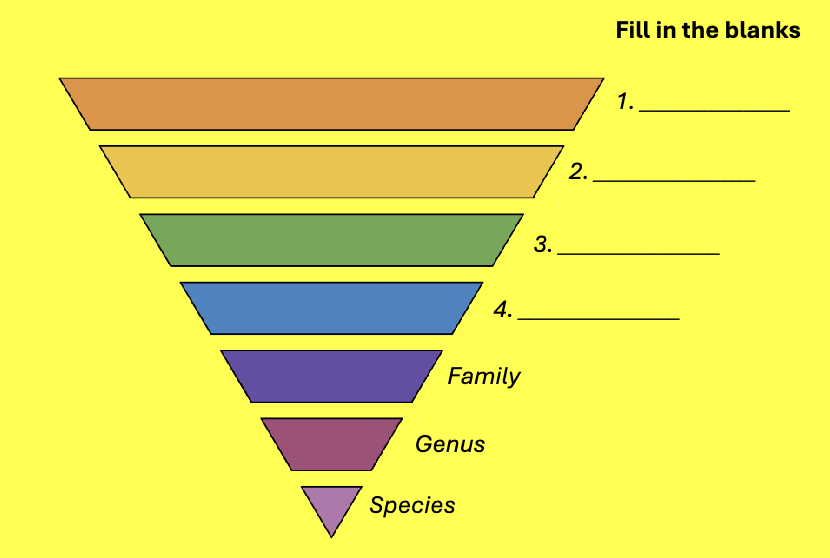
fill in the blanks
King plays chess on fine green sand
kingdom
phylum
class
order
family
genus
species

name the order
hemiptera-aphids

name the order
hemiptera-stink bug

name the order
hemiptera-leafhopper

name the order
orthoptera-grasshopper
holotype
single specimen designated as the name bearer to represent a species
who co-authored a paper with Darwin that summarized the theory of evolution
Alfred Russel Wallace
drawback of exoskeleton
growth has to occur in discrete stages (molting) so they will be more vulnerable to predation
limits the max size that they can grow (can be argued whether this is a drawback or not)
why are insects so diverse compared to vertebrates
smaller and fit into more niches
most insects can fly and disperse into new habitats
plant-insect co-evolution
what is the asexual phase in aphids called?
parthenogenesis
what modes of reproduction occur during sexual and asexual phase?
sexual phase: oviparous
asexual phase: viviparous
symbiotic relationships are always mutalistic
FALSE
types of relationships
nutritional (+,+)
reproductive (+,-)
pathogenic (+,-)
commensal (+,0)
vertical transmission
symbiont is inherited from the parent (usually mother)
symbiont and host co-evolve and may not survive without each other
horizontal transmission
symbiont is acquired from the environmental or other individuals (not inherited)
advantage of biological control
cost effective
self-sustaining in the case of classical biological control
no chemical environmental hazards
integrates well with other methods of control except insecticides
reasons pests aren’t naturally regulated in farms
enemy release: introduced pests are not controlled by natural predators, pathogens, or parasites
plant domestication makes crops more susceptible to pests
monocultures have fewer alternative resources and microclimates, thus reduces natural enemy diversity and abundance
pesticides harm natural enemies of pest (if present)
4 types of plants to disrupt pest establishment/activity
companion crops: releases chemical cues that masks main crop
repellant plants: releases chemical cues that actively repel pests
barrier plants: physically block pest establishment
trap crops: more attractive plant to pull pest away from crop
downsides of plants to disrupt pests
takes away area from planting main cash crops
additional plantings may require significant additional resources like water and fertilizer
plantings may compete with main cash crop for resources
plantings complicate crop care and harvesting
Steps of classical biological control
determine geographic region of origin of pest
search for pest and its natural enemies
test natural enemies for efficacy against pest
rear prospective natural enemies
test for safety against useful native insects
quarantine to avoid pathogens or parasites
release
direct pest
pest damage results directly from pest activity such as feeding or oviposition
indirect pests
insects that create conditions for another pest to cause damage
cultural method to control pests
cultural control: adopting farming practices to reduce pests
crop rotation: pathogen management, host switching
sanitation: solarization (create condition where heat from sunlight kills pests), treatment of machinery
nutrient/water management: avoiding overfertalization/overwatering
planting resistant crops
economic injury level (EIL)
pest density that causes more damage than the cost of control
economic threshold
level of pest population at which control should be begun to avoid reaching EIL
disadvantages of breeding plants to have pest resistance
long time (some plants take years for each generation)
not always achievable
not as well developed for ornamentals compared to crops
Categories of pest control methods
biological control
cultural control
genetic engineering
pesticides
pheromones to attract or repel pest
plant resistance
sterilizing insects
altruism
behaviors that increase the fitness of another individual at a cost to the actor
age polyethism
worker division of labor based on age
sperm competition
long sperm acts as a physical barrier to block the uptake of sperm from other males
penis covered in spines damage female reproduction to reduce likelihood of other males being successful with mating with the female
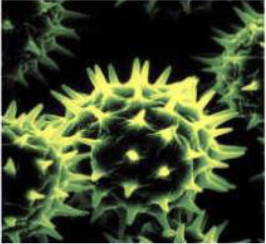
what category of pollination
Biotic spread by animals
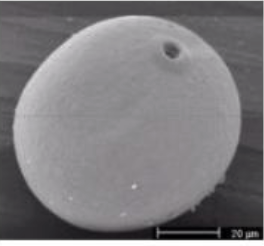
what category of pollination
abiotic spread by wind
animals that pollinate other than insects
birds: hummingbirds, honey creepers
mammals: bats, mice, monkeys
5 threats honeybees face
limited floral resources
fungicides
pesticides
parasites
pathogens
fauncal turnover
when a group of species disappear and are replaced by a different group of species
ways that climate change has affected bark beetles in the US
expanded range
increased survival of larvae during winter
more generations per year
3 things that need to happen for a mass extinction event
at least 75% of all species go extinct
extinction happens across taxonomic boundaries
must occur globally
How many mass extinction events have occurred? Which mass extinction event caused the most species to go extinct?
5 & Late Permian mass extinction
4 main causes of insect population declines
pesticides (insecticides, herbicides, fungicides)
habitat loss
climate change
light pollution
two types of entomology
forensic
urban
ways insects used in forensic entomology
determining postmortem interval (time elapsed between death and when a body is discovered)
locating remains
perimortem injury assessment
toxicological analyses
sources of human DNA
documenting abuse/neglect
reasons why raising insects for food is better than raising cattle
more efficient at converting feed into body mass
require significantly less water
produce fewer greenhouse gases
require less land
can be raised on waste to feed farm animals and fish
pose a low risk of transmitting zoonotic infections
reasons why eating insects is more common in the tropics
insects tend to be larger in the tropics
insects in the tropics often congregate in significant numbers, so it is easier to collect large quantities during a single harvest
greater variety of insects available year-round
harvests predictable
location predictable
category of pesticides most widely used in agriculture
herbicides
how is biotech used in agriculture to combat weeds while also protecting crops
genetically modify crops to be herbicide-tolerant
explain how transgenic organisms are used
Bt corn genetically modified to produce a protein from a bacterium which kills insects
male mosquitos are genetically modified with a leathal gene that disrupts protein synthesis in their offspring causing them to die before reaching adulthood
how can we present insect populations from becoming resistant to Bt crops
plant refuge zone adjacent to Bt crops
genetically modify crops with multiple Bt genes
what type of disease is malaria
anthroponosis (human→ mosquito→ human)
what are the 4 elements of a transmission cycle
disease agent
vector
primary reservoir or host
permissible environment
what is one insect responsible for natural red dyes, sometimes called cochineal or carmine extract?
Cochineal scale insect: females crushed up to make natural textile and food dyes
biomimicry
mimicking nature’s solutions to solve human problems
forensic entomology
application of insect biology to legal proceedings
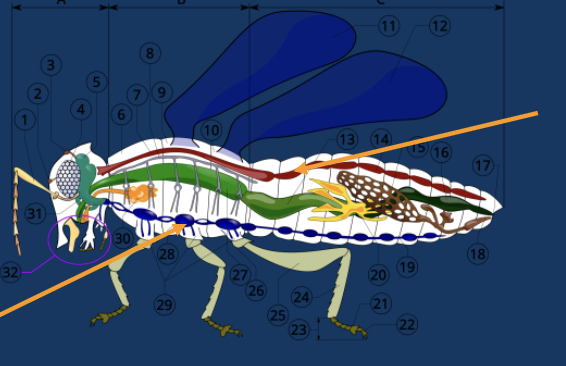
name the sections
top: dorsal heart
middle: alimentary canal
bottom: ventral nerve cord