Marine Vertebrate Zoology LEC 1
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lectures 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
What is the definition of Zoology?
Scientific study of the classification, structure, physiology, behavior, and distribution of animals
Meaning of Marine?
a system of open-ocean and unprotected coastal habitats
What’s the characteristics of Marine?
exposure to wave action, tidal fluctuation, and ocean currents, and by the absence of trees, shrubs, or emergent vegetation.
Meaning of Vertebrate?
An organism that has (or descended from an ancestor that has) a cranium and axial endoskeleton
What is the Vertebrate member of?
sub-Phylum Vertebrata
To make sense of diversity of life, what is needed?
naming and logical organization system
To name a group, there is multiple ways we can, what are they?
color, size, habitat, ecological function, etc…
What is a Trait?
an observable characteristic of an organism or species
What is a Taxon?
Group of organisms that share a unique set of traits
What is the most basic unit of classification of life?
“Species”
What is the Biological species concept?
One or more groups of individuals that can interbreed, produce viable offspring, and don’t breed with other groups.
Why is the species concept problematic?
Asexual reproduction, extinct species, and hybridization, ring species, and etc…
What are the standards of the species concept?
two part name (Genus species), all italicized, only genus is capitalized, “sp.” is for unknown and “spp.” for multiple species in a genus
What is a Systematic?
Scientific study of kinds of organisms, their diversity, and their evolutionary relationships
What is a Phylogeny?
Evolutionary history of species or group of species
What is a Cladistics?
Making hypotheses about evolutionary relationships
What is the visual summaries of relationships?
Phylogenetic trees and cladograms
What do the nodes represents?
Common ancestors
What is the Sister Groups?
two or more lineages that emerge from a node; so they share a common ancestor
What is an Outgroup?
It “roots” the tree; not as closely related to the other species
What is a Clade?
a group of organisms that includes all descendants of a common ancestor and that ancestor.
What is the definition of Phylogenetics?
Study of the evolutionary history and relationships among species and higher taxa (scientifically classified groups of organisms)
What is Phylogenetics based off?
Observed heritable traits, such as DNA sequences or morphology—under a model of evolution of these traits
Phylogenetic hypotheses and theories often presented as a _______.
Tree
What is a Character?
Quantifiable, heritable trait
What are the two character states that are compared to the other character states of the same trait and determined to be?
Primitive (plesiomorphic) and Derived (apomorphic)
Group species based off _________.
Shared characters
Having what is the results in different species having shared characters?
Common ancestor
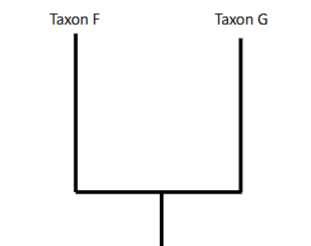
What kind of group is this picture? ( Mono, para, poly-phyletic groups)
Monophyletic
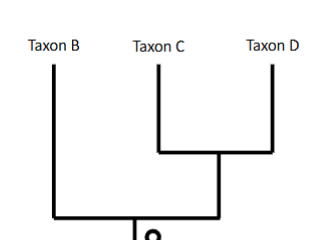
What kind of group is this picture? ( Mono, para, poly-phyletic groups)
Monophyletic
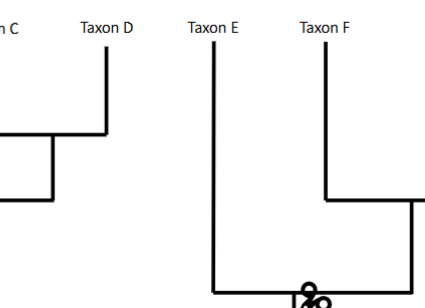
In this picture of this clade, is it monophyletic group?
No, Paraphyletic
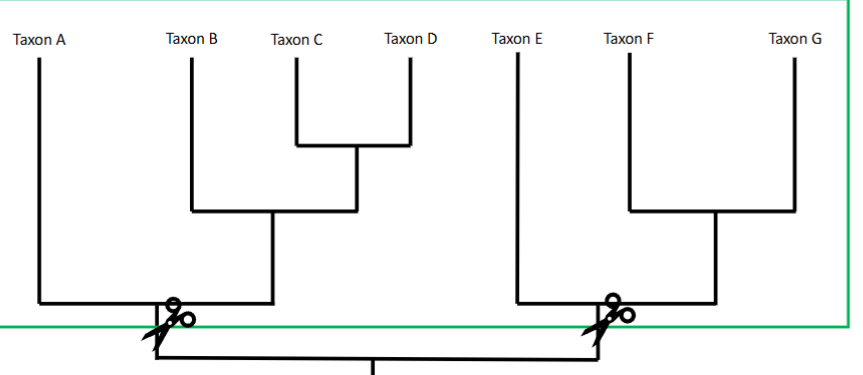
In this picture, what is this grouping of Taxon D and Taxon E called?
Polyphyletic group
What is the definition of Polyphyletic Group?
Descendants from 2 or more separate lineages; shared traits due to convergent evolution
What is the definition of Paraphyletic Group?
Common ancestor but not all descendants
What is a Original Characters?
“ancestral condition” refers to retaining traits that were derived in ancient ancestors. acquired by ancestors deeper in the phylogeny
What is a Derived Characters?
Those acquired by the most recent common ancestor of the taxa under consideration.
What is a Homologous Structures?
Similar structures in different organisms due to common ancestry
What is a Analogous Structure or Homoplasy?
Similar structure in different organisms due to convergent evolution, not common ancestry
What is Convergent evolution?
Process where different species evolve similar traits independently, often in response to similar environmental pressures.
They relate by having shared traits that are _____ and only present in a ____ and not in clade’s ancestors or other organisms (synapomorphies)
novel…clade
What is Symplesiomorphy?
Shared, primitive character
What does a Monophyletic group contain?
common ancestor that contains the shared, derived trait(s) and all the descendants.
Which kind of tree is the one that requires the fewest evolutionary events (appearance of shared derived characters)?
Parsimonious
Cladograms are what?
Hypotheses
Phylogenetic trees have branches that reflect?
evolutionary time and amount of character change
In cladograms, what do the branches order mean?
they are meaningless
In phylograms, what do the branches order mean?
It shows branch order and branch lengths
What are the three major clades domains?
Archaea. Eukaryota, and Bacteria?
What are the Eukaryote traits?
Cytoskeleton, Cell division, Endomembrane system(Nucleus, Mitochondria, plastids) Linear, protein-bound DNA stored in nucleus.
What are characteristics of Metazoa (Animalia)?
Multicellular, Heterotrophic, Motile at some stage, Most develop from hollow ball of cells (blastula), has differentiated tissues
What are some characteristics of Bilateria?
Bilateral symmetry and develop from three layers of differentiated cells (triploblastic)
What are some characteristics of Dueterostomia?
Blastopore develops into anus, Indeterminate development — cell differentiation occurs relatively late in development
In Deuterostomia, what are some characteristics within Chordata?
Notochord, Dorsal hollow nerve cord, visceral clefts and arches, endostyle, and Post-anal tail
In Dueterostomia, what are some characteristics within Vertebrata?
Vertebral column and Cranium
Fishes are not apart of what group but can be a convenient description for a diverse group of organisms.
Monophyletic group
What kind of marine life fit this description? Poikilothermic, aquatic vertebrates with appendages (when present) developed as fins, whose chief respiratory organs are gills and whose bodies are usually covered with scales.
Fishes
Sometimes “fishes” do not fit the description given but it can teach us about?
evolutionary processes
Fish were the first?
Vertebrates
Fishes have _______ diversity. (size, shape, ecological function, life history, reproduction, etc.)
Tremendous
Greatest diversity is found where?
tropics (Indo-west pacific for marine spp.)
What is the Superclass Gnathostomata?
Jawed fishes
What is in the Class Chondrichthyes?
Cartilaginous fishes
What is within Holocephali?
chimeras
What is in the Elasmobranchs?
Rays, Skates, and Sharks
What is in the Class Osteichthyes?
Bony fishes and tetrapod
What is in the Subclass Sarcopterygii?
lobe-finned fishes and tetrapod
What is in the Subclass Actinopterygii?
Ray-finned fishes
What is in the Infraclass Cladista?
Birchirs
What is in the Infraclass Chondrostei?
Paddlefishes and sturgeons
What is in the Infraclass Holostei?
Gars and bowfin
What is in the Infraclass Teleosteomorpha (Division Teleostei)?
Teleost fishes
What kind of fishes are considered more primitive to spiny-rayed fishes (Superorder Acanthoterygii)?
Soft-rayed fishes
What kind of fish is the largest group of fish (60%)?
Acanthopterygii
Spiny-rayed fishes have what in dorsal and anal fins?
Spiny rays
Lungfish can live up to ____ years in dry mud.
4