CEM 252 - Alcohols
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What is the rule when numbering the longest carbon chain with an alcohol group?
Always give the OH the lowest possible number
When do we use trans/cis or E/Z?
-Use trans/cis when there are H's on either side of a double bond
-Use E/Z when the there are different priority substituents on a double bond (ex. Br and H)
When do we include stereochemistry when naming compounds?
When there is a chiral center (often a wedge/dash)
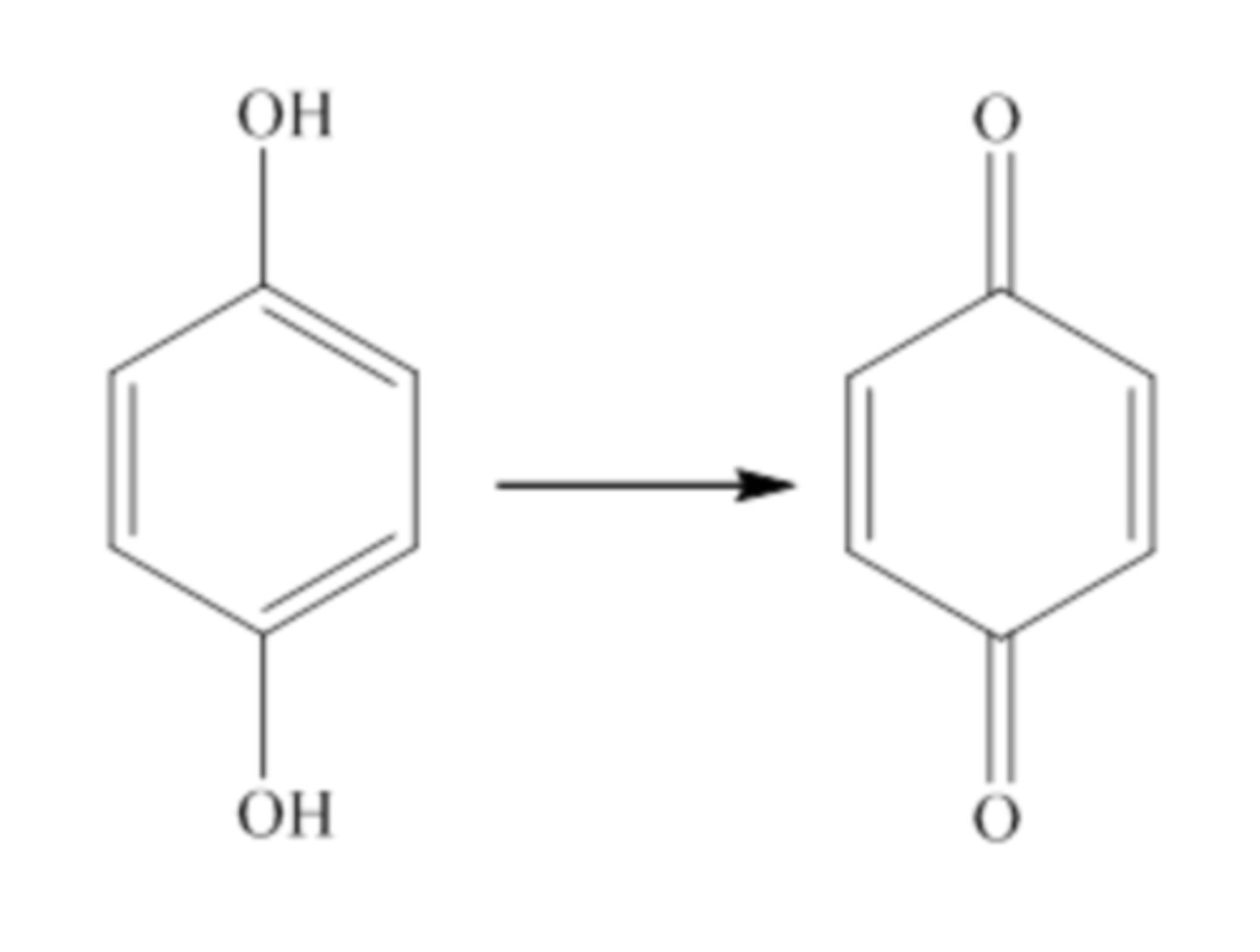
What name do we use when there is two OH groups on a compound?
Diol
What is a phenol?
A double bonded ring with and OH group coming off of it
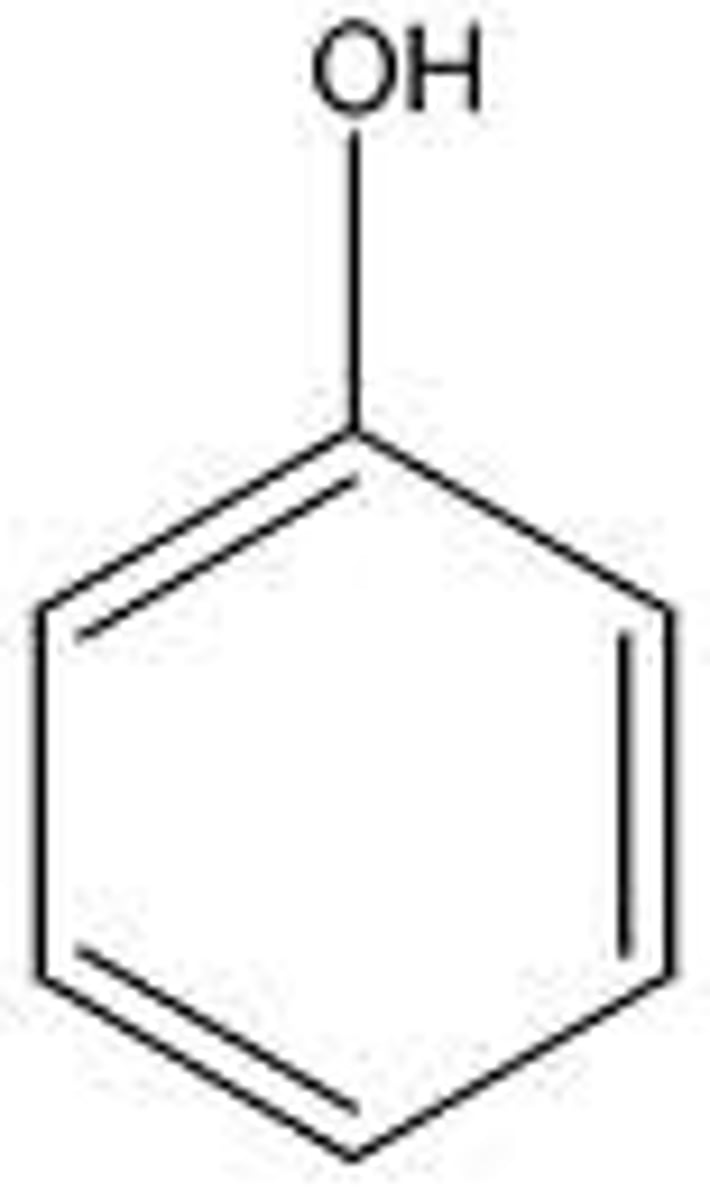
If there is more than one OH group on a double bonded ring, what is it called?
Benzene
What are the names of the following different types of substitutions on aromatics?:
1. 1, 2
2. 1, 3
3. 1, 4
1. ortho (o-)
2. meta (m-)
3. para (p-)
Hydrogen bonding ___________ solubility.
increases
Solubility ______________ with the increasing length of the carbon chain.
decreases
Acid =
molecule that likes to donate protons (H+)
Is alcohol a strong or a weak acid?
Weak
What are the pKa's of the following acids?:
1. H-Cl
2. Carboxyl
3. Water + alcohol
4. Ammonia + amine
5. Alkane
1. -7
2. 5
3. ~16
4. ~30-35
5. 60
The lower the pKa value, the _______ acidic an acid is.
more
What are the 4 parameters that increase acidity?
1. Electronegativity
2. Size
3. Resonance
4. Induction
What are the traits of a group that is ED through resonance?
Atoms with lone pairs can share their electrons through bonds (resonance)
What are the traits of a group that is EW through resonance?
Atoms in pi-bonds (usually heteroatoms) can accept electrons through bonds
What are the traits of a group that is ED through induction?
-R groups
-Make area around them more electron rich
What are the traits of a group that is EW through induction?
-Halogen groups (F, Cl, Br, I)
-Electronegative, attract electrons
Electron donating groups _____________ acidity.
decrease
What are the common bases for an acid base reaction?
Na+ and NH2- or Na+ and H-
Nucleophile =
molecule with lone pair
What are the traits of an SN2 reaction?
-1-step
-Happens with methyl, 1°, 2°
-Nucleophile attacks the carbon and kicks out/replaces LG
-Stereochemistry changes (opposite)
What are the traits of an SN1 reaction?
-2-step (carbocation intermediate)
-Happens with 2° and 3°
-Rearrangement can occur to form a more stable cation
-Stereochemistry does not matter (can be wedge or dash)
How do we decide between SN1 or SN2 for 2° halides?
-Look at the nucleophile
-If the nucleophile is neutral, then SN1
-If the nucleophile is negative, then SN2
What are the products of an addition of H-OH when the reactants are H+(cat) and H-OH?
-An H and OH
-The OH goes on the more substituted carbon
-Carbocation intermediate (possibility for rearrangement)
-Stereochemistry does not matter
What are the products of an addition of H-OH when the reactants are HgSO4, H2C and NaBH4?
-An H and OH
-The OH goes on the more substituted carbon
-No rearrangement
-Can show both stereochemistry or just lines
What are the products of an addition reaction when the reactant is H3O+?
-An H and OH
-OH goes on the more substituted carbon
-Rearrangement can occur from carbocation
What are the products of an addition reaction when the reactants are BH3 and H2O2?
-An H and OH
-The OH goes on the LEAST substituted carbon
-Stereochemistry needs to be the same for OH and H
What are the products of a dihydroxylation reaction when the reactants are OsO4 and NaHSO3?
-2 OH's
-The stereochemistry of the OH's needs to be the same
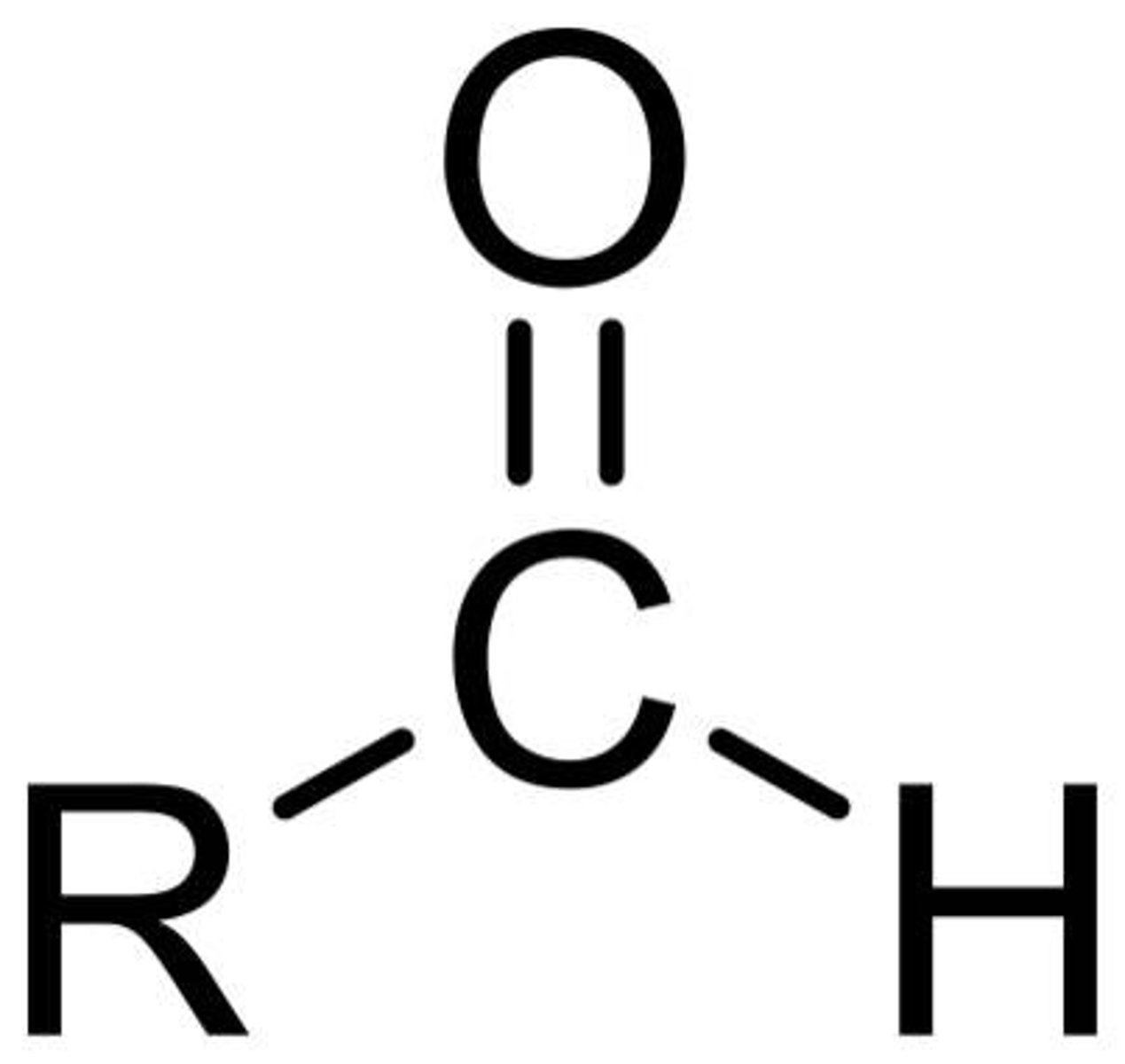
What is an aldehyde?
R-O=C-H
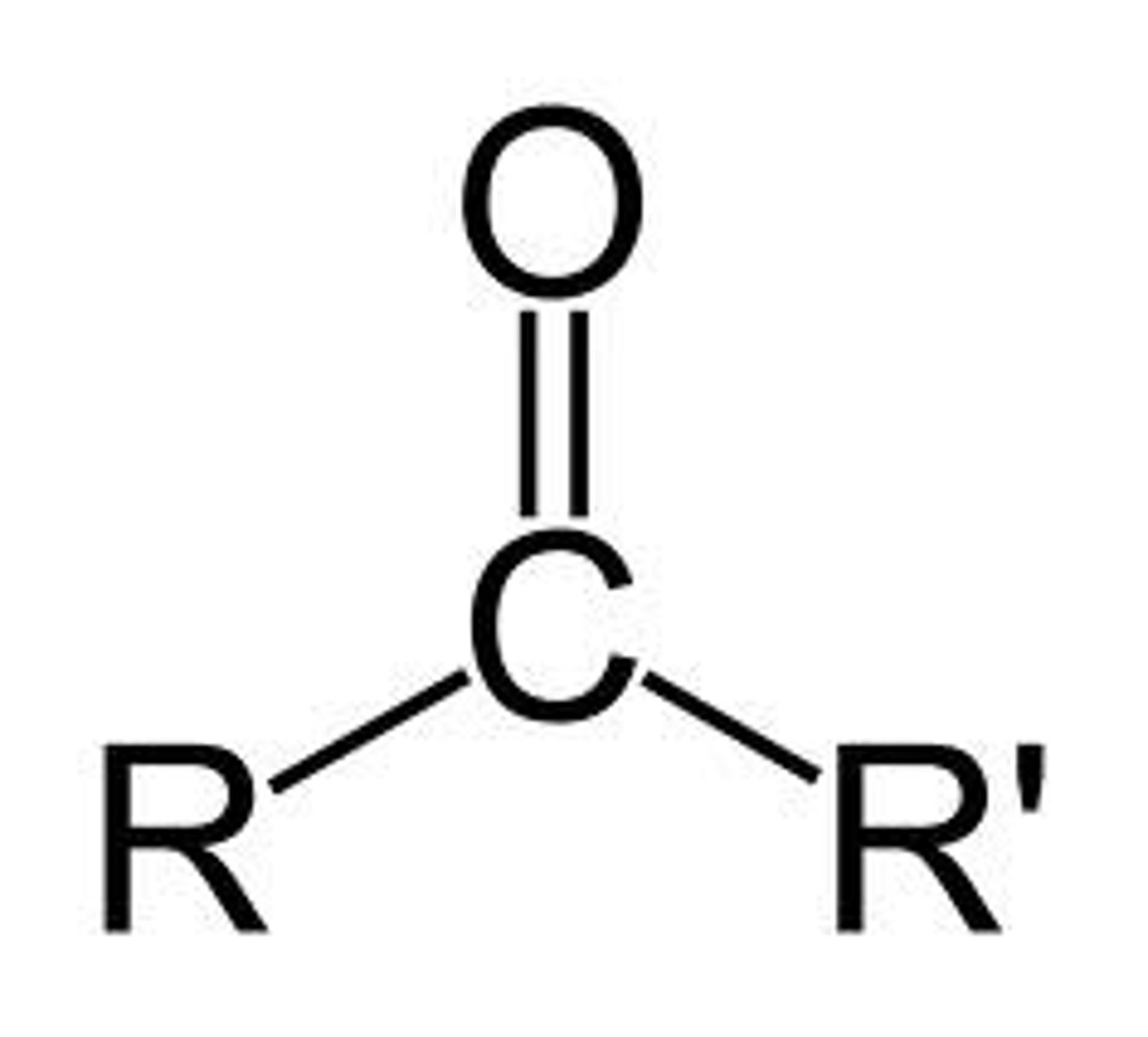
What is a ketone?
R-C=O-R
What are the products of a reduction reaction when the reactants are NaBH4 or LiAlH4 and H+?
-The C=O is replaced with an H and OH
How can we make OH a better leaving group?
Add acid (H+) to make OH2+
What are the products of an acidic dehydration reaction when the reactants are H+ (H2SO4) and heat?
-A double bond will form on either side of the LG
-The major product will be formed on the more substituted carbon
-Rearrangement can occur with E1 reactions
What are the products of a POCl3 dehydration reaction when the reactants are POCl3 and pyridine?
-A double bond will form on the more substituted side of the LG
-POCl3 does NOT have rearrangement
True or false: OH cannot be used as a leaving group in a substitution reaction unless it is reacting with an acid.
True
What is the best acid and the worst acid out of the following?:
HBr, HCl, HI
HI > HBr > HCl
What are the products of an SN2 SOCl2 reaction?
-The LG will be replaced by a Cl
-The stereochemistry will be the opposite
What are the products of an SN2 PBr3 reaction?
-The LG will be replaced by a Br
-The stereochemistry will be the opposite
What are the traits of a tosylation reaction?
-OH can be a LG group with Ts-Cl because it removes the H
-Stereochemistry stays the same
-A Ts-Cl bonds to the oxygen
-Can have substitution reactions where a OTs product is formed and stereochemistry changes
What are the definitions of the following?:
1. Oxidation =
2. Reduction =
1. Losing hydrogen
2. Addition of hydrogen
Oxidation depends on the type of ______________.
alcohol (ex. 1°, 2°, or 3°)
What reactants may be used in a strong oxidation reaction?
CrO3, H3O+ or KMnO4 or K2Cr2O7 or Na2CrO4
What reactants may be used in a mild oxidation reaction?
PCC
What type of products can a 1° alcohol form in an oxidation reaction?
-An aldehyde if it is a weak oxidant (ex. PCC)
-Carboxylic acid if it is a strong oxidant (ex. CrO3)
What type of products can a 2° alcohol form in an oxidation reaction?
A ketone (regardless of a strong or mild oxidant)
What type of products can a 3° alcohol form in an oxidation reaction?
No oxidation because there is no H