3. Law & Ethics 5: Non-Medical prescribing
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Define non-medical prescribing (NMP)?
prescribing by specially trained nurses, optometrists, pharmacists, physiotherapists, podiatrists and radiographers, working within their clinical competence as either independent or supplementary prescribers.
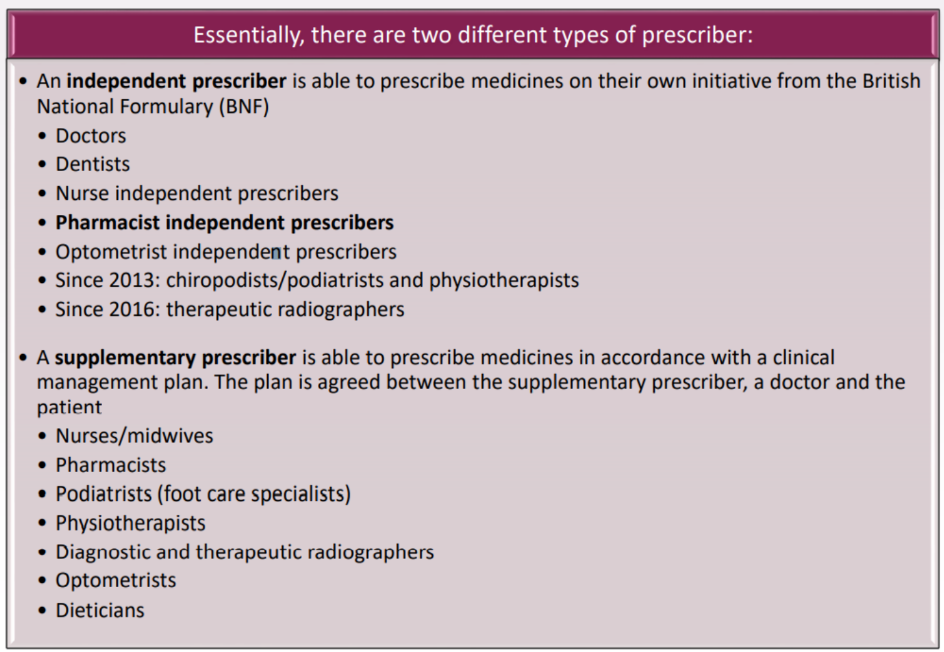
What is the difference between an independent & supplementary prescriber? Give examples.
In what other situations can medicines be given by NMPs?
A Patient Specific Direction (PSD) is an instruction from an independent prescriber for another professional to administer medicine to a specific patient.
A Patient Group Direction (PGD) is a written instruction for authorised health professionals to supply or administer specific medicines to a defined patient group.
Outline some examples of authorised health professionals that can supply/administer under a PGD.
Chiropodists, podiatrists, dental hygienists, and dental therapists
Dieticians, midwives, nurses, and occupational therapists
Optometrists, orthoptists, orthotists, and prosthetists
Paramedics, pharmacists, physiotherapists, and radiographers
Speech and language therapists
Is a prescription needed in the case of emergencies?
No, prescriptions are not needed for administration of POMs specified in schedule 19 for the purpose of saving life in an emergency.

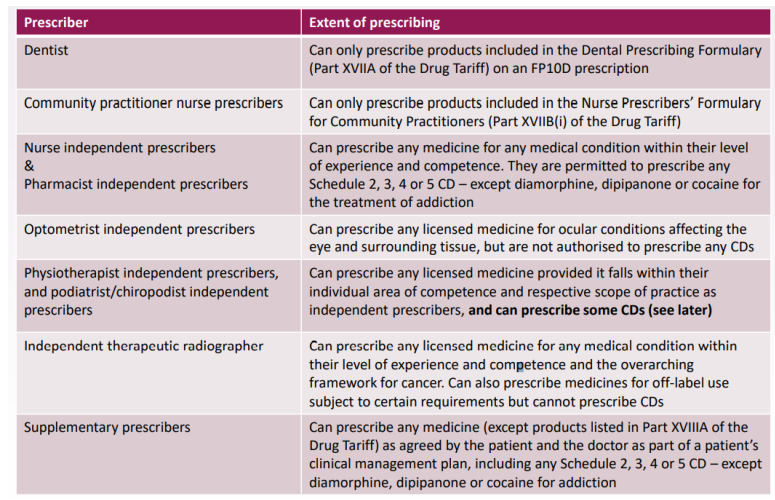
Doctors can basically prescribe everything, how about other prescribers?
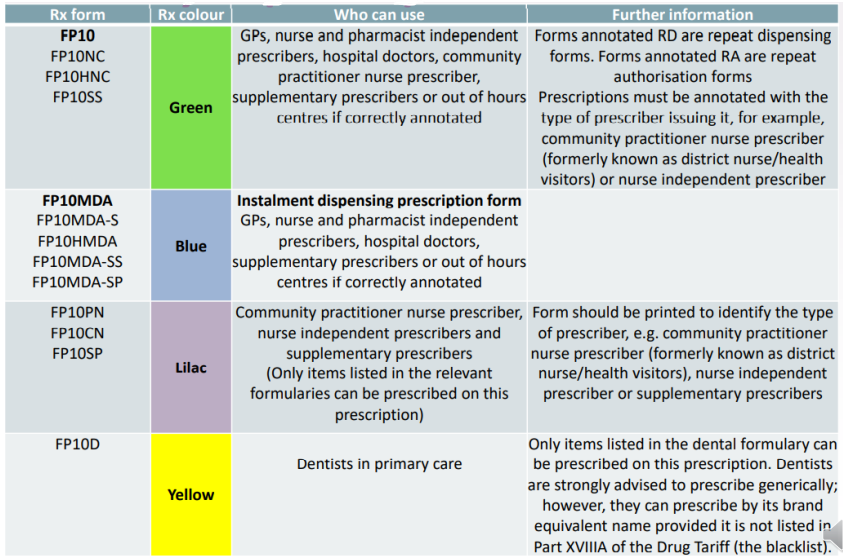
Outline the diff Rx forms, Rx colours and who can use the.
What is a pink prescription used for?
Schedule 2 or 3 CDs on FP10CD form.
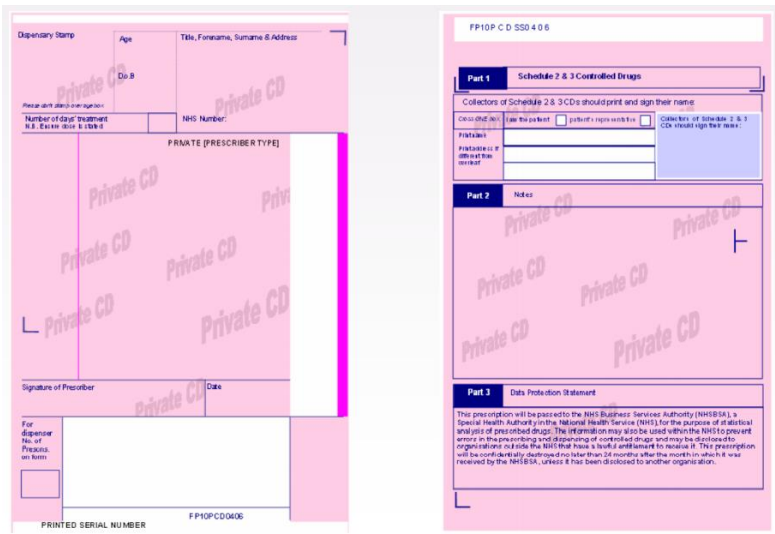
Other than the normal legal requirements for a prescription, what else needs to be on a FP10CD?
a 6 digit prescriber identification number
sch 2 or 3 CDs cant be dispensed without it
If a private prescriber doesn’t have one, they need to contact their NHS area team to get one.
What CDs can be prescribed by prescribers?
Doctors - CDs sch 2-5 but needs special home office licence
Dentists - CDs in dental prescribing formulary on an FP10D prescription
Nurse & pharmacist independent prescribers - CDs sch 2-5, except diamorphine, dipipanone or cocaine
physiotherapist IP - CDs administered by specific methods
podiatrist/chiropodist IP - CDs with specific administration for treatment of organic disease or injury
Who cant prescribe any CDs?
community practitioner nurse prescriber
optometrist independent prescriber
What is a good resource if you ever forget any info about the CDs?
MEP - Medicines, Ethics & Practice
Outline the benefits of NMP?
Better and quicker access to services
Time-saving
Promotes integrated care
Optimises clinical workforce skills
Enables cost-effective quality services
Increases choice of services
Compare the roles of the pharmacist & pharmacist IP.
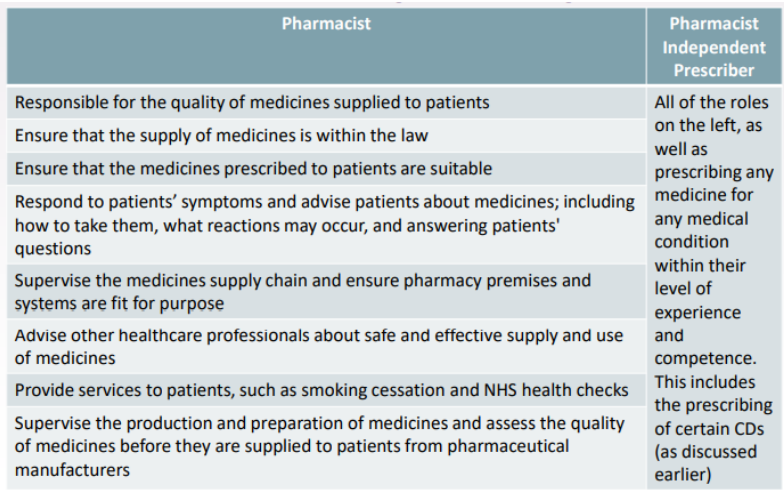
How can a pharmacist become independent?
be registered with GPhC
relevant experience
designated prescriber agreed to supervise
GPhC-accredited training (independent prescribing programme - 6 months & min 26 days of teaching & learning activities)
complete 12 days of learning in a practice environment whilst being mentored by a DPP