Bootcamp.com - Molecular Genetics
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
159 Terms
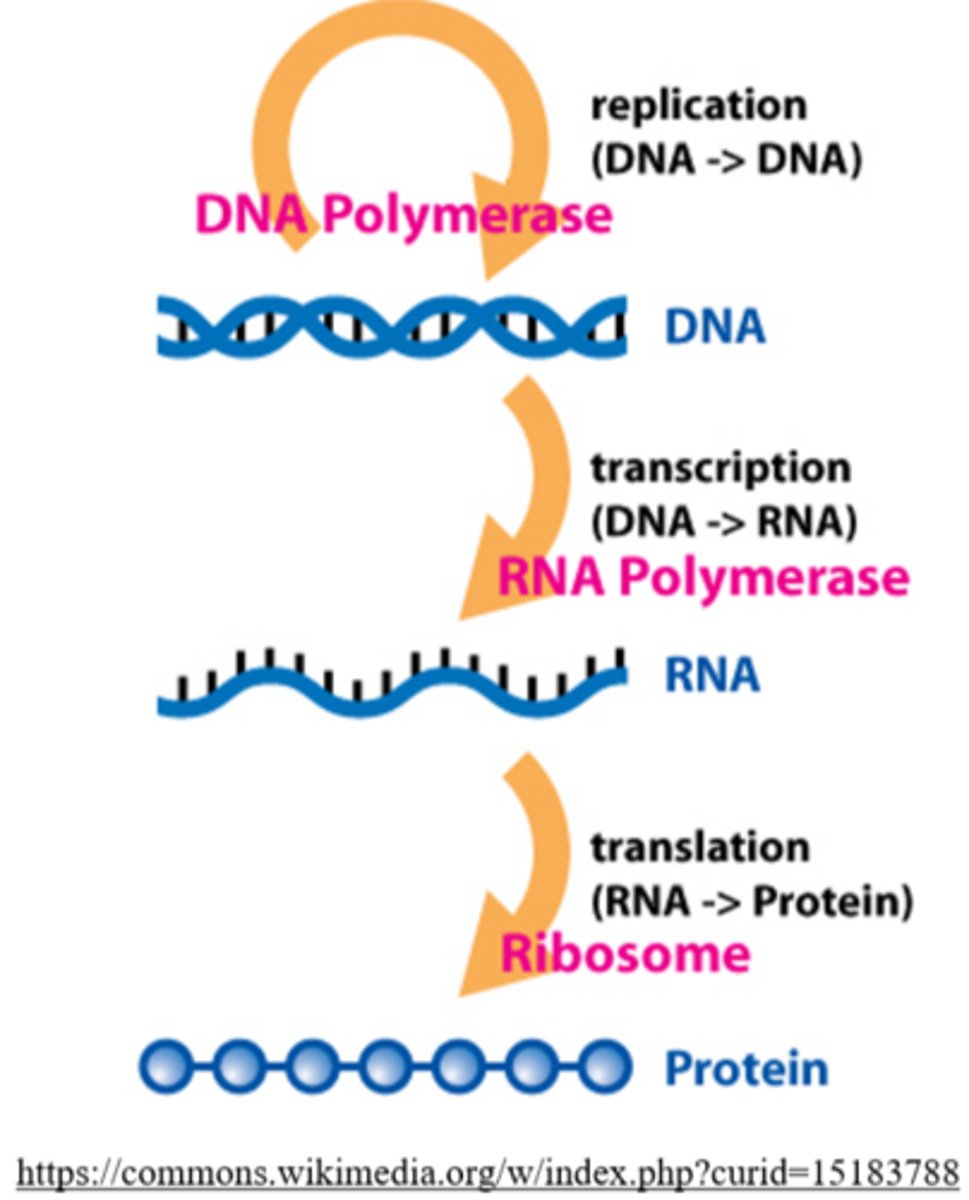
the _____ is a theory that states that in cells, information only flows from DNA to RNA to proteins
central dogma
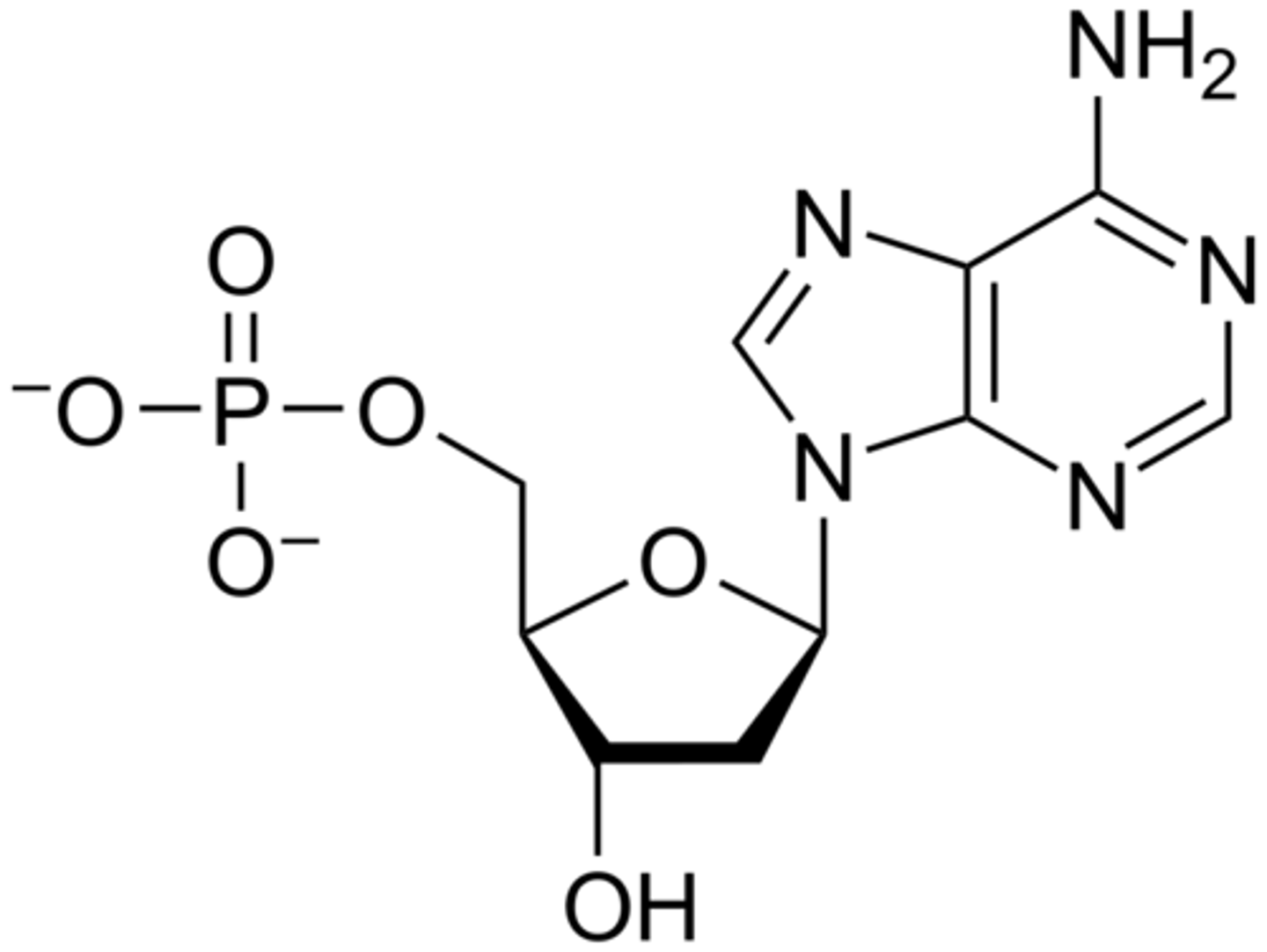
a _____ is the basic unit of DNA
nucleotide
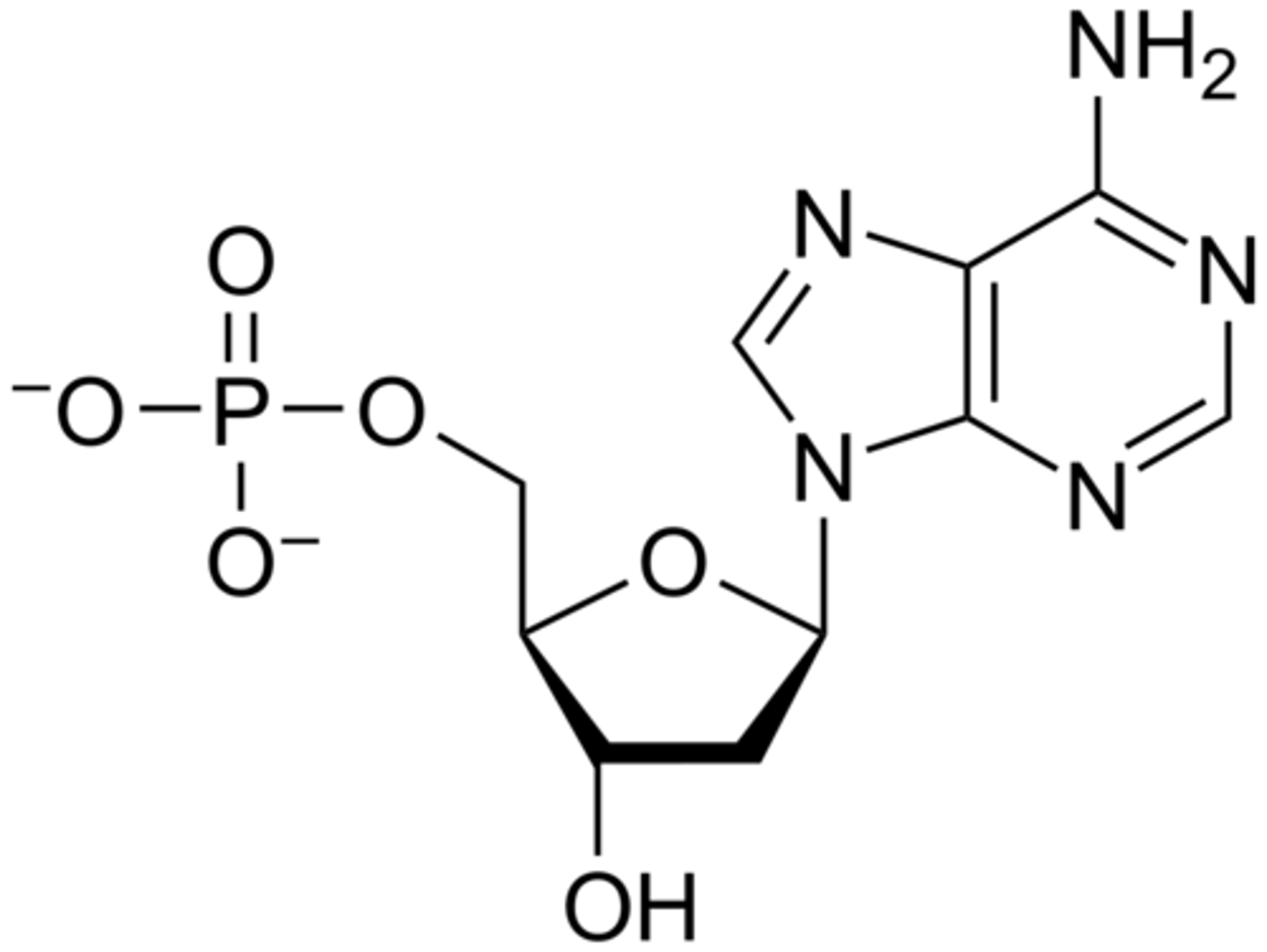
a nucleotide is composed of a ______ bonded to both a ______ and a _______
sugar, phosphate group, nitrogenous base
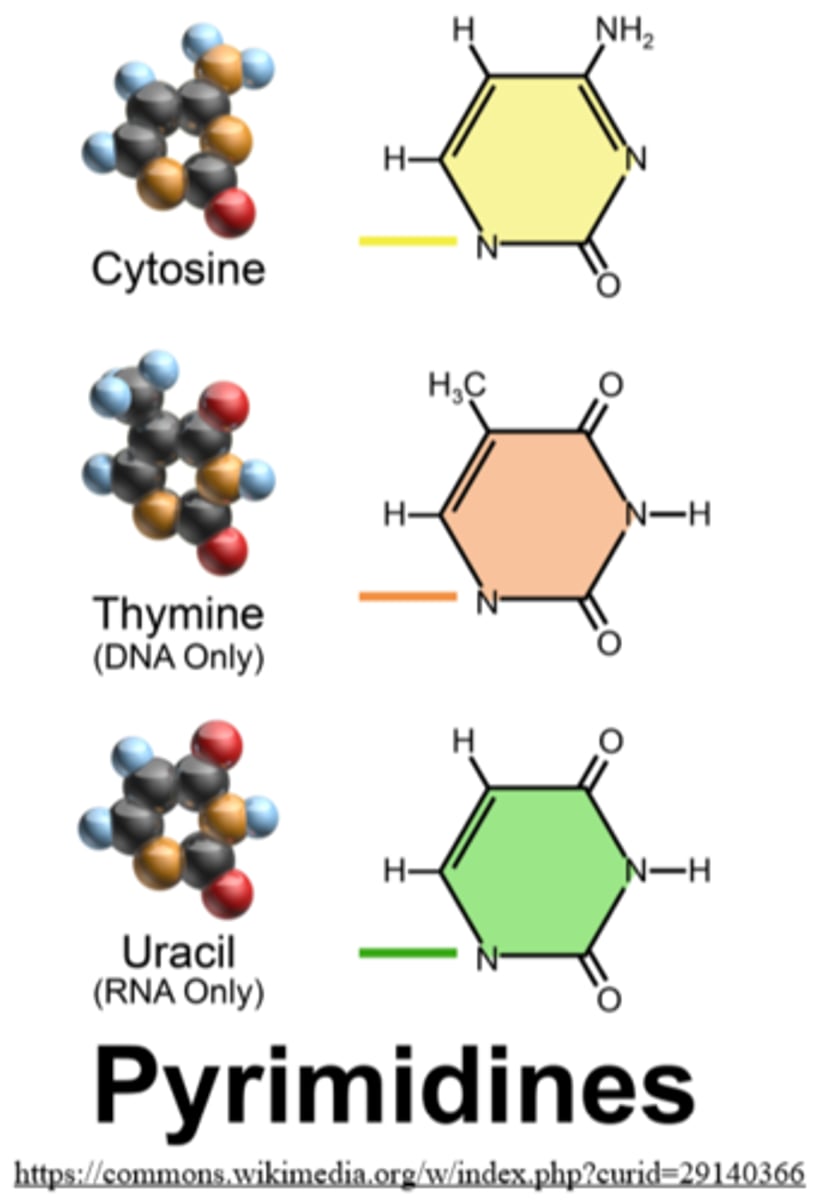
what are the two classes of nitrogen bases found in nucleic acid?
purines, pyrimidines
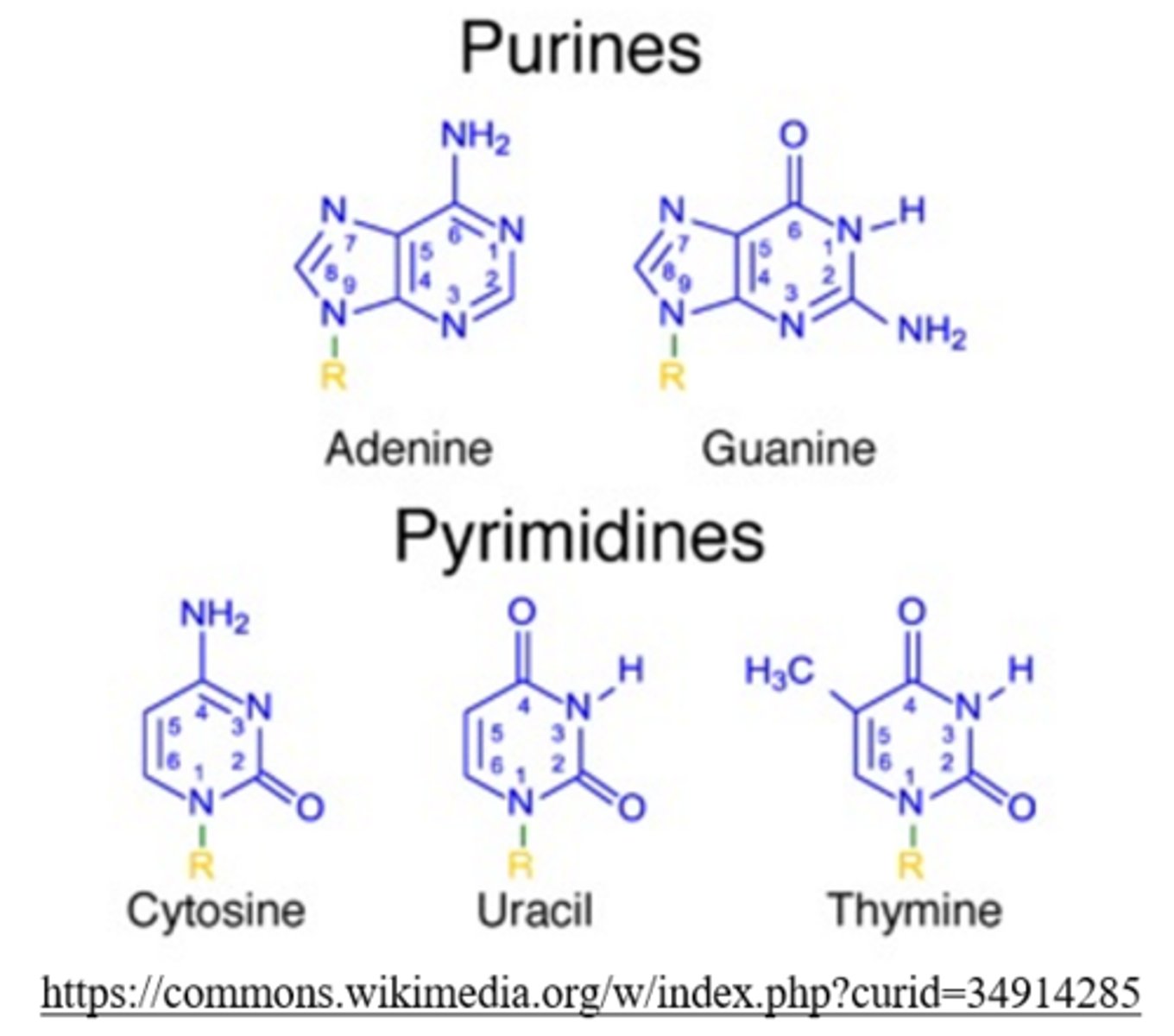
the purines include _____ and _____
adenine, guanine
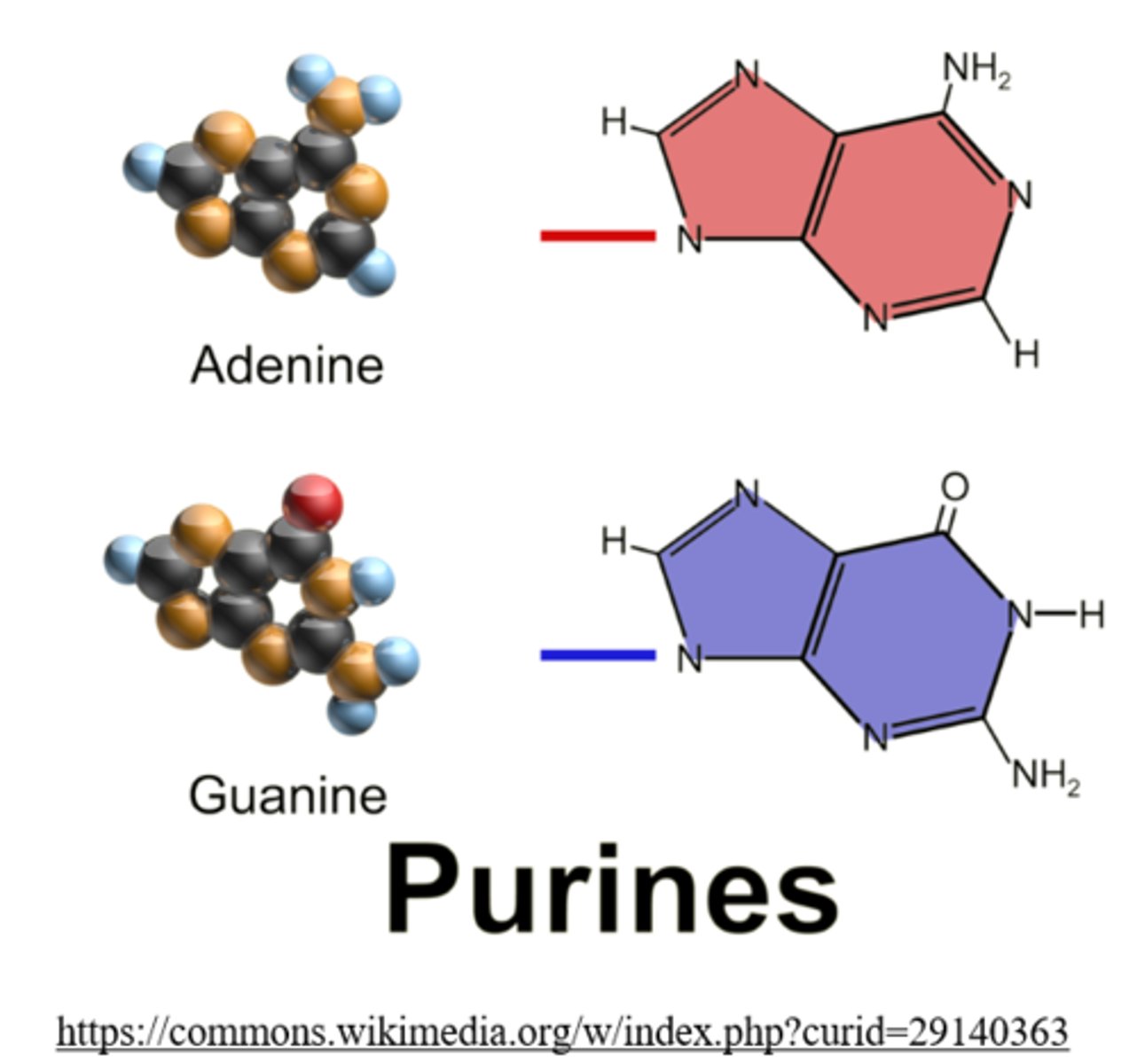
the pyrimidines include _____ and _____
cytosine, thymine, uracil (replaces thymine in RNA)
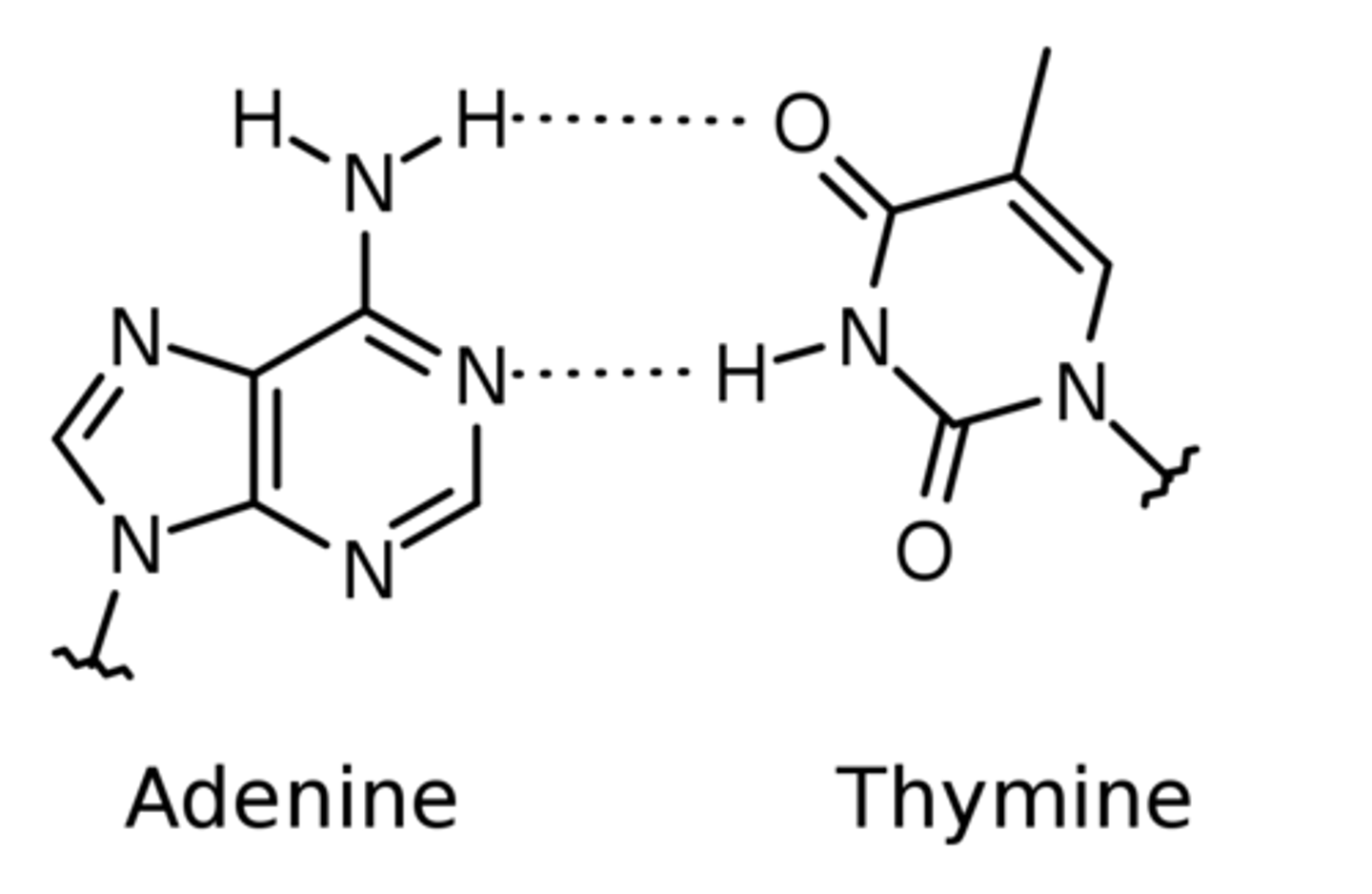
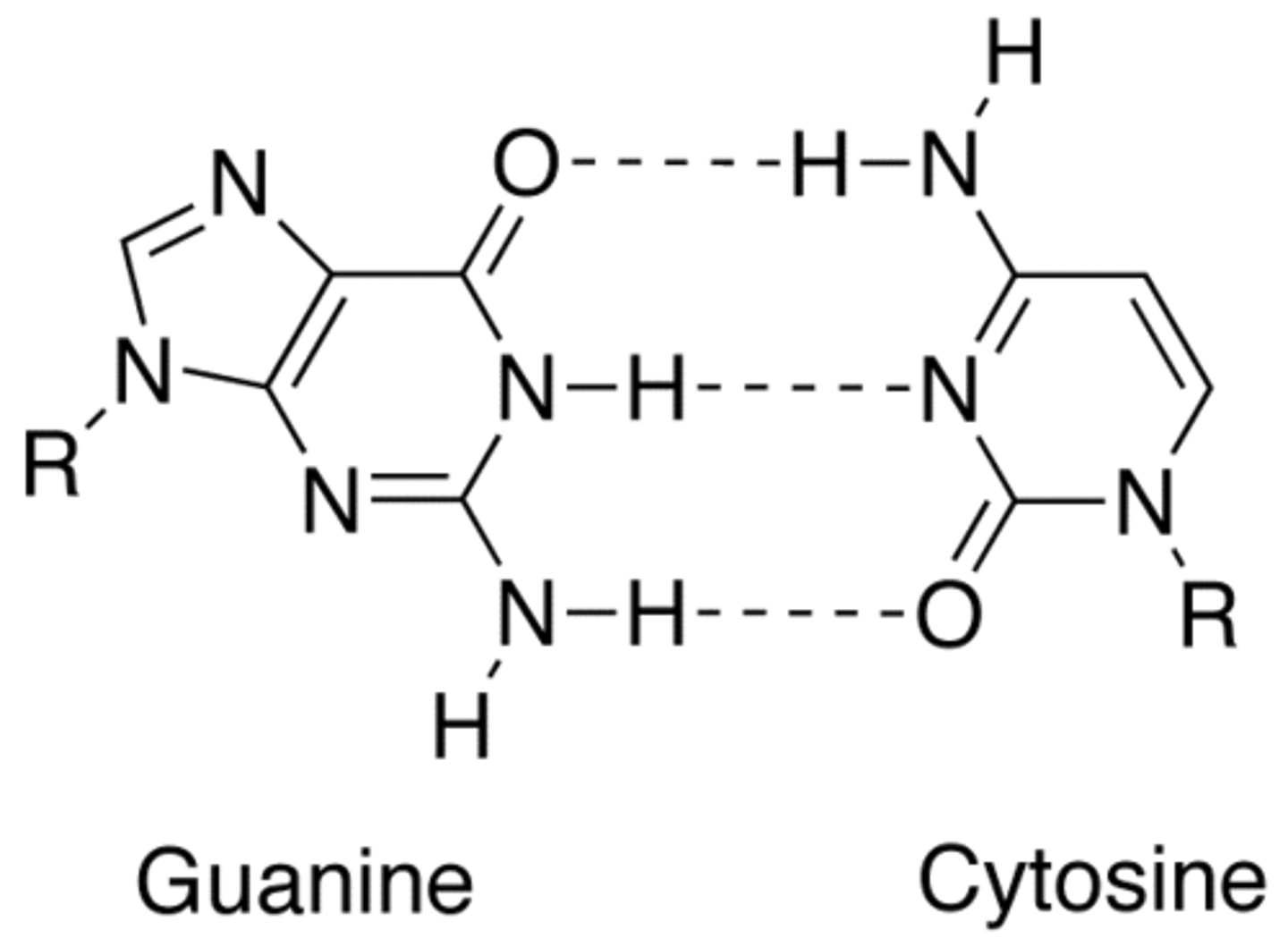
antiparallel DNA strands are held together by _____ _____ between the bases oriented toward the center
hydrogen bonds
in DNA, thymine forms 2 hydrogen bonds with _____
adenine
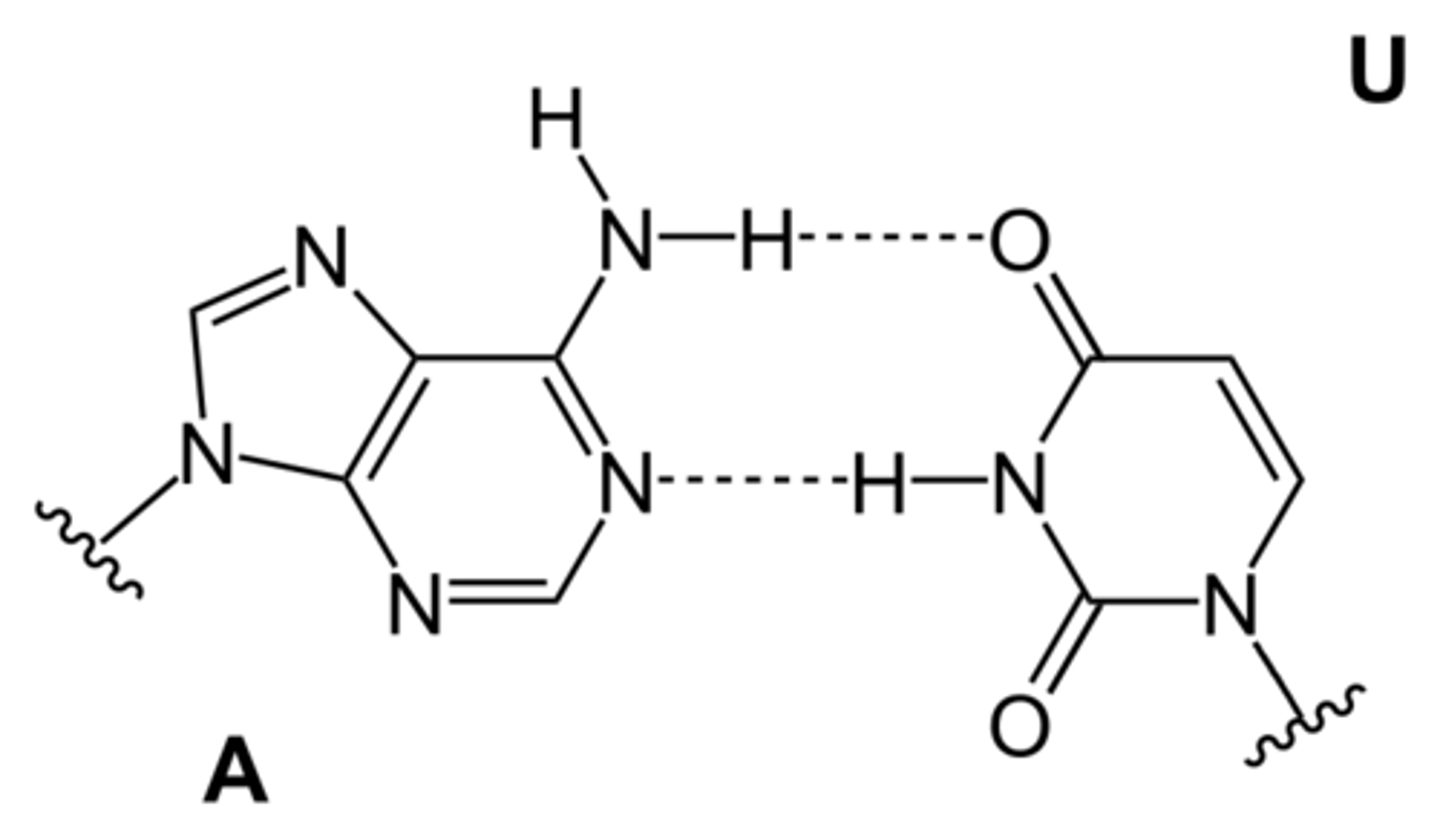
in RNA, _____ forms 2 hydrogen bonds with adenine
uracil
in DNA and RNA, guanine forms 3 hydrogen bonds with _____
cytosine
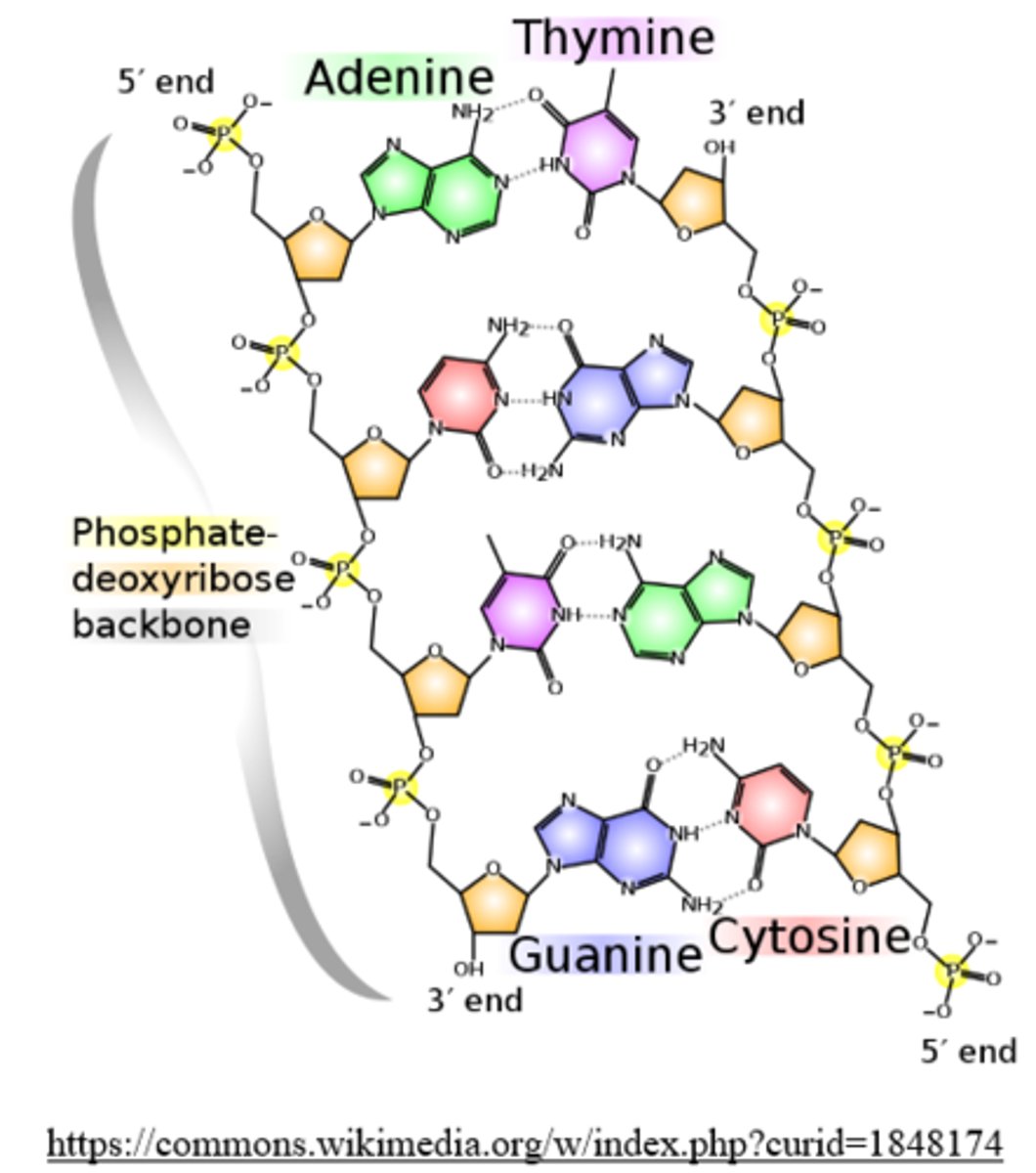
1 side of the DNA helix runs in the opposite direction to the other (5' to 3' and 3' to 5') - this is known as the __________ of DNA
antiparallel arrangement
the DNA structure was discovered by _____ and _____
Watson; Crick
what is the enzyme that breaks the hydrogen bonds between nitrogenous bases during DNA replication?
DNA helicase
the _____ is a Y-shaped region where the parental strands of DNA are being unwound
replication fork
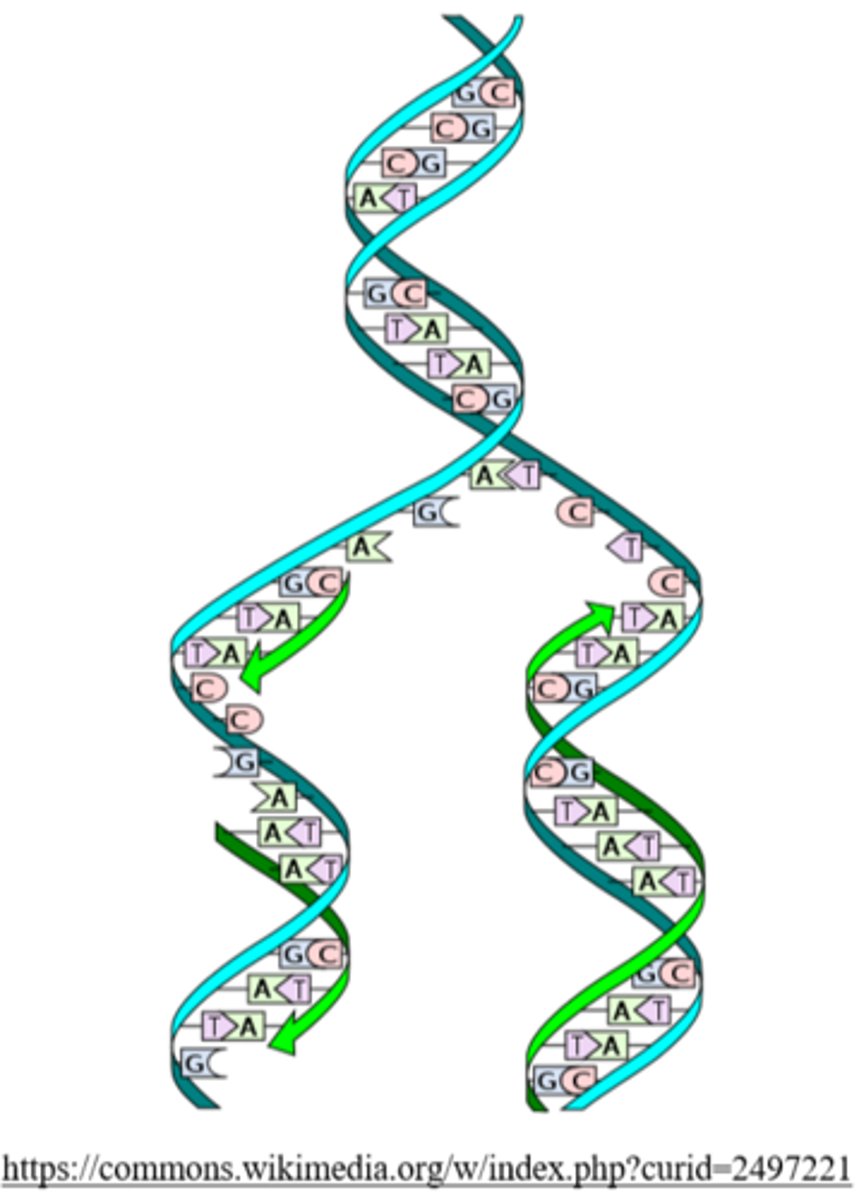
DNA replication is _____, meaning that each daughter strand will have 1 new and 1 old strand
semiconservative
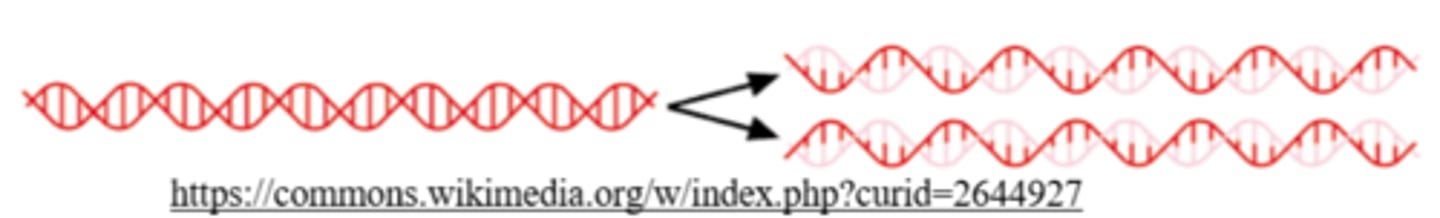
_____ is the enzyme that reads the parent DNA strand and creates a complementary, antiparallel daughter strand
DNA polymerase
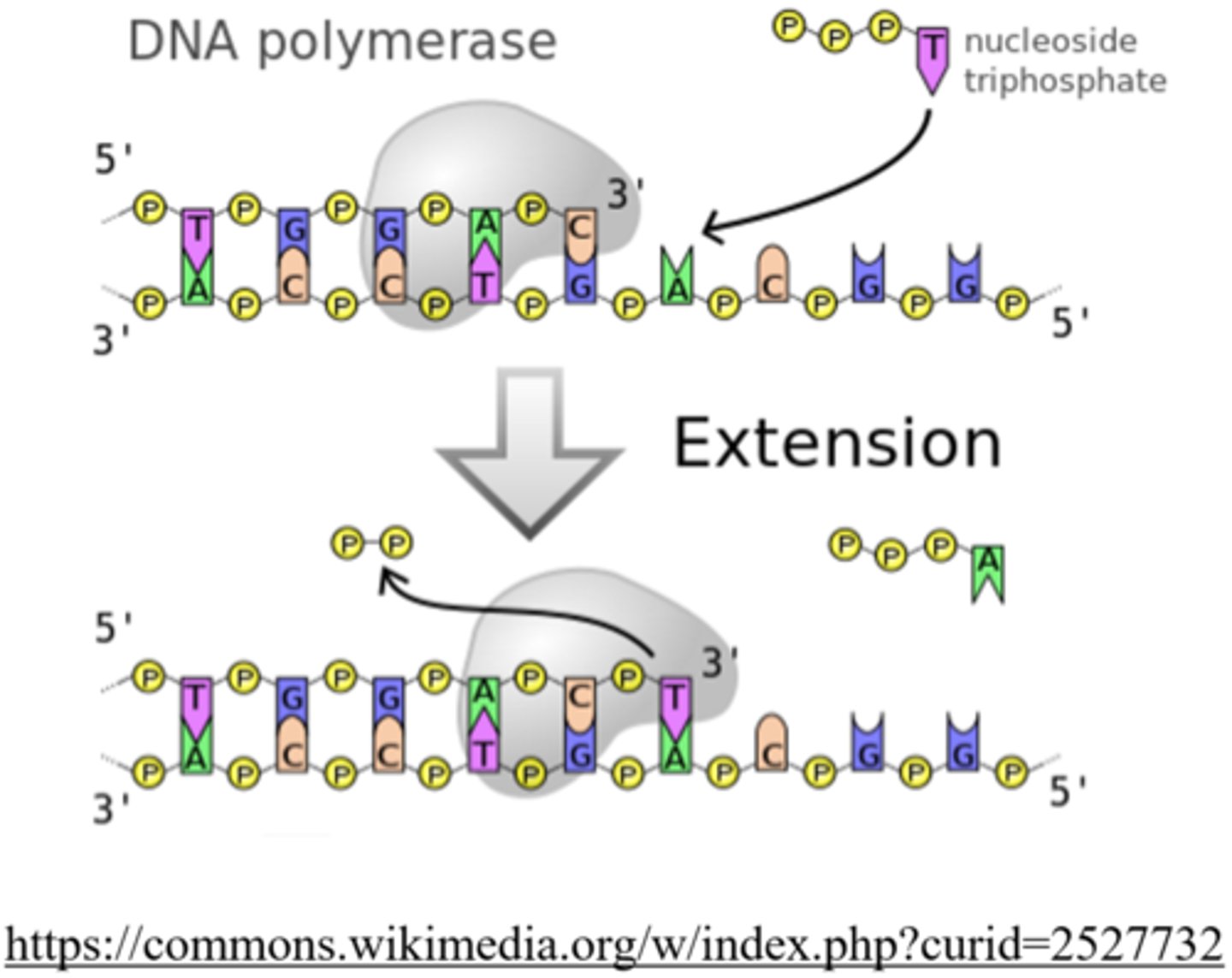
DNA polymerase always reads the template strand in the _____ direction
3' --> 5'
DNA polymerase creates the complimentary strand in the _____ direction
5' --> 3'
the _____ is the DNA strand that is continually synthesized by DNA polymerase
leading strand
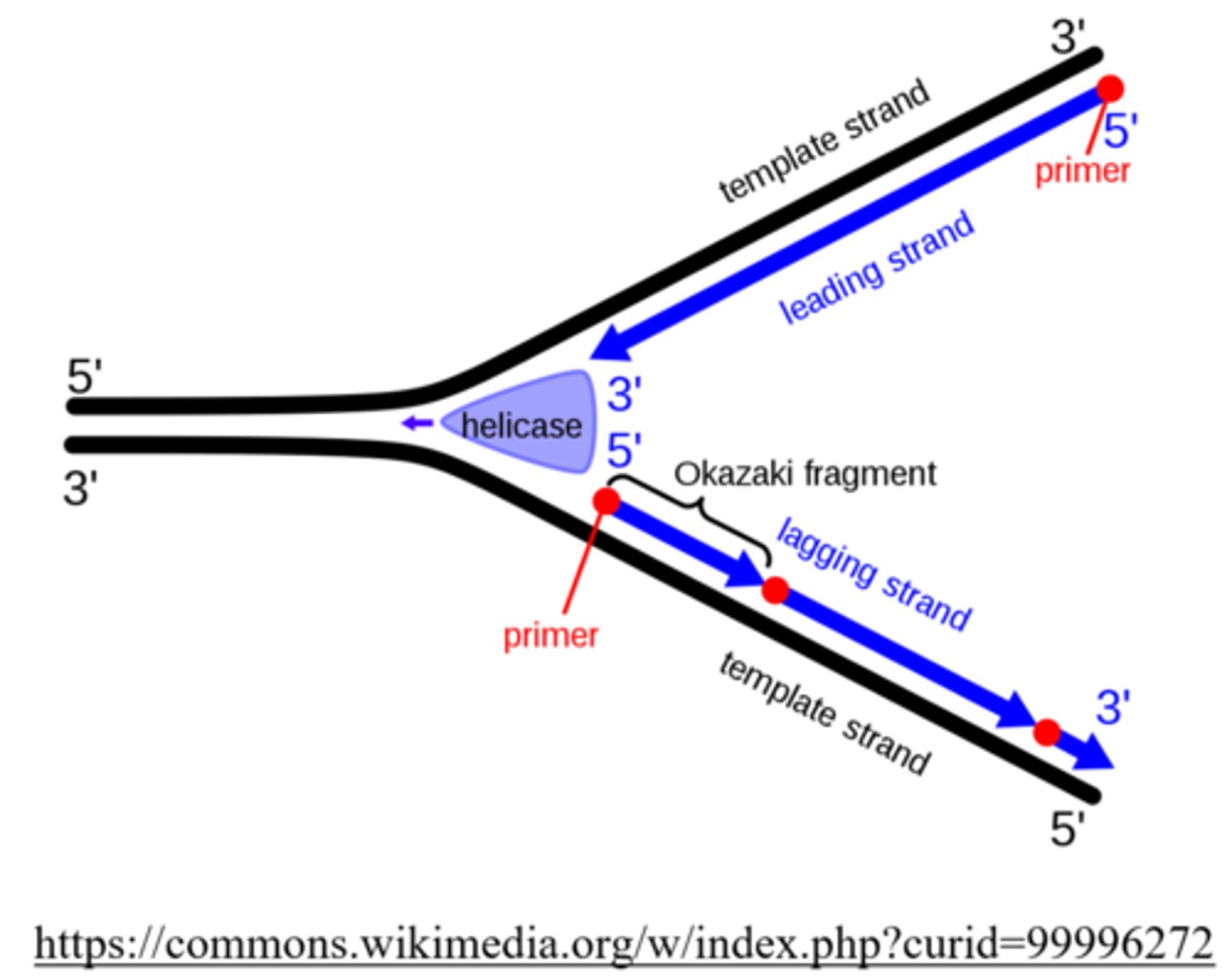
the _____ is the DNA strand that is synthesized discontinuously, due to a limited reading direction of DNA polymerase
lagging strand
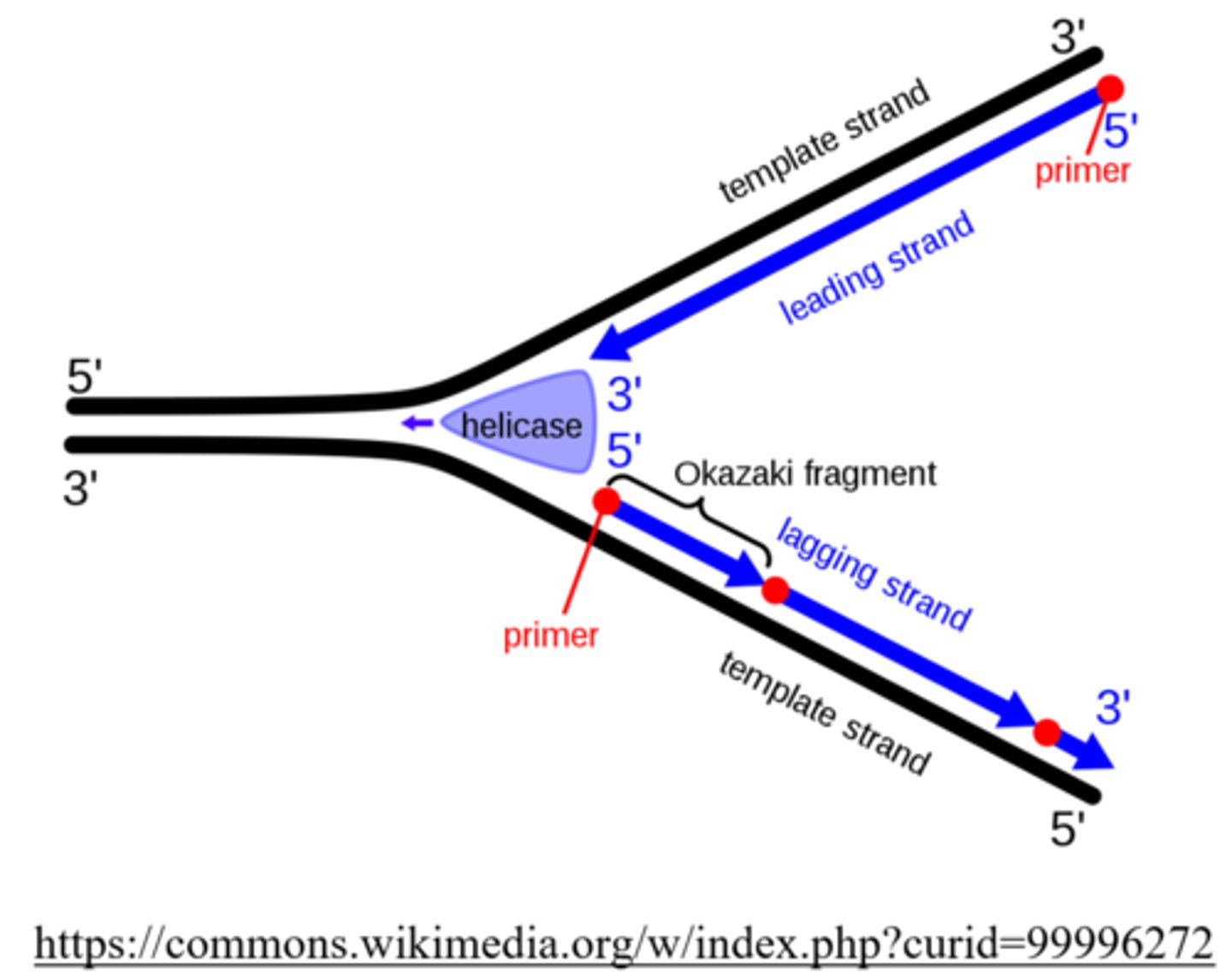
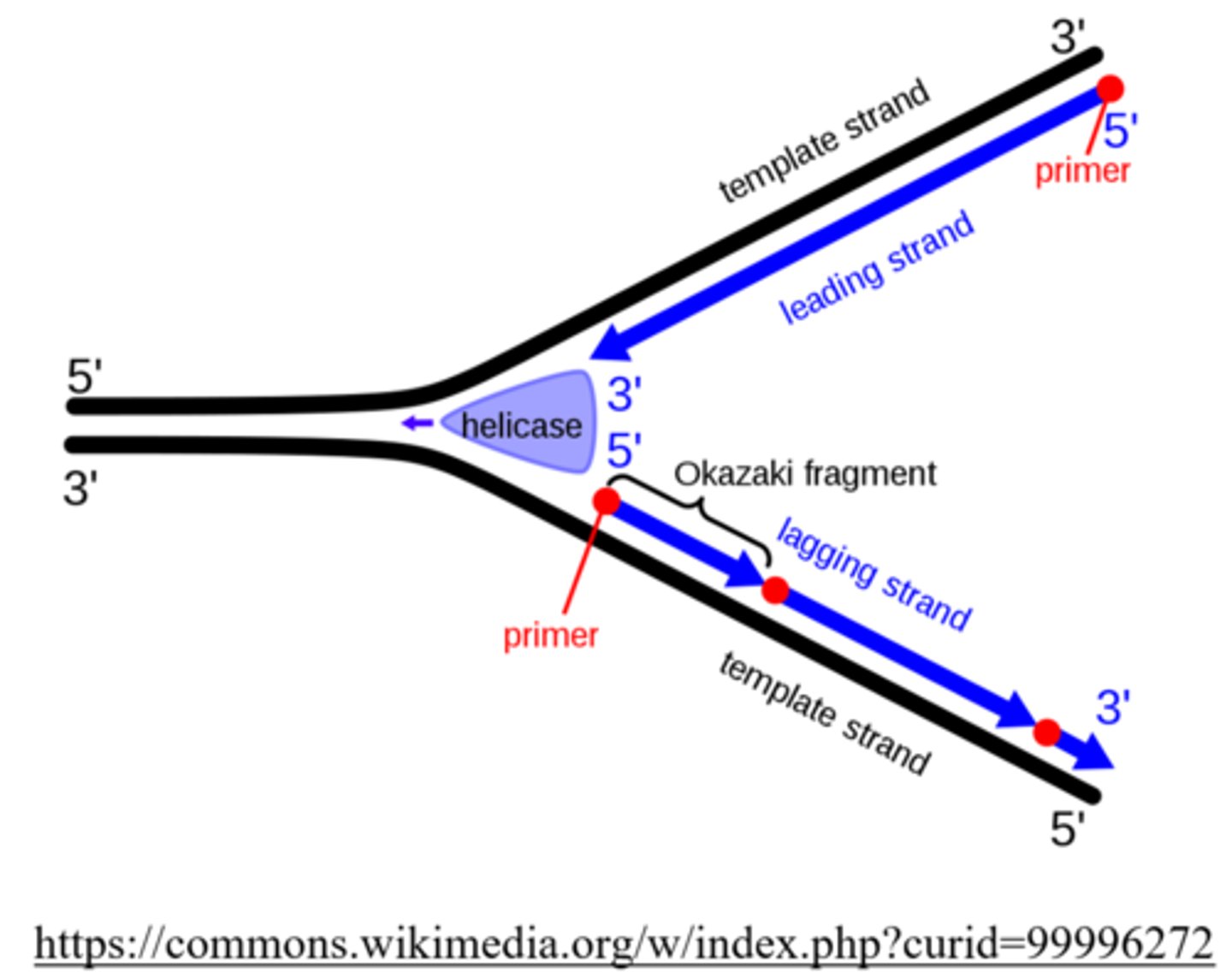
_____ are short fragments that result from the discontinuous synthesis of the lagging strand
Okazaki fragments
in RNA, thymine is replaced with _____
uracil
(both are pyrimidines)
DNA is transcribed into mRNA and arranged into triplets known as _____
codons

codons are translated from mRNA into _____
amino acids

most amino acids have more than one codon coding for them - this is known as _____ or _____
degeneracy; redundancy
_____ carries the complement of a DNA sequence from the nucleus to the ribosomes for protein synthesis
messenger RNA (mRNA)
_____ assists in translation by bringing amino acids to the ribosomes during protein synthesis
transfer RNA (tRNA)
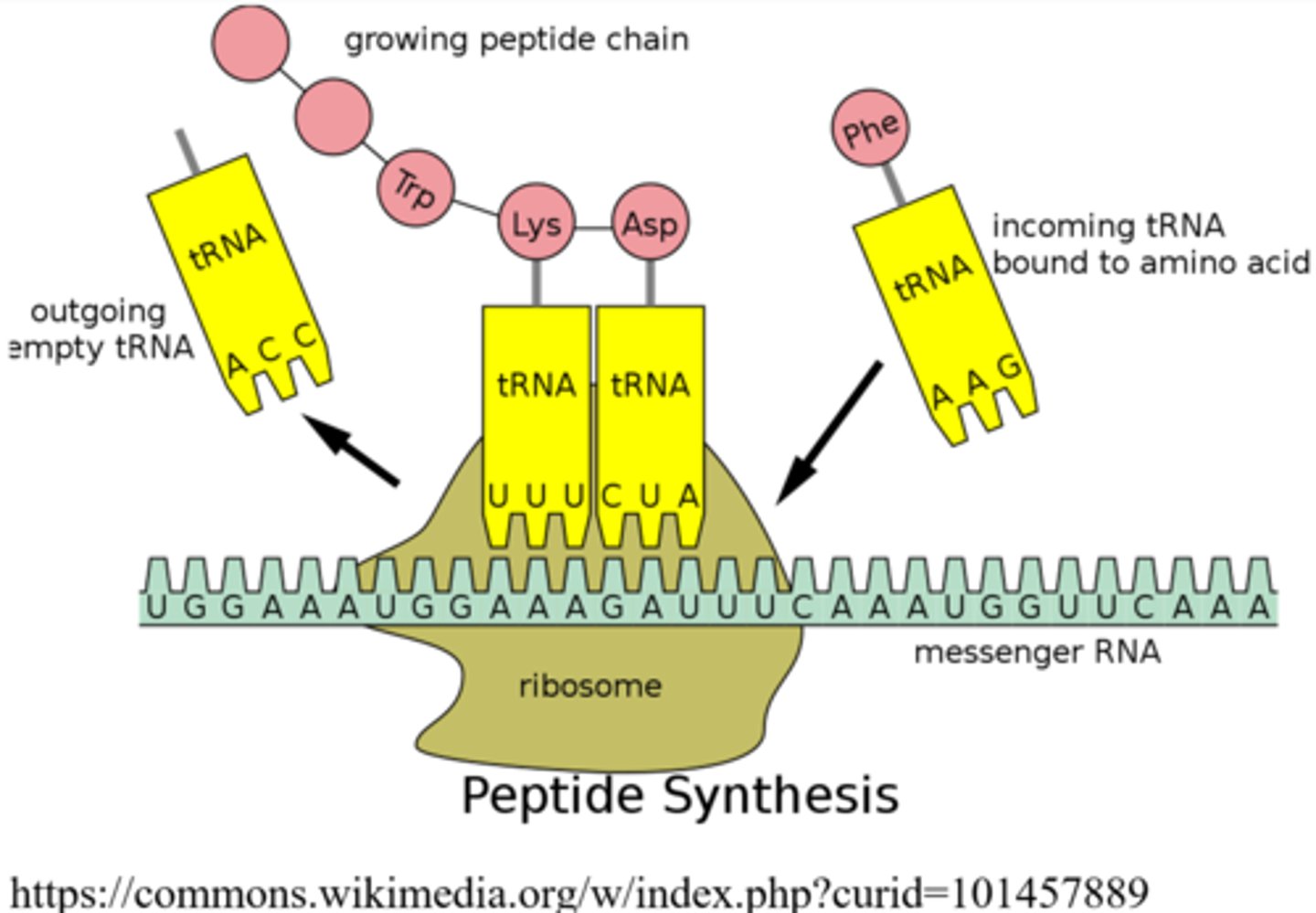
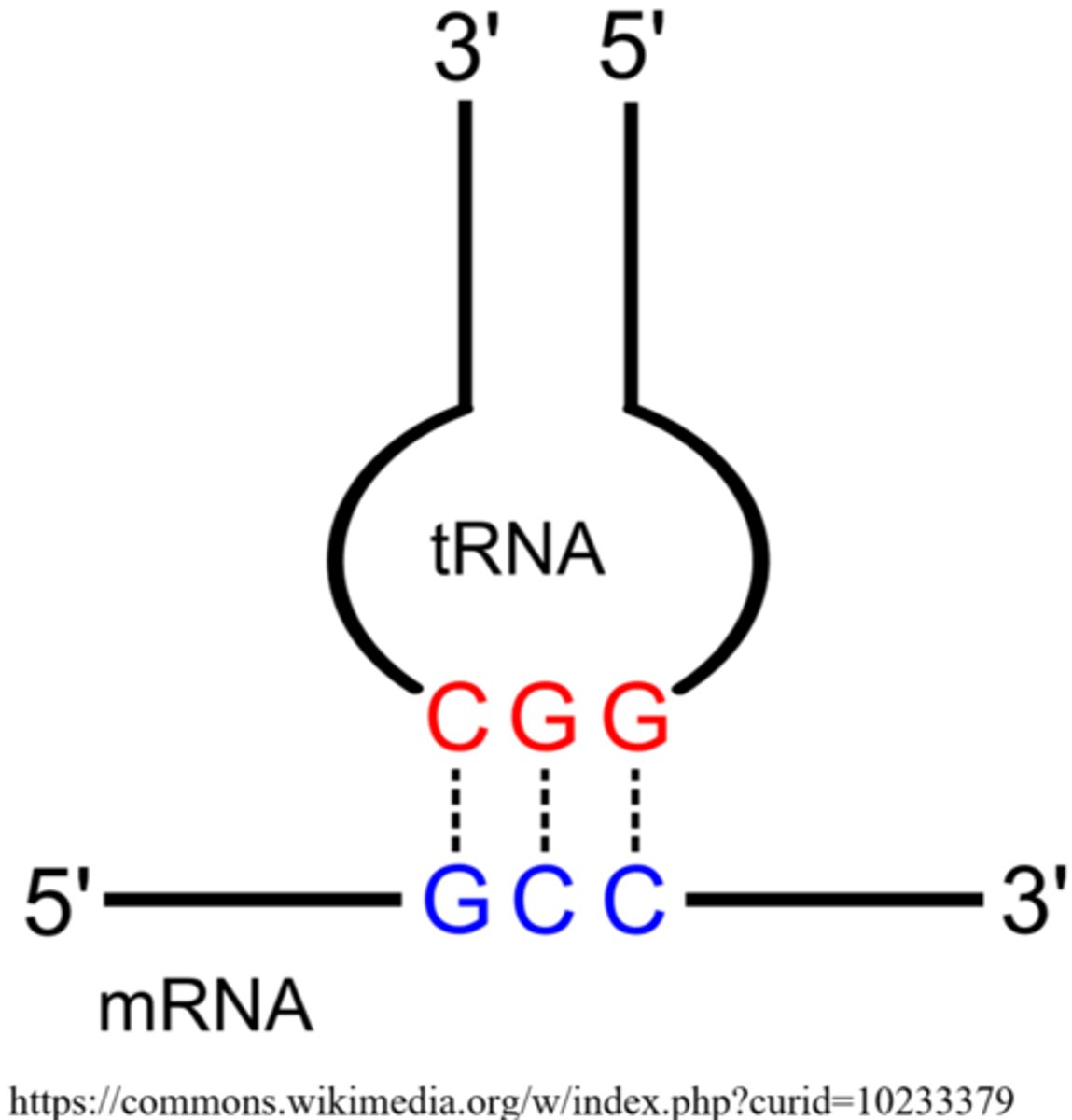
in tRNA, triplet sequences of nucleotides that are complementary to mRNA codons are called _____
anticodons
the nucleotide structural component of ribosomes is _____
ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
mRNA sequences pass through _____ ribosomal subunits during translation
two
what is the process where DNA gene sequences are copied into mRNA?
transcription
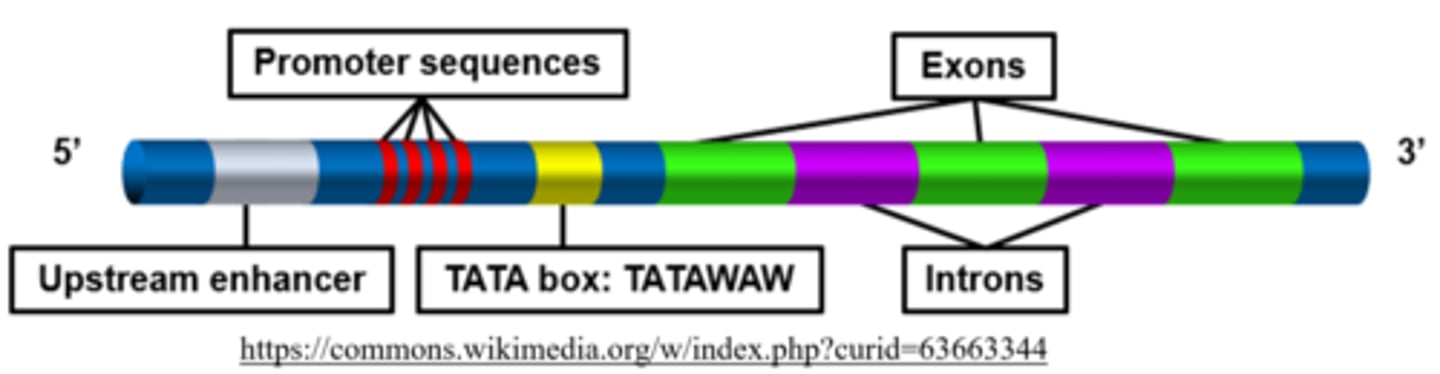
the promoter region is where _____ binds to DNA during transcription
RNA polymerase
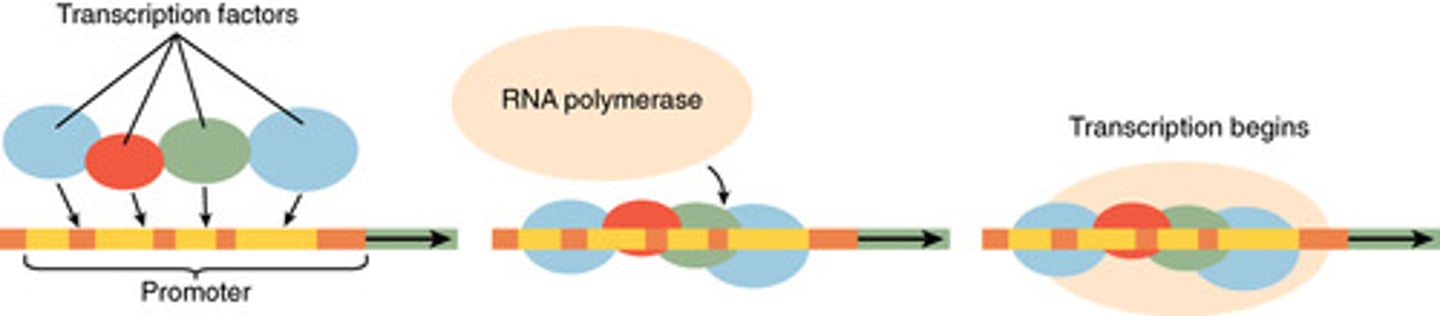
the _____ is a short DNA sequence found upstream from the site where transcription of a specific RNA is going to take place
promoter region
what is the typical human promoter region?
TATA box
RNA polymerase is the enzyme that binds to DNA and creates a _____
transcription bubble
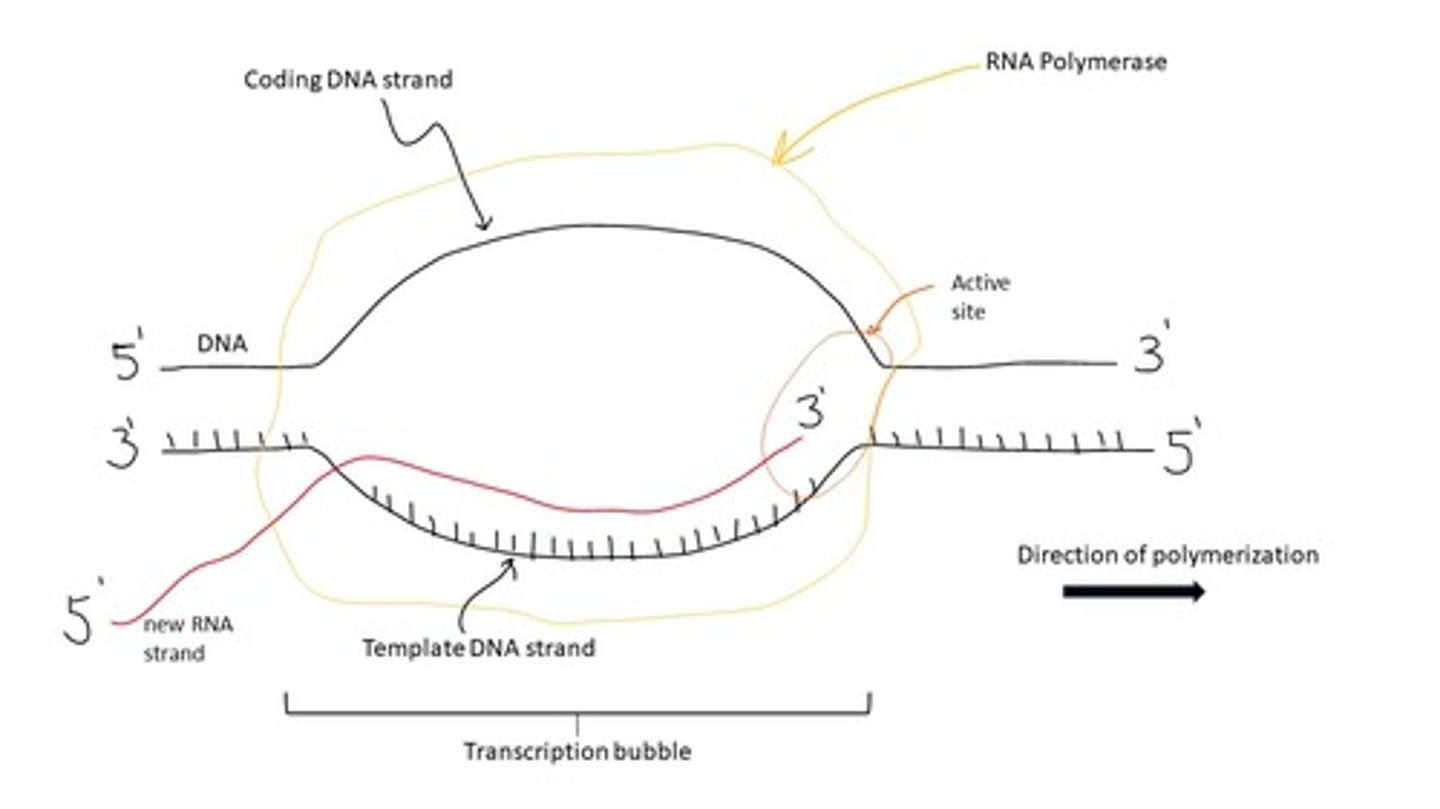
RNA polymerase recruits and adds complementary _____ based on the DNA sequence during transcription
RNA nucleotides
RNA polymerase synthesizes a daughter strand of RNA in the _____ direction
5' --> 3'
_____ are extra sequences of nucleotides that are not necessary to create the corresponding protein
introns
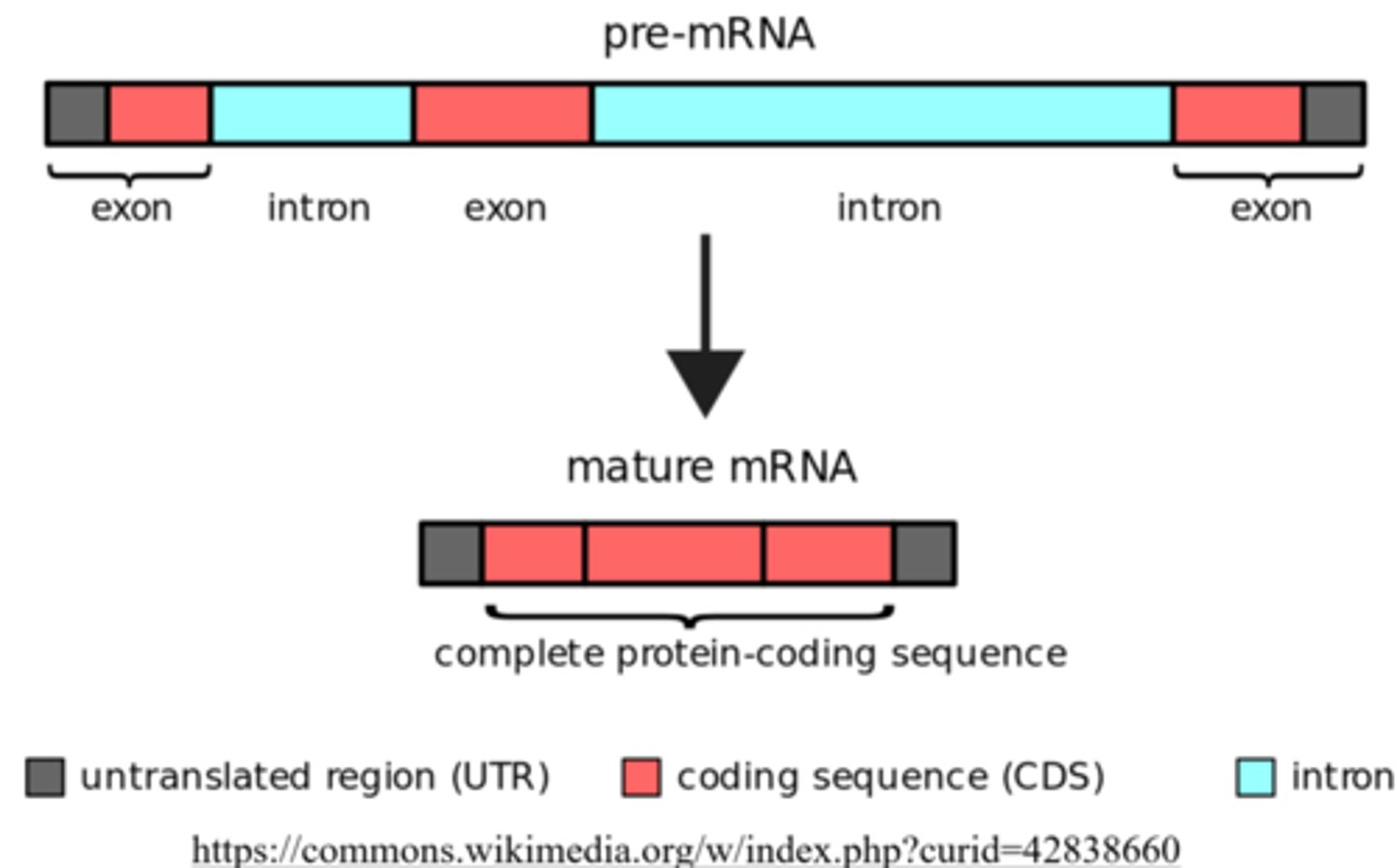
_____ are the nucleotides necessary to make the protein
exons
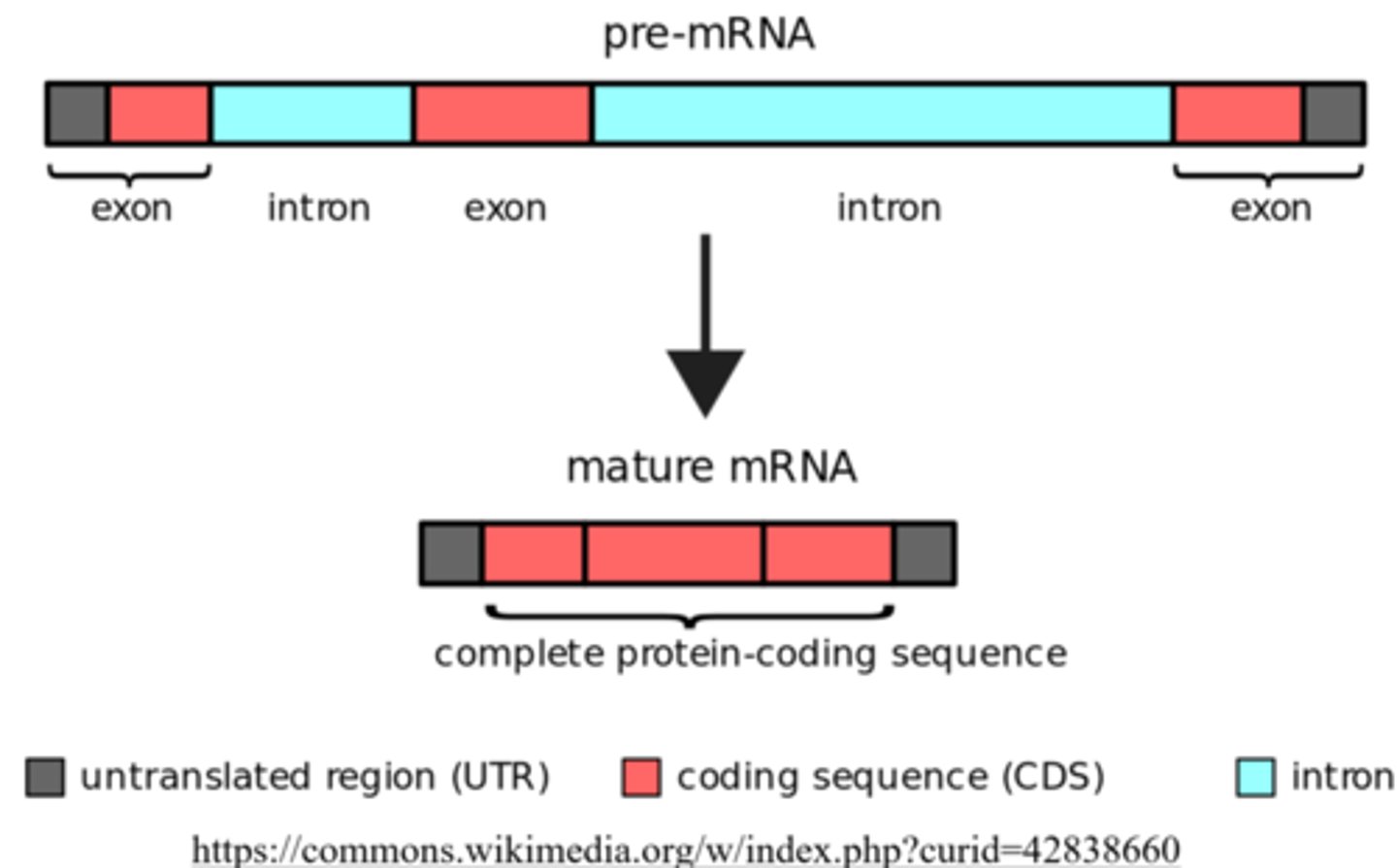
the introns are _____ out by the _____ leaving only the exons behind
spliced, spliceosome
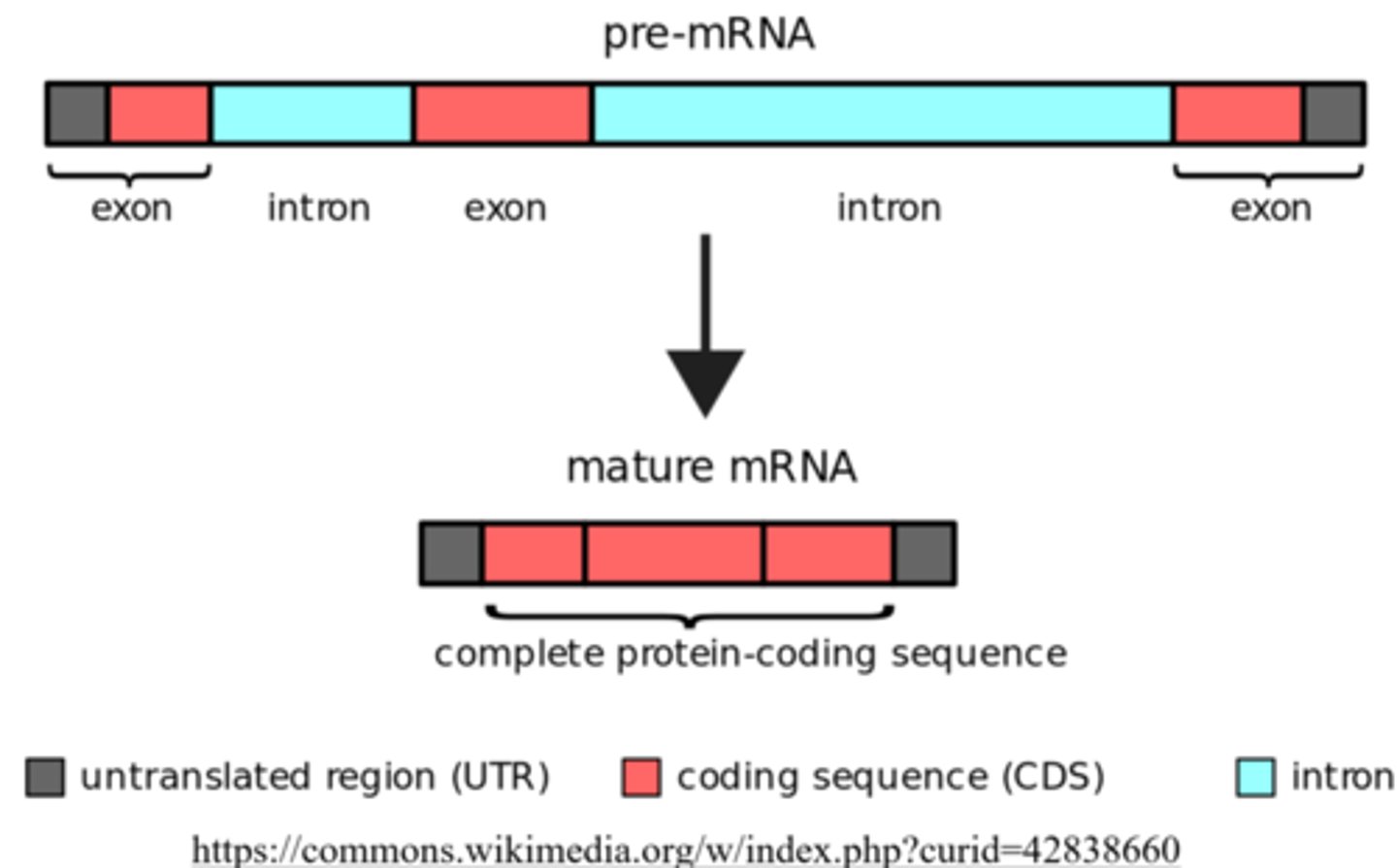
the spliceosome is only found in _____
eukaryotes
(most prokaryotes lack introns (archaea have them))
a 5' _____ _____ and a 3' _____ _____ are post-transcriptional modifications to mRNA, which provide protection against enzyme degradation after the mRNA leaves the nucleus
guanine cap, poly-A tail
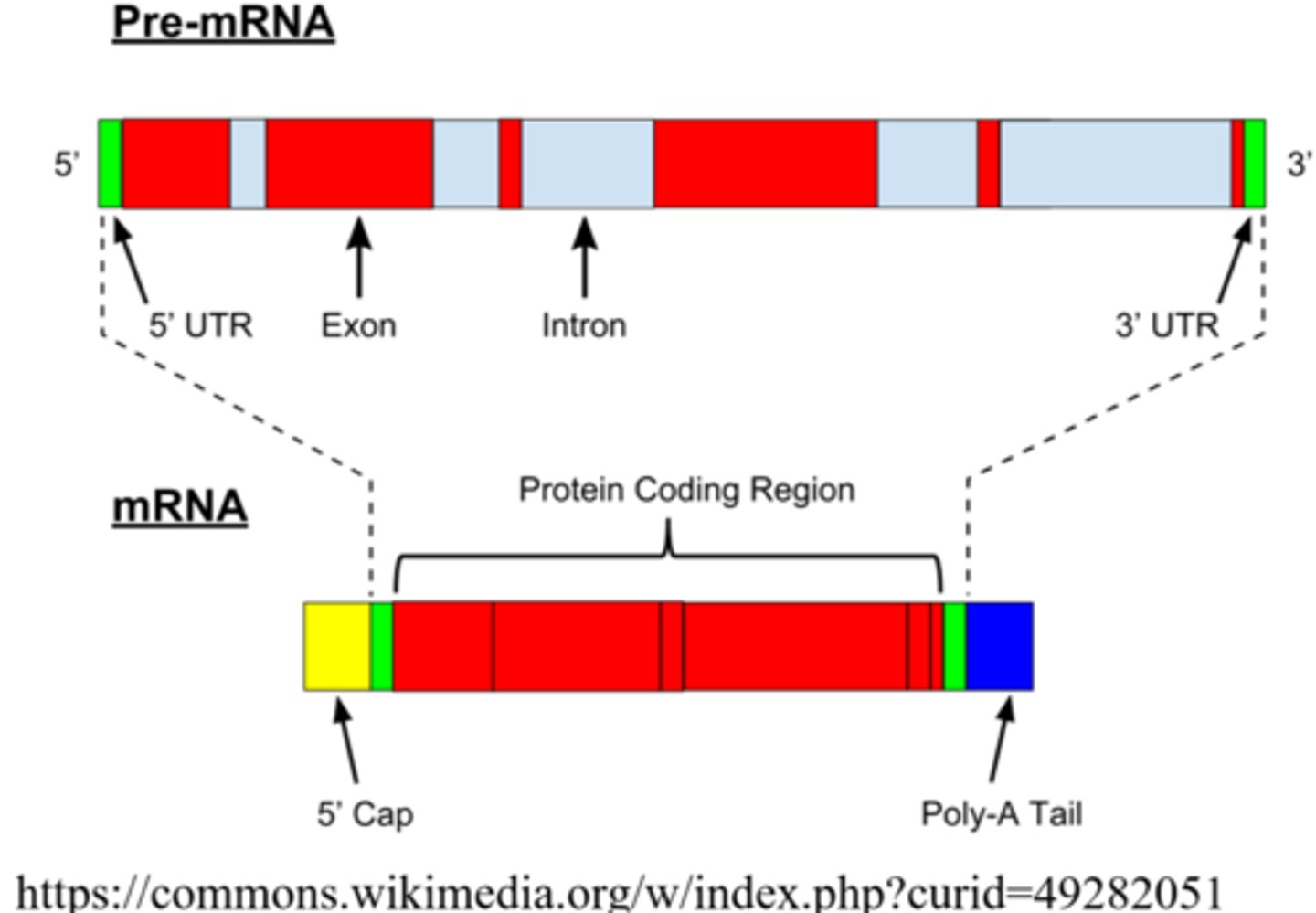
translation occurs in the _____, and it is the process through which mRNA codons produce a _____
cytoplasm; polypeptide
what are the three distinct stages of translation?
initiation, elongation, termination
initiation is the stage of translation in which the ribosome binds to the mRNA near its _____
5' end
in translation initiation, the ribosome scans the mRNA until it binds to the _____
start codon (AUG)
the start codon is the codon that signals the start of translation - what is it and what amino acids does it code for?
AUG = methionine
the initiator aminoacyl-tRNA complex, _____, base pairs with the start codon during translation initiation
methionine-tRNA
_____ is the stage of translation in which hydrogen bonds form between the mRNA codon in the A site of the ribosome and its complementary anticodon on the incoming aminoacyl-tRNA complex
elongation
a _____ is formed between the amino acid attached to the tRNA in the A site and the amino acid attached the tRNA in the P site of the _____ during elongation
peptide bond; ribosome
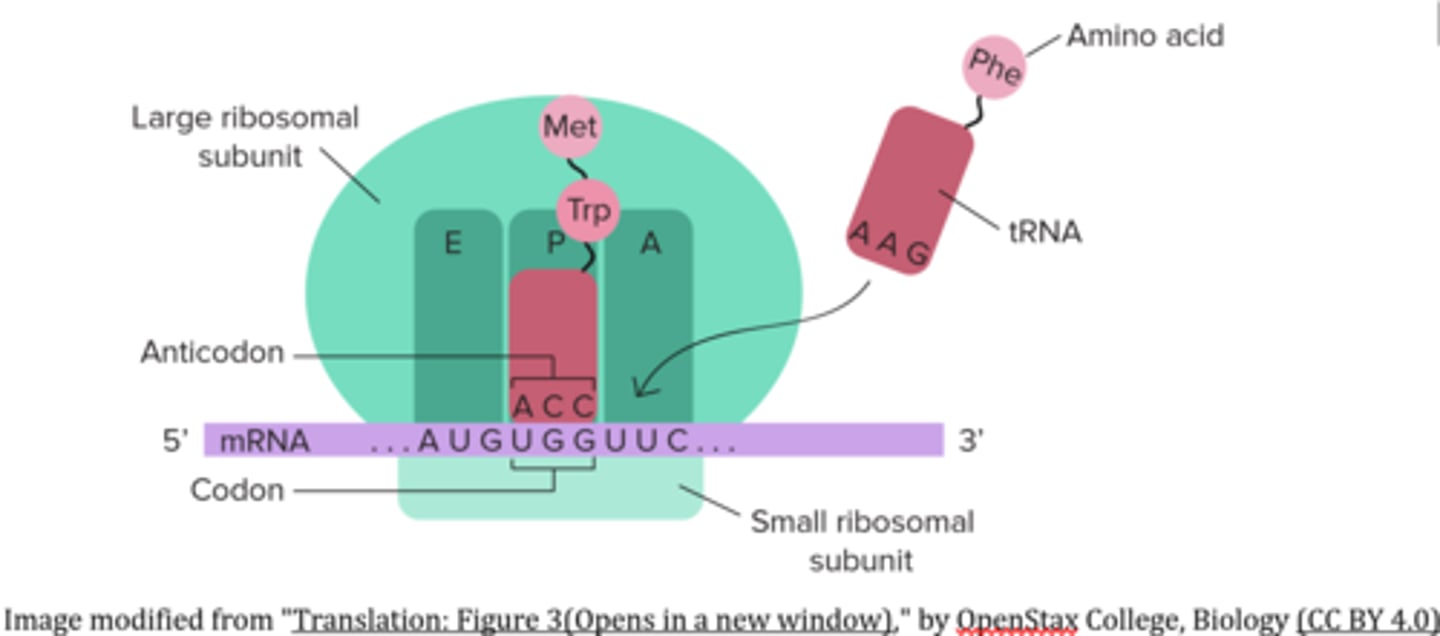
after the peptide bond formation of elongation, a ribosome caries unbound tRNA in the _____ and peptidyl-tRNA in the _____
P site; A site
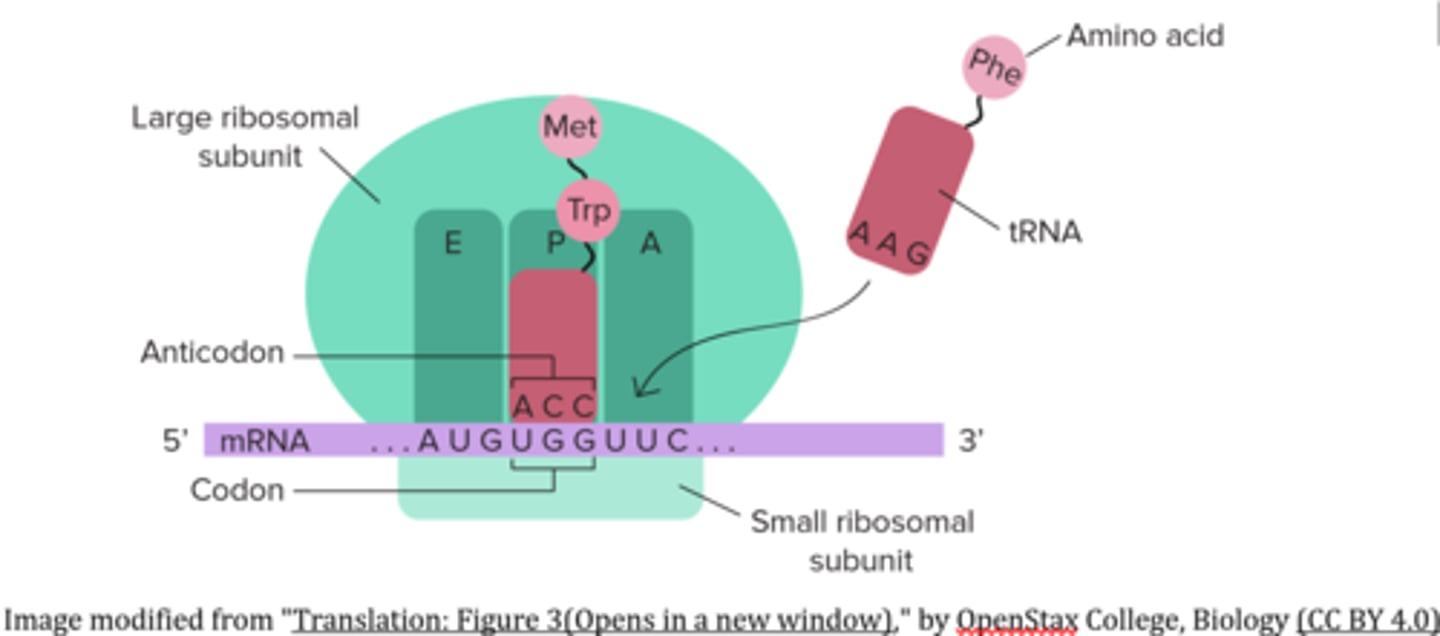
_____ is the stage of translation in which the ribosome advances three nucleotides along the mRNA in the 5' --> 3' direction
translocation
the unbound tRNA from the P site is expelled at the _____ and the peptidyl-tRNA from the A site moves into the _____ during translocation
E site; P site
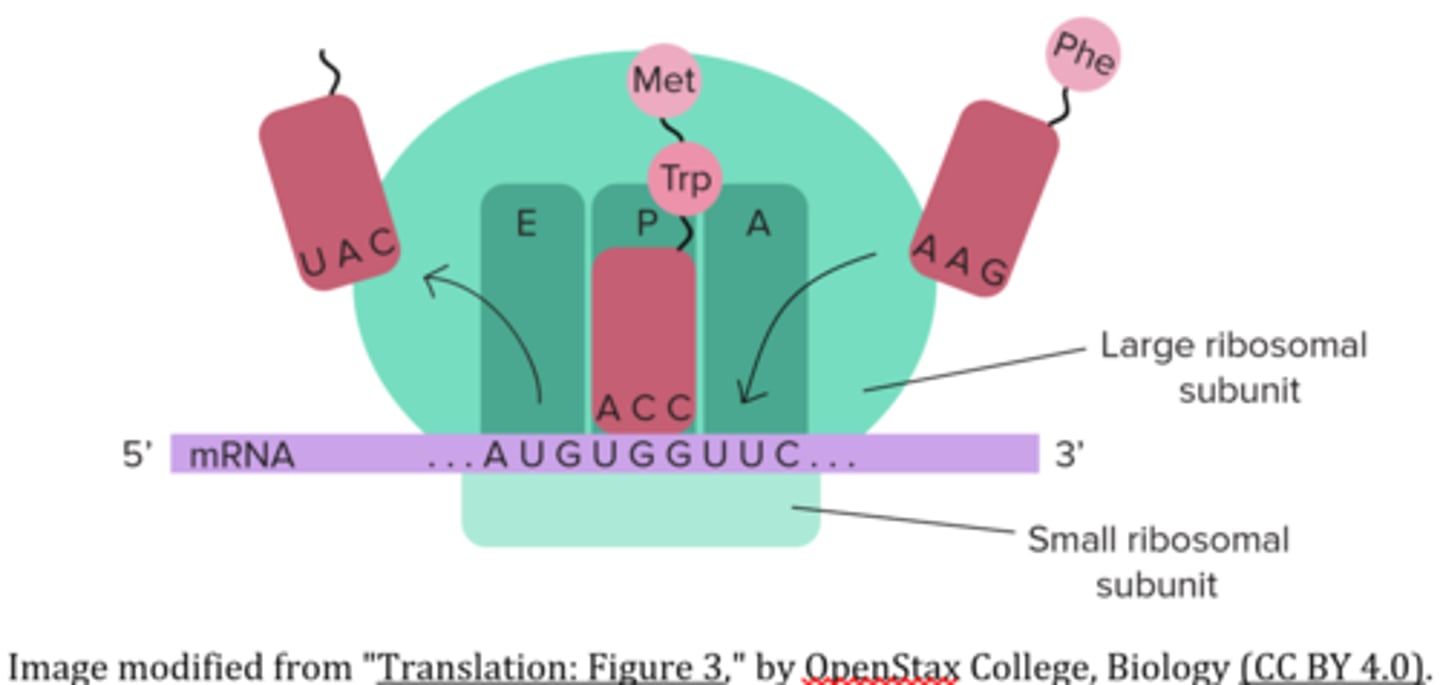
a _____ is a group of several ribosomes attached to, and translating, the same messenger RNA molecule
polyribosome
_____ is the stage of translation in which 1 of 3 special mRNA codons, or stop codons, arrives in the A site
termination
_____ do not code for amino acids; rather, they signal the ribosome to stop translation (termination)
stop codons
what are the 3 stop codons?
UAG, UAA, or UGA
(they do not code for amino acids)
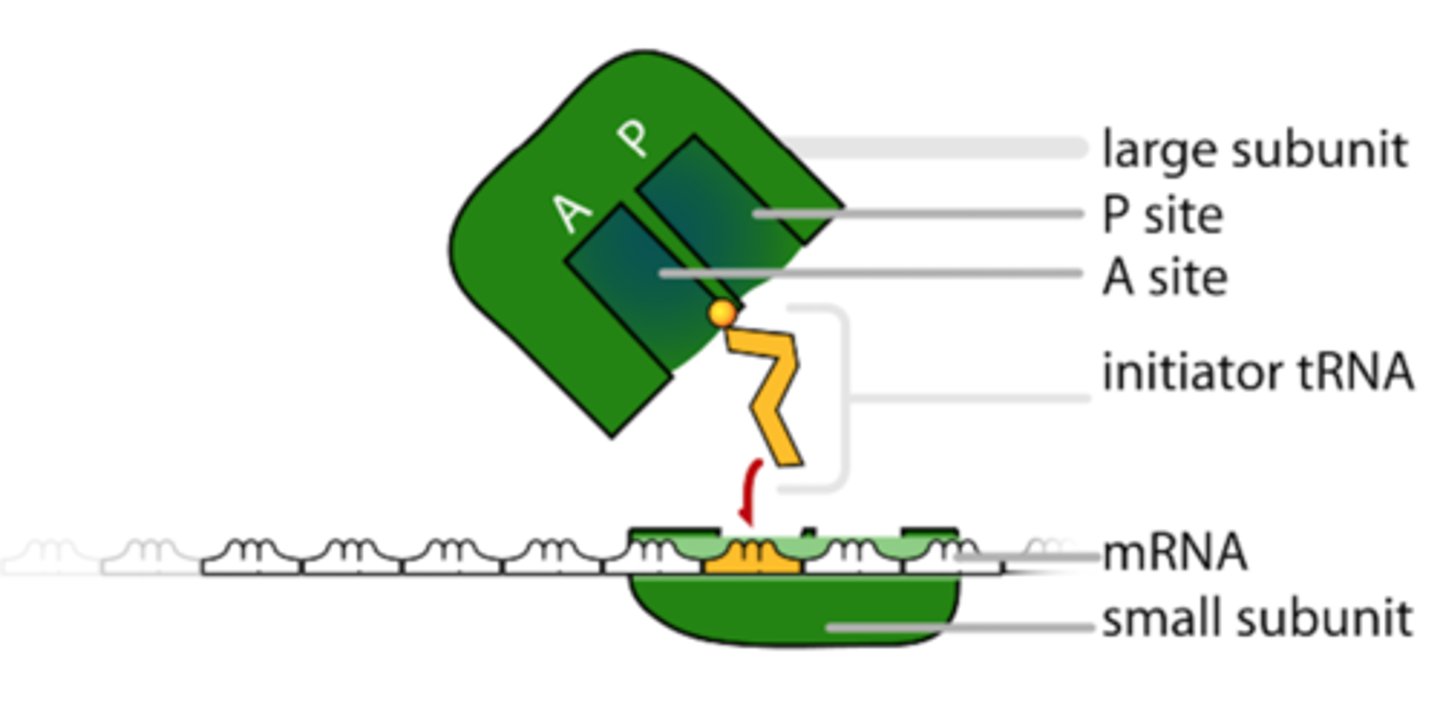
what is the machine that carries out translation?
ribosome
the ribosomal _____ binds to the next incoming aminoacyl-tRNA complex
A site
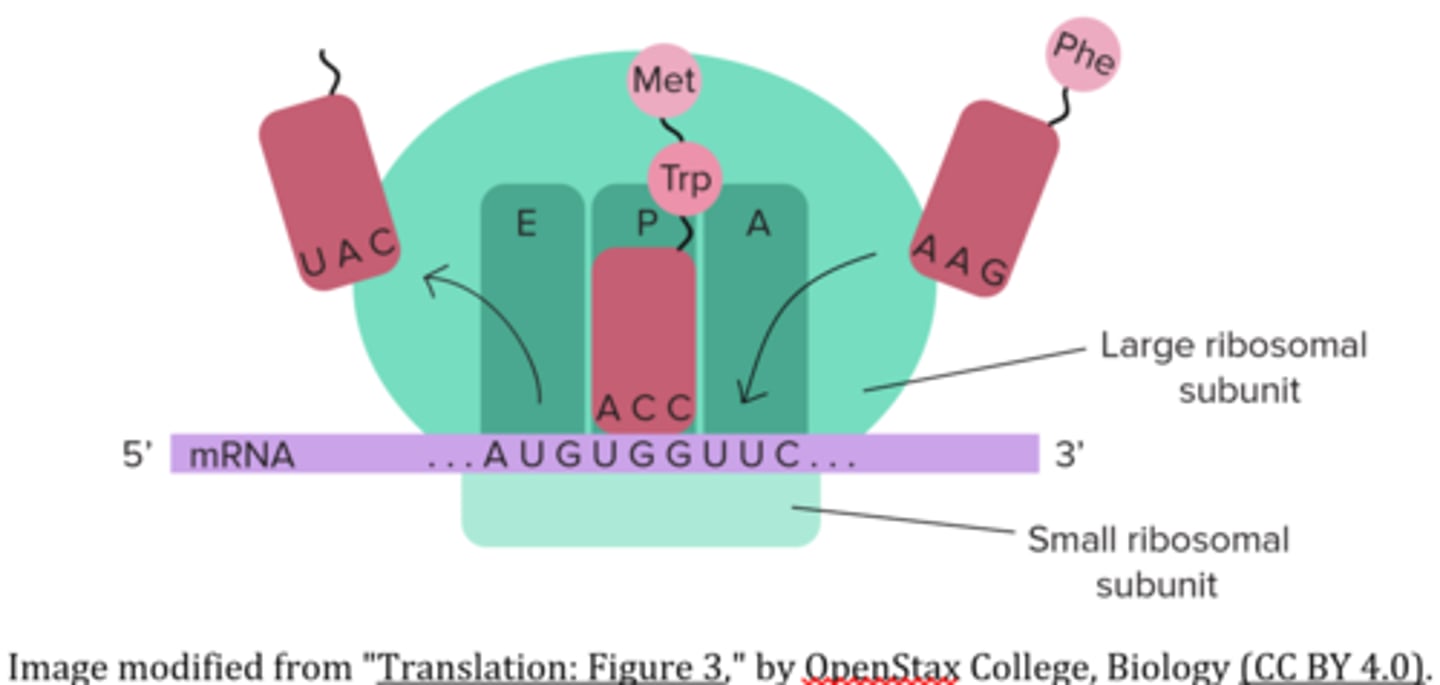
the _____ is the ribosomal binding site for peptidyl-tRNA
P site
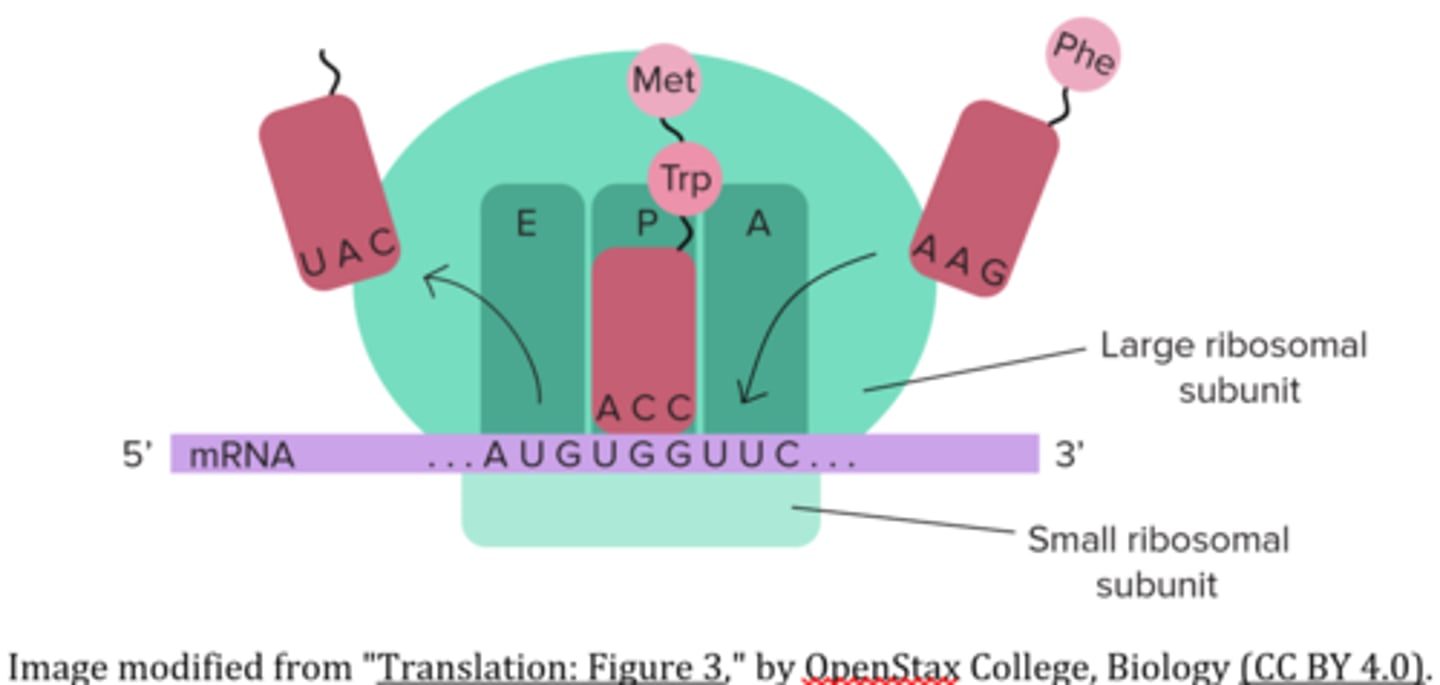
the _____ releases empty tRNAs from the ribosome
E site
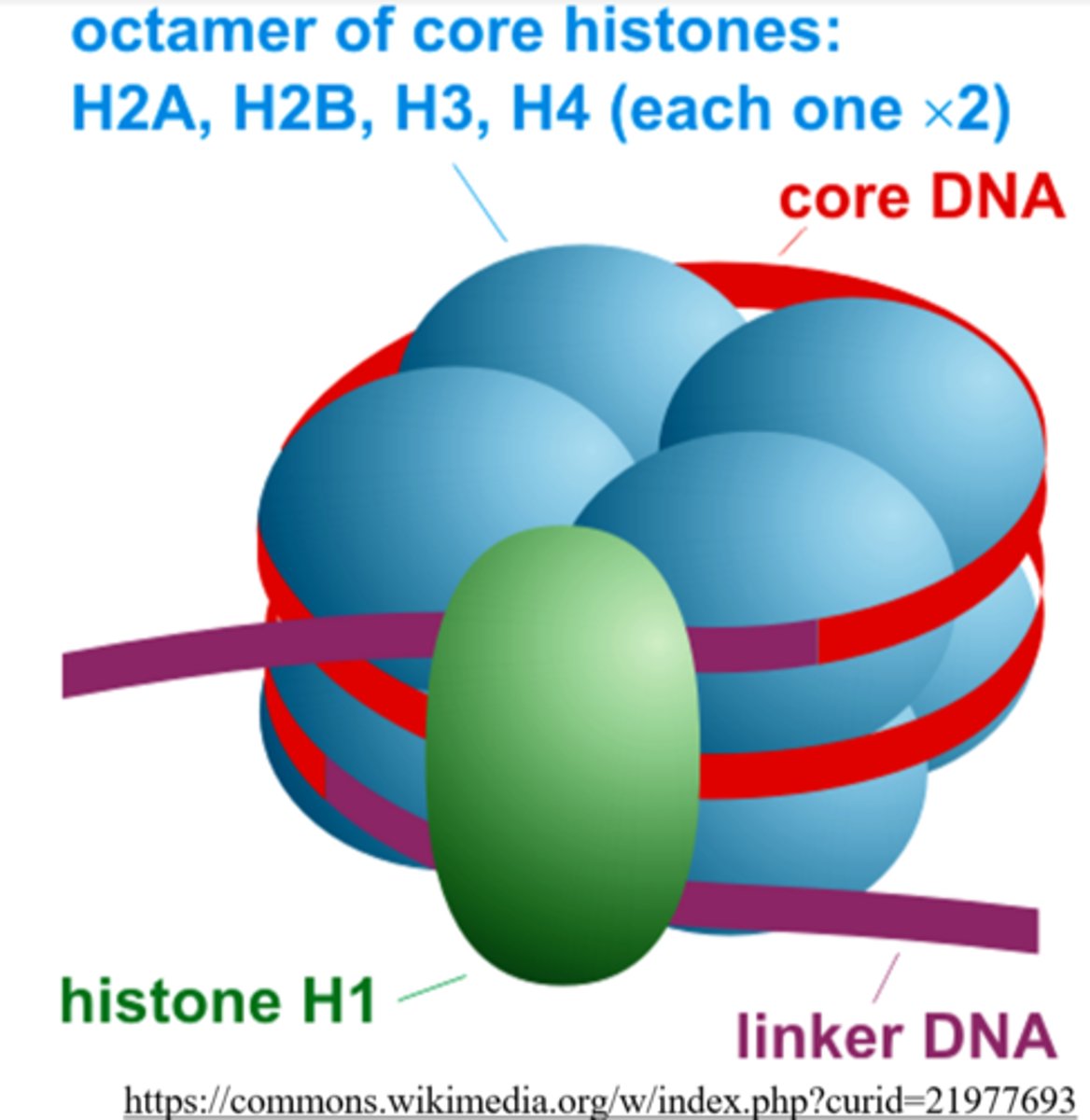
a _____ is a unit of chromatin consisting of a DNA strand wrapped around histone proteins
nucleosome
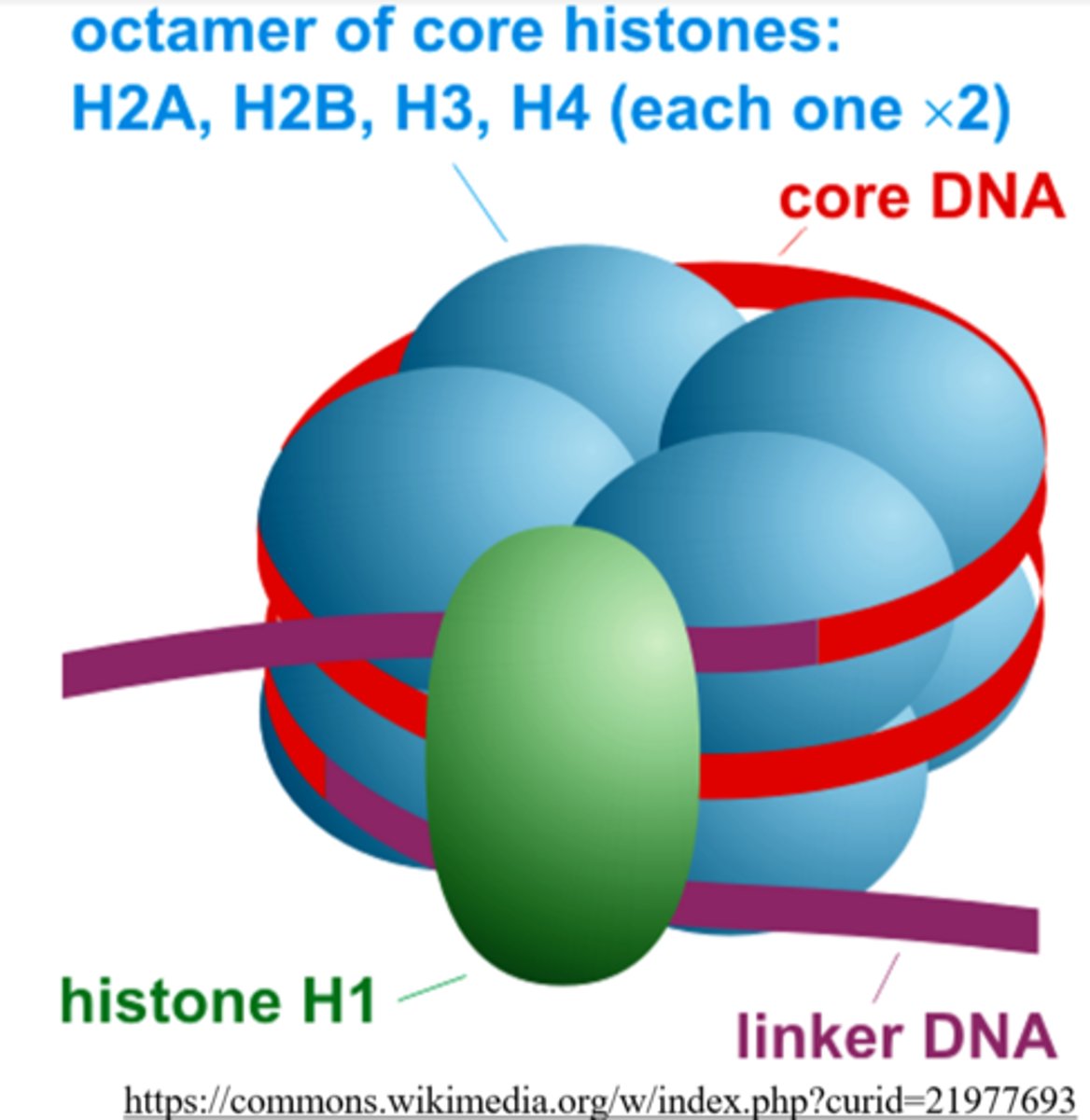
histone proteins are not found in _____ DNA
bacterial
each nucleosome contains _____ histone proteins
nine
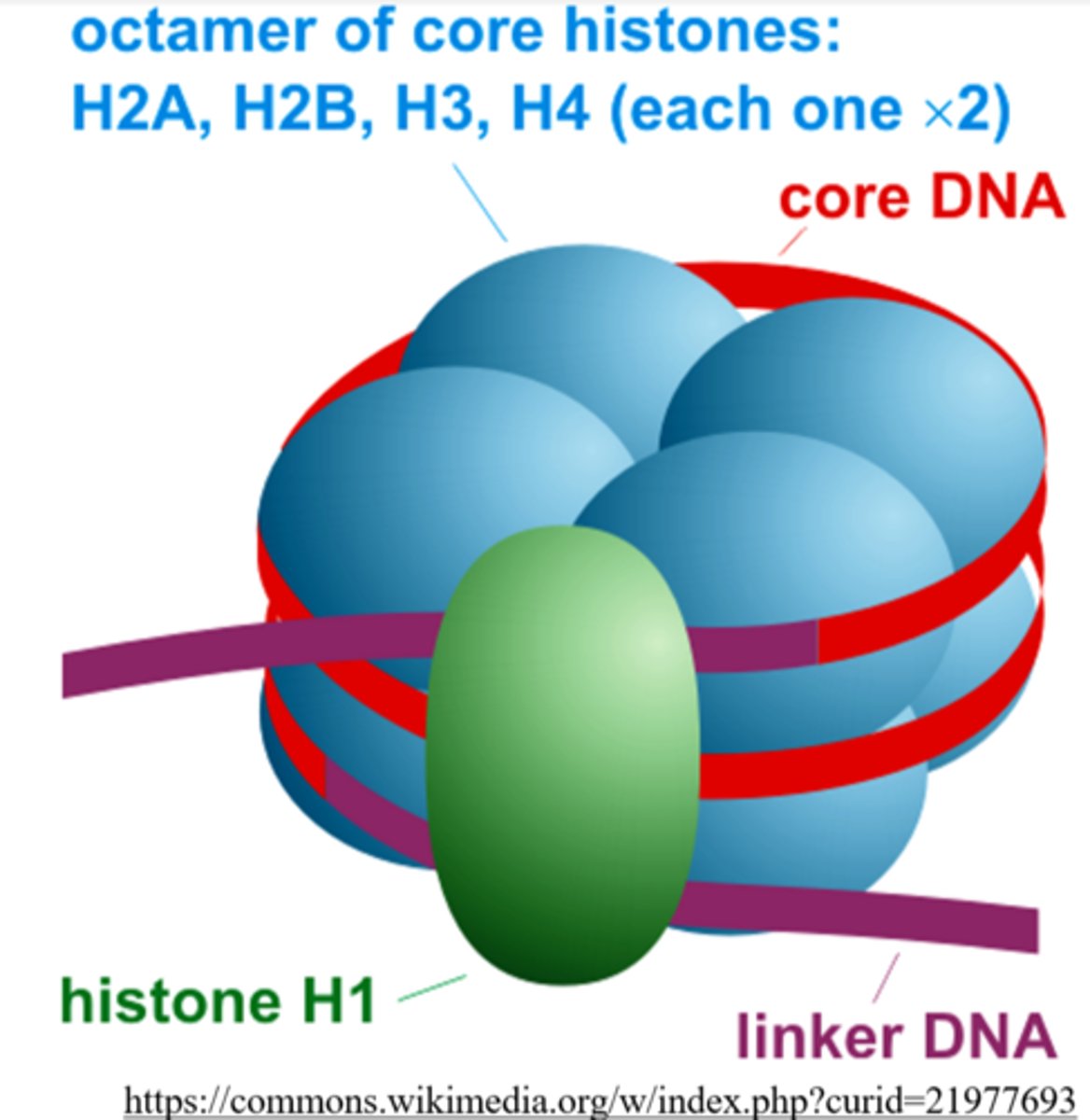
which histone protein keeps the DNA wrapped around the histone core in a nucleosome?
H1
_____ represents parts of DNA that consist of "loosely-packed" nucleosomes
euchromatin
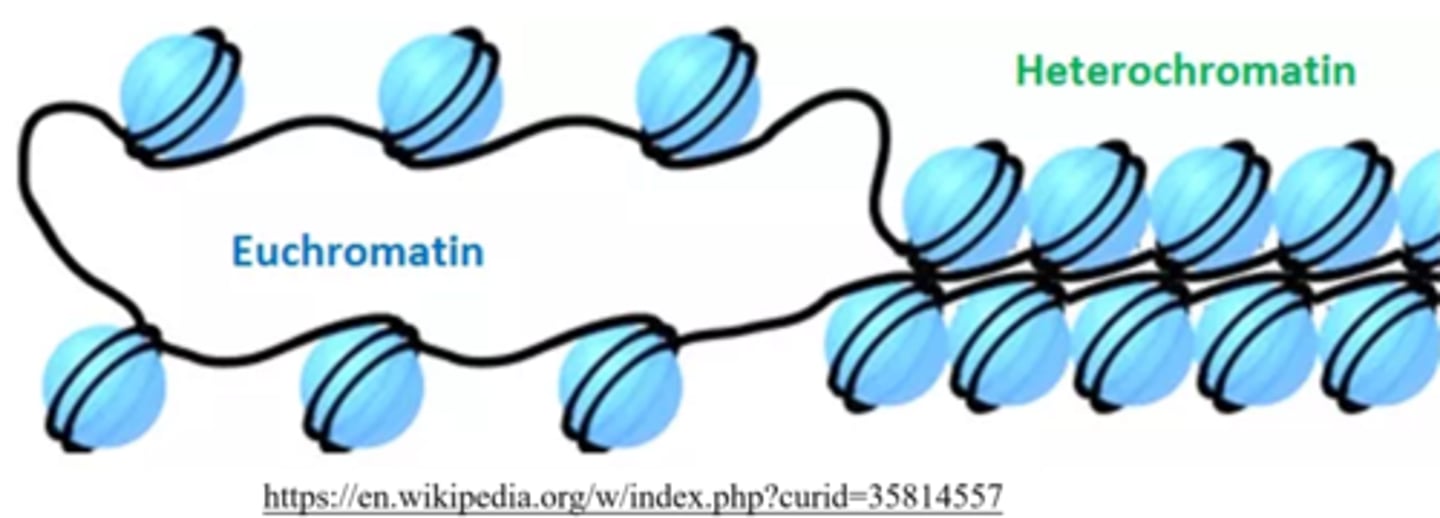
euchromatin is _____ for RNA polymerases to access and transcribe
easy
_____ represents parts of DNA that consist of "tightly-packed" nucleosomes
heterochromatin
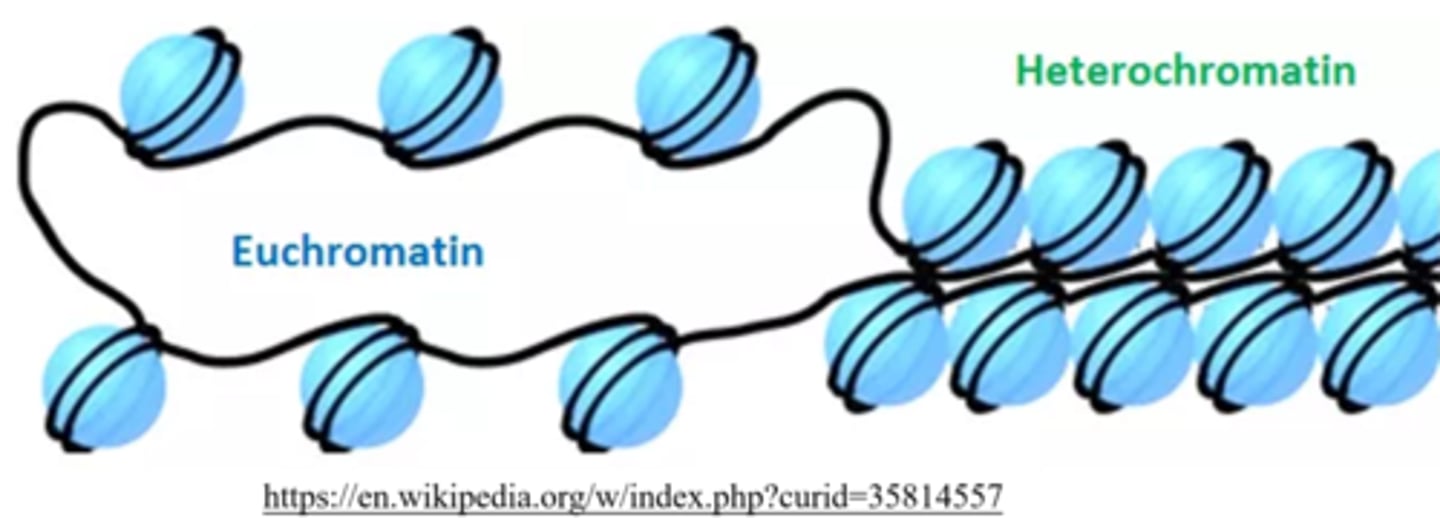
heterochromatin tends to be _____ in transcription
inactive
histones are _____ charged
positively
DNA is _____ charged
negatively
acetylation of histones increases _____ levels and therefore increases _____
euchromatin; transcription
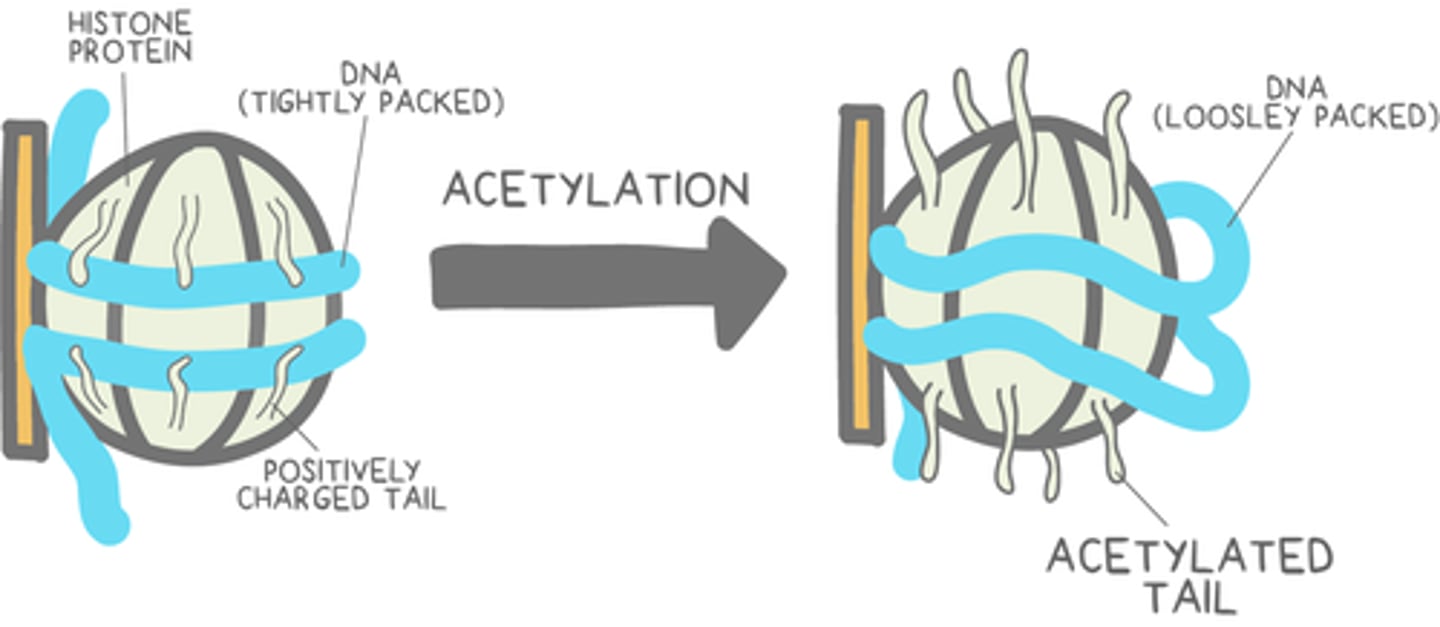
deacetylation of histones increases _____ levels and therefore decreases _____
heterochromatin; transcription
histone methylation _____ DNA transcription levels
both increases and decreases
DNA methylation typically _____ transcription levels
decreases
what is the origin of replication?
particular sequence of DNA where replication begins
how does the origin of replication differ between eukaryotic and bacterial DNA?
bacteria only have one origin, while eukaryotes have multiple
each single strand of DNA is made of a chain of nucleotides, which are linked together by _____ bonds
phosphodiester
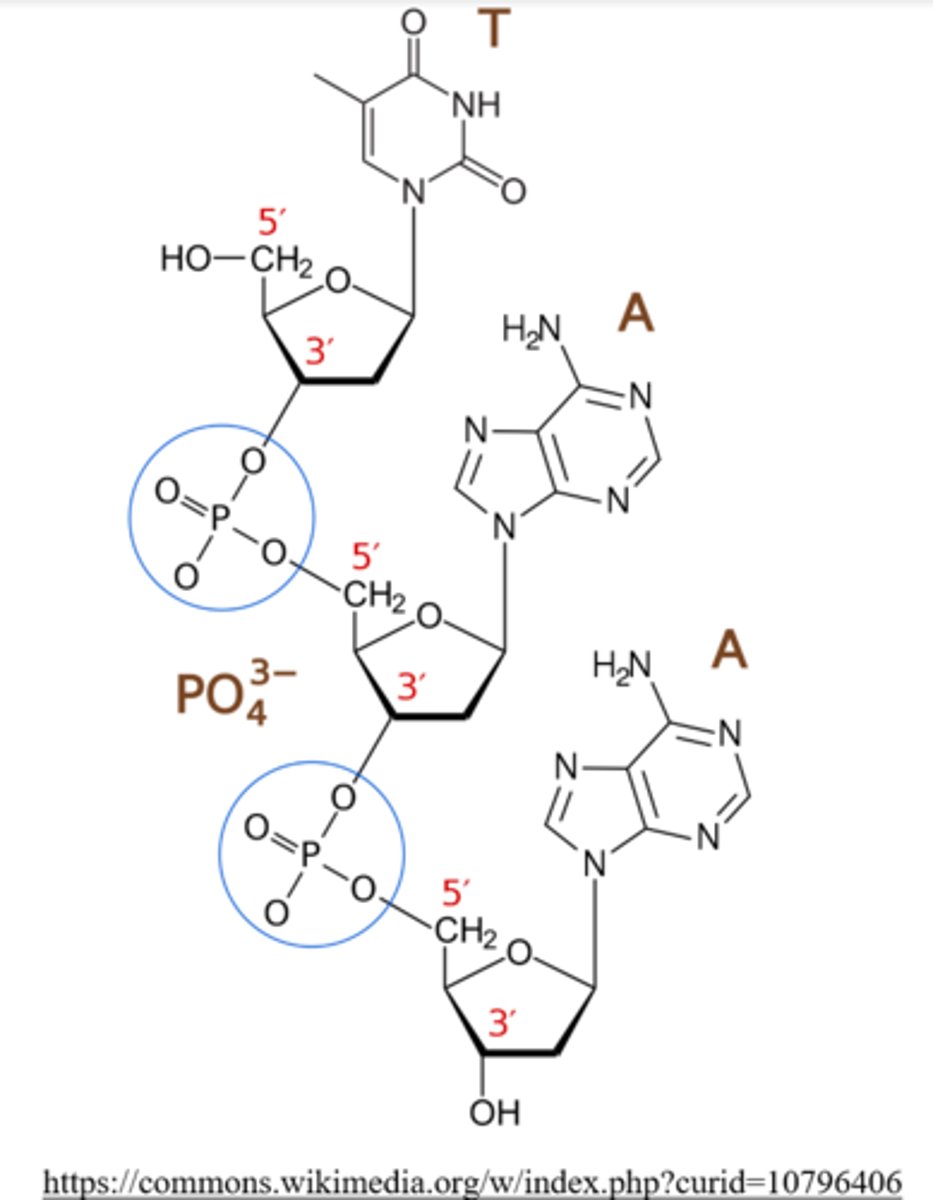
the ______ end of DNA has the terminal phosphate group
5'
the _____ end of DNA has the terminal hydroxyl group
3'
origins of replication tend to occur at _____ rich segments
A=T
after helicase unzips DNA during replication, _____ attach to each strand of uncoiled DNA to keep them separated
single-strand binding proteins
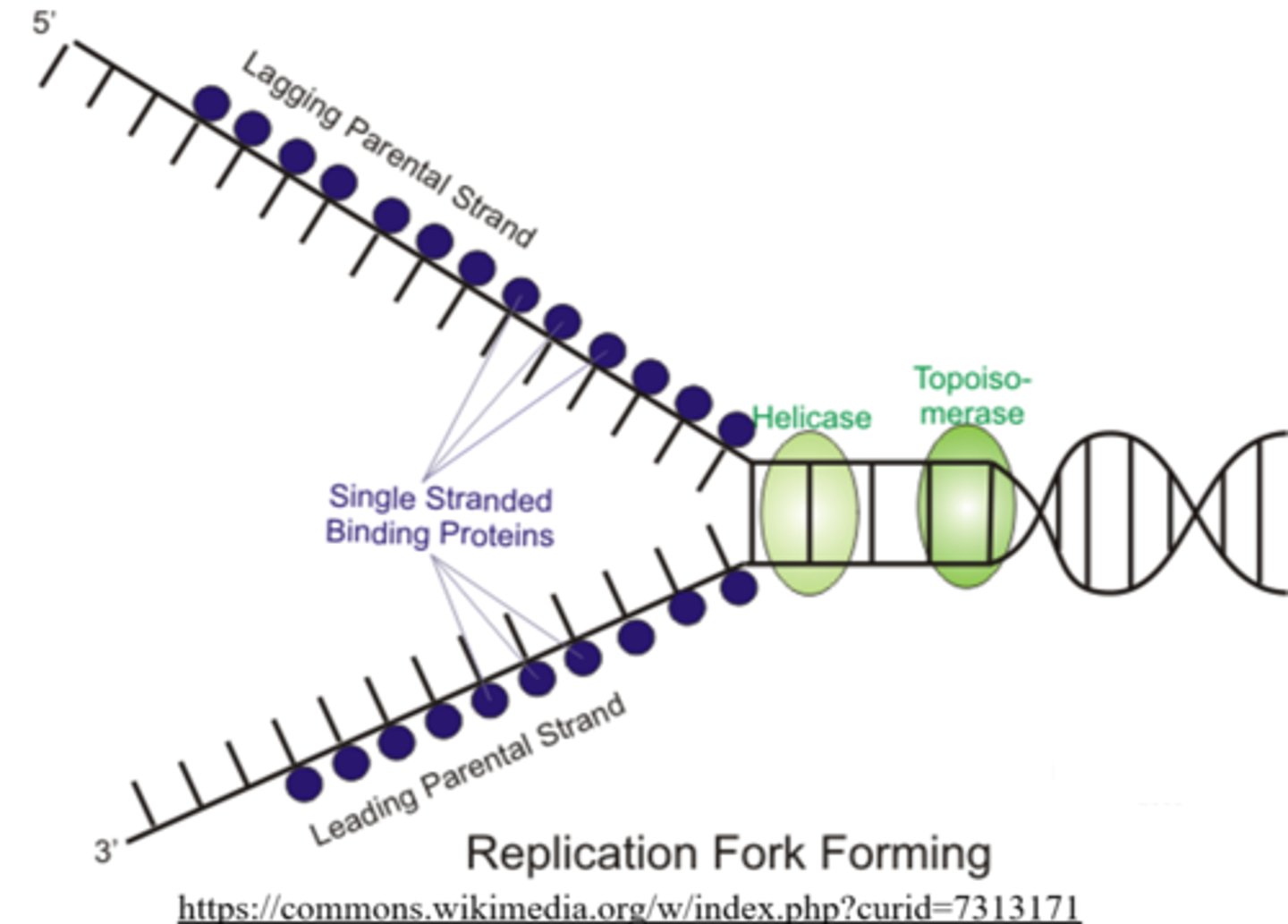
_____ creates small nicks within the DNA double helix ahead of the replication fork, to relieve tension created by DNA helicase
topoisomerase
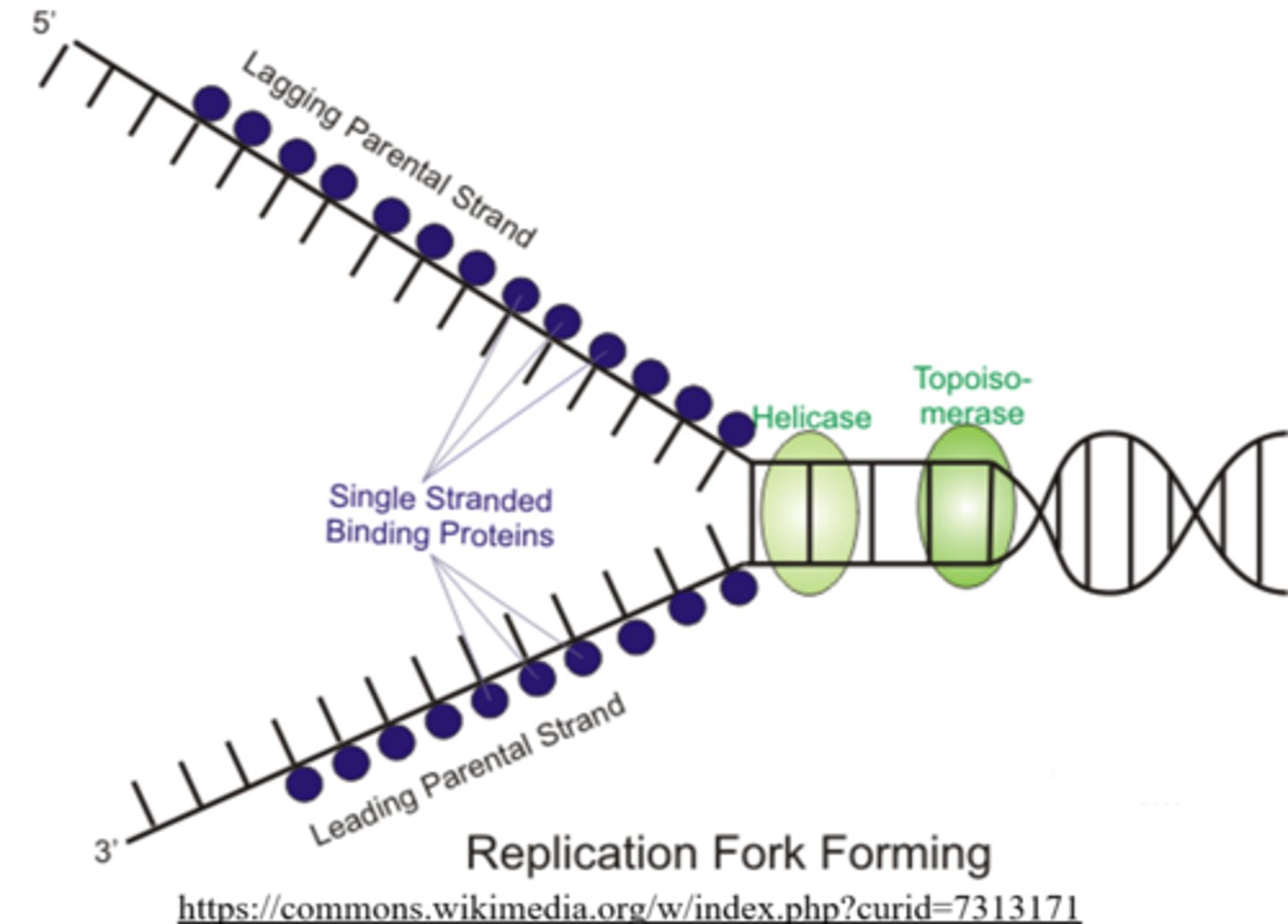
_____ is a subtype of DNA topoisomerase found in bacteria and plants
DNA gyrase
_____ are sequences of repeated nucleotides at the end of a chromosome that don't code anything
telomeres
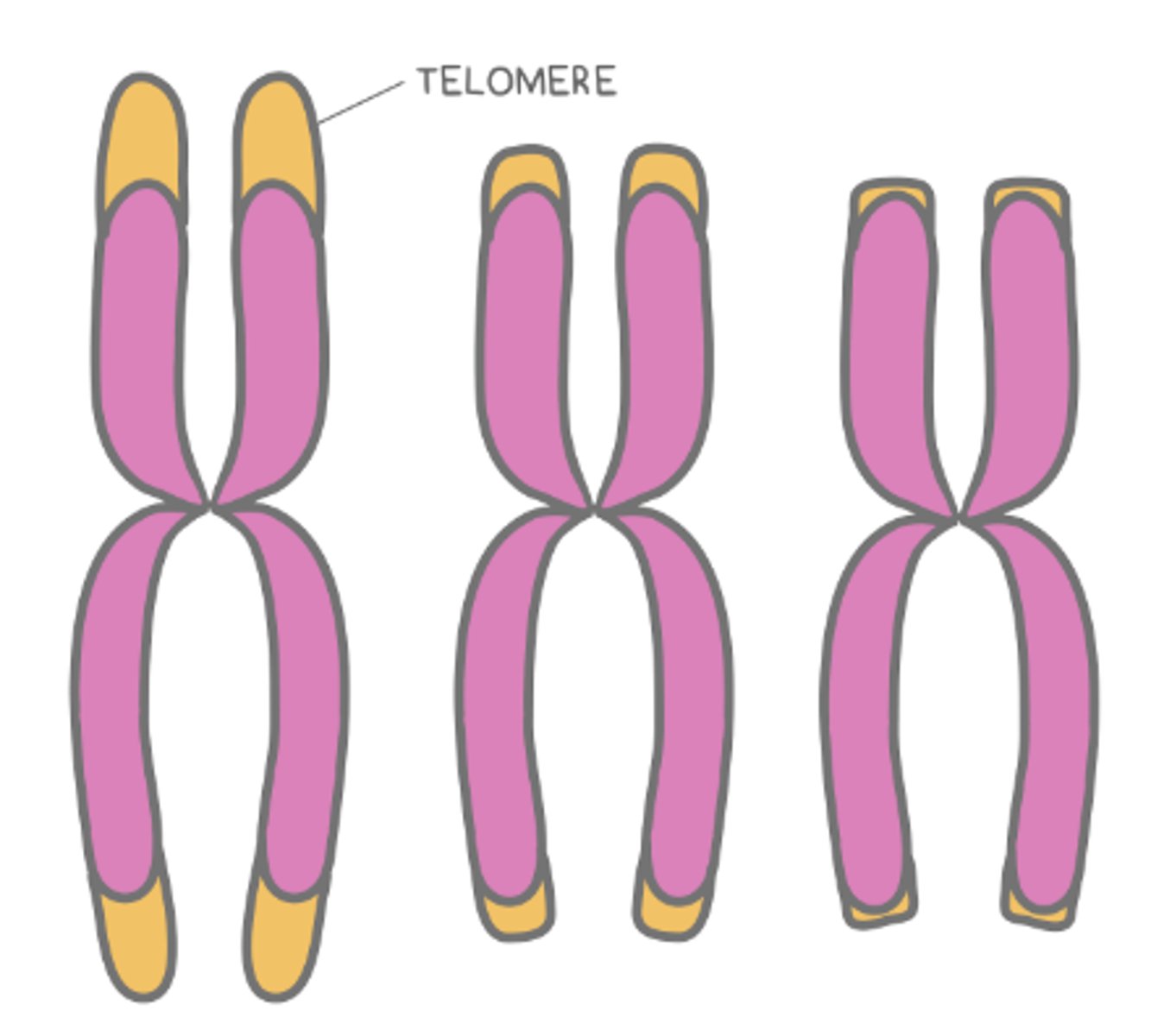
telomeres are only necessary in ______ organisms
eukaryotic
why are telomeres not necessary in prokaryotes?
they have circular chromosomes
_____ is an enzyme that catalyzes the lengthening of telomeres in eukaryotic cells
telomerase
DNA polymerase can only add DNA nucleotides off an existing _____
3' hydroxyl group
_____ provides a 3' hydroxyl group for DNA polymerase to attach new nucleotides to
primase
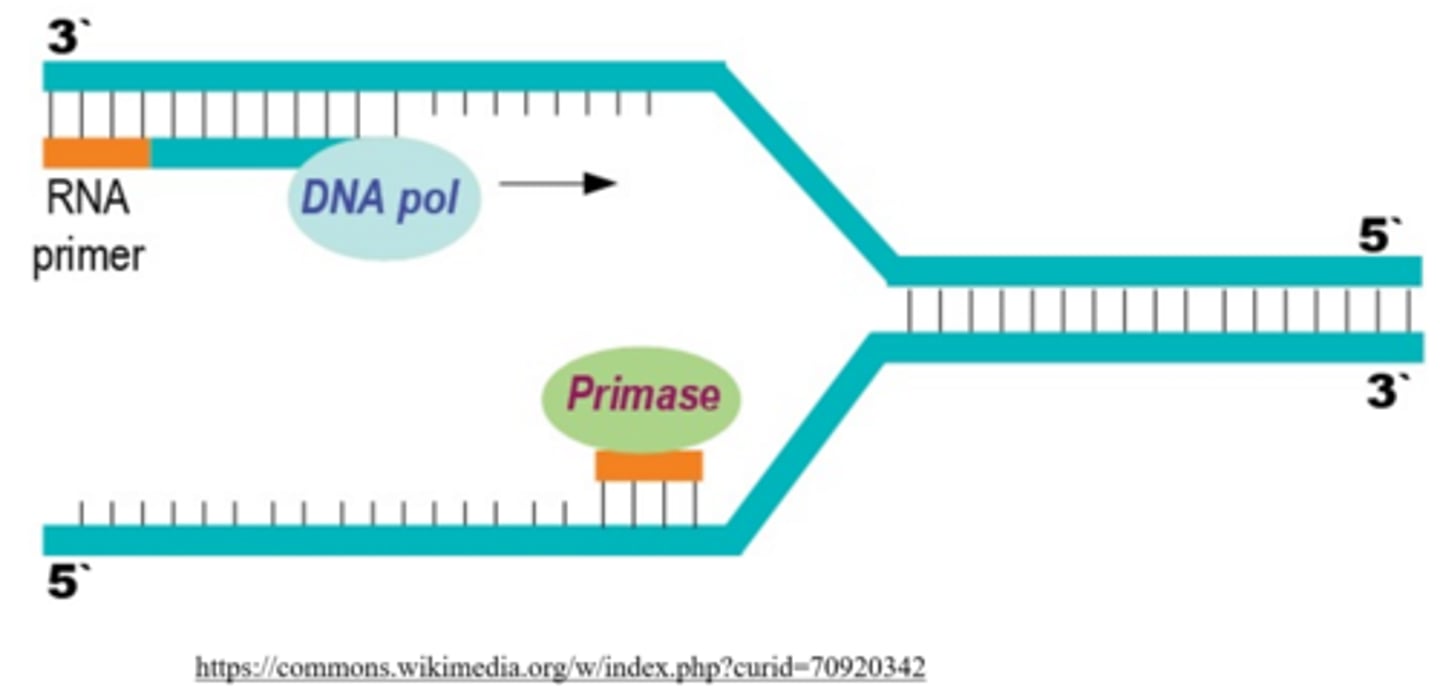
a _____ is a protein that helps to hold DNA polymerase to the template strand
DNA sliding clamp
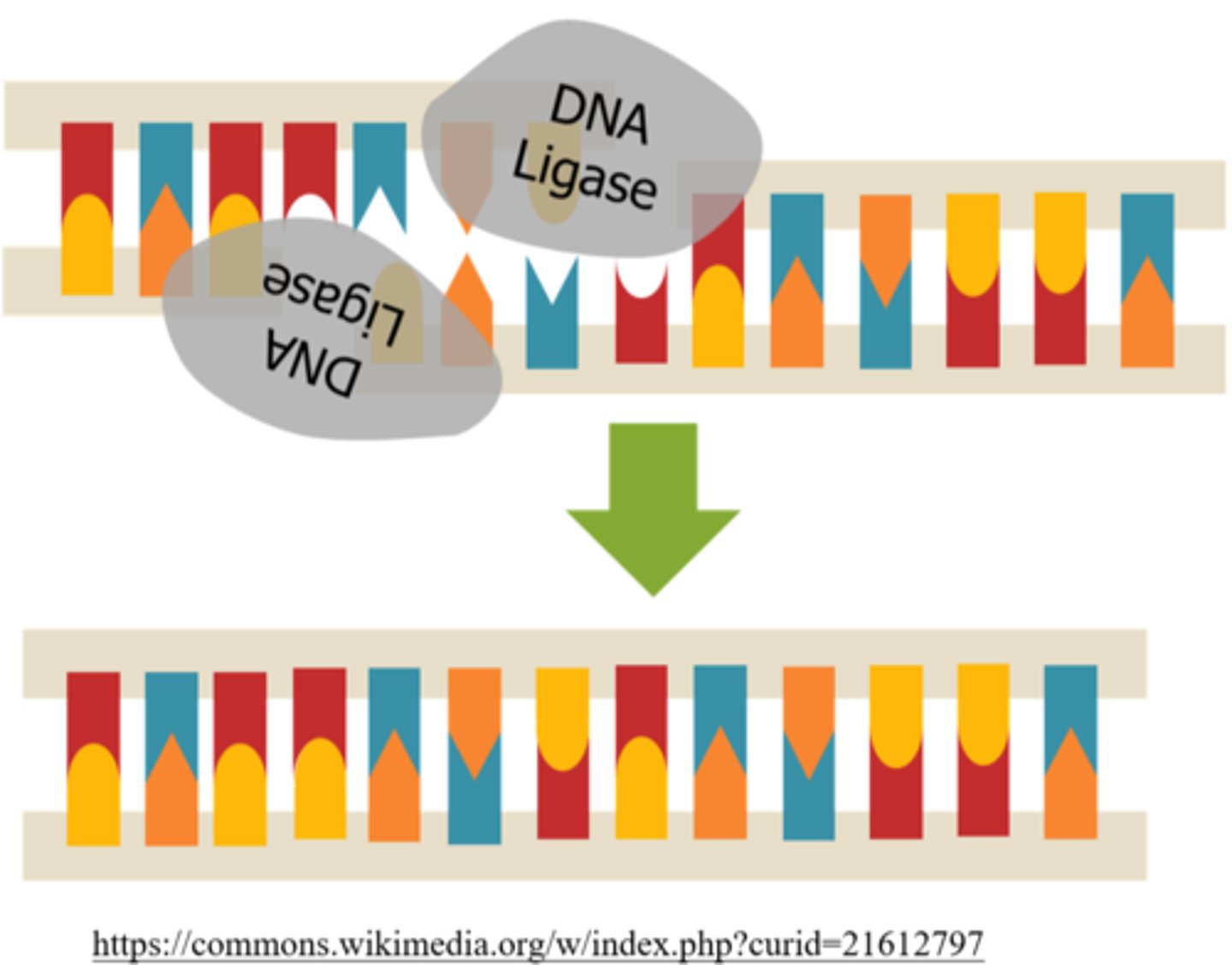
_____ is an enzyme that covalently links DNA ends together, which is important for connecting Okazaki fragments
DNA ligase
in prokaryotes, transcription occurs in the _____ (location)
cytosol
which two elements are present in bacterial promoters that help initiate transcription?
-10 and -35 elements
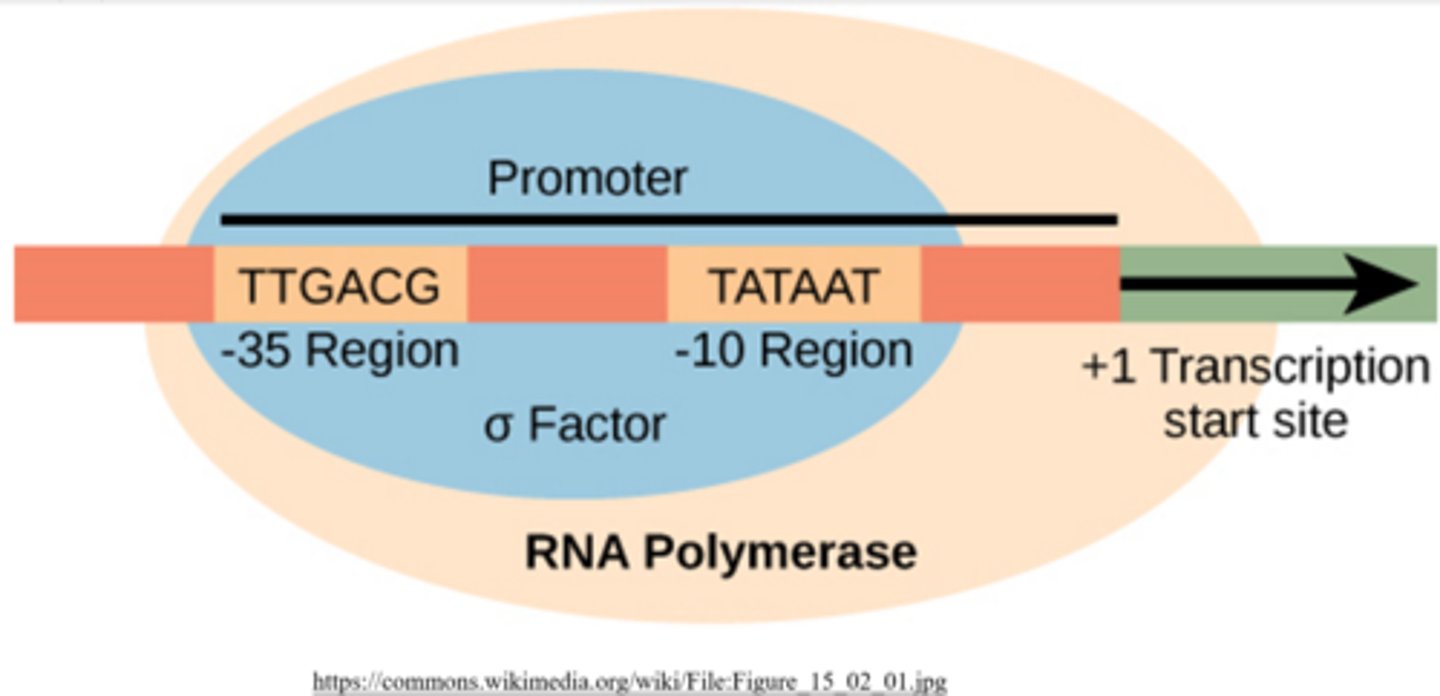
prokaryotic core RNA polymerase combines with _____ to form _____, which has the ability to target the promoter region of bacterial DNA
sigma factor; RNA polymerase holoenzyme
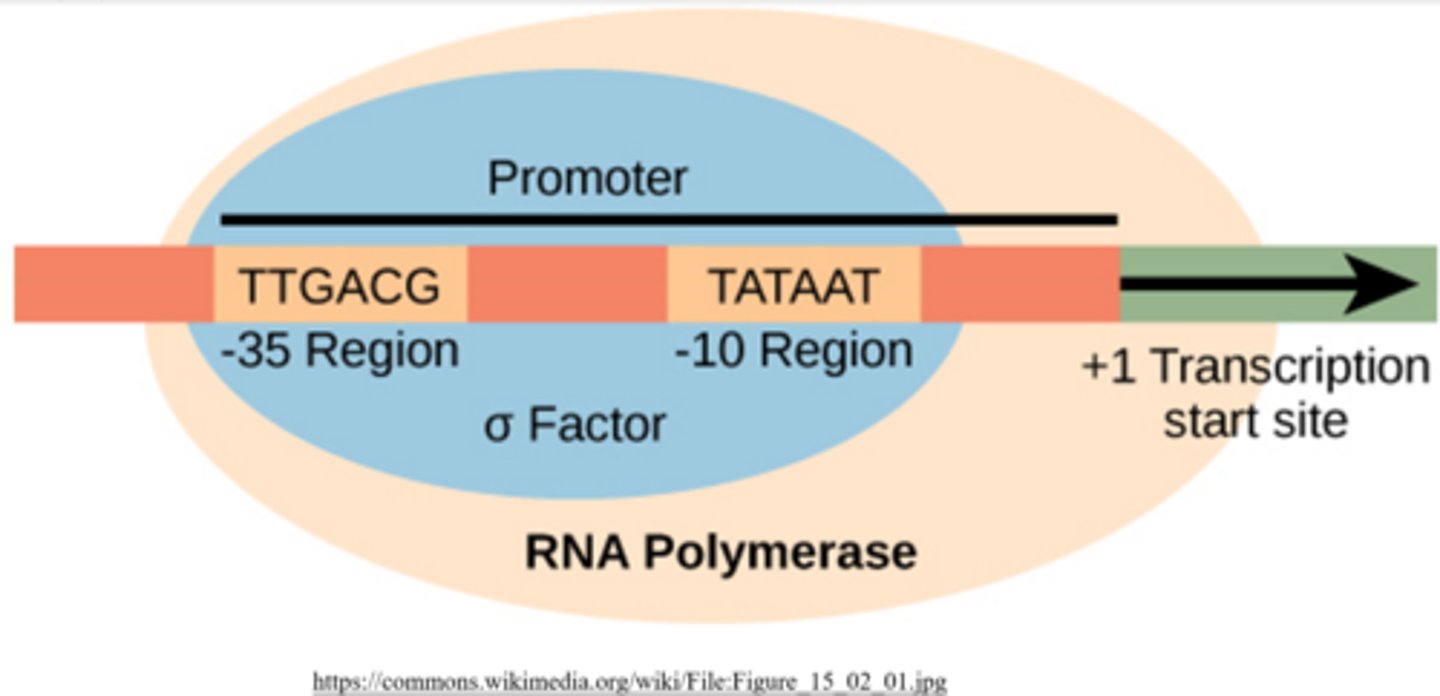
what are the two types of transcriptional termination in bacteria?
rho dependent, rho independent
an _____ is when a group of related genes are under the control of 1 promoter site, and they function to make sure the cell conserves its resources
operon
the _____ is an inducible operon that aids in control of transcription of lactose metabolizing genes in E. coli
lac operon
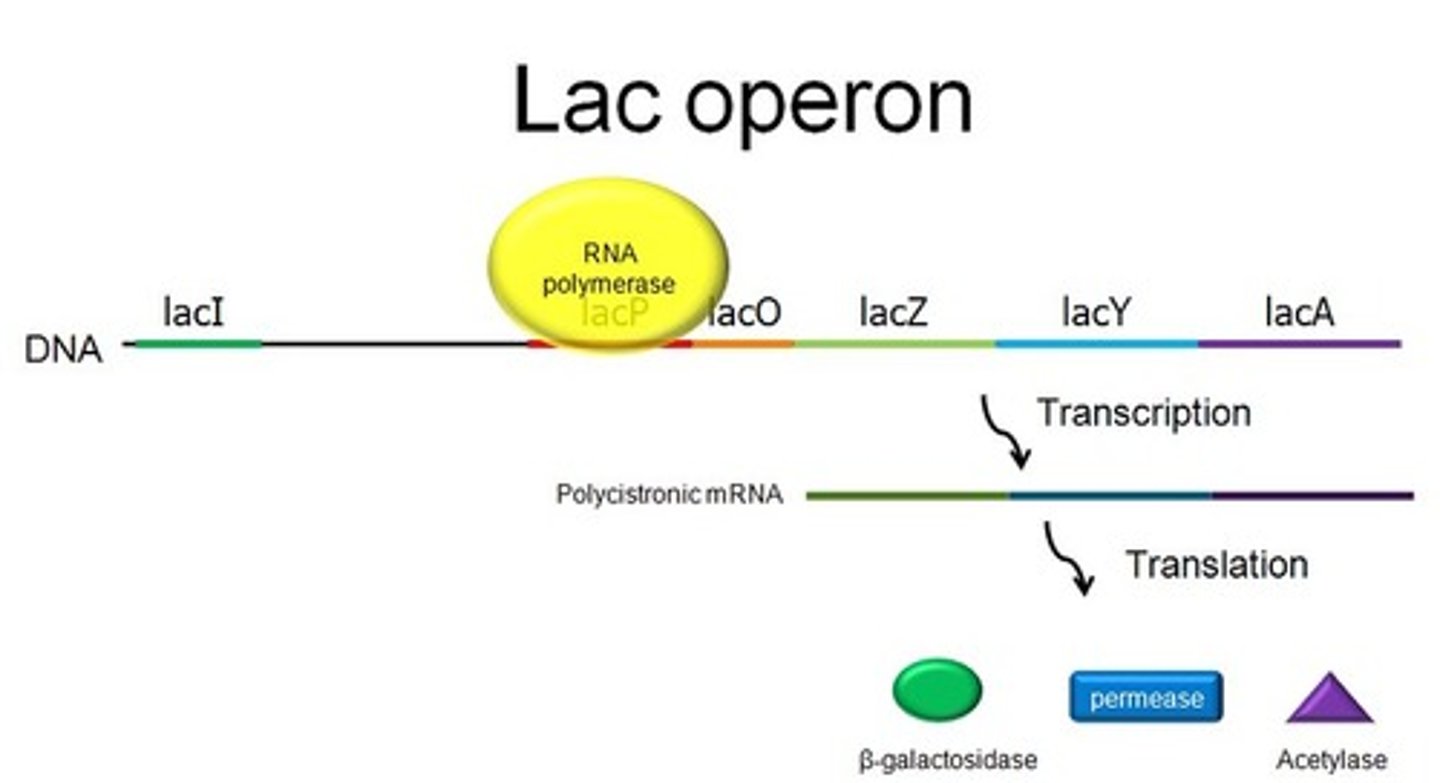
an _____ operon is one that is usually inactive, unless it is made to become active
inducible
a gene that is always being transcribed and translated is _____ expressed
constitutively