BIOL 1030 / Topic 2c: Animal Phyla - Deuterostomia
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Phylum Echinodermata
Phylum charactered by being spiny-skinned deuterostomes with a water vascular system, bearing larvae exhibiting bilateral symmetry but most adults exhibiting pentaradial symmetry.
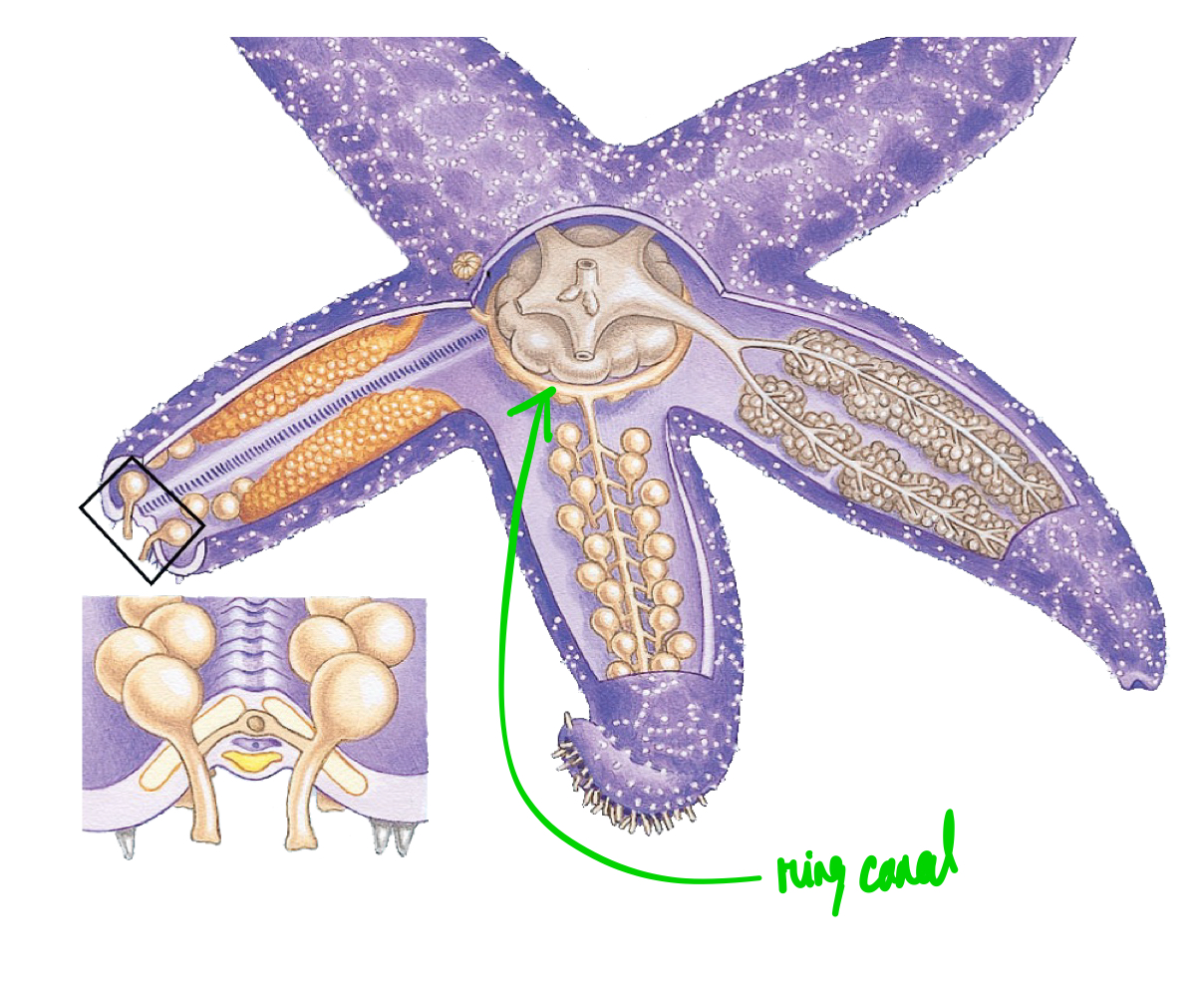
Ring canal
Circular water-filled tube, connecting to radial canals, functioning as a central hub for nutrient distribution and waste expulsion.
Water vascular system
System of tube feet, canals, smooth muscle generating water pressure, and chemical glue attaching to substrate.
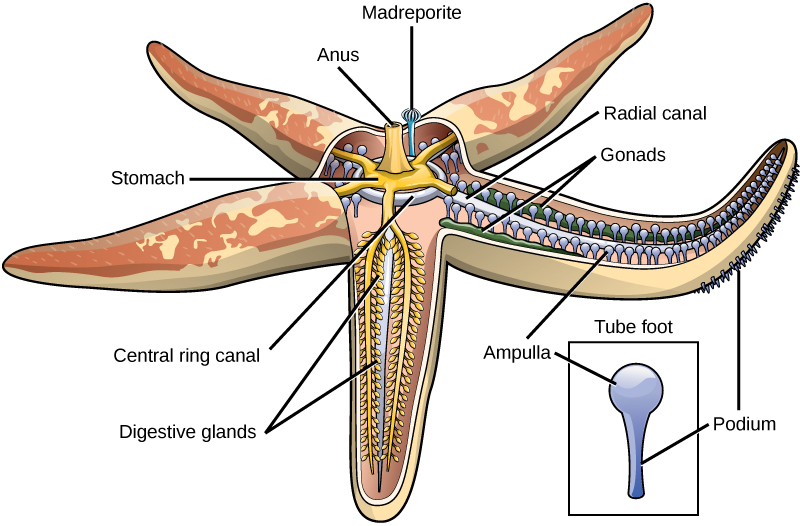
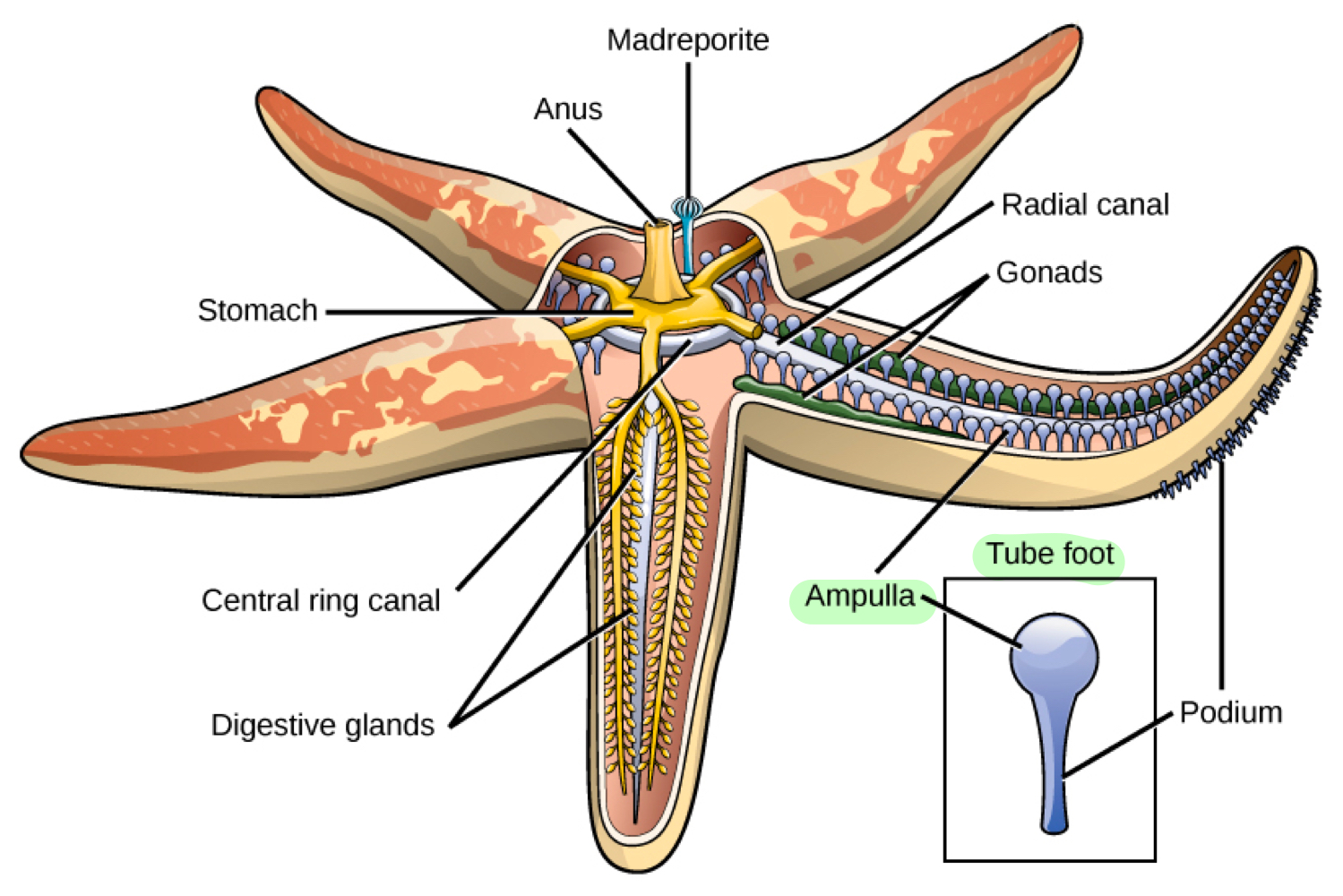
Tube feet
Hydraulic structures functioning for locomotion, with each tube foot containing an ampulla, a small bulb-like structure.
How do echinoderms move?
Ampullae sucks water into the tube foot, stretching the tube foot, and muscles in the tube foot contract to shorten them, pulling the animal along.
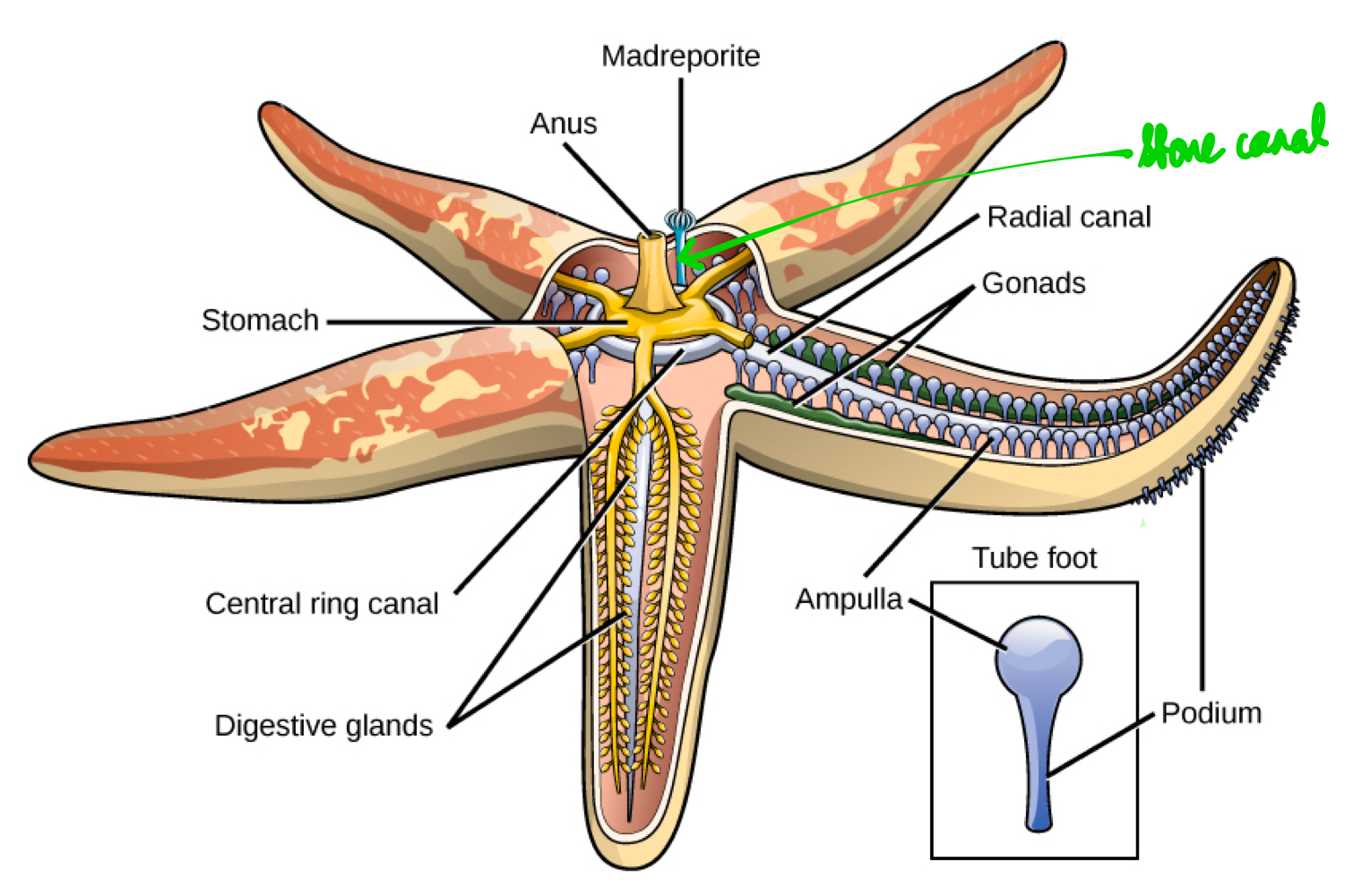
What’s a madreporite? And what is the order of how water enters the echinoderm?
Tiny plate at the centre of the echinoderm, allowing water inside.
Water flows to the madreporite, to the stone canal, to the ring canal, to the radial canal, and to the tube feet.
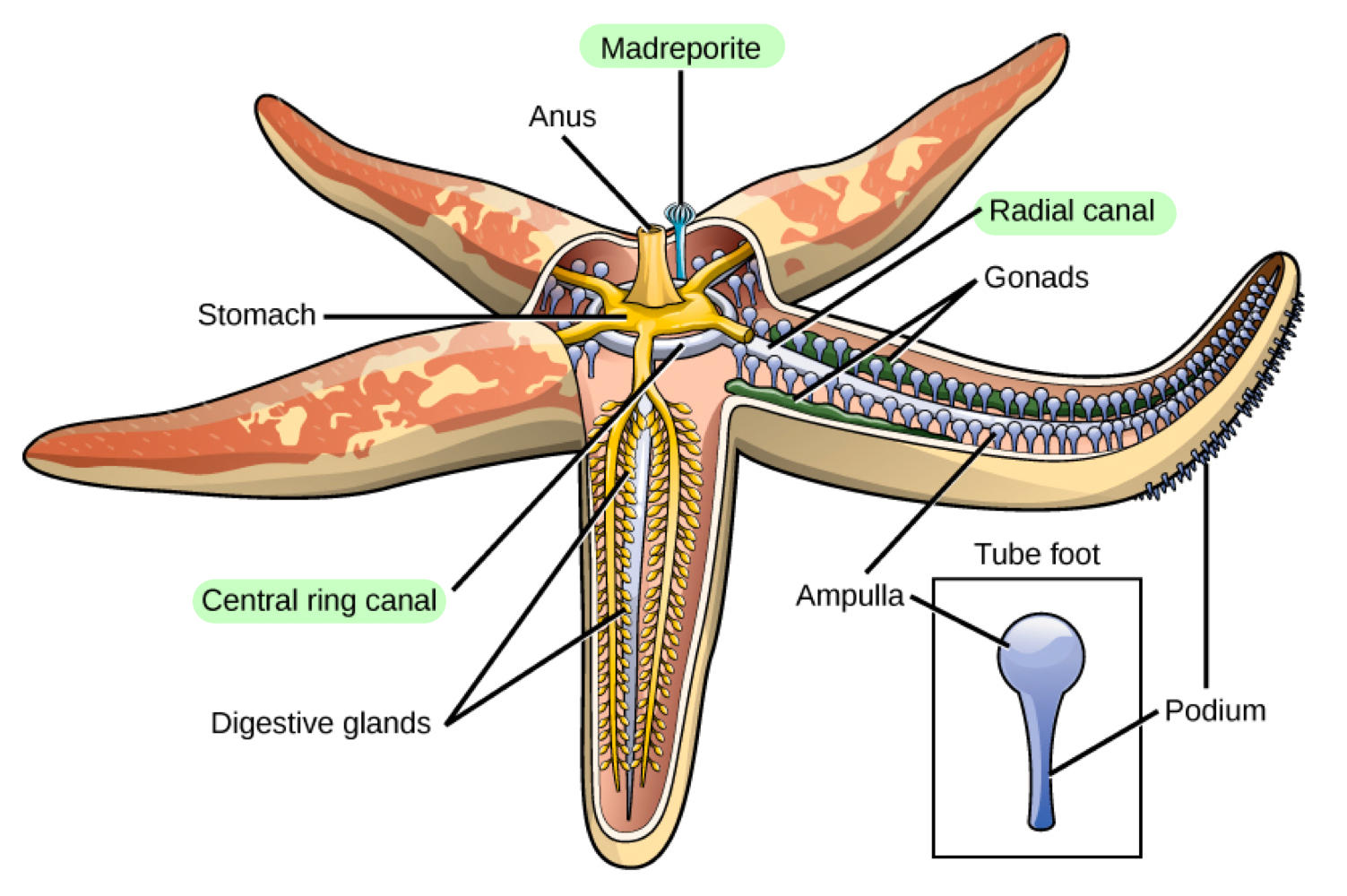
Stone canal
Tubular structure connecting madreporite to ring canal.
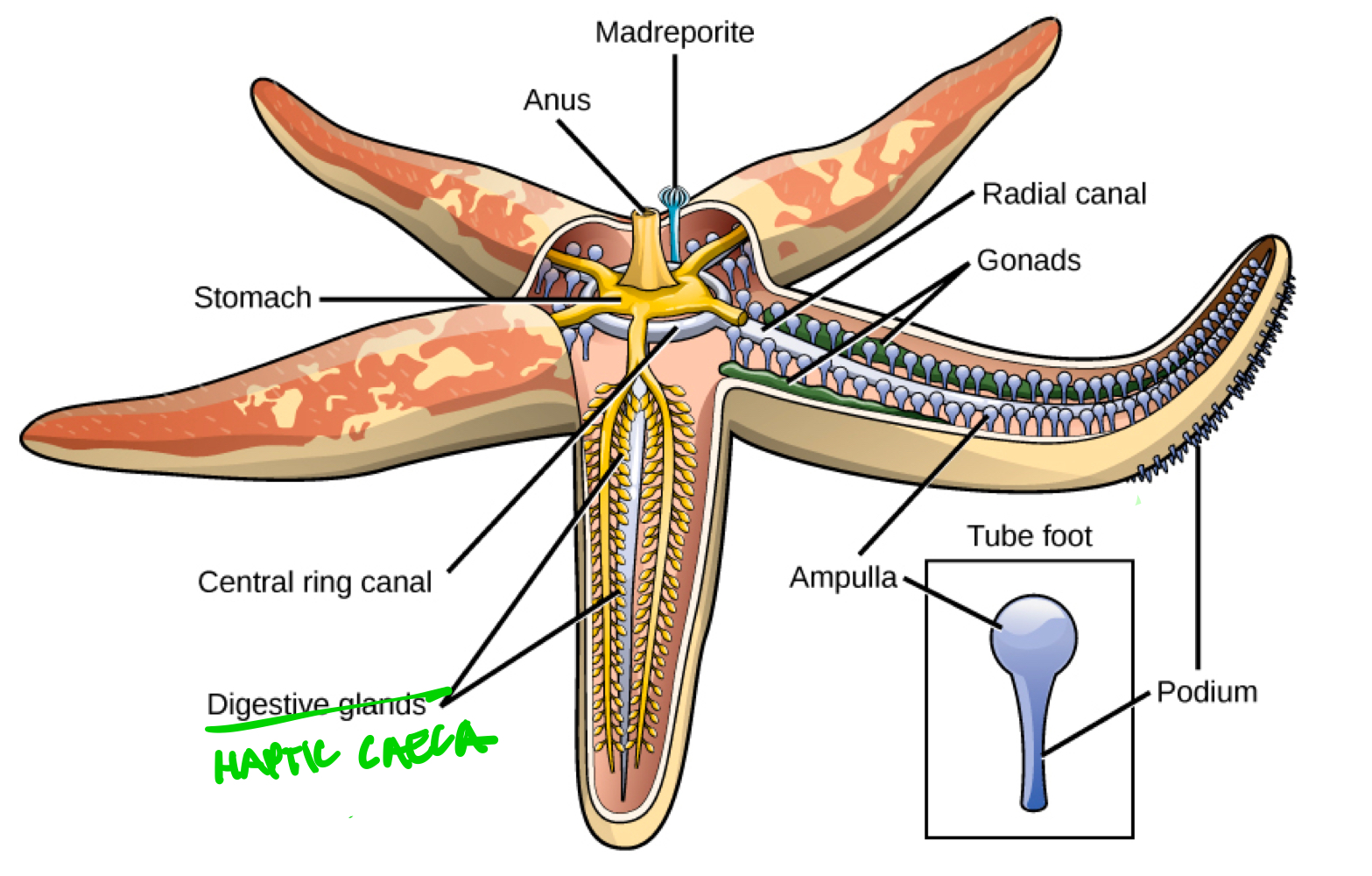
Hepatic caeca
Literally meaning “liver-like gut,” they are the digestive glands of echinoderms.
Echinoderm’s cardiac stomach
Part of digestive system turning inside out through its mouth to engulf and digest prey.
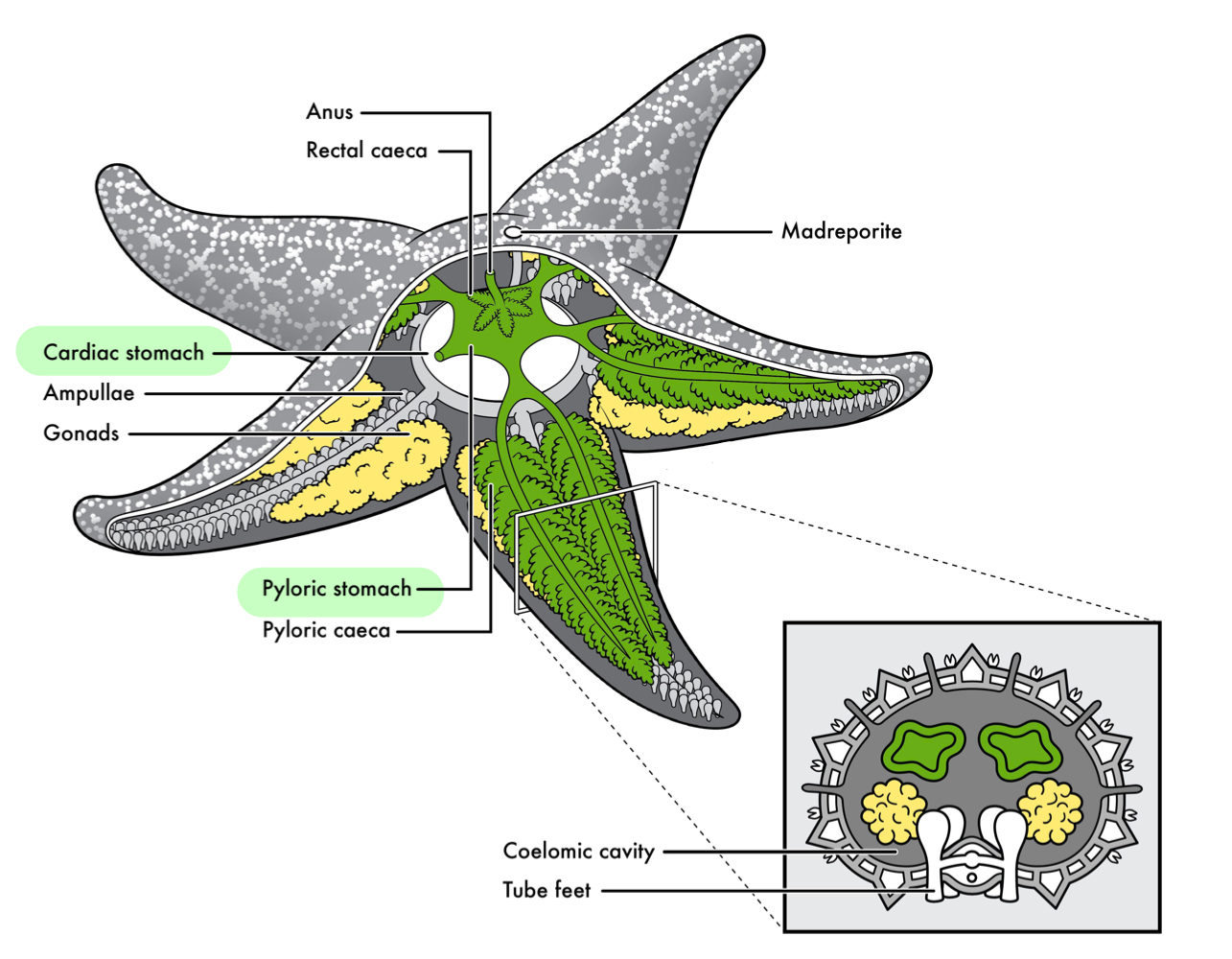
Echinoderm’s pyloric stomach
Part of digestive system where food is transferred after its placement in cardiac stomach.
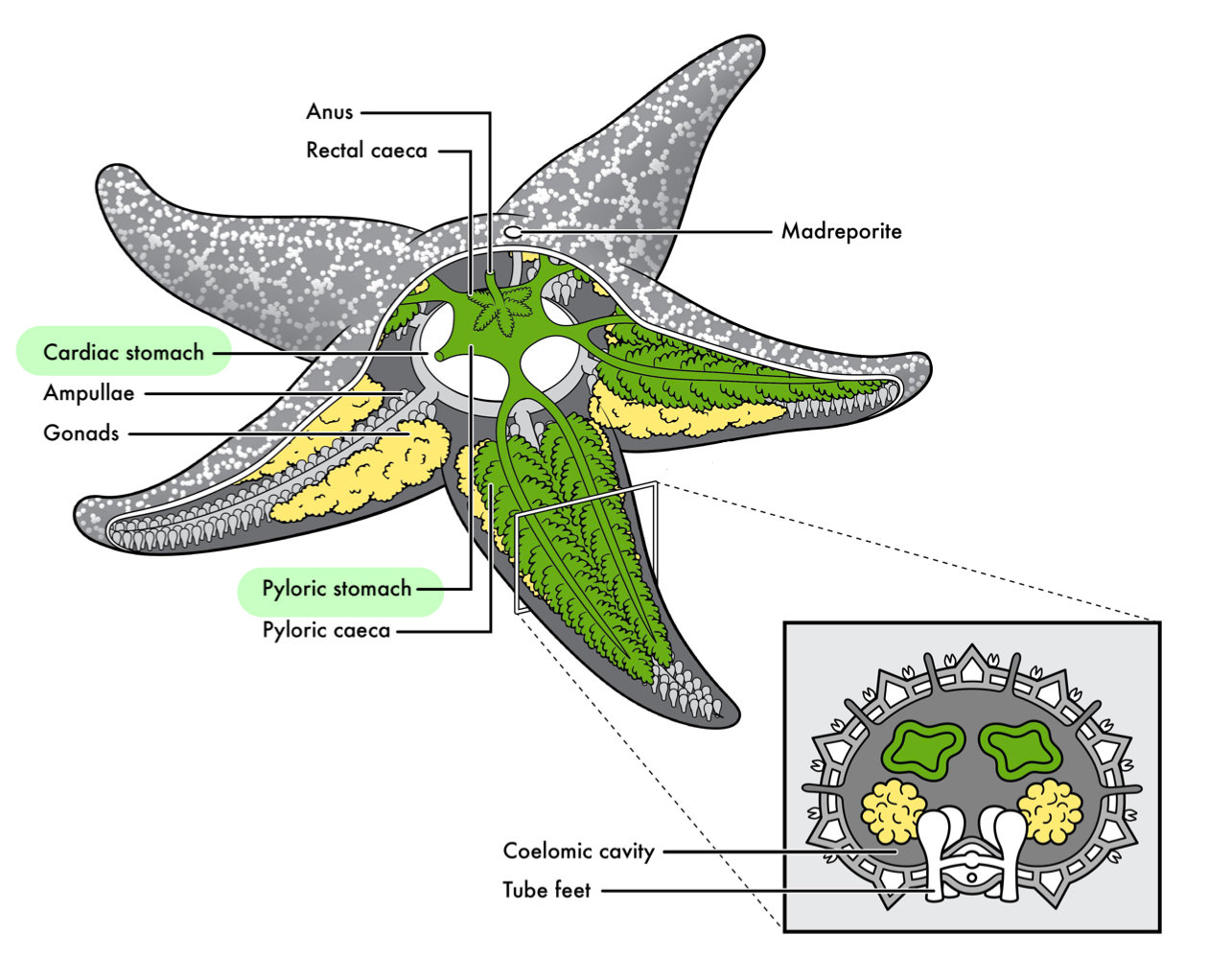
How do echinoderms eat, digest, and expel waste?
Food enters mouth, goes to hepatic caeca for breakdown, and waste is expelled out the anus.
How do echinoderms reproduce?
Sexually and asexually by fission.
There are 3 clades within the phylum Echinodermata. Name them and differentiate them.
Clade Asteroidea, wherein Ec looks like a star.
Clade Echinoidea, wherein Ec looks like a spiney sphere.
Clade Holothuroidea, wherein Ec has modified tube feet for physical intimidation. They don’t use it much for physical defense.

Phylum Chordata
Phylum charactered by their notochord, dorsal hollow nerve chord, pharyngeal gill slits, and post-anal tail.
What’s the difference between the gills, the gill slits, and the gill arches?
Gills are respiratory organs found in aquatic animals that extract oxygen from water and release carbon dioxide.
Gill slits are individual openings to gills.
Gill arches are skeletal structures, supporting the gills.
Define each of the four anatomical features in chordates.
The notochord provides skeletal support, developing into the vertebral column in vertebrates.
The dorsal hollow nerve cord develops into the central nervous system.
The gill slits are openings in the pharynx that, commonly: (a) in invertebrate aquatic chordates, filters water; (b) in vertebrate aquatic chordates, develop into gill arches, such as in bony fish, and; (c) in terrestrial animals, develops into the jaw and inner ear bone.
The post-anal tail is a muscular region of the body aiding locomotion and balance.
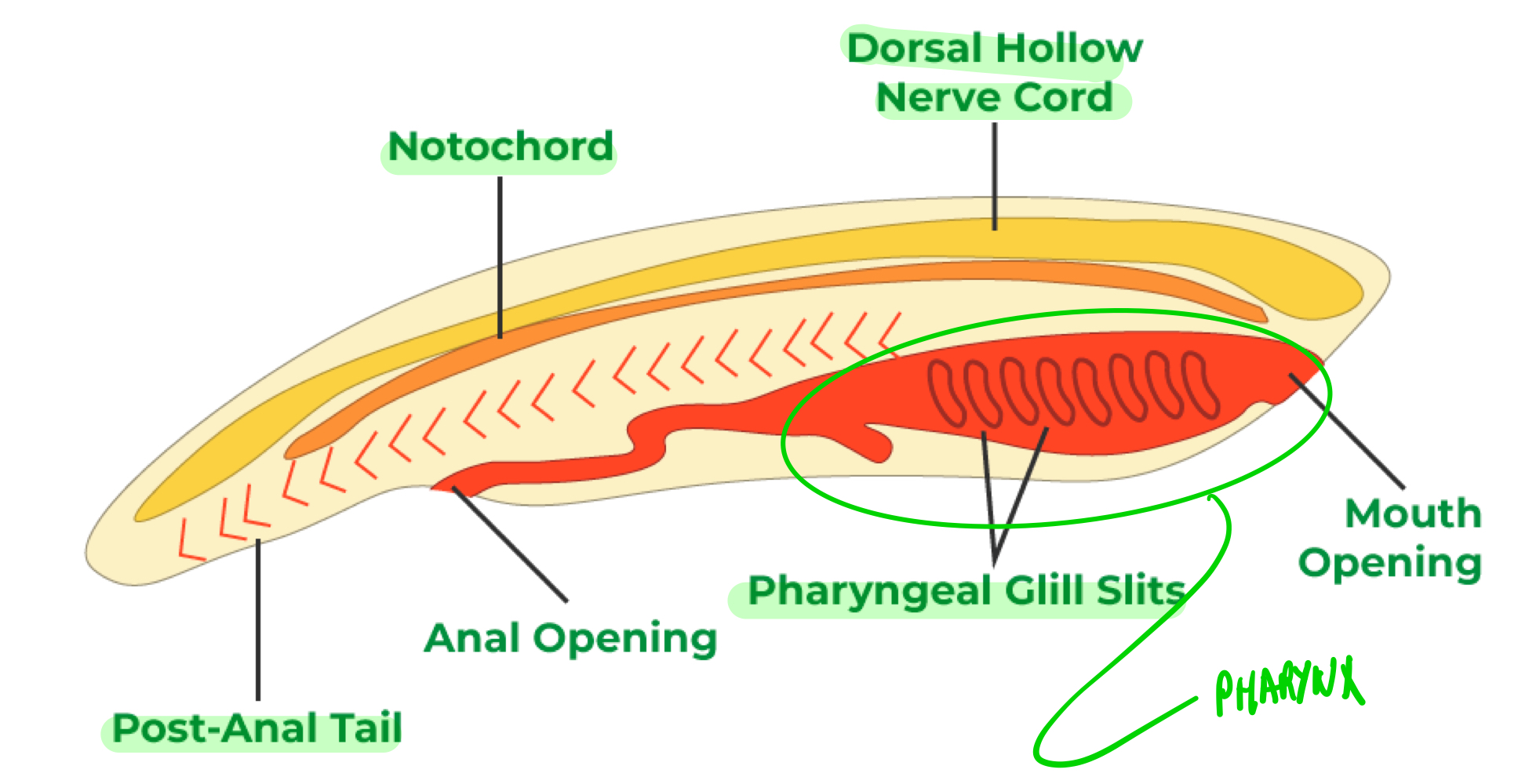
Pharynx
The region leading from the mouth and nose to the esophagus and larynx.
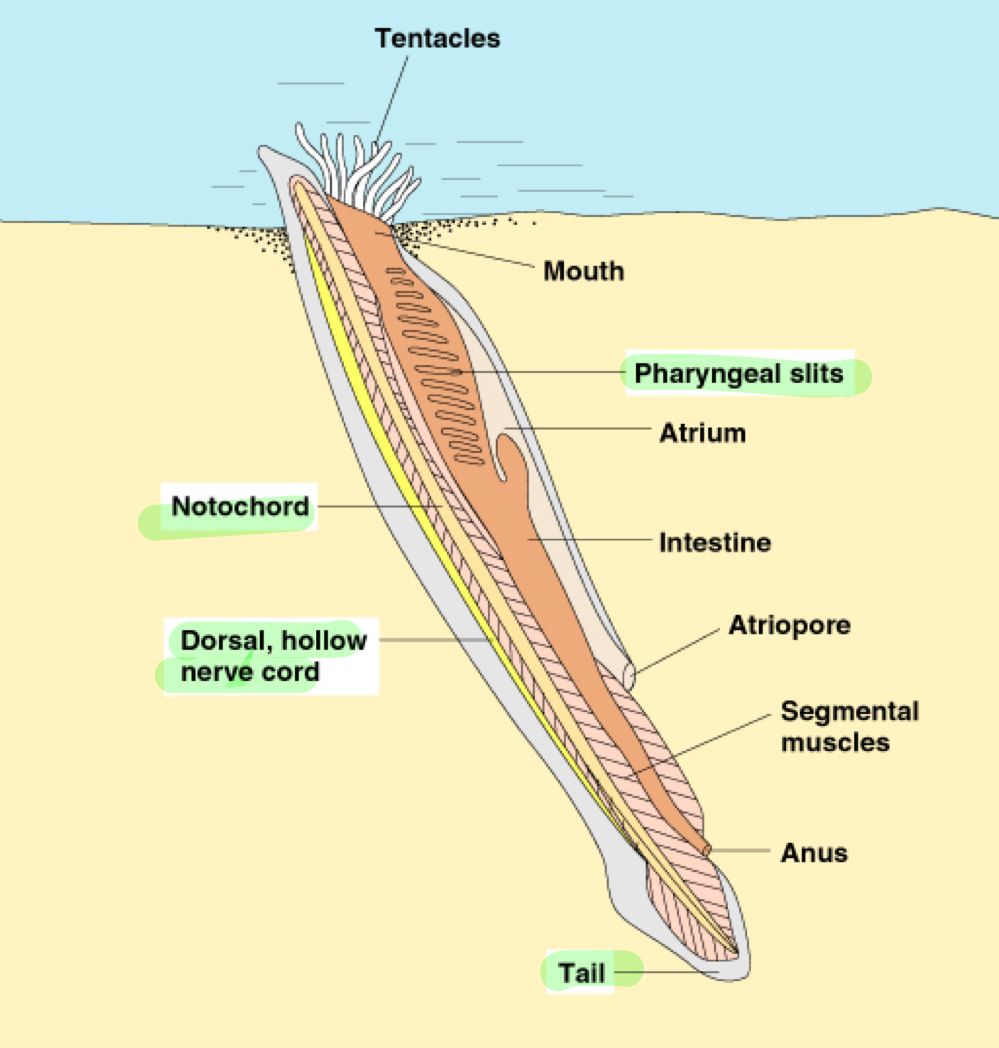
Cephalochordata
Chordata clade made of the lancelets, they are small, fish-like animals that are the only chordates retaining the big four throughout their life.
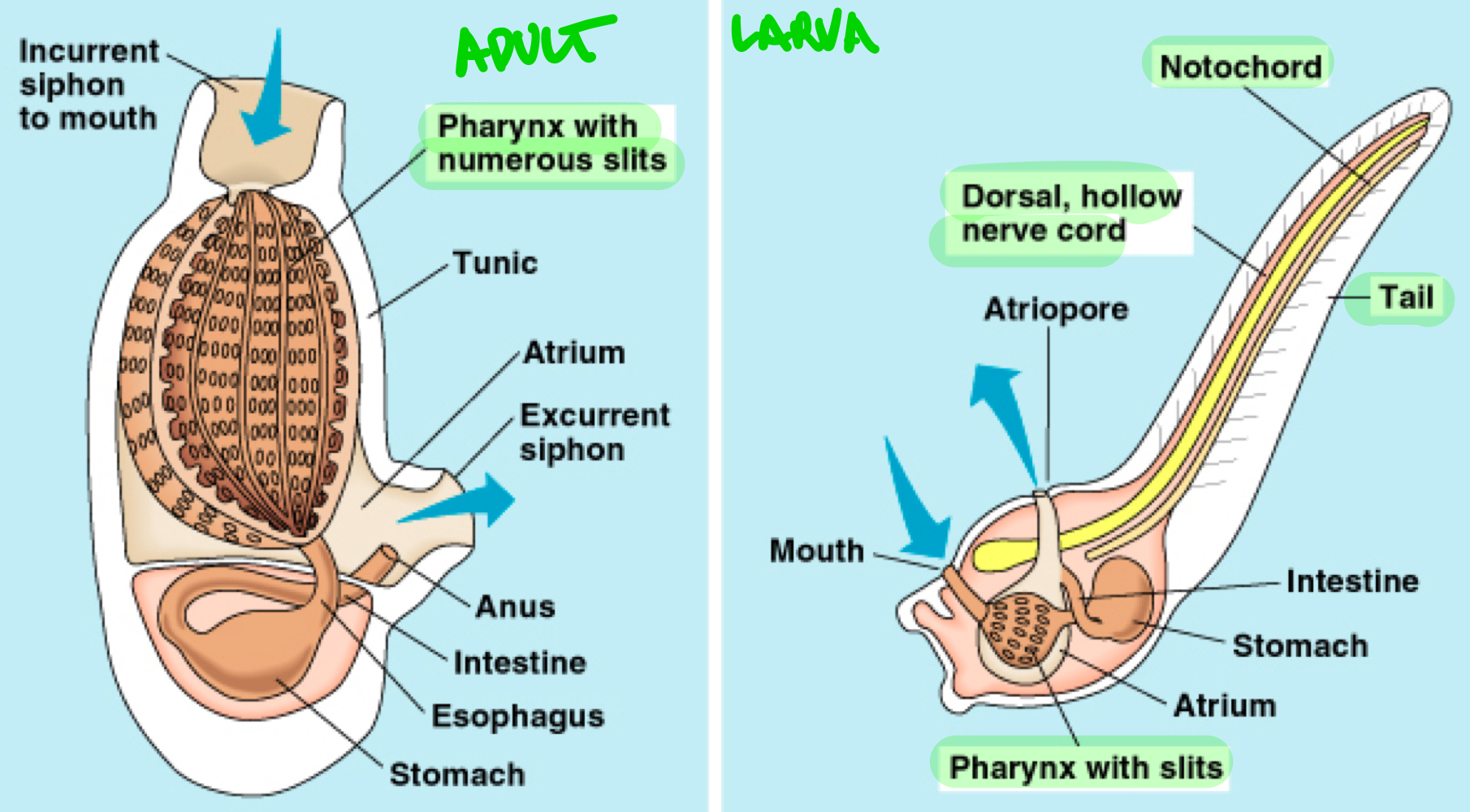
Urochordata
Chordata clade made of the tunicates or “sea squirts,” they possess the big four during their larval stage but only keep the gill slits during their adult stage, modifying the slits into a pharyngeal basket to filter water and food particles.
Vertebrata
Chordata clade composing most of the phylum, charactered by a vertebral column and cranium.
What are cyclostomes? Provide 2 examples of a cyclostome.
Basal vertebrate clade, possessing a circular mouth with no jaws, capability of producing slime through slime glands as defence mechanism, and capability of absorbing nutrients using their skin. E.g. hagfish and lampreys.
Gnathostomes
Vertebrate clade possessing hinged jaws from gill arches to capture prey.
Chondrichthyans
Basal gnathostome clade, possessing skeletons made of cartilage, e.g. ratfishes, rays, and sharks.
Osteichthyans
Gnathostome clade with bones and lungs, with the first forming a skeleton hardened with calcium phosphate and the latter evolving to take oxygen from air when it was scarce in water.
Actinopterygians
Basal osteichthyan clade with fishes that have rayed and upgraded, membranous fins.
Sarcopterygians
Osteichthyan clade with fishes that have lobed and fleshy fins.
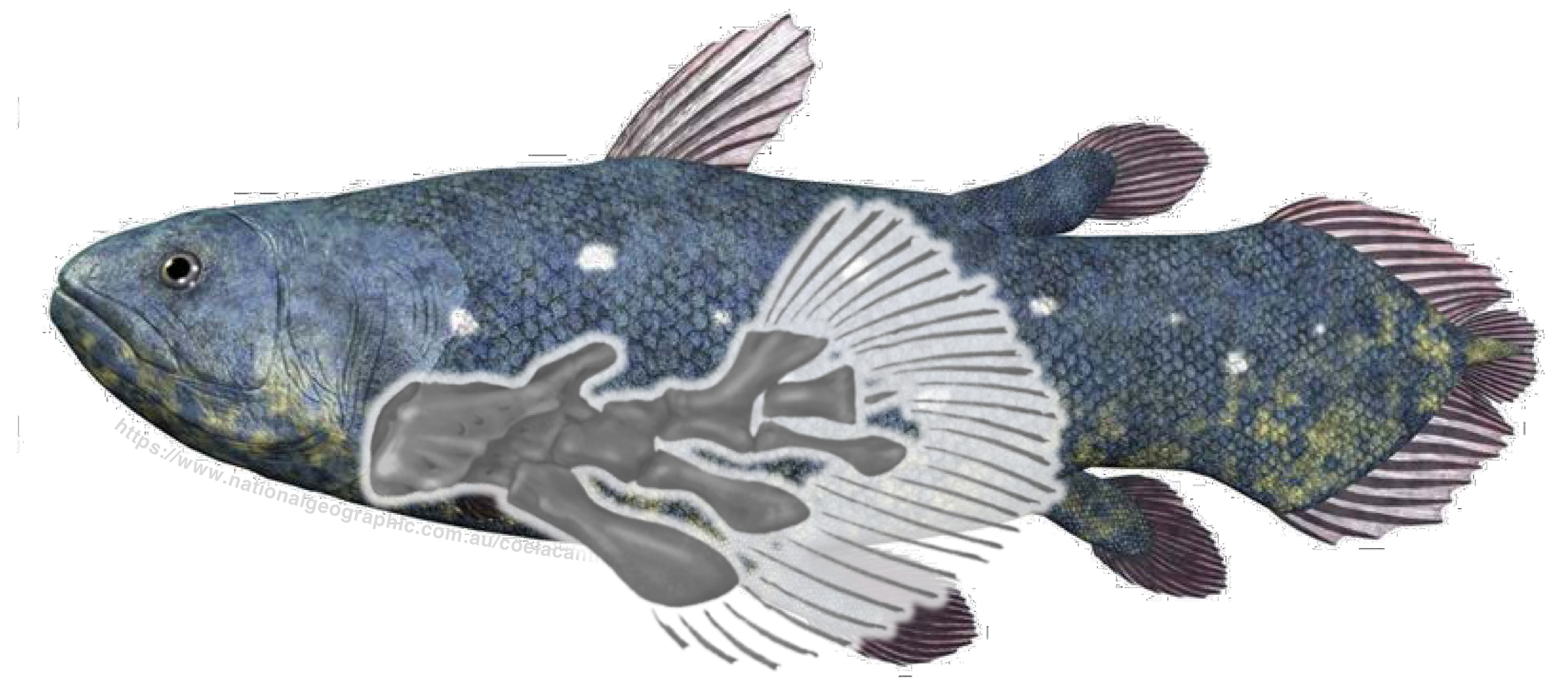
Tetrapods
Osteichthyan paraphyletic group, possessing four limbs, composed of the amphibians, reptiles, and mammals
Amphibians
Basal tetrapod clade that walked on land but still needed water in which to deposit their eggs.
Amniotes
Tetrapod clade with extra-embryonic membranes, consisting of reptiles, birds, and mammals.
What are the four extra-embryonic membranes in amniotes?
Amnion, surrounding embryo.
Yolk sac, surrounding yolk.
Allantois, surrounding wastes.
Chorion, surrounding everything.
Amniotes have two clades. What are they?
Diapsids, composed of reptiles and birds, characterised by the presence of two holes in each side of their skulls.
Synapsids, composed of mammals, characterised by the presence of one hole in each side of their skulls.
Mammals
Amniotes with hair and mammary glands, consisting of monotremes, marsupials, and eutherians.
Monotremes
Basal clade of mammals laying eggs.
Placenta
The structure connected to the offspring, it is where diffusion of nutrients occur from the mother’s blood
Marsupials
Mammalian clade charactered by bearing early-born offspring in short gestation.
Eutherians
Mammalian clade with placenta, bearing late-born offspring so that they can walk and run real fast.