3.2: Cenbral Lobes, Basal Nuclei, Diencephalon, Limbic System, Midbrain, Pons, Medulla Oblongata, & Cerebellum
1/94
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Cenbral Lobes, Basal Nuclei, Diencephalon, Limbic System, Midbrain, Pons, Medulla Oblongata, & Cerebellum
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
The _ is the largest portion of the brain and is divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres
cerebrum
Each hemisphere contains neural tissue arranged in numerous folds called _
Gyri
The gyri are separated by shallow grooves called _ and by deeper grooves called Fissure
Sulci

The main sulcus that can be detected in MRI is the _, which divides the Precentral Gyrus of the Frontal Lobe from the Postcentral Gyrus
Central Sulcus
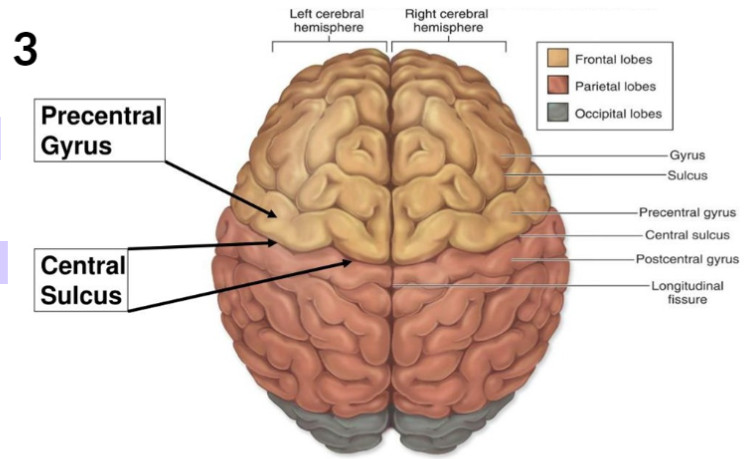
The _ is considered the motor strip of the brain
precentral gyrus
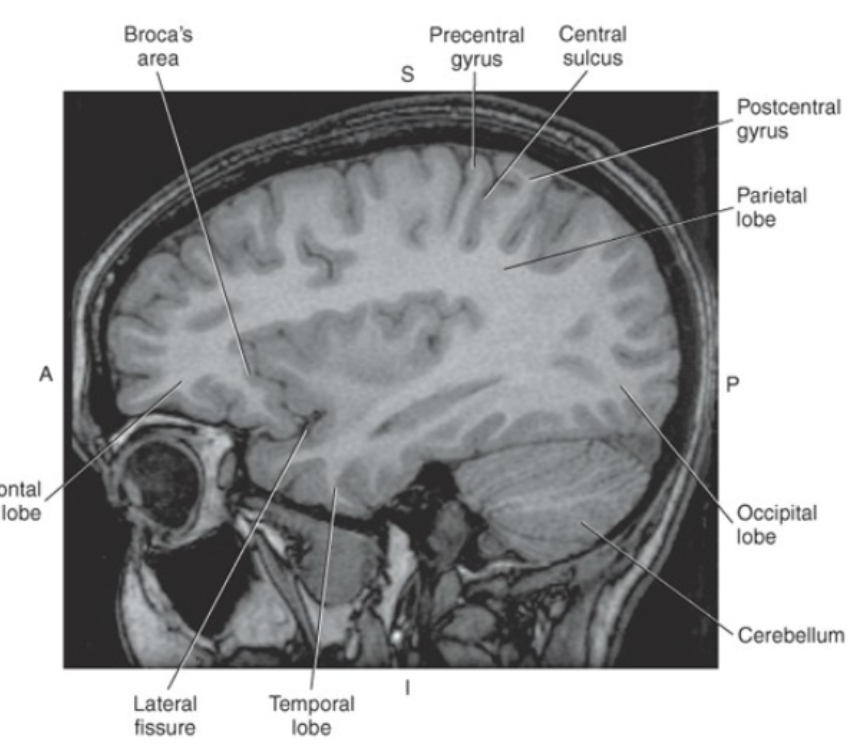
The _ is considered the sensory strip of the brain
postcentral gyrus
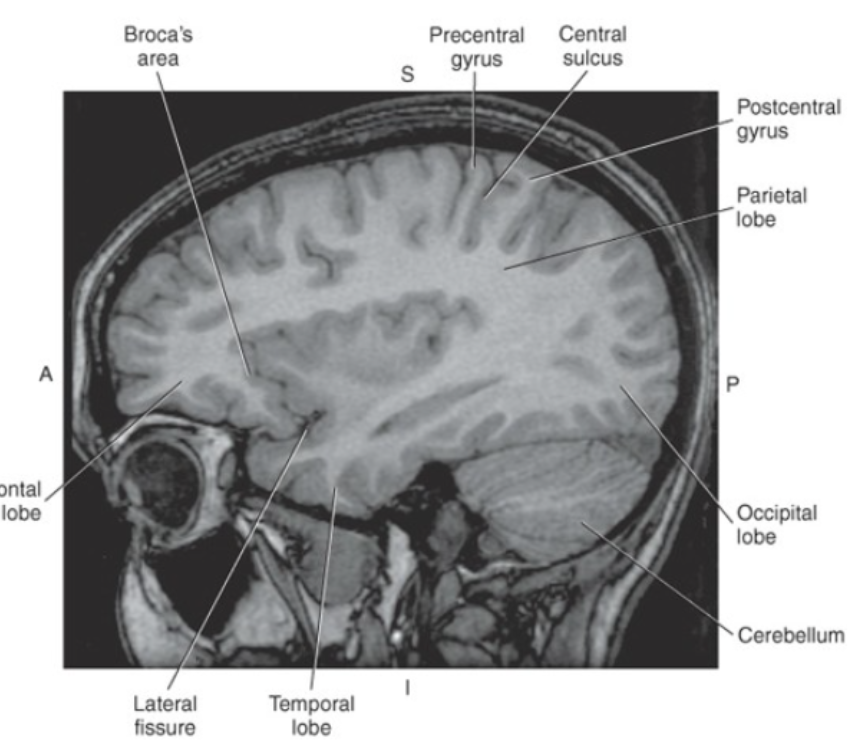
The two main fissures of the cerebrum are the_
Longitudinal Fissure and the Lateral Fissure or Sylvian Fissure
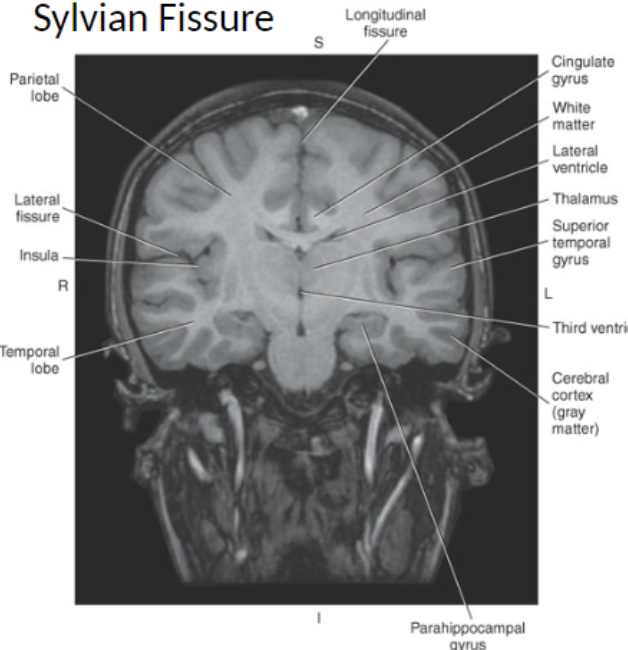
The Longitudinal Fissure is a long, deep furrow that divides the _
left and right cerebral hemisphere
Within the longitudinal fissure is the _
Falx cerebri and superior sagittal sinus
The Lateral Fissure is a deep furrow that separates the
frontal and parietal lobes from the temporal lobe
The lateral fissure contains _
several blood vessels
The cerebrum consists of
Grey Matter (Neuron Cell Bodies) and White Matter (Myelinated Axons)
The Cerebral Cortex, the outermost portion of the Cerebrum is composed of _ 3 to 5mm thick
Grey Matter
The Cortex is responsible for sensory input, and sends information to the muscles and glands for _
control of bodily movement and activity
_ is deep to the cortex, and contains fibers that transmit nerve impulses to and from the cortex
White matter
The largest and densest bundle of white matter fibers within the cerebrum is the
Corpus Collosum
The other two important bundles of white matter ribers are the
anterior and posterior commissures
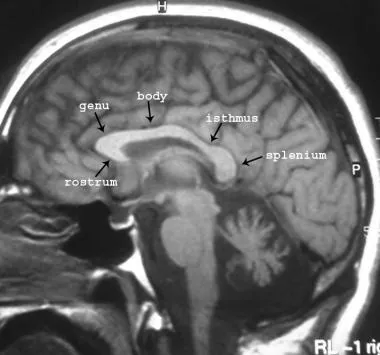
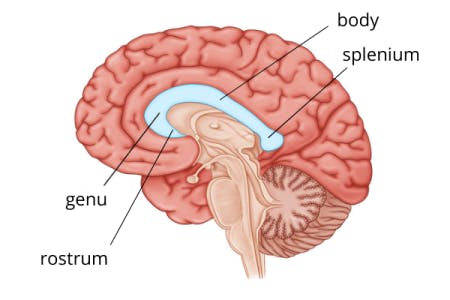
The Corpus Callosum is made of white matter, and forms the
roof of the Lateral Ventricle
The four portions of the corpus callosum, from anterior/inferior to posterior, are the:
Rostrum
Genu
Body
Splenium
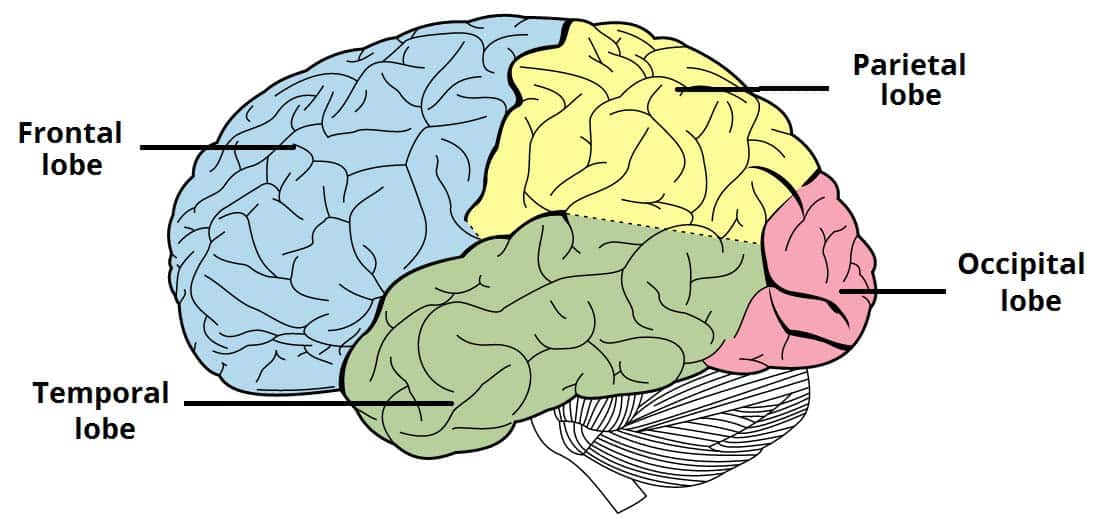
The cerebral cortex of each meisphere can be divded into four lobes, which correspond with the cranial bones of the same name:
Frontal
Pariteal
Occipital
Temporal
The _ is the most anterior lobe of the brain
Frontal Lobe
The frontal lobe is separated from the parietal lobe by the
central sulcus
The frontal lobe is separated from the temporal lobe by the
lateral fissure of sylvian fissure
Reasoning
frontal lobe
judgement
frontal lobe
emotional response
frontal lobe
planning and execution of complex action
frontal lobe
control of muscle movement
Frontal Lobe
The frontal lobe is also involved in the production of speech and contains the motor speech center, _
Broca’s area
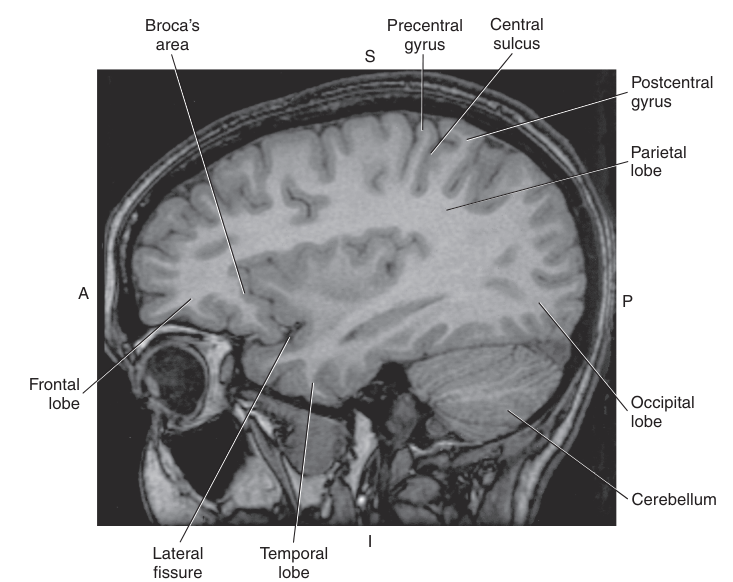
Broca’s area lies unilaterally on the _
inferior surface of the frontal lobe dominant for language (typically the left frontal gyrus)
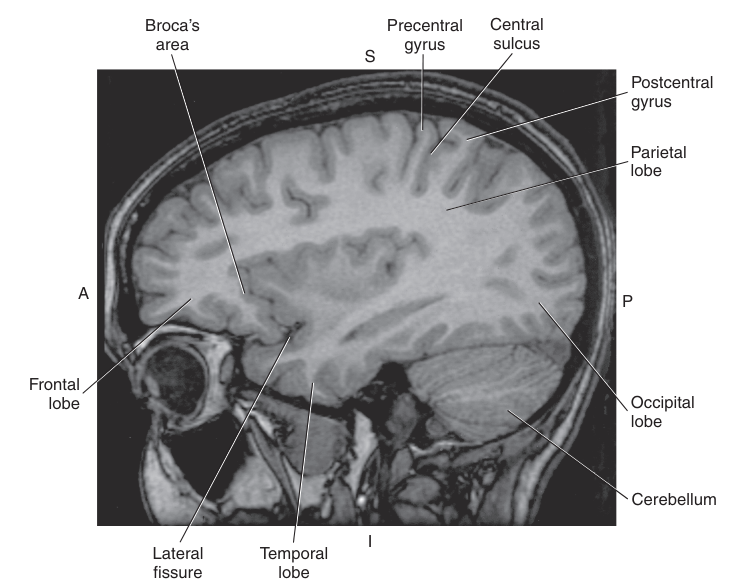
The _ is located in the middle portion of each cerebral hemisphere just posterior to the central sulcus
Parietal Lobe
The_ seprates the parietal love from the temporal lobe
horizontal portion of the lateral fissure
temperature
parietal lobe
touch & pressure
parietal lobe
vibration
parietal lobe
pain
parietal lobe
taste
parietal lobe
involved in writing and in some aspects of reading
parietal lobe
The most posterior lobe, the Occipital Lobe is separated from the parietal lobe by the
parieto-occipital fissure
The _ is involved in the conscious perception of visual stimuli
occipital lobe
The primary visual area receives input from the optic tract via the
optic radiations extending from the thalamus
The Temporal Lobe is anterior to the Occipital Lobe and is separated from the Parietal Lobe by the
Lateral Fissure
Conscious perceptions of auditory and olfactory stimuli are functions of the _, as well as dominance for language
temporal lobe
Memory processing occurs via the
amygdala and hippocampus in the parahippocampal gyrus
Deep to the temporal lobe is an area of cortical gray matter termed the _ often referred to as the fifth lobe
Insula or Island of Reil,
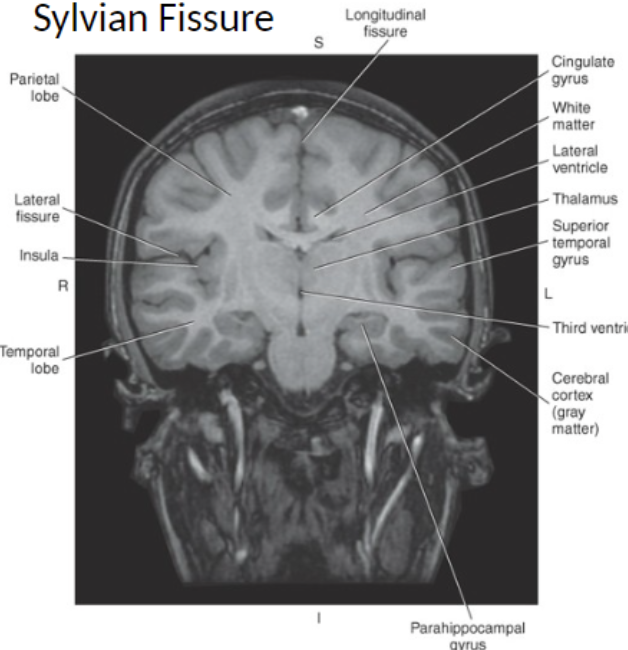
The _ is thought to mediate the motor and sensory functions of the viscera
Insula
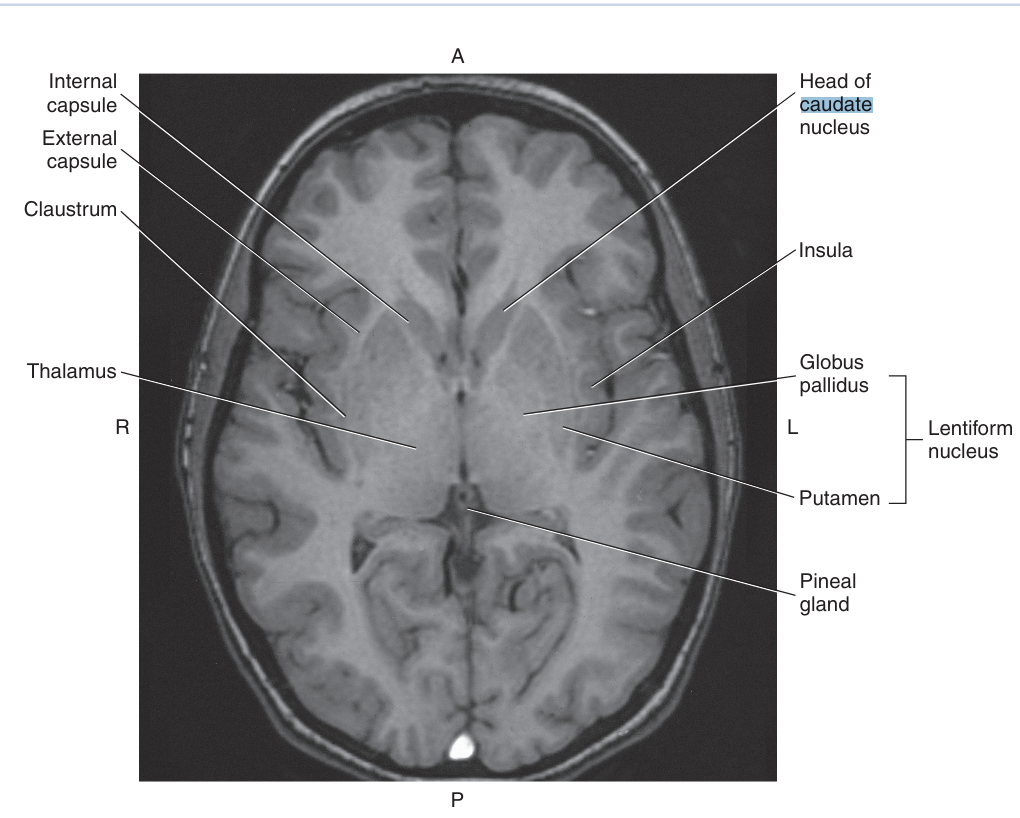
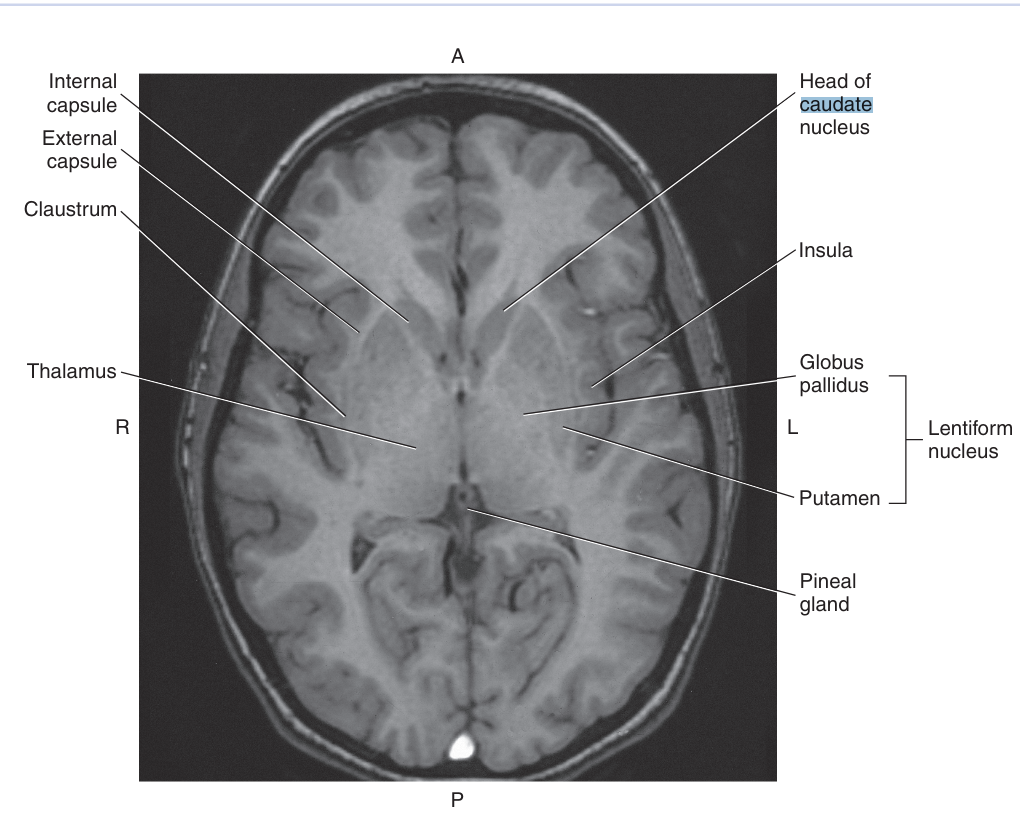
The Basal Nuclei are a collection of subcortical gray matter consisting of the
caudate nucleus, lentiform nucleus, and claustrum
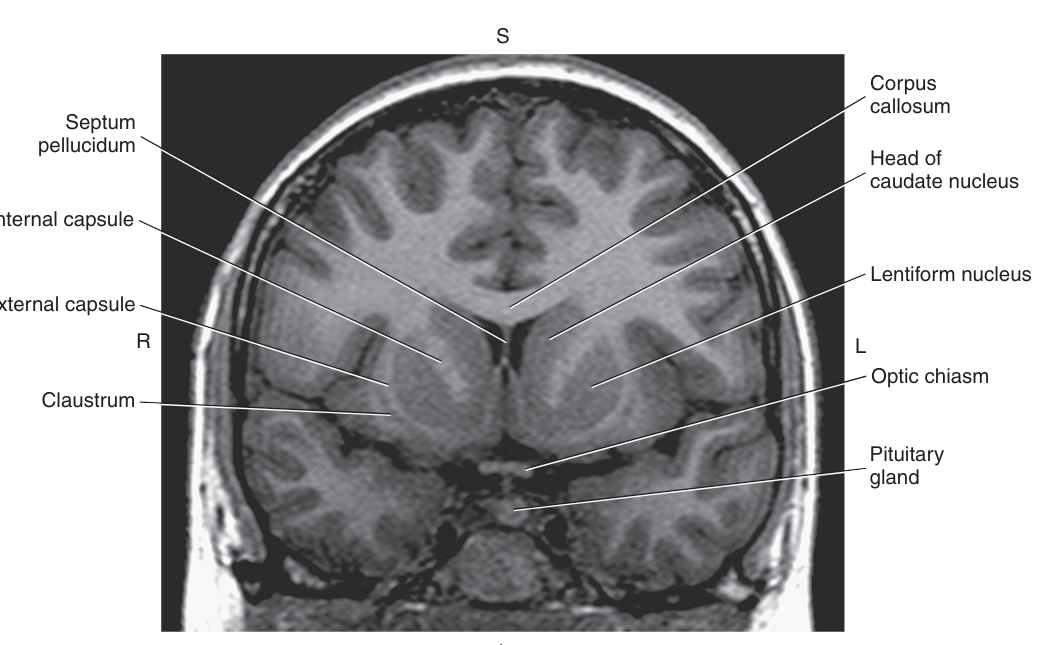
The largest basal nuclei are the
caudate nucleus and the lentiform nucleus
The caudate nucleus parallels the lateral ventricle and consists of a
head body and tail
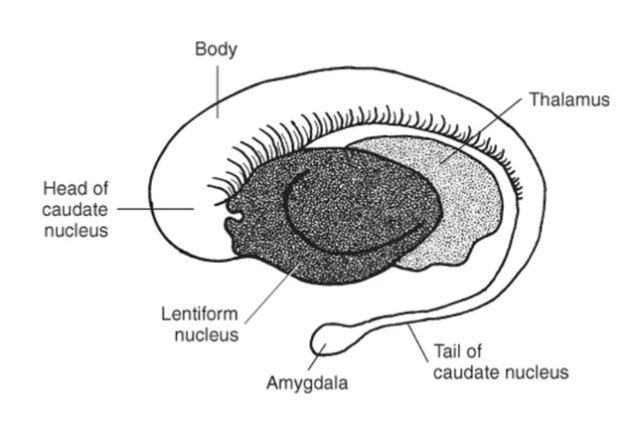
The head of the caudate nucelus causes an indentation to the frontal horns of the lateral ventricles, and the tail
terminates at the amygdal
The lentiform nucleus is a biconvex lens-shaped mass of gray matter located between the
insula, caudate nucleus, and the thalamus
The lentiform nucleus can be further divided into the
globus pallidus and the putame
The _ is a thin linear layer of gray matter lying between the insula and lentiform nucleus
claustrum
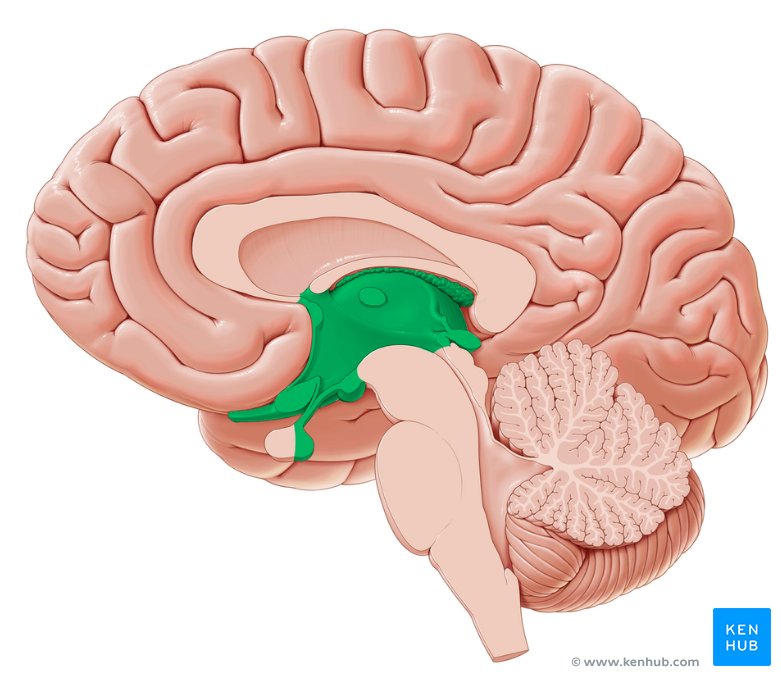
The diencephalon consists of the
Thalamus, Hypothalamus, and the Epithalamus
The _ consists of a pair of large, oval gray masses that are interconnected with most regions of the brain and spinal cord via a vast number of fiber tracts
thalamus
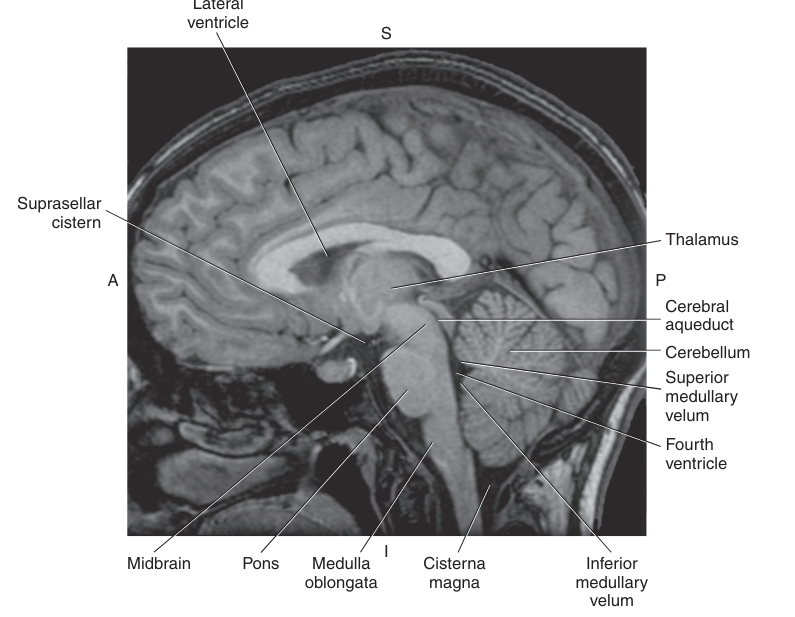
The thalamus makes up a portion of the walls of the third ventricle by adhesions known as
massa intermedia
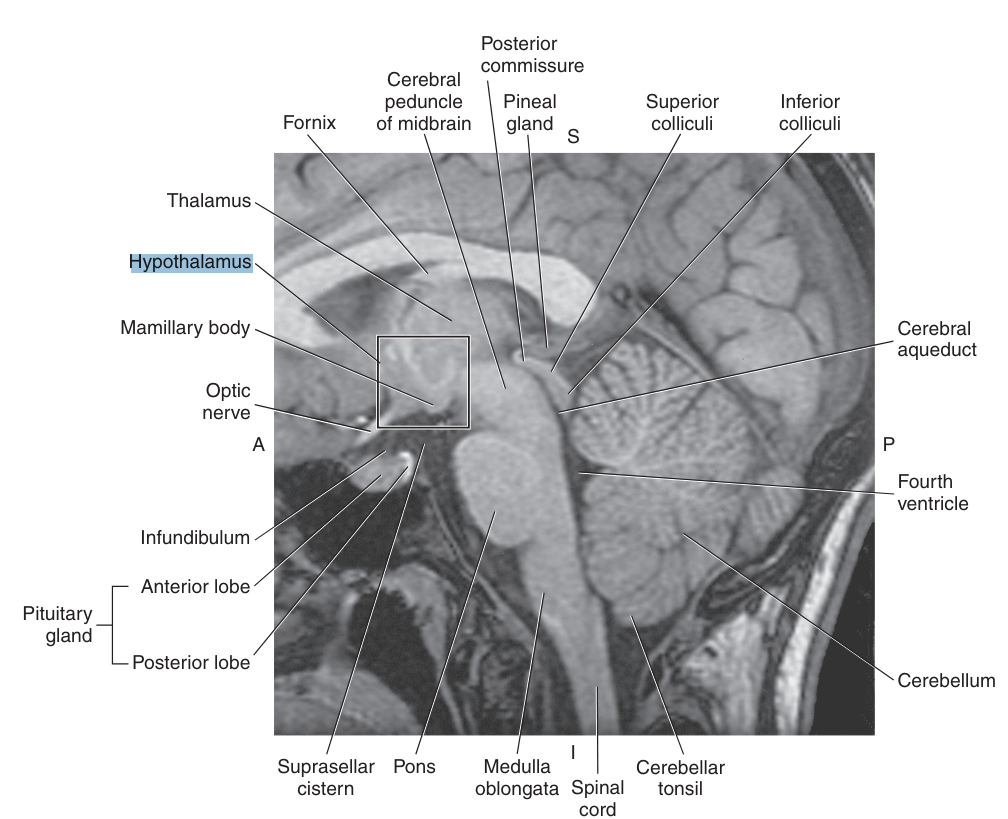
The _ consists of a cluster of small nuclei
hypothalamus
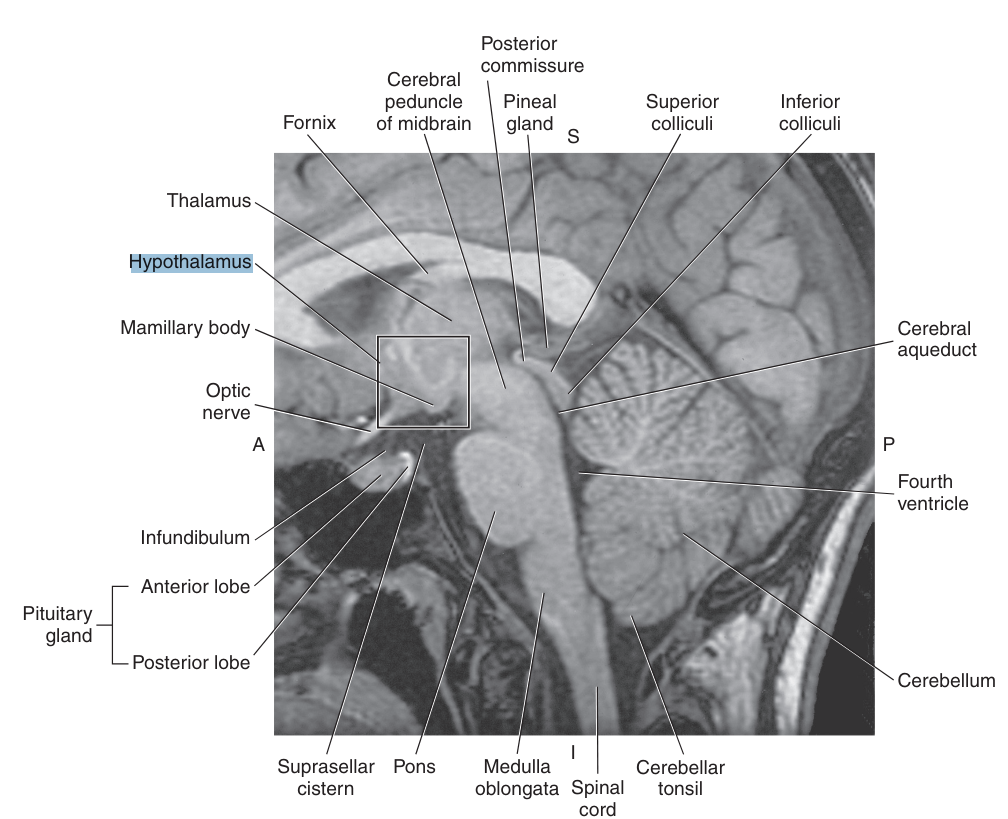
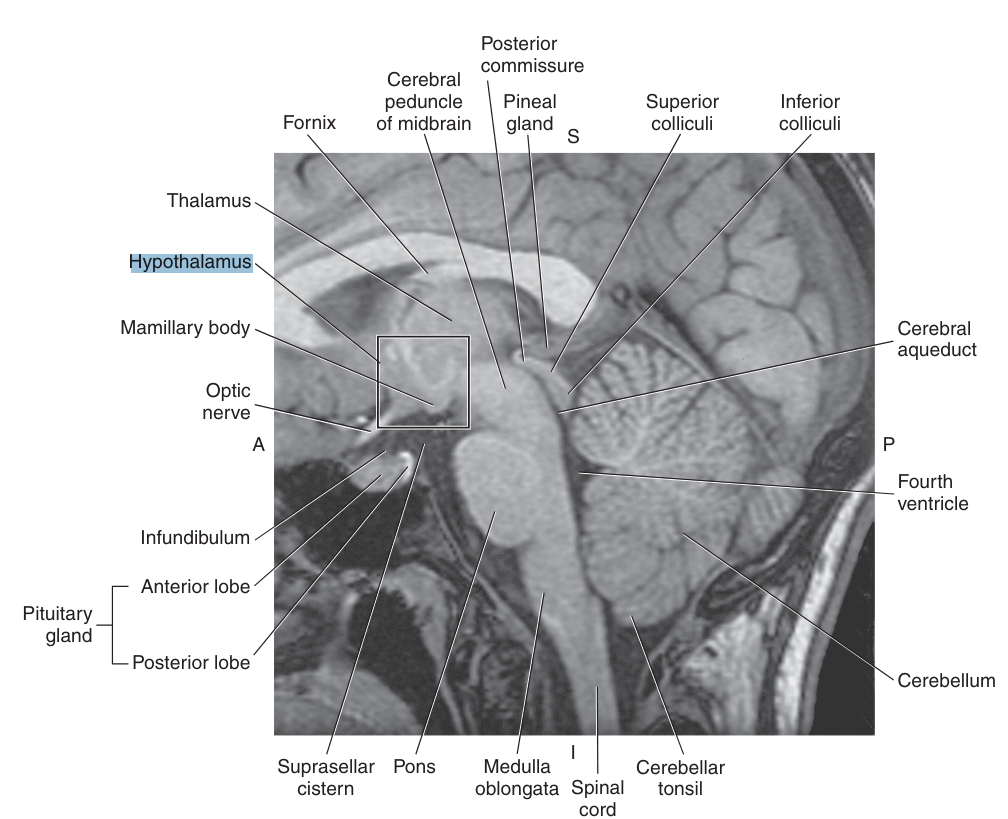
The hypothalamus is located below the
thalamus, just posterior to the optic chiasm, and forming the floor of the third ventricle
The pituitary gland is an endocrine gland connected to the hypothalamus by the
infundibulum
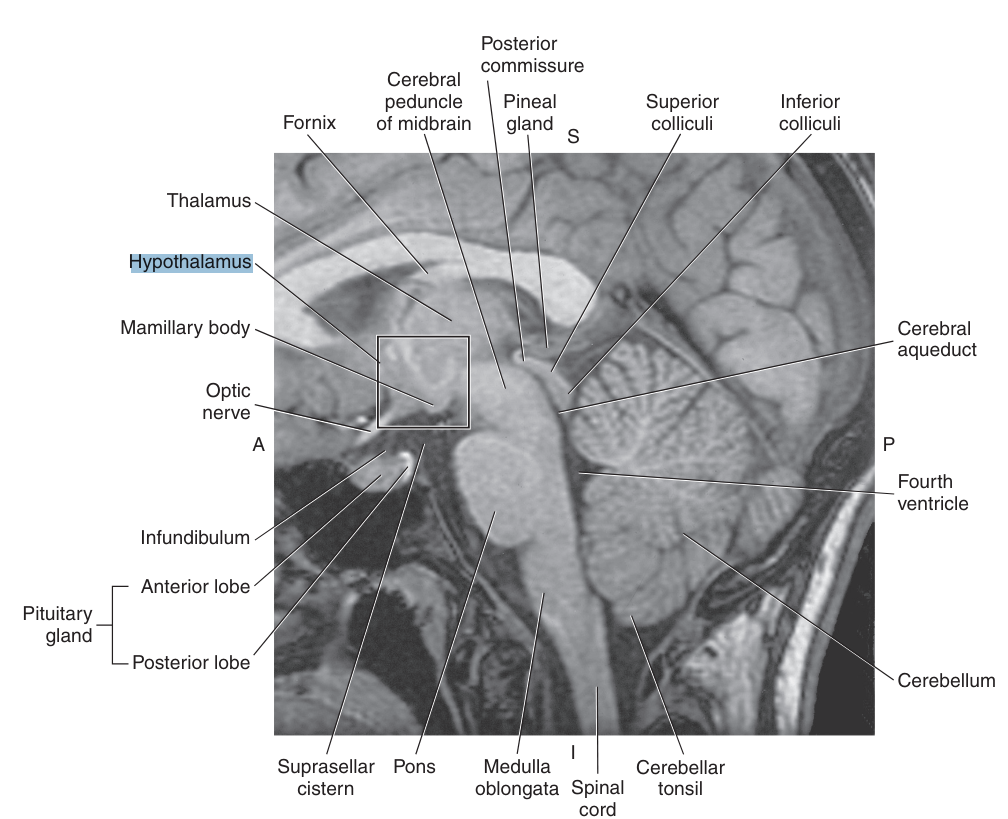
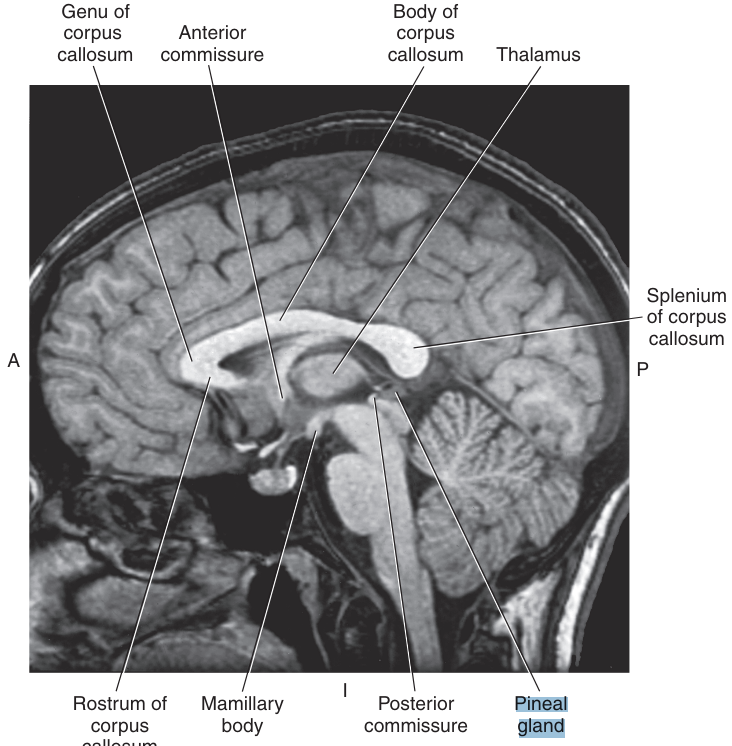
The pineal gland is an endocrine gland that sits on the roof of the midbrain, just posterior to the
third ventricle and below the splenium of the corpus callosum
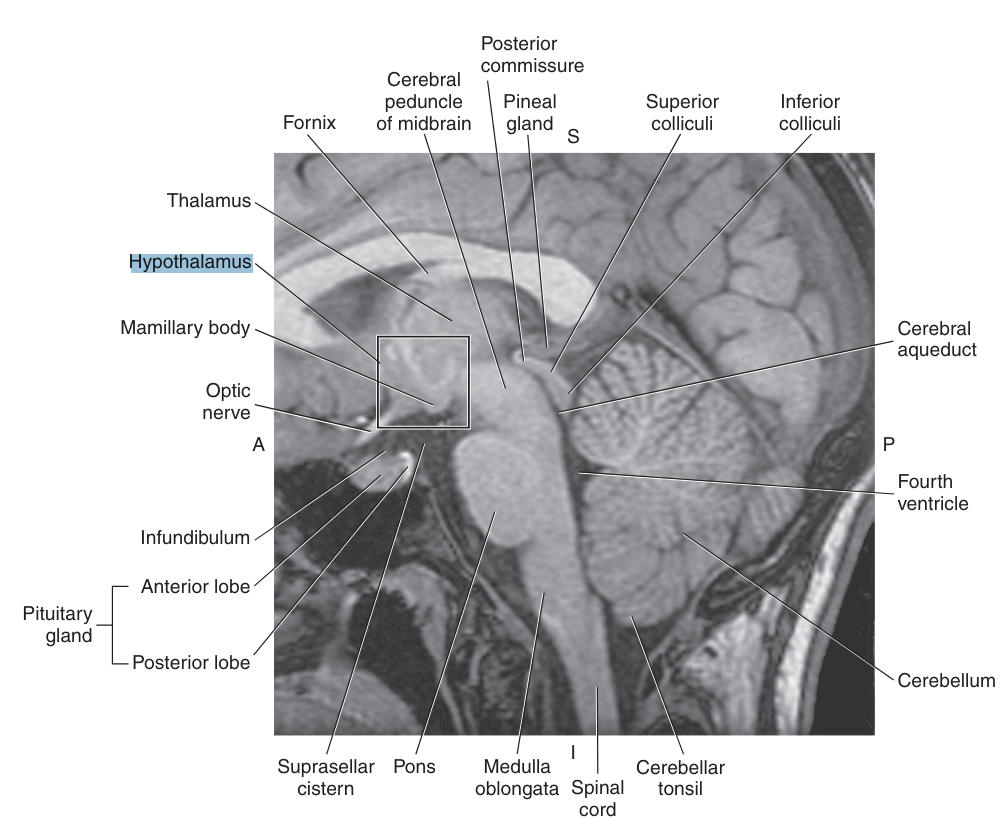
The _ is a complex group of interconnected brain structures and fiber tracts
limbic system
The limbic system includes the
hippocampus, amygdala, olfactory tracts, fornix, cingulate gyrus, and mamillary bodies
The parahippocampal gyrus, containing the _ is the enrolled medial border of the temporal lobe
hippocampus and amygdala
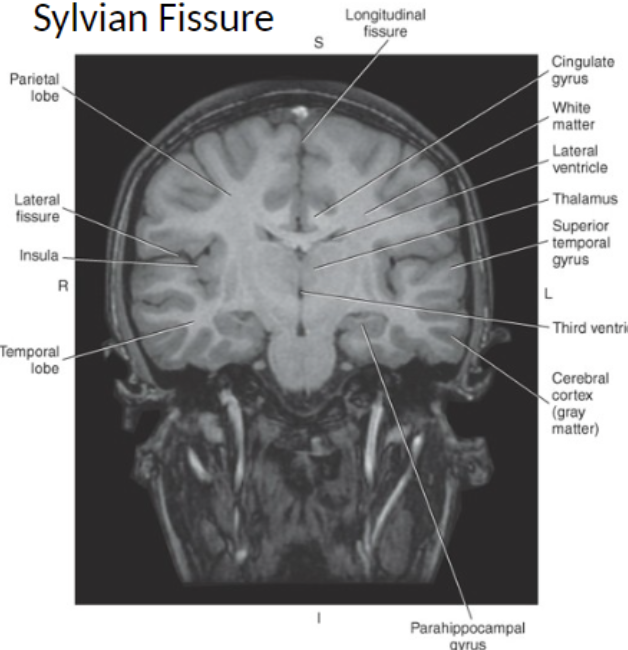
The amygdala is an almond-shaped mass of gray matter located deep within the parahippocampal gyrus, lateral to the
hypothalamus and adjacent to the hippocampus
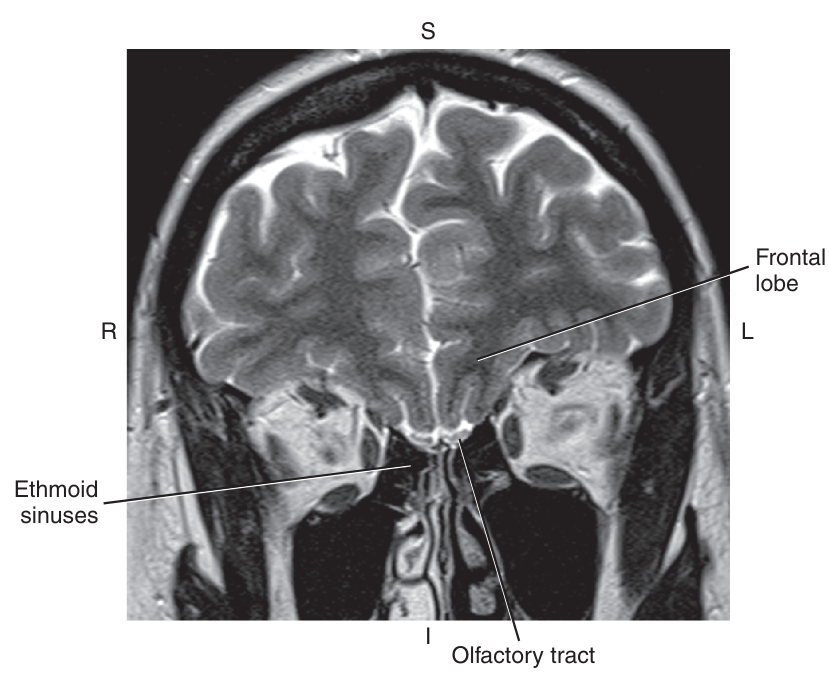
The olfactory tracts run underneath the
frontal lobes and connect to the amygdala
The _ is an arch-shaped structure that lies below the splenium of the corpus callosum and makes up the inferior margin of the septum pellucidum
fornix
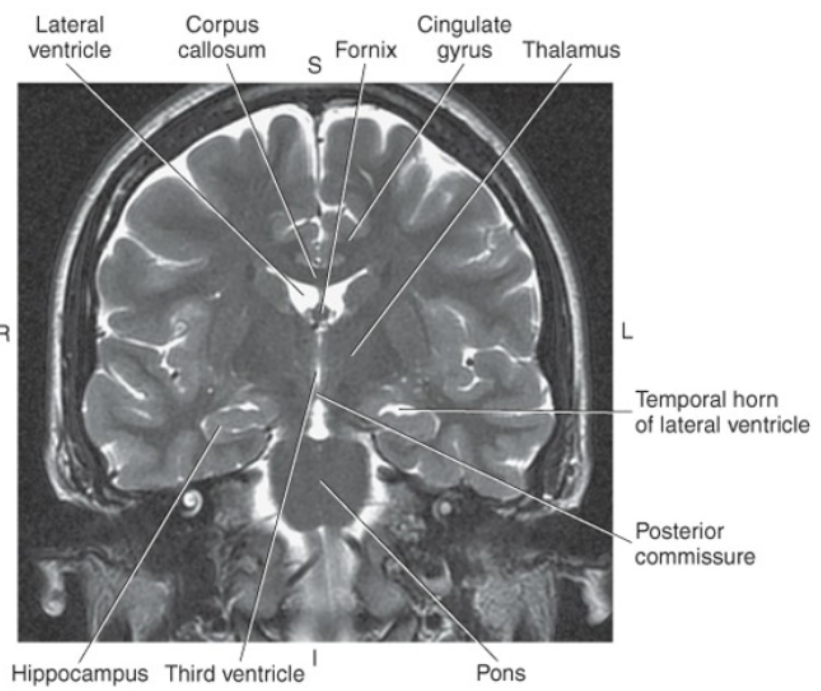
The cingulate gyrus is a prominent gyrus located on the medial border of
each cerebral hemisphere just superior to the corpus callosum
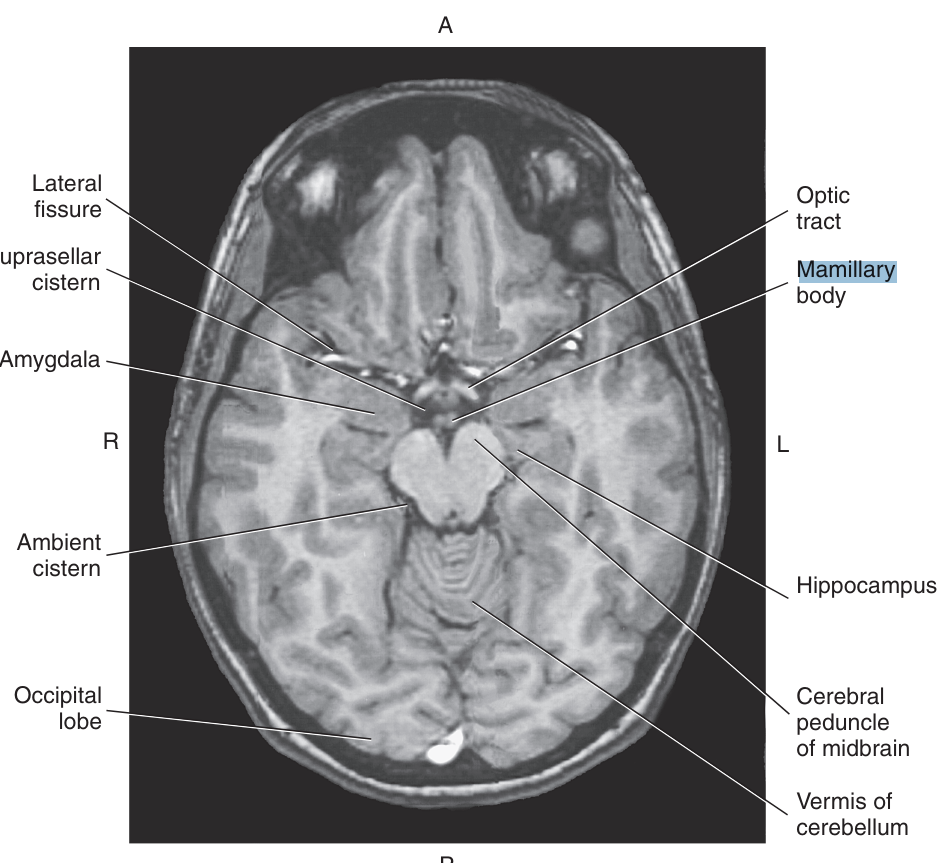
The mamillary bodies are two small rounded bodies in the floor of the posterior hypothalamus, that
receive direct input from the hippocampus via the fornix,
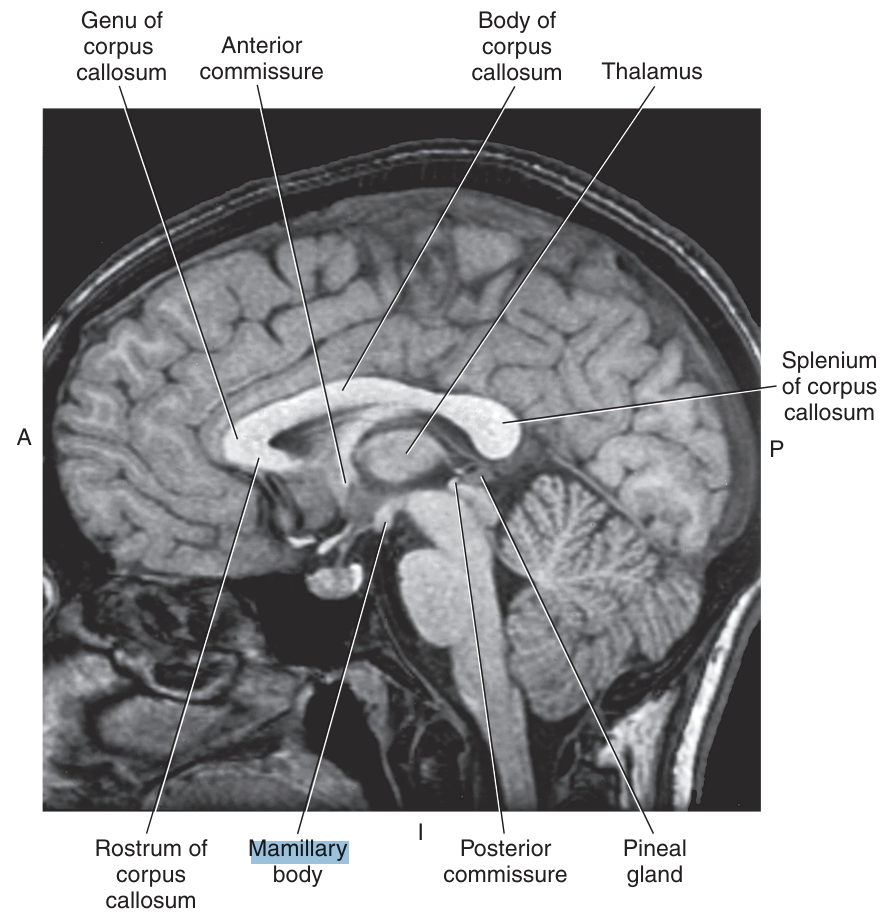
The mamillary bodies give rise to the fibers that terminate in the
periaqueductal gray matter of the midbrain and anterior thalamus
The brainstem as a whole acts as a conduit between the
cerebral cortex, cerebellum, and spinal cord
Located within the central portion of the brainstem and common to all three segments of it, is the
tegmentum
The tegmentum is responsible for
complex motor actions, aspects of respiratory and cardiovascular activity, and regulation of consciousness
The central core of the tegmentum contains the
reticular formation, containing many nuclei
Ten of the twelve cranial nerves originate from the
nuclei of the brainsteam
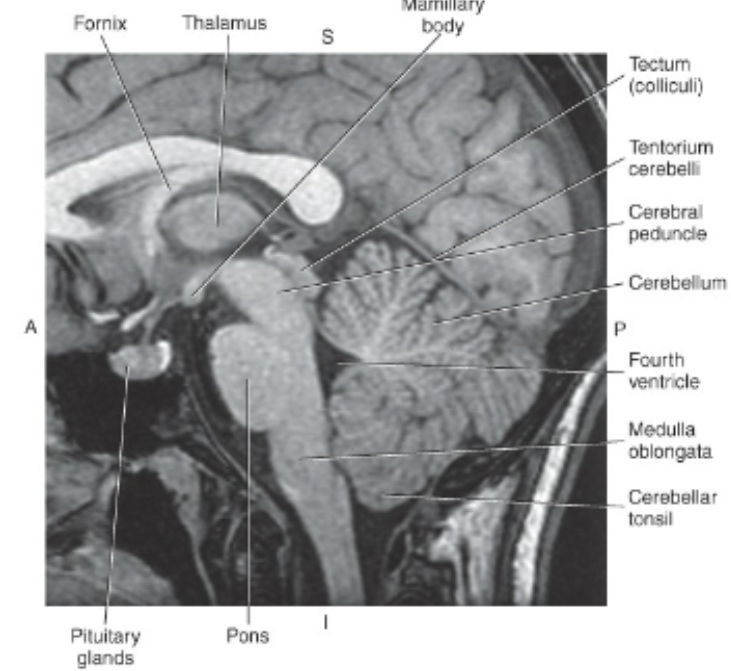
The midbrain or mesencephalon is located
superior to the pons and inferior to the Third Ventricle and Thalami
The midbrain or mesencephalon is, composed primarily of massive bundles of nerve fiber tracts and can be divided into two major segments:
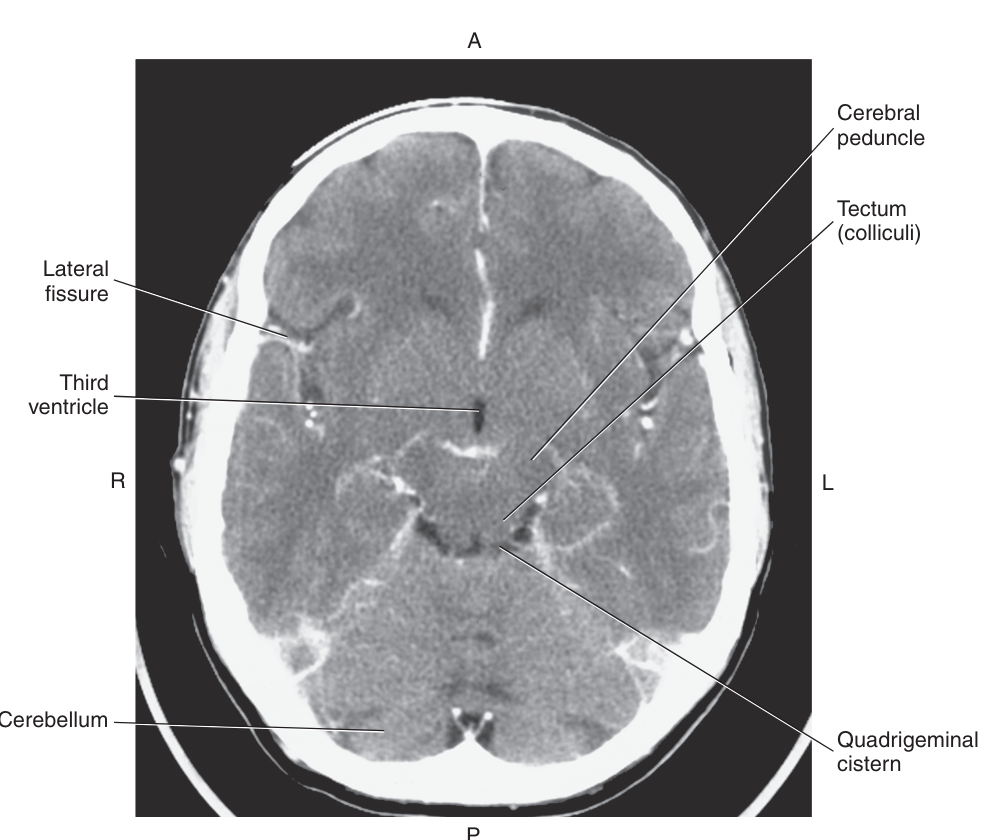
cerebral peduncles and the tectum or colliculi
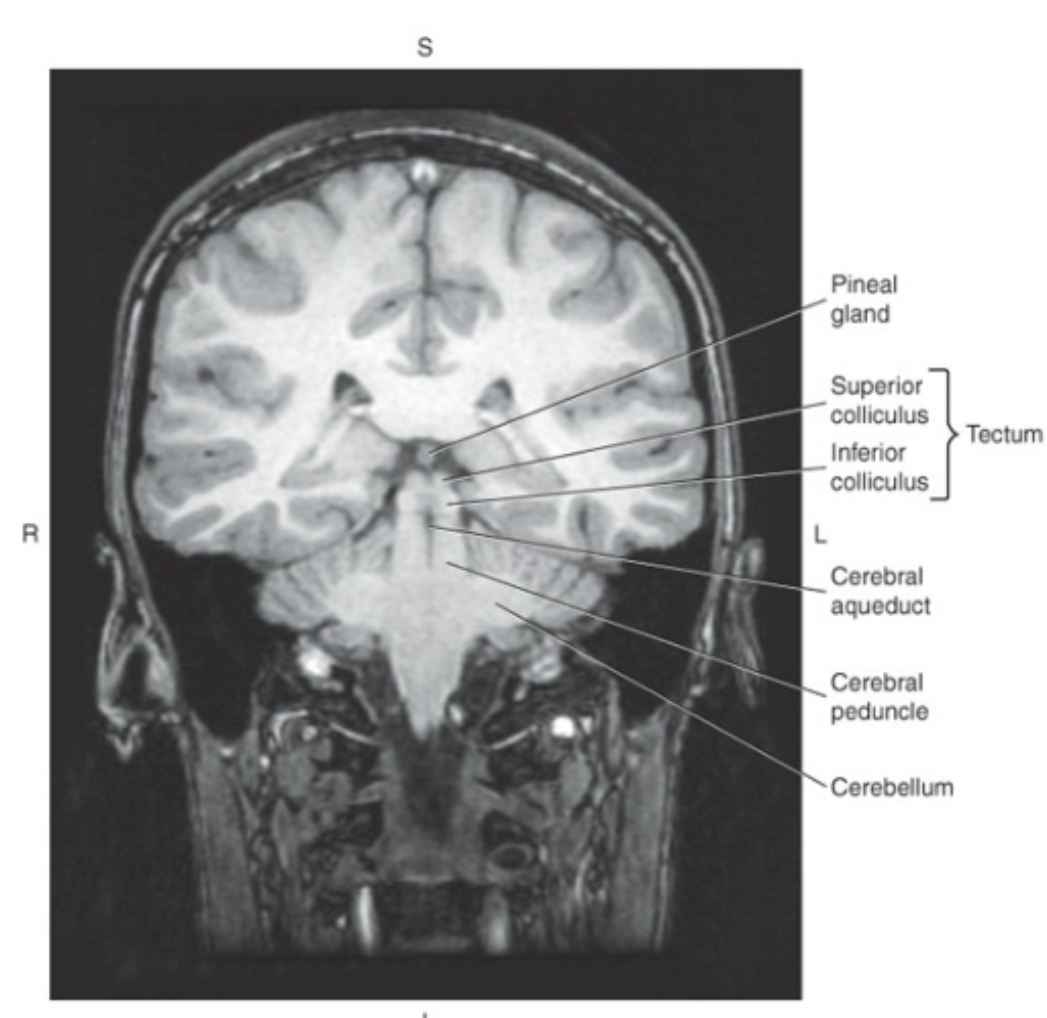
The midbrain surrounds the
cerebral aqueduct
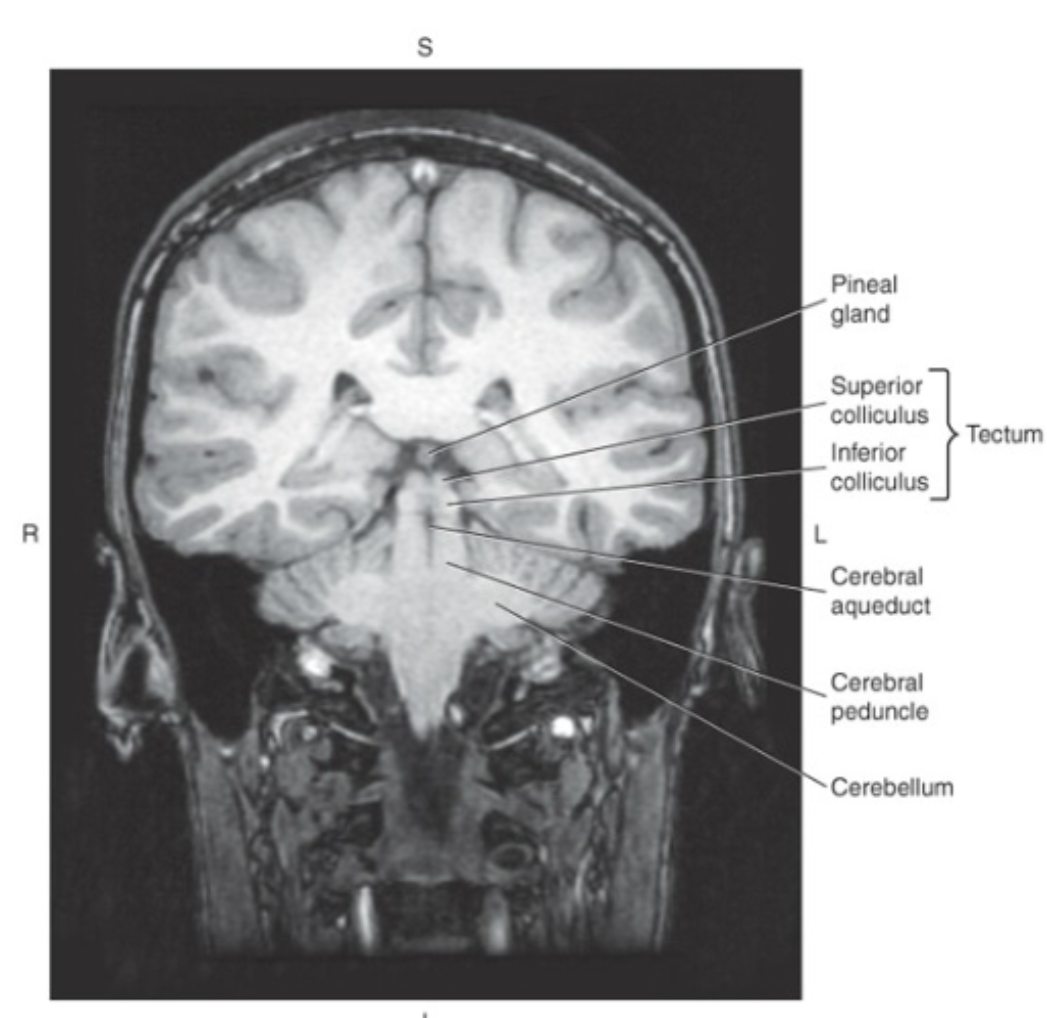
Posterior to the cerebral aqueduct is the_ which makes up the roof or dorsal surface of the midbrain
tectum, or quadrigeminal plate
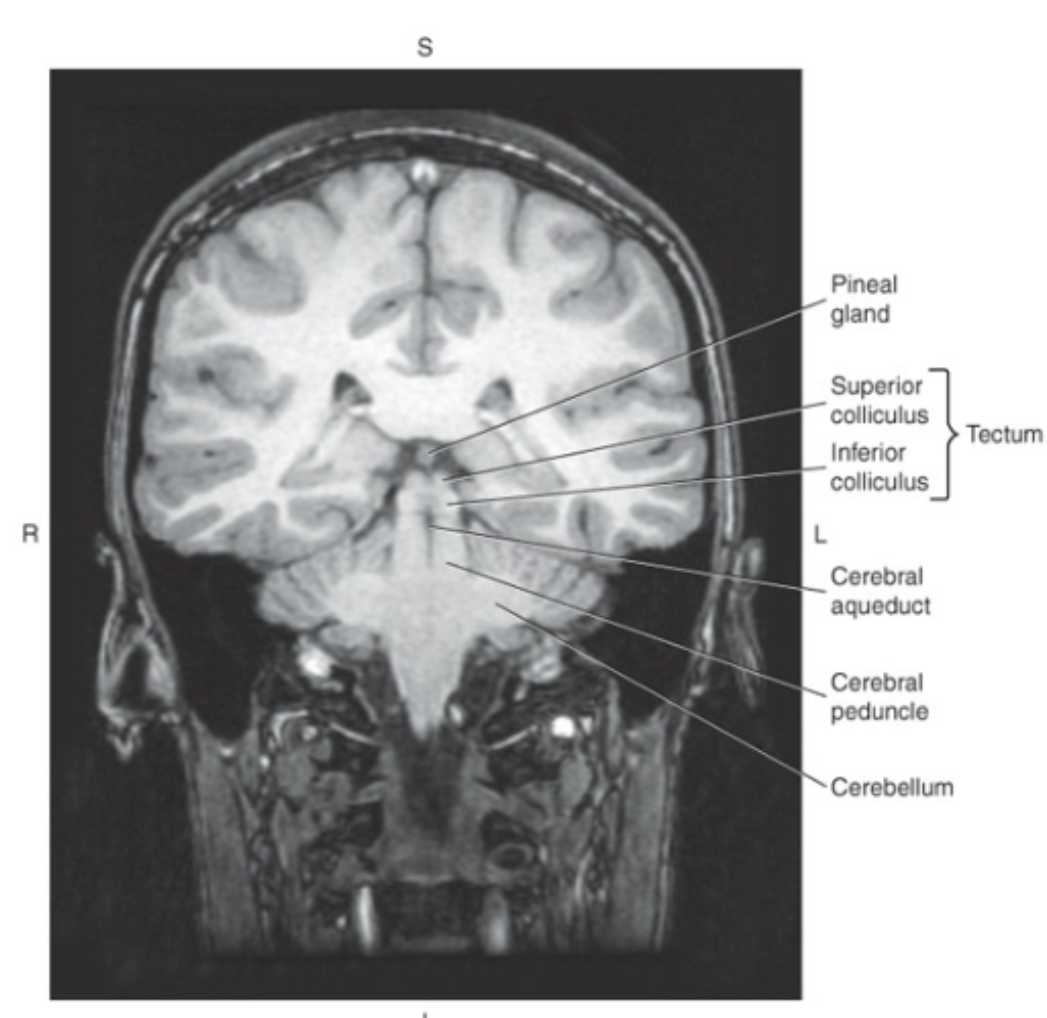
The tectum consists of four rounded protuberances termed the colliculi:
superior colliculi (visual reflexes) and inferior colliculi (auditory reflexes)
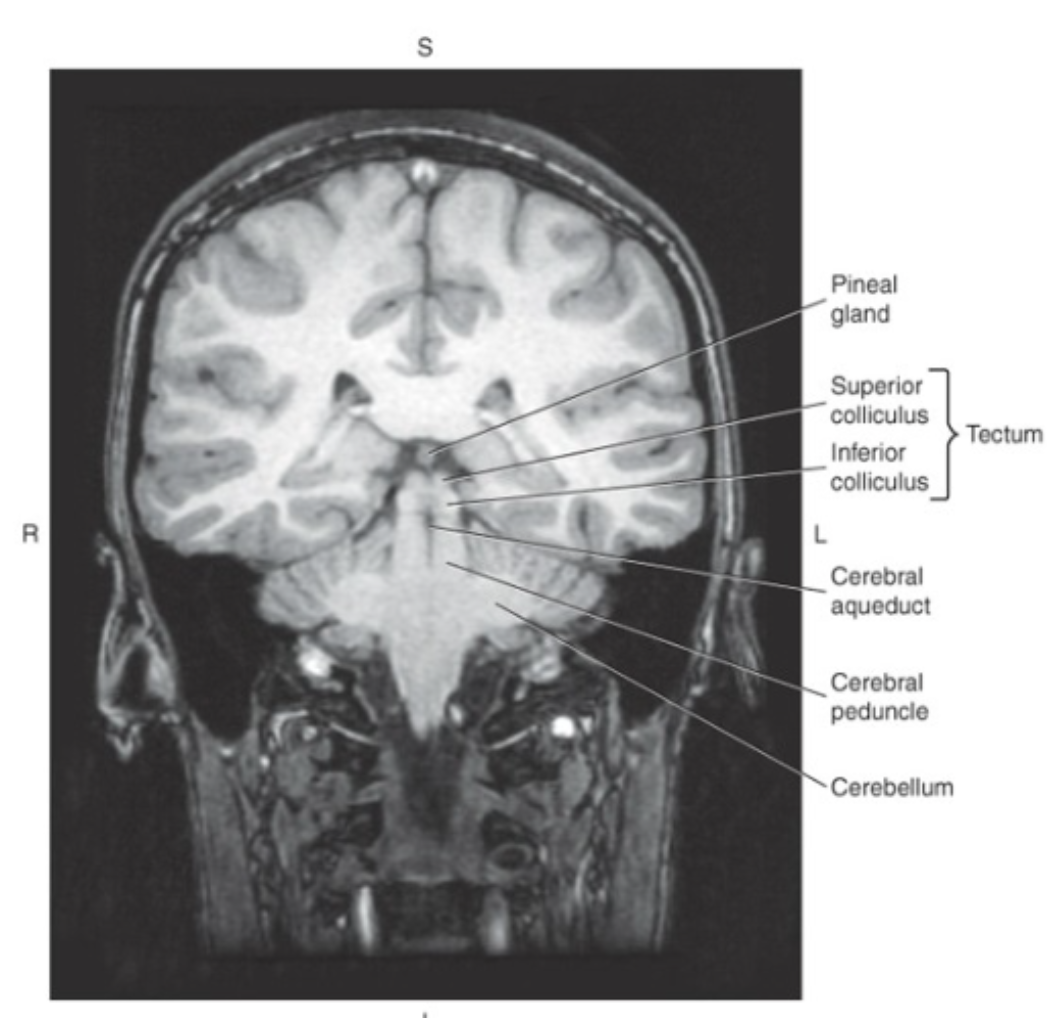
Anterior to the cerebral aqueduct are the two large _, composed predominately of axons that extend from the cerebral cortex to the spinal cord
cerebral peduncles
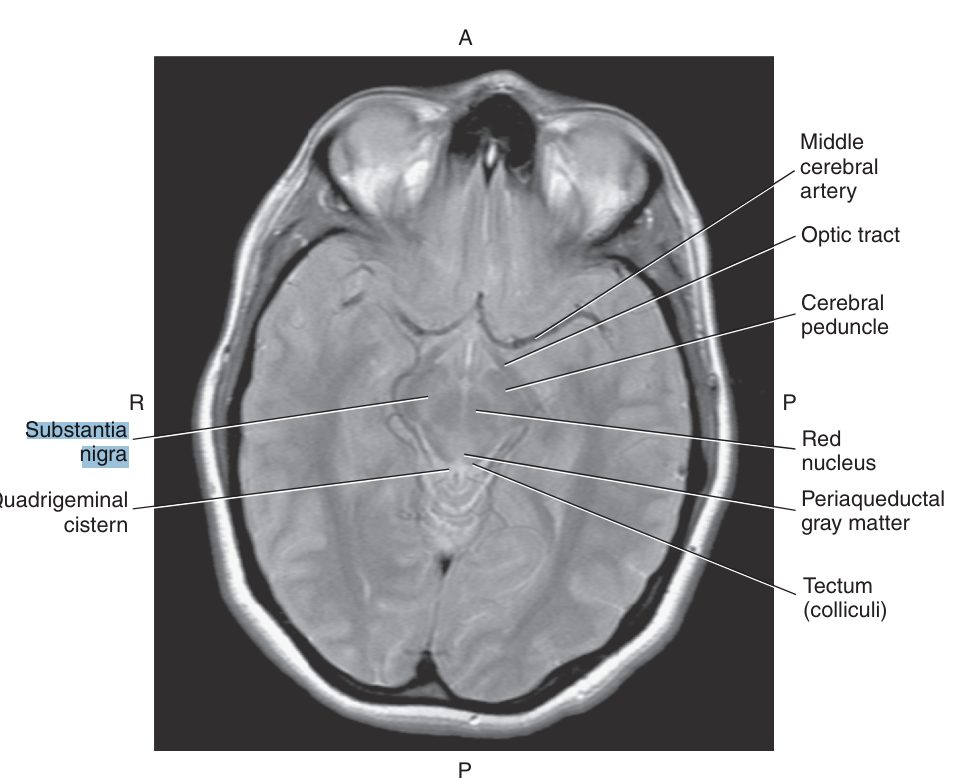
The cerebral peduncles are made more noticeable by the presence of darkly pigmented _, a broad layer of cells that contain melanin
substantia nigra
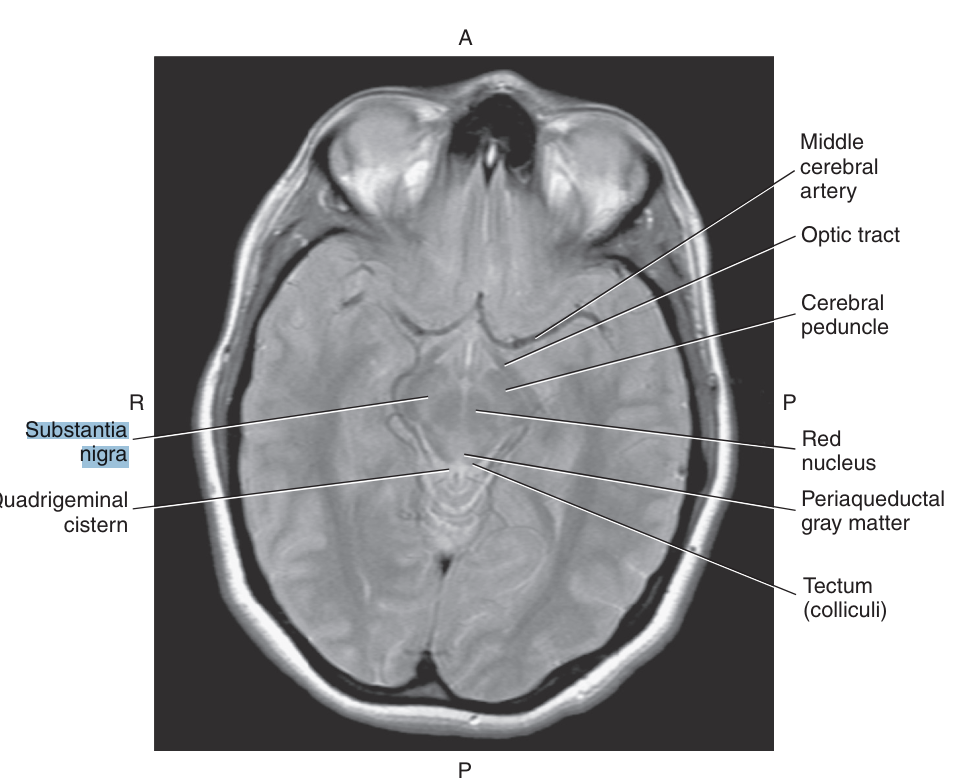
Within the tegmentum of the midbrain, at the level of the superior colliculi, is the
red nucleus, composed of motor nerve fiber
The_ is the large oval-shaped expansion of the brainstem, centrally located between the midbrain and the medulla oblongata
pons
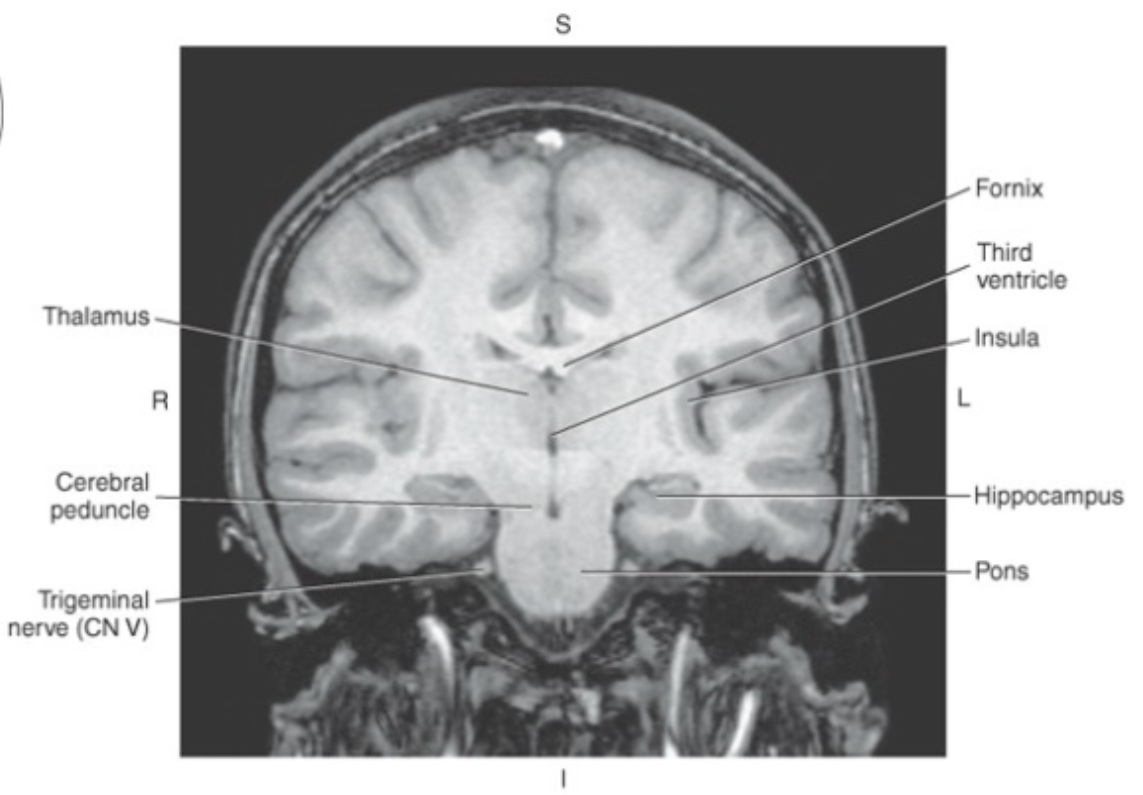
The pons, whose name means bridge,
relays signals between the spinal cord and the cerebral and cerebellar cortice
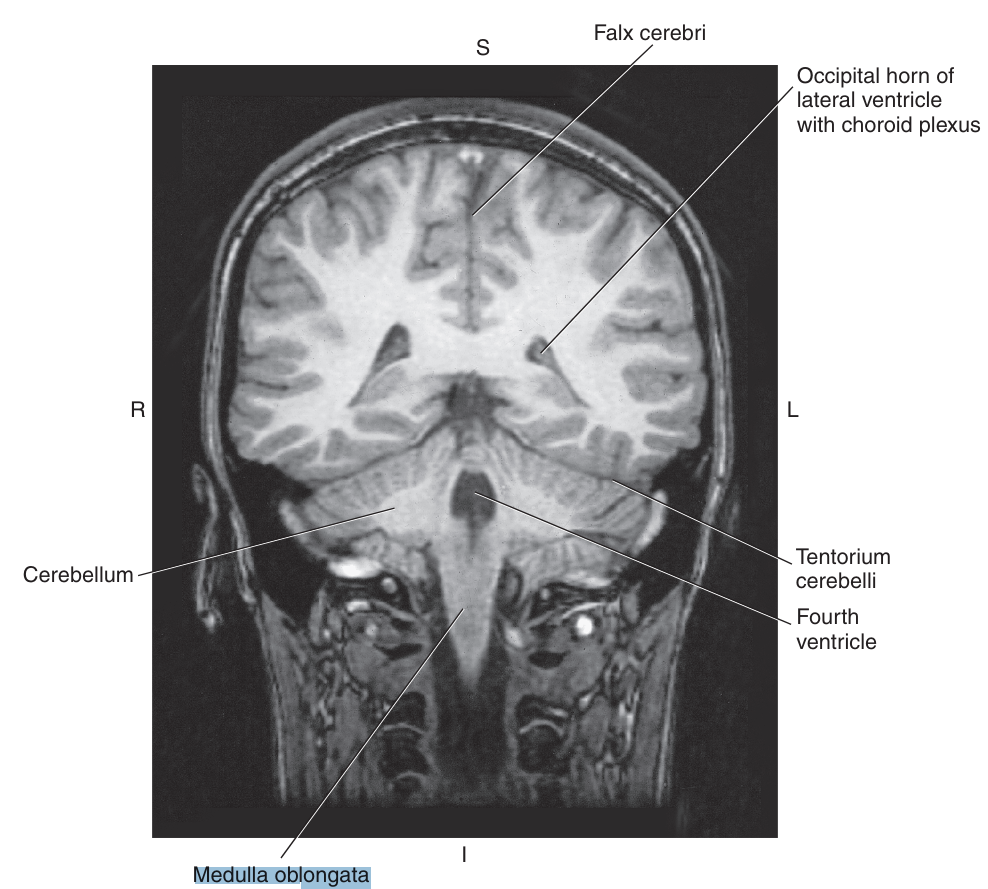
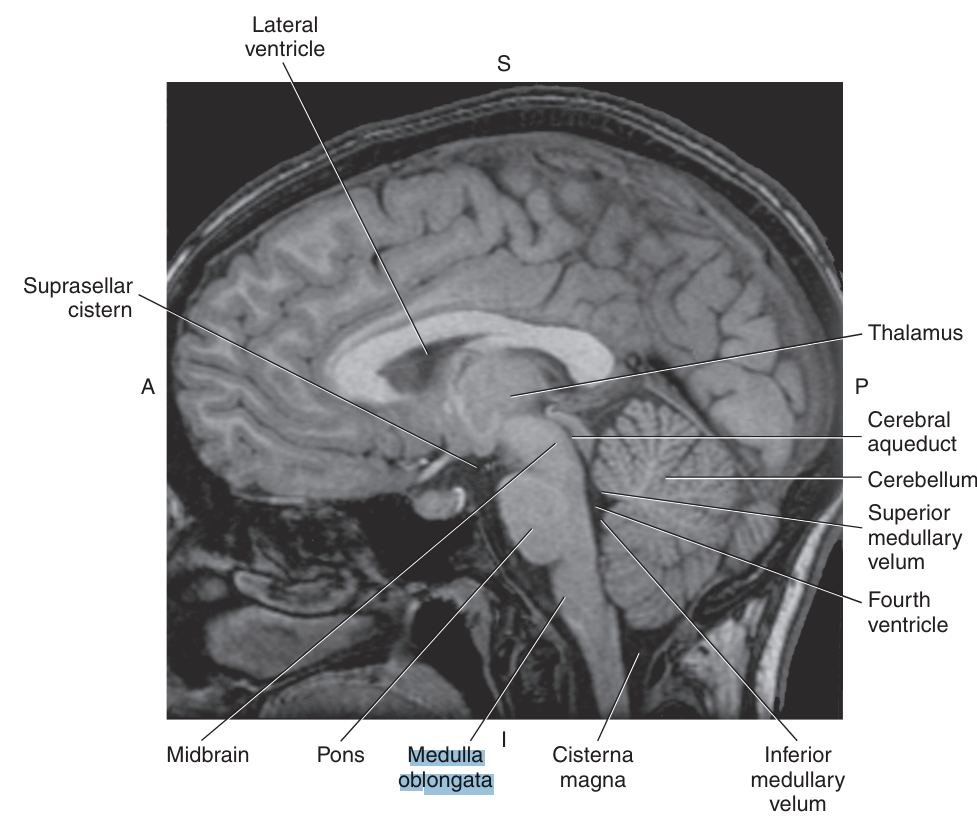
The _ extends from the pons to the foramen magnum, where it continues as the spinal corrd
medulla oblongata
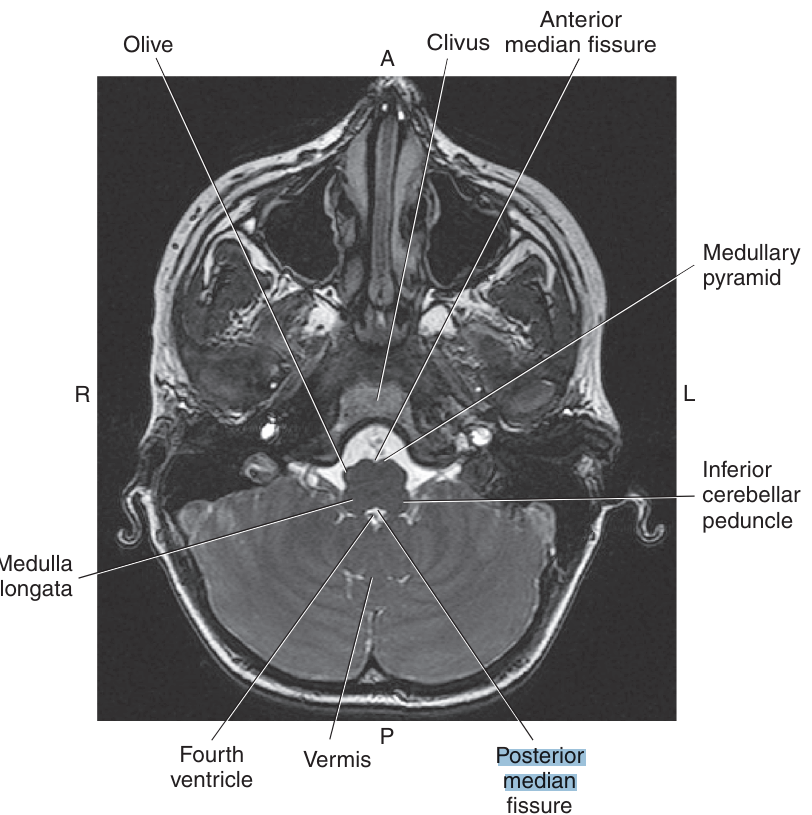
Located in the center of both the anterior and posterior surfaces of the Medulla Oblongata, are the _, which divide the Medulla Oblongata into two symmetrical halves
anterior median fissure and posterior median sulcus
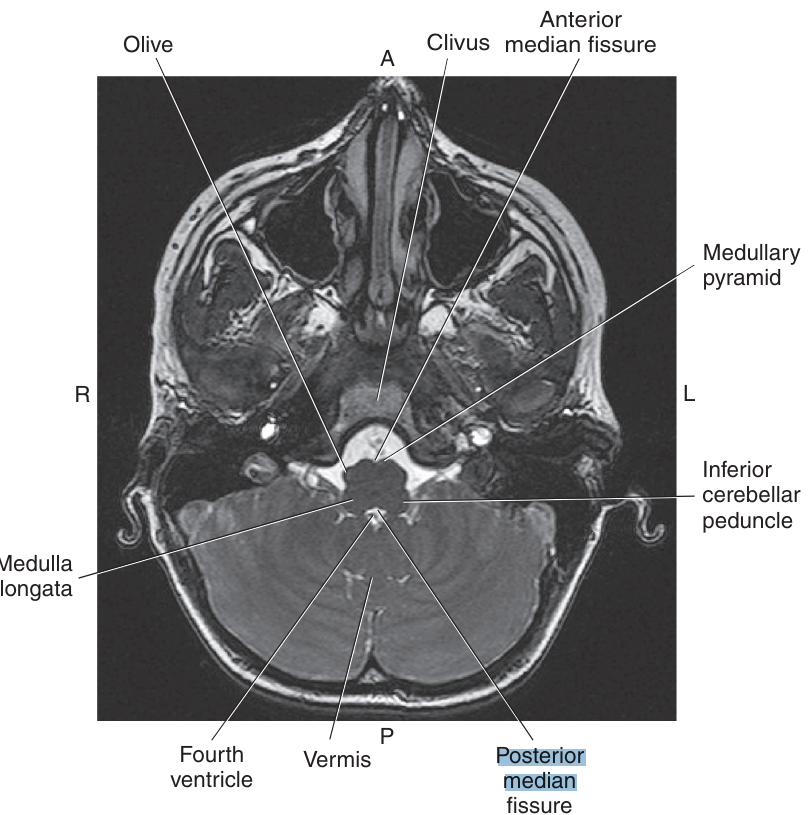
Located on either side of the anterior median fissure are two bundles of nerve fibers called the
pyramid
At the lower end of the pyramids, some of the nerve tracts cross over (decussate) to the opposite side, which in part accounts for the fact that
each of the brain controls the opposite half of the body
On each lateral sufrace are rounded oval prominences called the
olive
True or false: The cerebellum lays in the posterior cranial fossa, and is composed of two cerebellar hemisphere
True
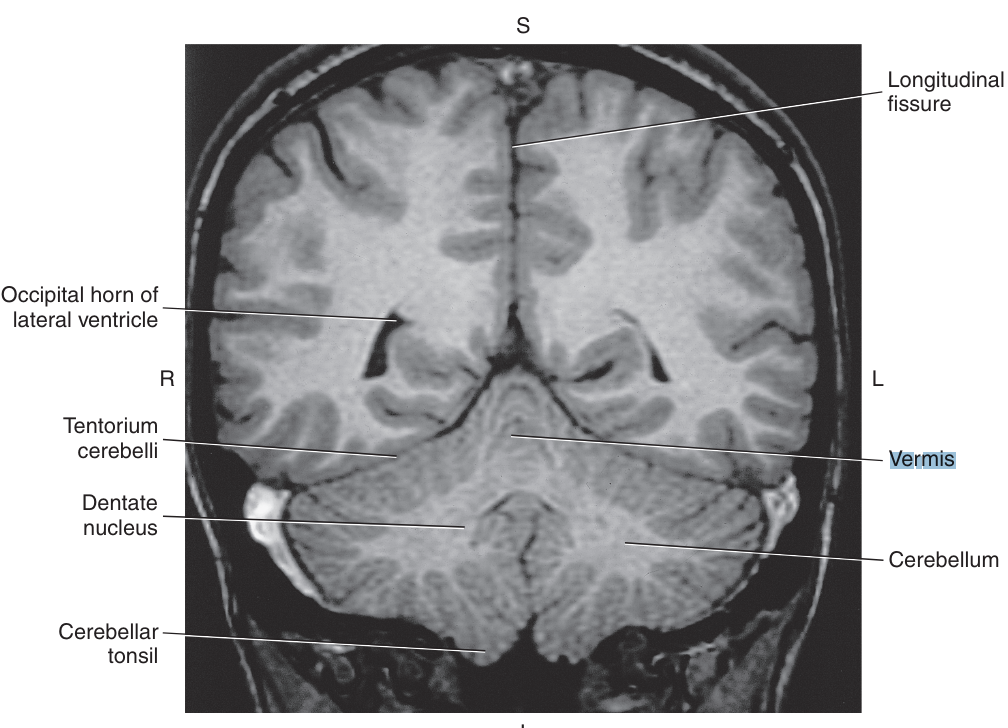
a midline structure named the _ connects the two hemispheres
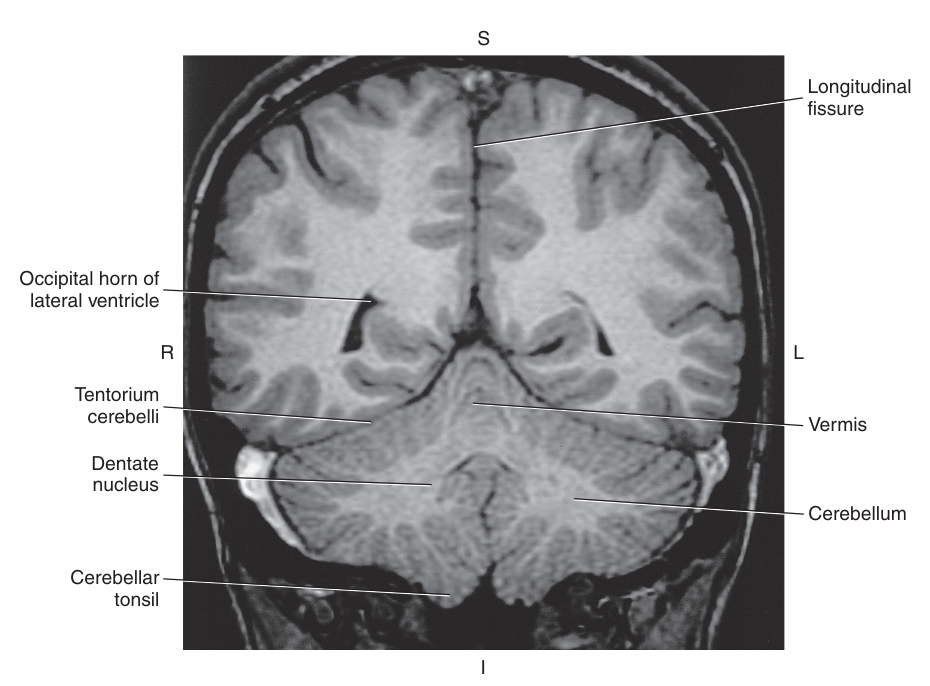
vermis
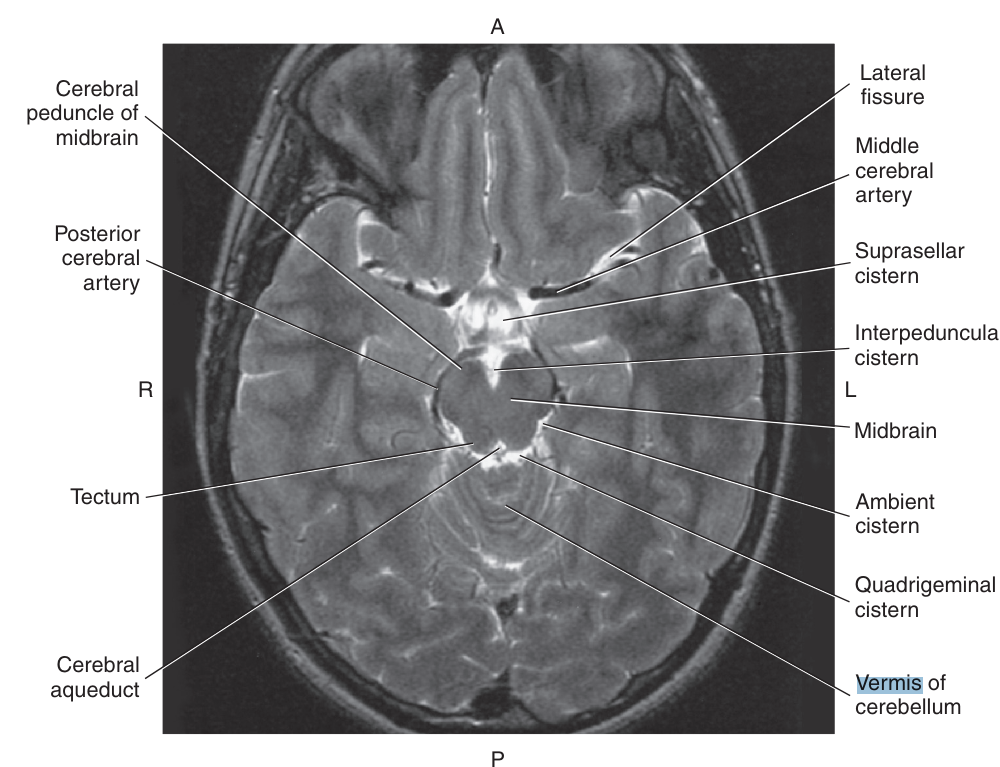
On the inferior aspect of each hemisphere are two rounded prominences, termed the _
cerebellar tonsils
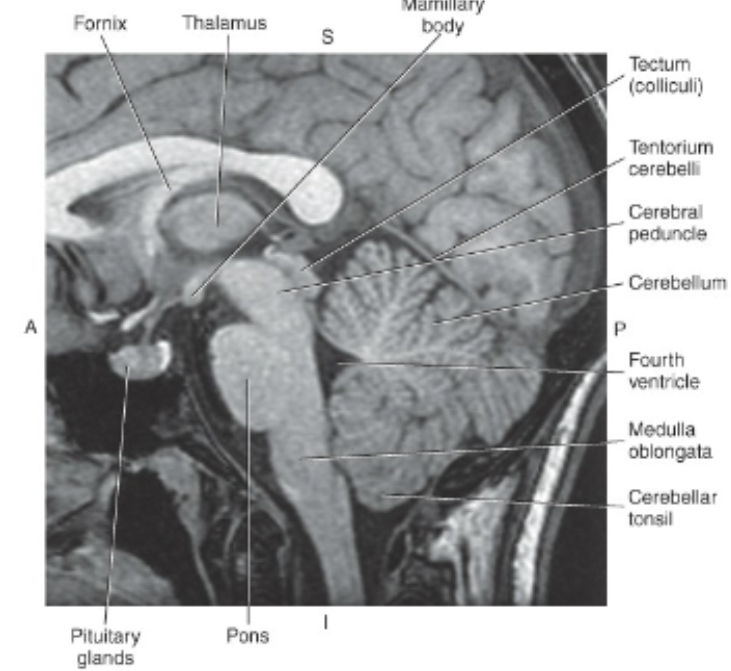
_ conncet the cerebellum to the brainstem
three pairs of nerve fiver tracts, the cerebellar peduncles,
the superior cerebellar peduncles connect the _
cerebellum to the midbrain, the middle to the pons, and the inferior to the medulla oblongata
Deep within the center of each cerebellar hemisphere is a collection of nuclei called the
dentate nucleus