Biology Final MC Questions
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Which of the following is necessary for the formation of a generalized (typical) lipid?
alcohol
__ substances readily mix with water
hydrophilic
A surfactant:
facilitates the mixing of water and hydrophobic substances
The “typical” lipid is called a:
triglyceride
The difference between a fibrous protein with a pleated-sheet configuration and an enzyme is that an enzyme possesses:
teritiary structure
Which of the following is NOT a function of carbohydrates
waterproofing
Which of the following does NOT contain nitrogen?
glycerol
Water always behaves as if it is bounded by a membrane. This phenomenon is called:
surface tension
Which of the following is true of DNA but not of RNA?
configured as a double-helix
A substance that donates a hydrogen ion when in solution is a(n):
acid
Isotopes differ in their respective numbers of:
neutrons
The reaction A + B —> AB + H2O is called:
dehydration synthesis
The healthiest lipid of lipid componet in the diet is a(n):
omega-3 fatty acid
If an organic molecule is composed of O, H, C, and nothing else that molecule CANNOT be a(n):
amino acid
The monomeric unit of a nucleic acid is a(n):
nucleotide
Which substance would have a pH of 7?
solution of CaCl in water
A positively charged chemical particle is called a(n):
cation
A salt is a substrate that:
is ionically bound and neither donates nor accepts a hydrogen ion in a solution
H-O-H the molecular structure drawn above represents a(n):
inorganic compound
A relatively high level of __ in the blood stream is indicative of a healthy lipid profile
HDL
The Endosymbiotic Hypothesis explains the existence of ___ in a eukaryotic cell
mitochondria and chloroplasts
Nucleic acid is a component of:
ribosomes
The rate of osmosis increases with:
Either heat or concentration gradient or both
Mitochondria contain:
cristae
The nucleolus is a collection of molecules of:
RNA
Patrick Star lives in Bikini Bottom, which is in osmotic equilibrium with his body. His environment is therefore:
isotonic
Placing Patrick in fresh water will causes his cells to:
gain water until they rupture
Placing Patrick in the Great Salt Lake of Utah will cause his cells to:
lose water
Movement of water across a membrane is called:
osmosis
The skeletal structure of a cell membrane is composed of 2 layers of
phospholipid
Schleiden and Schwann are given credit for the development of theL
Cell theory
__ are able to move freely across a cell membrane by simple diffusion
lipids
The difference between active transport and facilitated transport is the necessary input of:
energy
The cytoskeleton includes:
spindle fibers
The difference between vesicles and vacuoles is that vacuoles:
are bigger
Adjacent cells communicate in a multicellular plant via:
plasmodesmata
The net, high energy output of the Calvin Cycle is:
PGAL
Cyclic photophosphorylation differs from noncyclic photophosphorylation in the cyclic photophosphorylation does not:
split water and release O2
The Calvin Cycle represents the light-independent reactions of:
C-3 plants
The complete respiration of a molecule of glucose includes all of the following except:
noncyclic photophosphorylation
Which of the following processes is anaerobic?
glycolysis
The high-energy outputs of noncyclic photophosphorylation include ATP and:
NADPH2
Which of the following best describes the process by which NADP becomes NADPH2 in photosynthesis?
reduction
Electron transport that results in phosphorylation is carried out by:
cytochromes
To avoid photorespiration, C-4 plants utilize the biochemical pathway __ as the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis
Hatch-Slack pathway
The molecule known as the “energy currency of the cell” is:
adenosine triphosphate
The molecules that represents one-half of a glucose molecule is:
PGAL
Which molecule has the least available energy for a cell?
CO2
Energy can neither be created nor destroyed. This is a statement of the:
First Law of Thermodynamics
No energy conversion is 100% efficient. This is a statement of the:
Second Law of Thermodynamics
Which of the following represents the most reduced compound?
CH4 (methane)
The molecule known as P700 represents:
a primary pigment in photosynthesis
Xanthophylls and carotenoids are examples of:
accessory pigments in photosynthesis
Thylakoids are part of the:
chloroplast
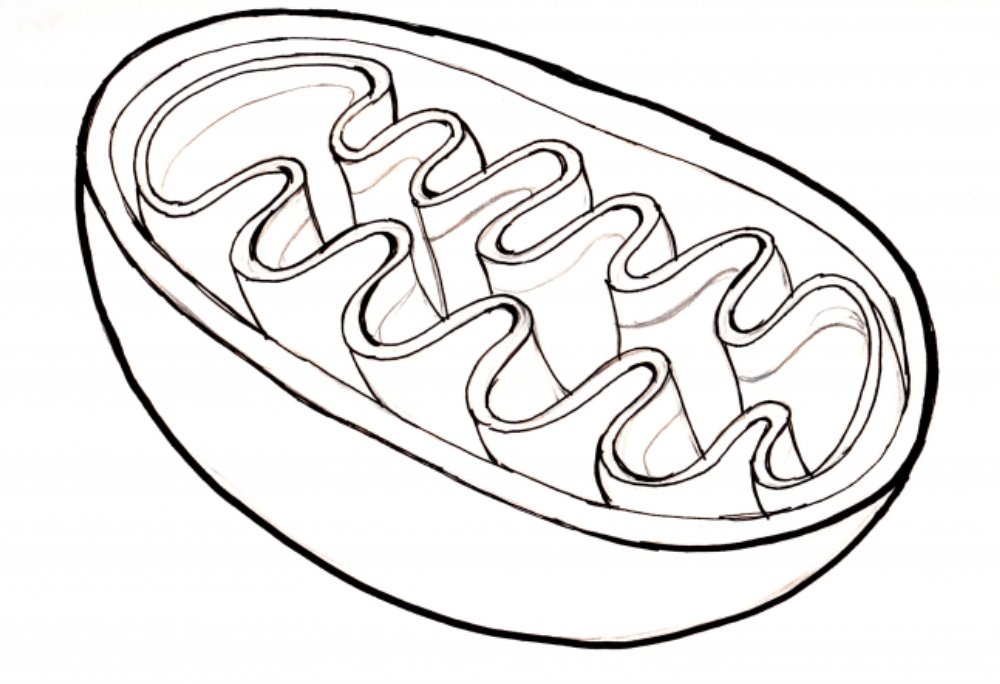
This drawing depicts the cellular organelle:
mitochondrion
The Calvin Cycle takes place in the __ of the chloroplast:
stroma