Anat&Phys 338 Exam 2
1/301
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
302 Terms
Rostral
refers to the most frontal portion of the brain. rhymes with nostril.
Caudal
refers to structures closer to the back of the head.
Dorsal
refers towards the top of head (superior)
Ventral
refers towards the bottom of the head (inferior)
sulci
folds diving inward, the grooves of the brain
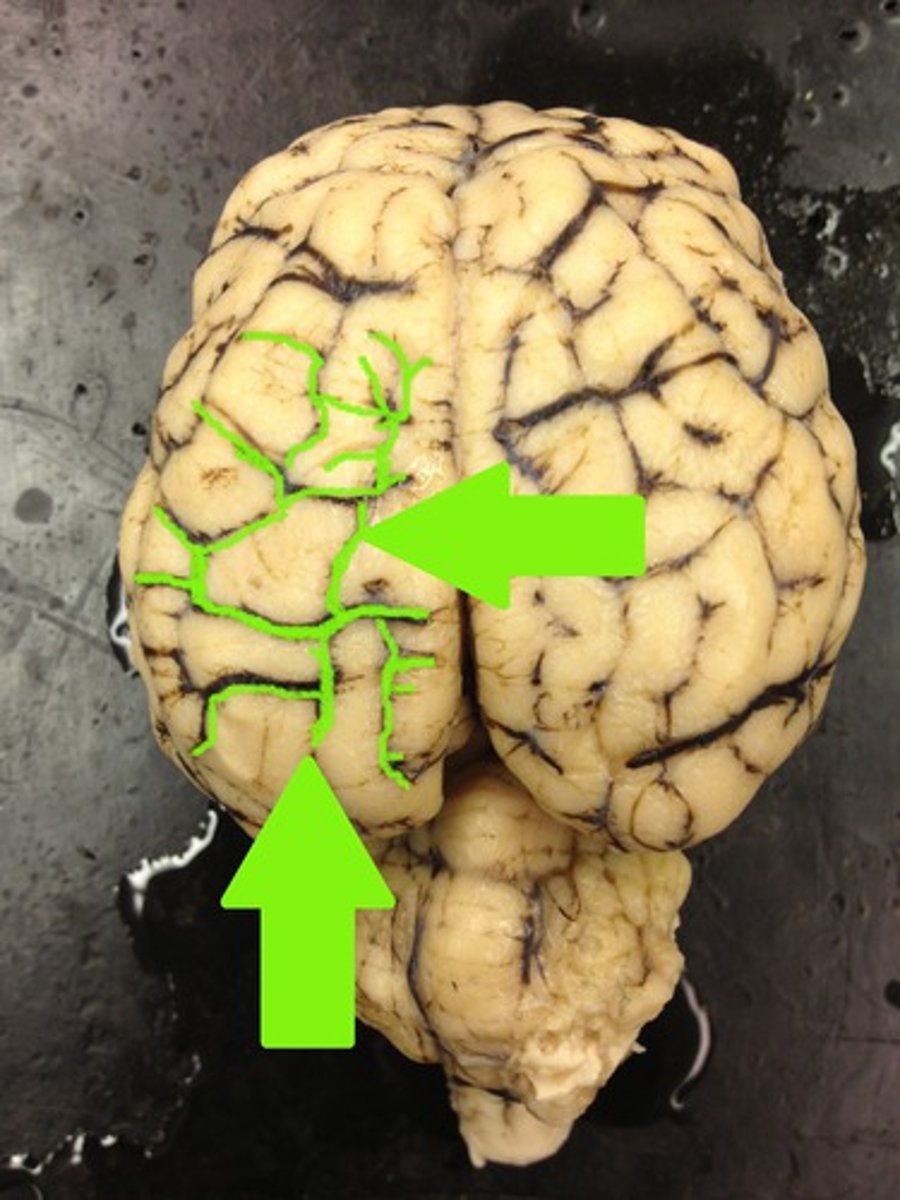
gyri
ridges of the cortex, visible on the surface of the brain
cerebral cortex
surface layer of the cerebral hemispheres, composed of grey matter, form sulci and gyri
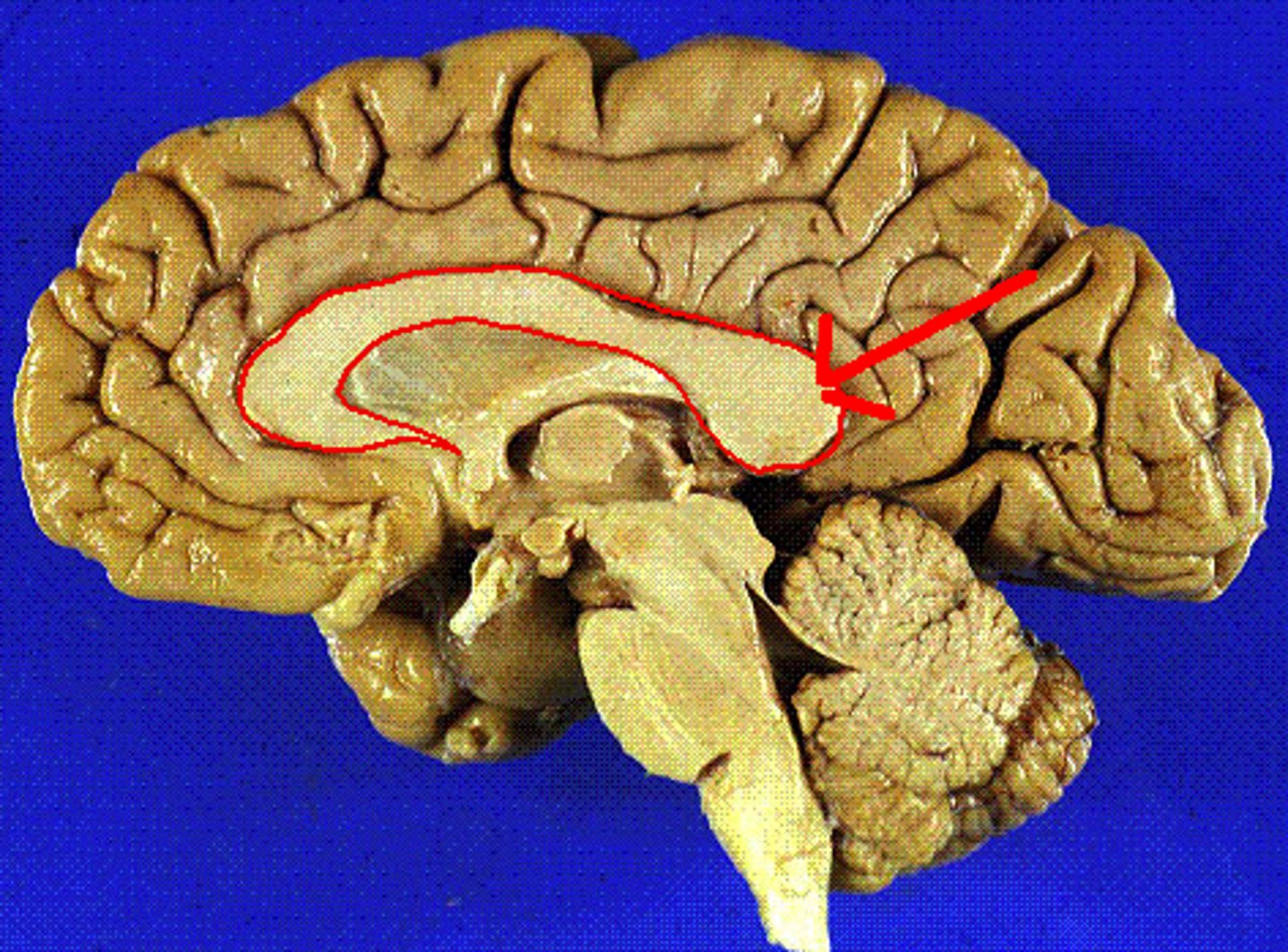
corpus callosum
The large bundle of axons (white matter) that connects the brain's two hemispheres, responsible for relaying information between the two sides.
median longitudinal fissue
separates the R and L hemispheres
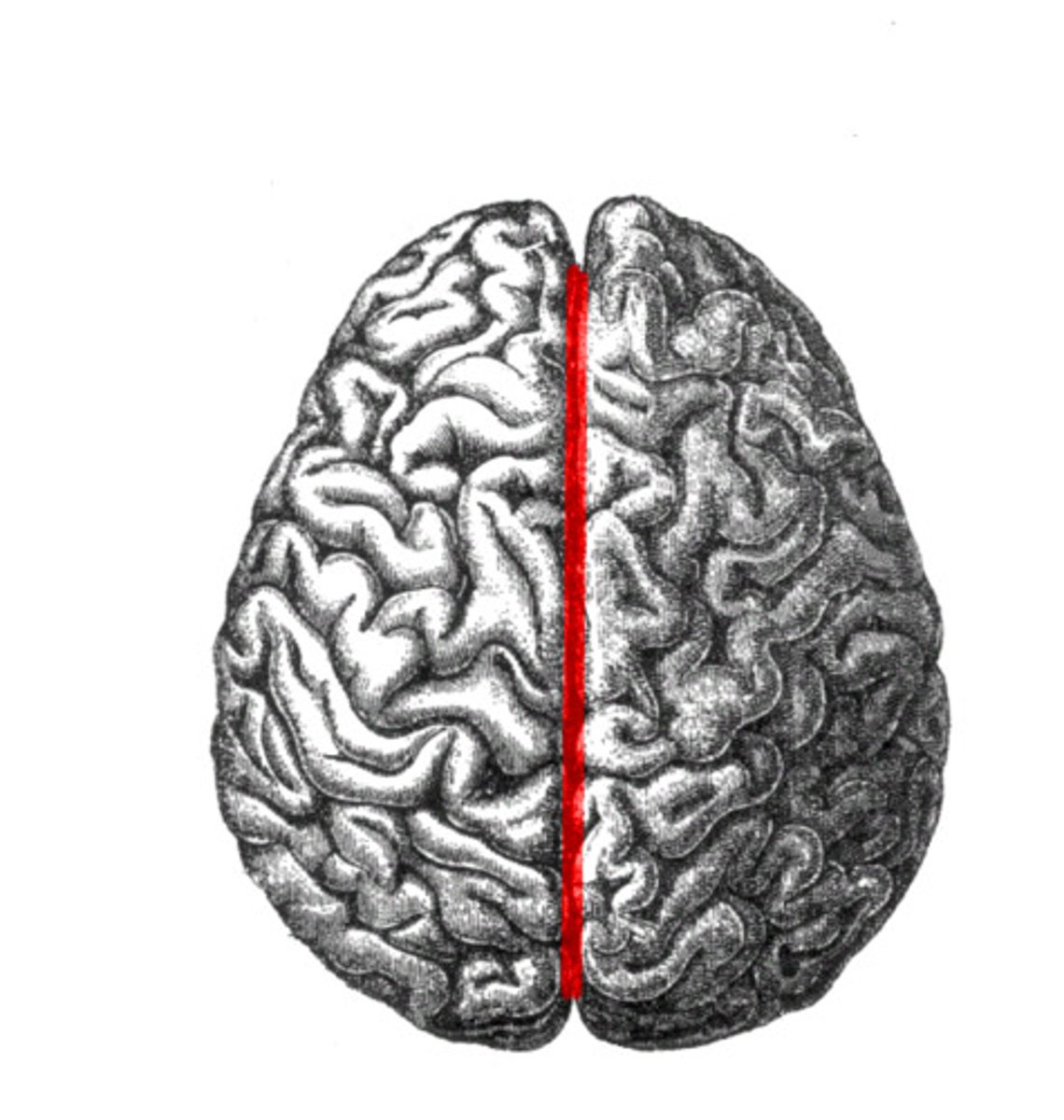
central sulcus
marks the boundary between the frontal+parietal lobes
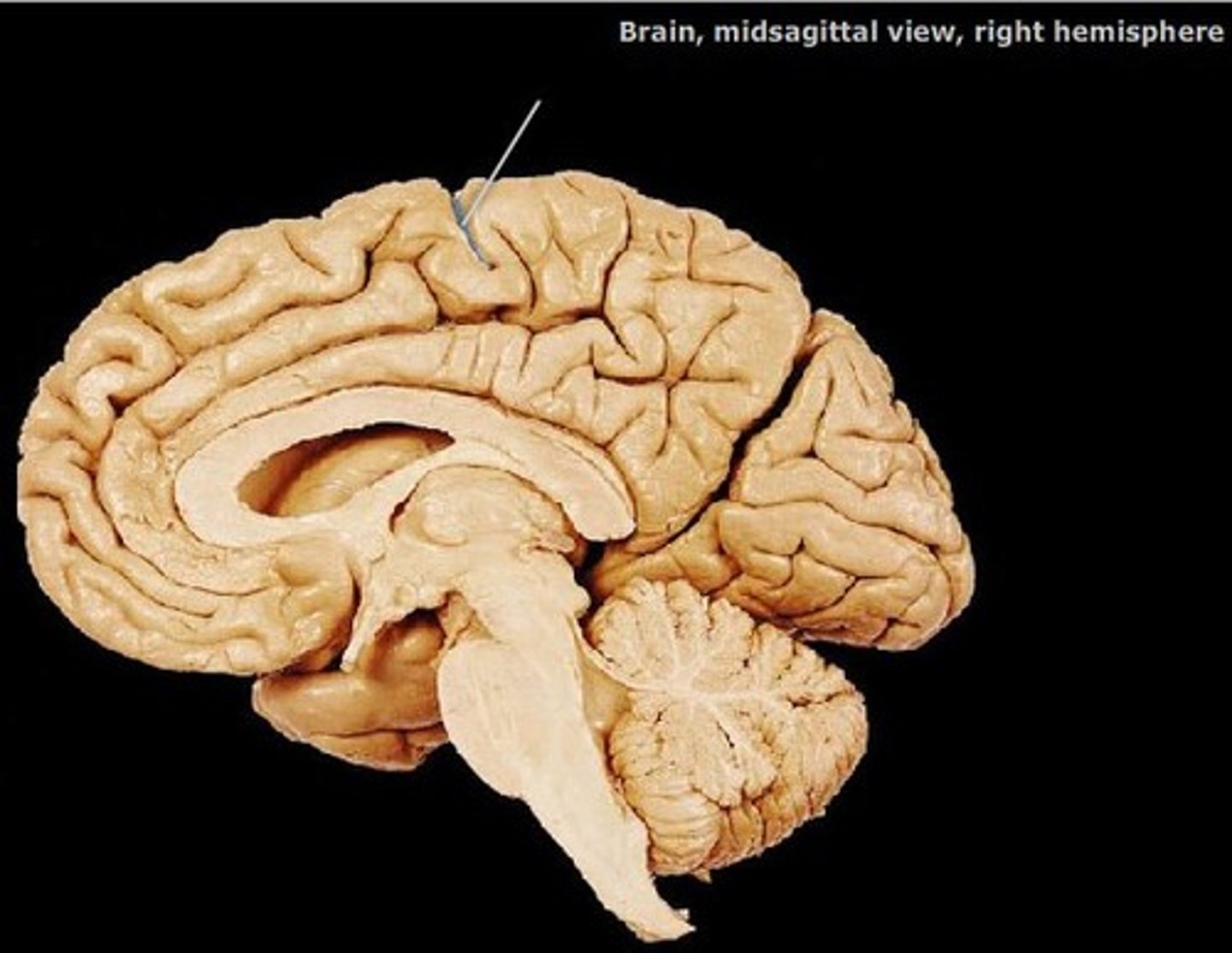
frontal lobe
The lobe at the front of the brain associated with movement, speech, and impulsive behavior.
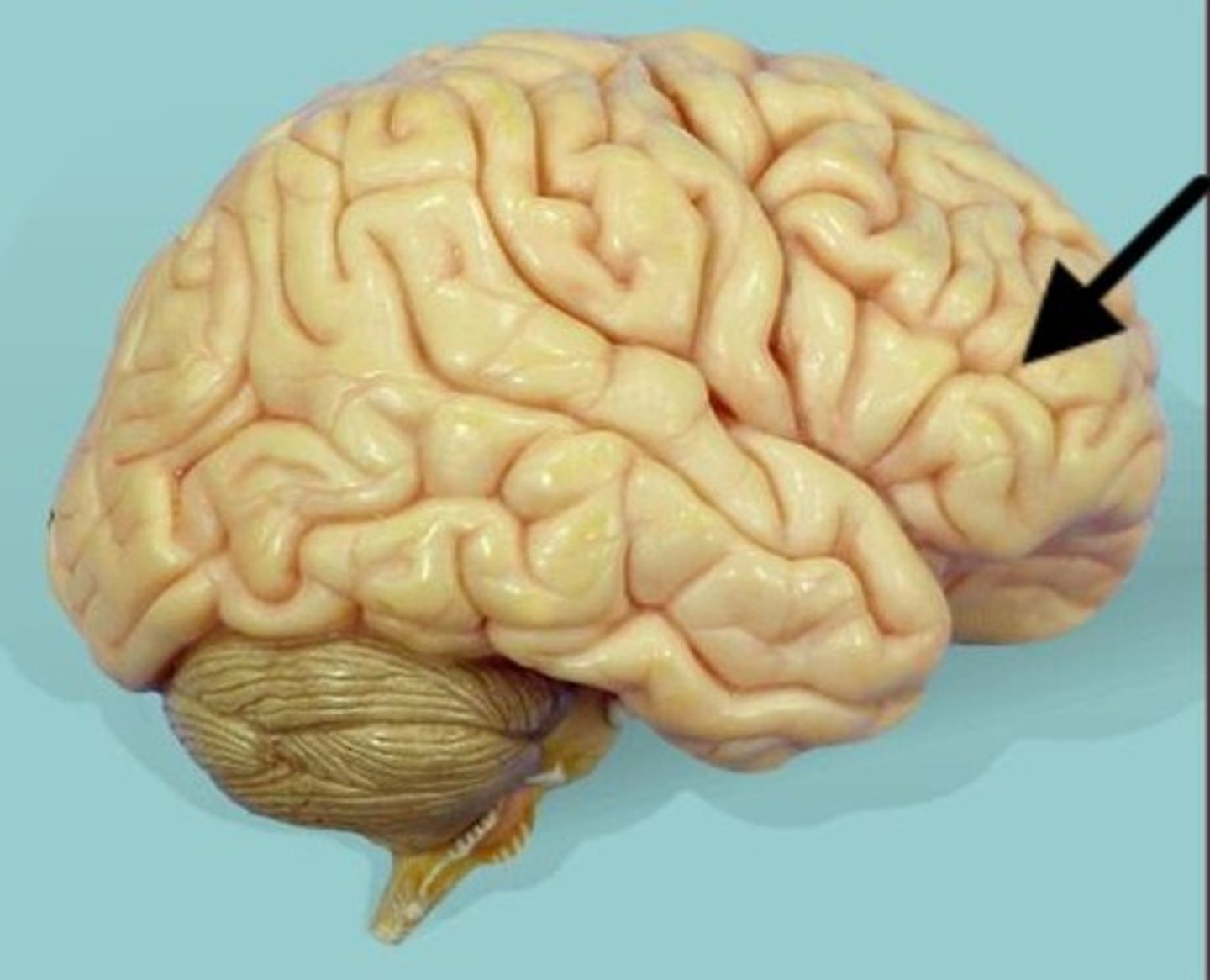
precentral gyrus
located in the frontal lobe, just anterior to the central sulcus. Location of the primary motor cortex.
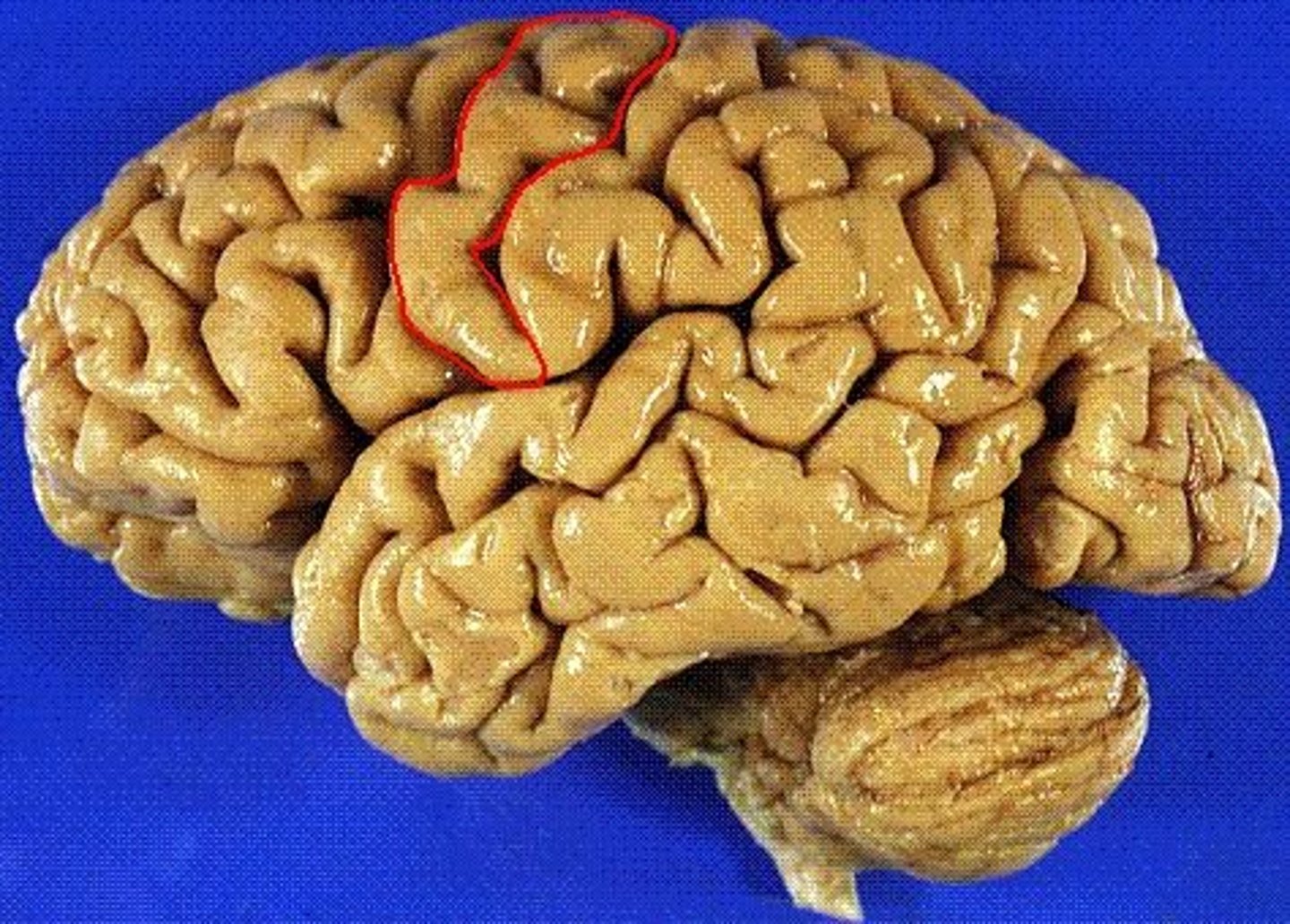
postcentral gyrus
located in the parietal lobe, just posterior to the central sulcus. Location of the primary sensory cortex.
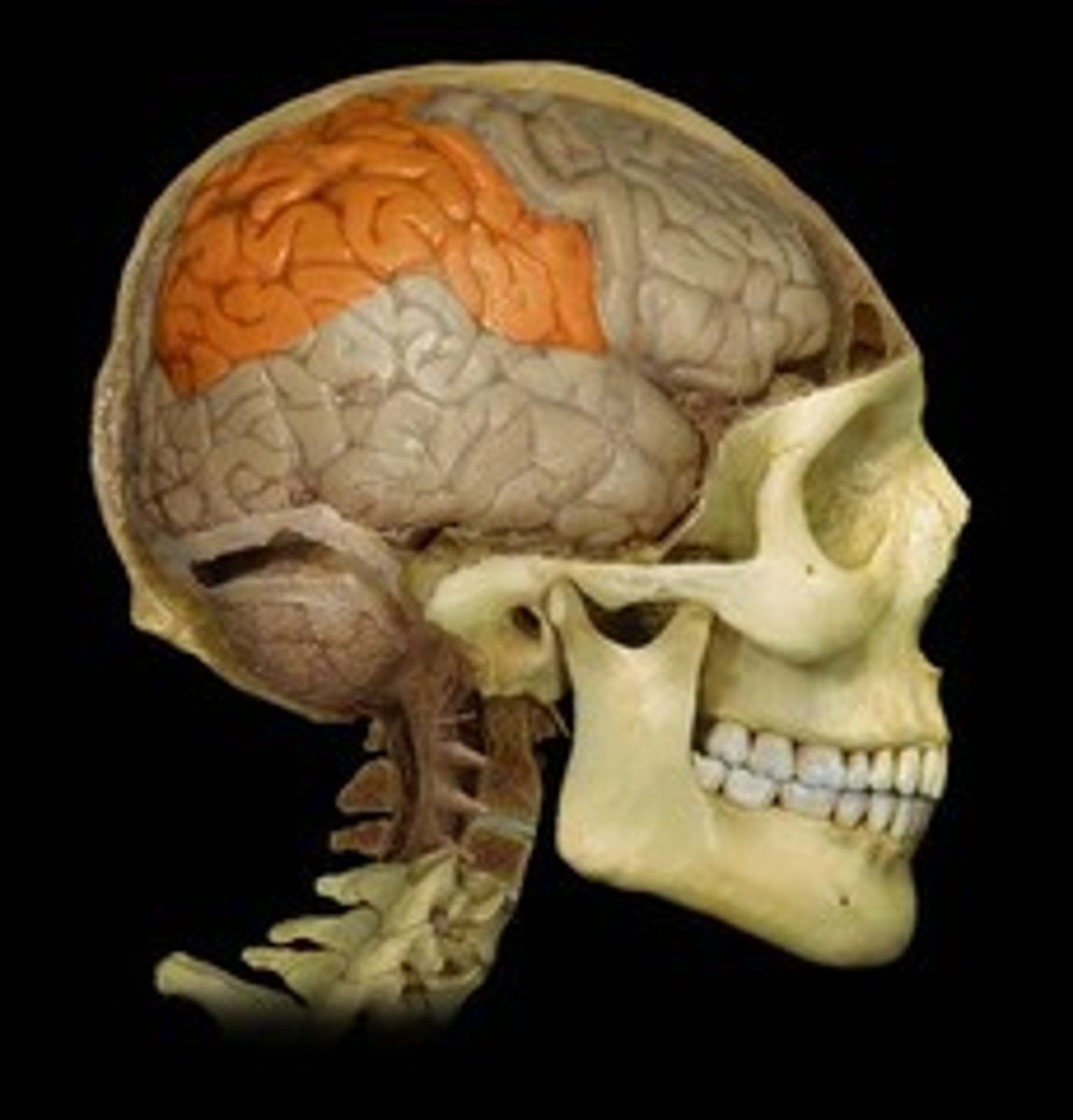
Parietal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex whose functions include processing information about touch.
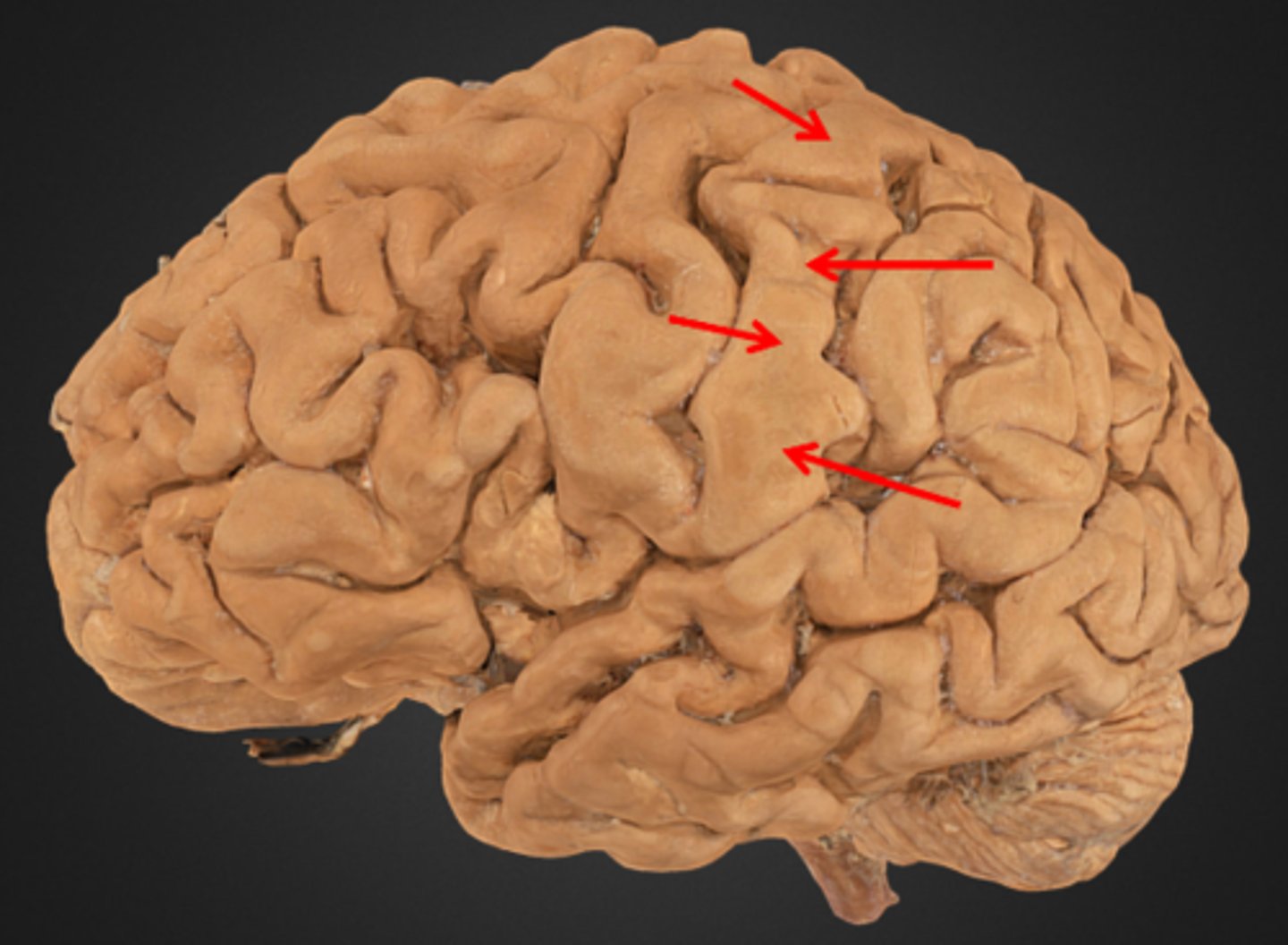
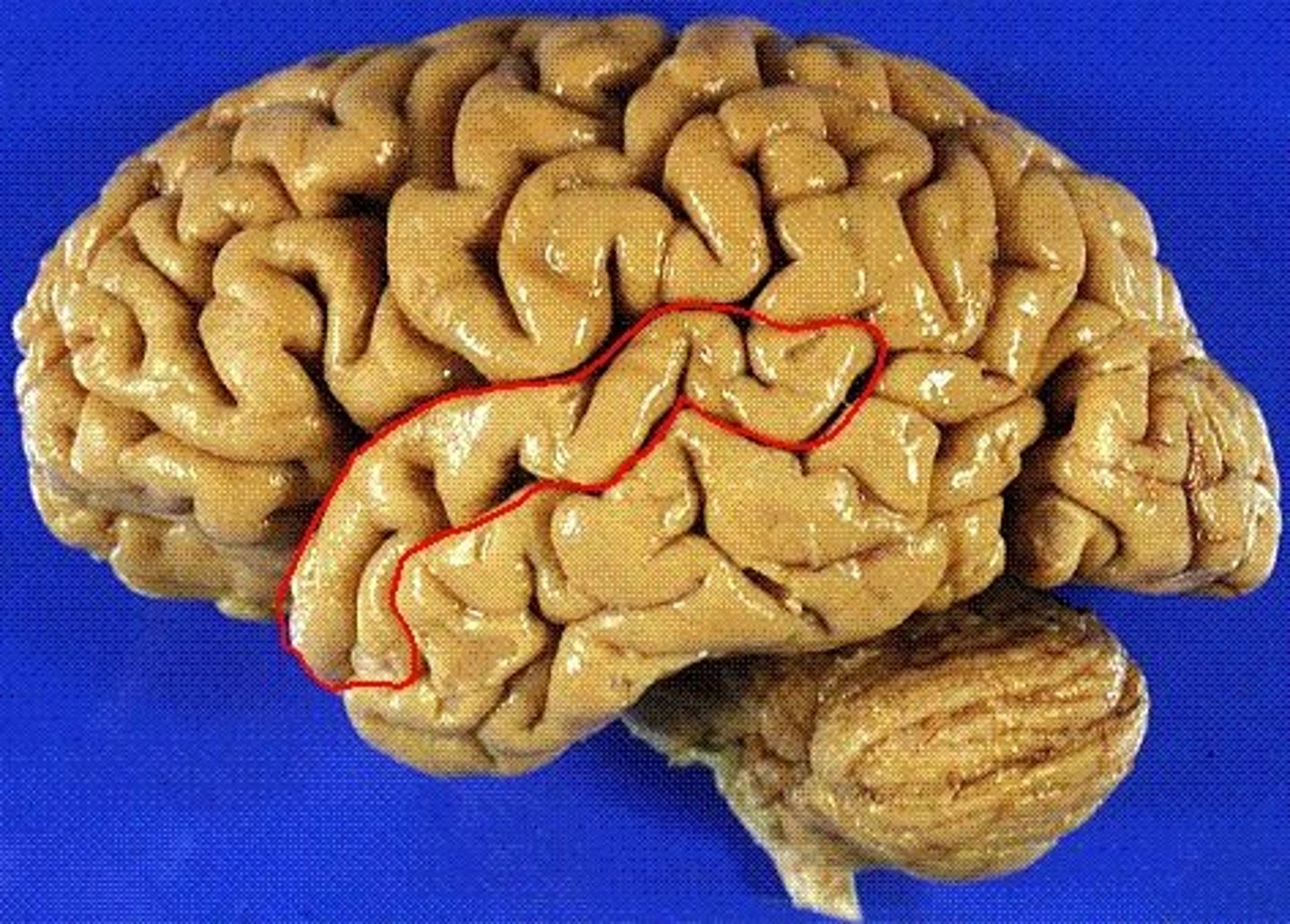
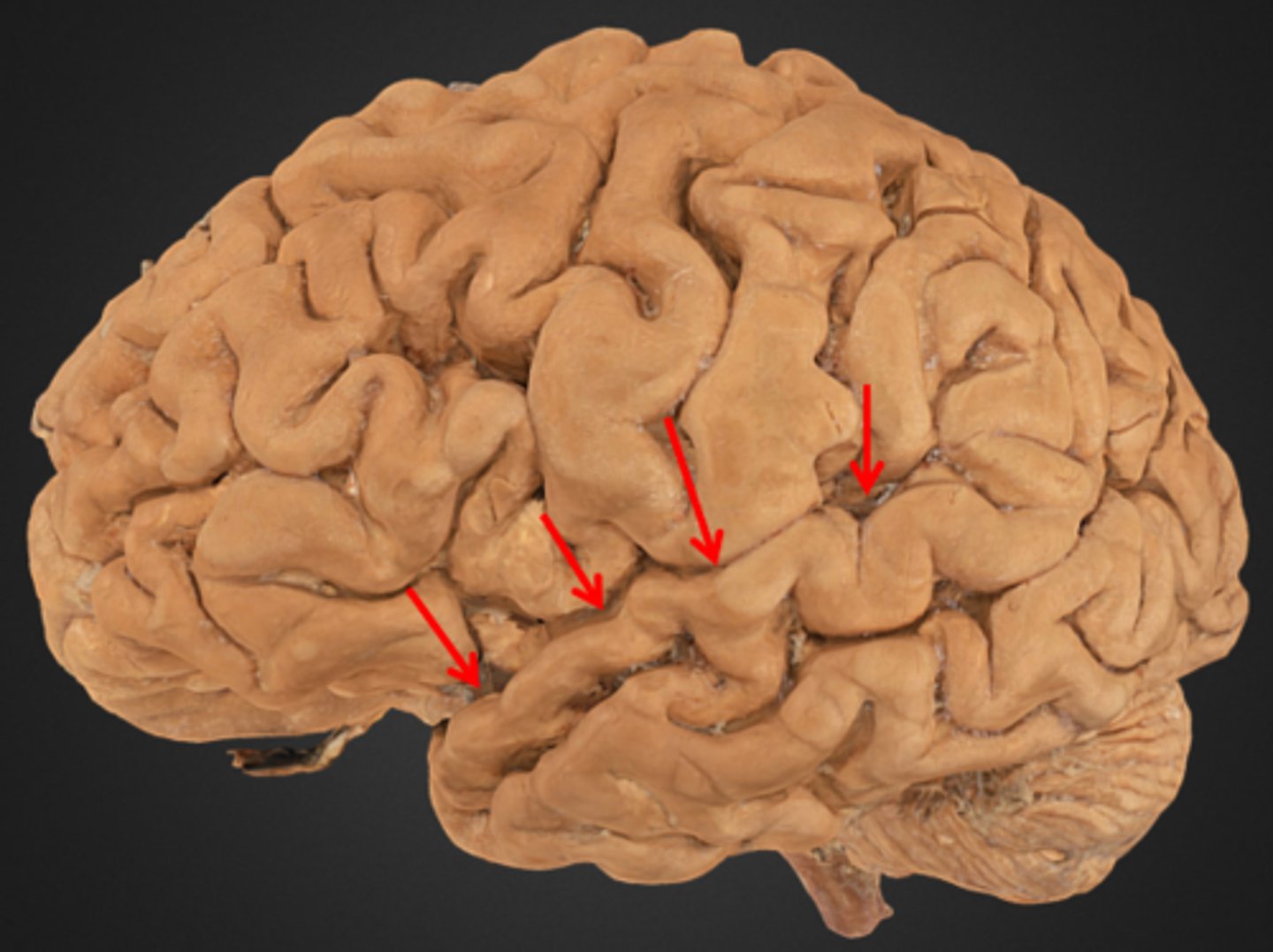
temporal lobe
A part of the brain located behind the ears that is crucial for processing auditory information, memory, emotion, and language. Contains three gyri parallel to the lateral fissure.
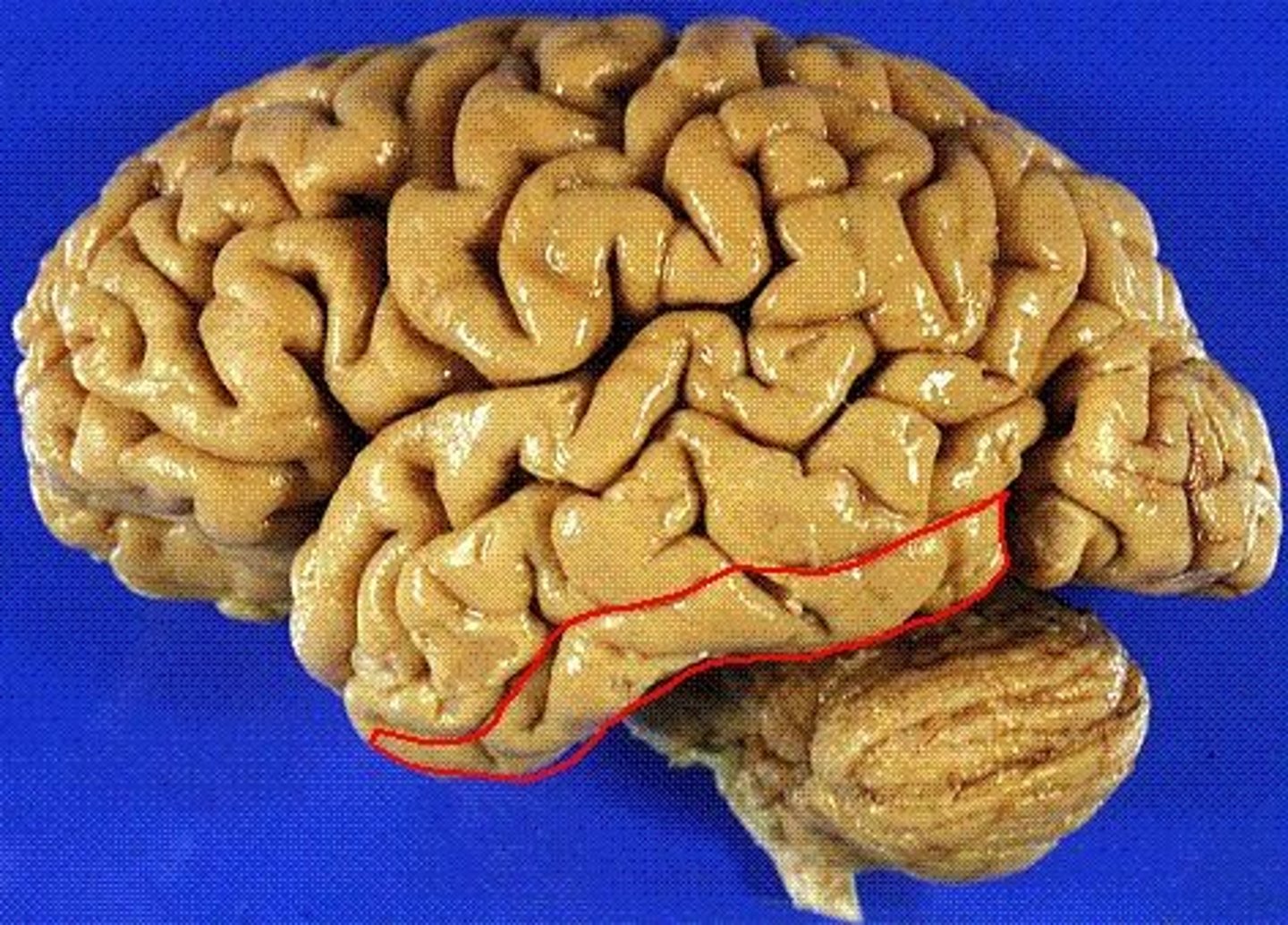
superior temporal gyrus
nearest to the lateral fissure. location of the primary auditory cortex.
middle temporal gyrus
the temporal lobe gyrus that is located between the superior and inferior temporal gyri
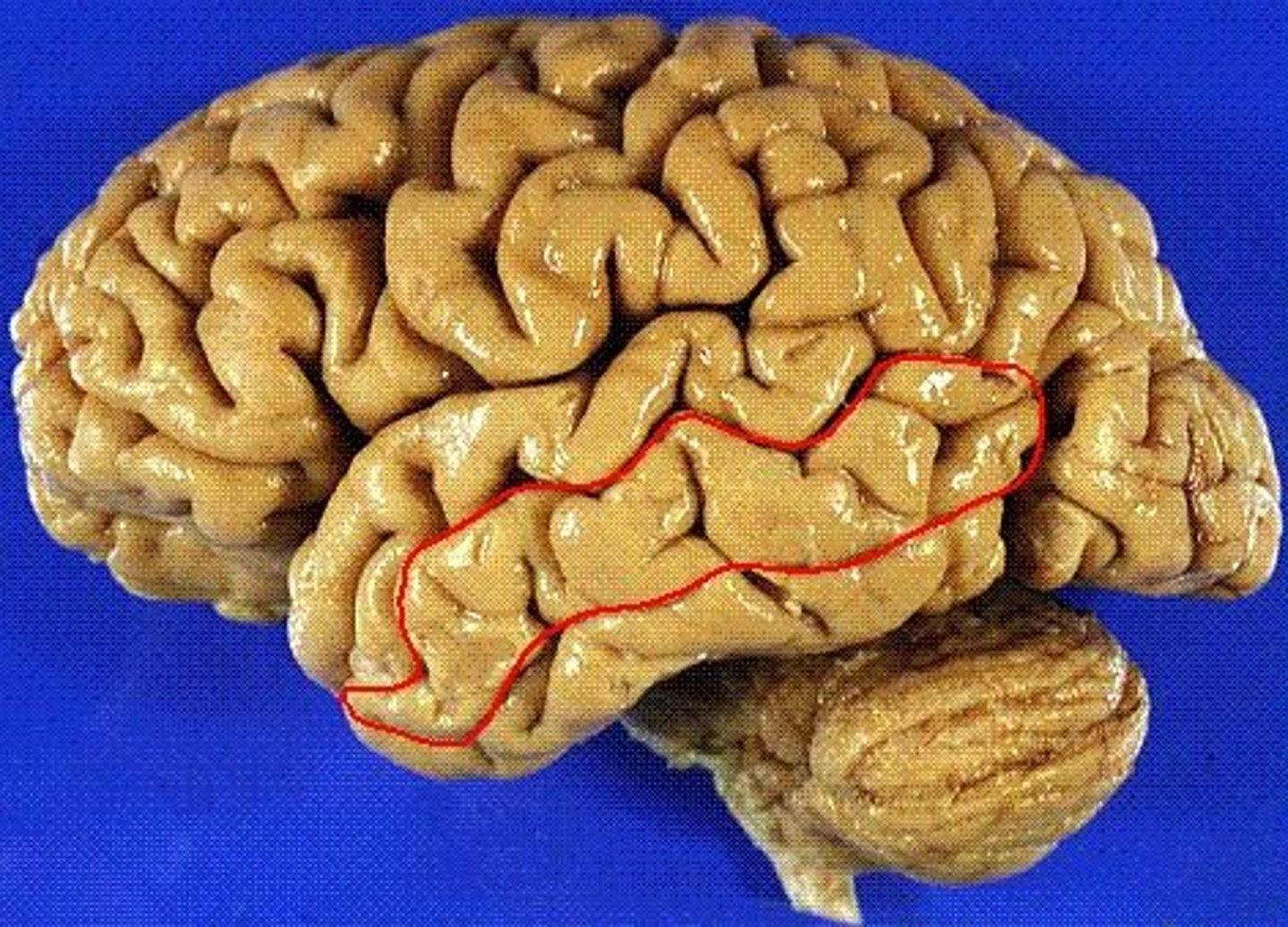
inferior temporal gyrus
the temporal lobe gyrus that is located just inferior to the middle temporal gyrus
hippocampus
the region of the brain more caudal than the amygdala, snail appearance medial in the temporal lobe. Appears with the thalamus+third ventricle. plays a role in memory.
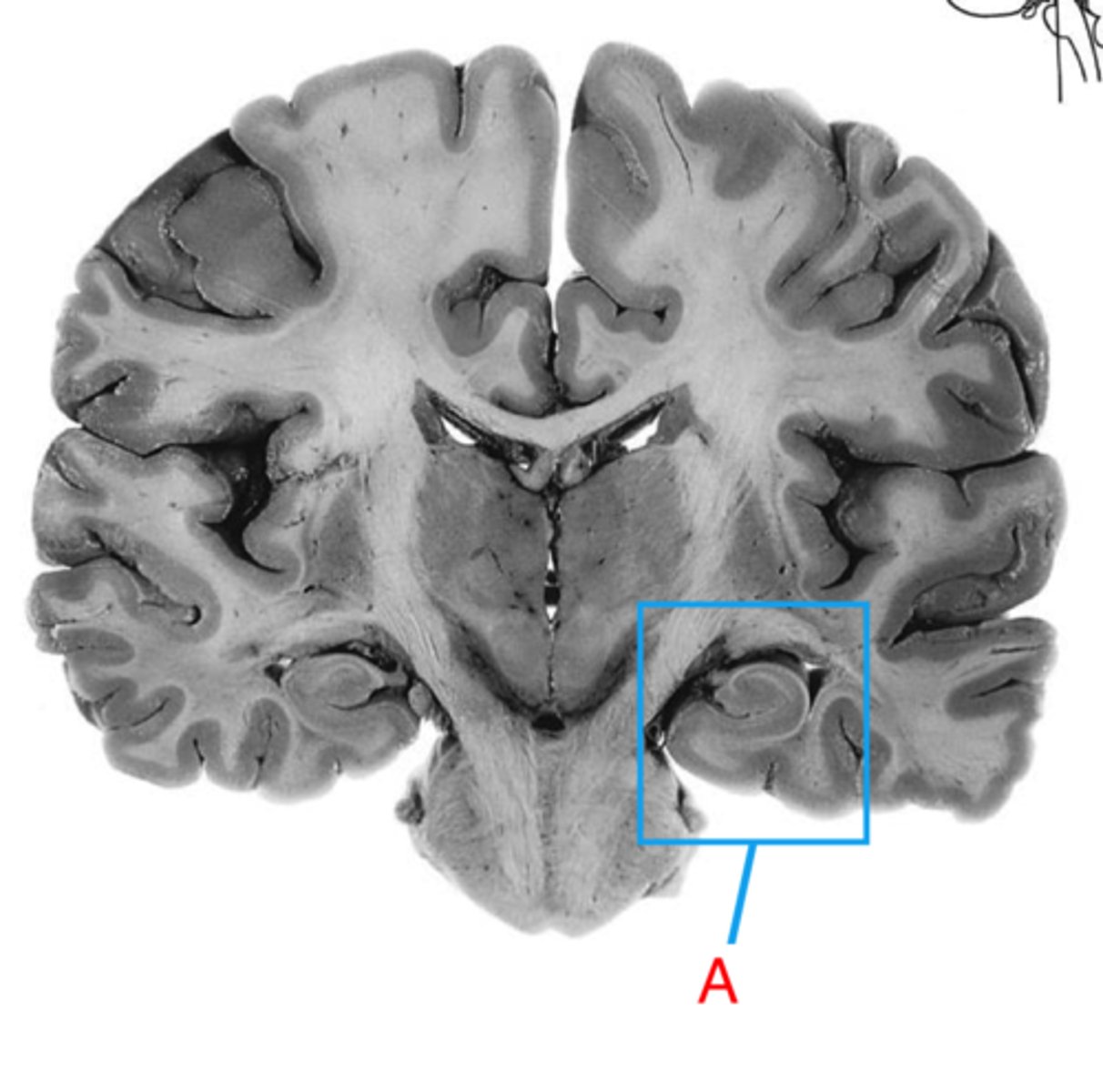
amygdala
rounded shape located medially in the temporal lobe. Appears with the hypothalamus, more rostral than the hippocampus. Plays a role in emotion.
Occipital lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information. Most caudal lobe.
calcarine sulcus
Located in the occipital lobe, runs roughly perpendicular to the parieto-occipital sulcus. Contains the primary visual cortex.
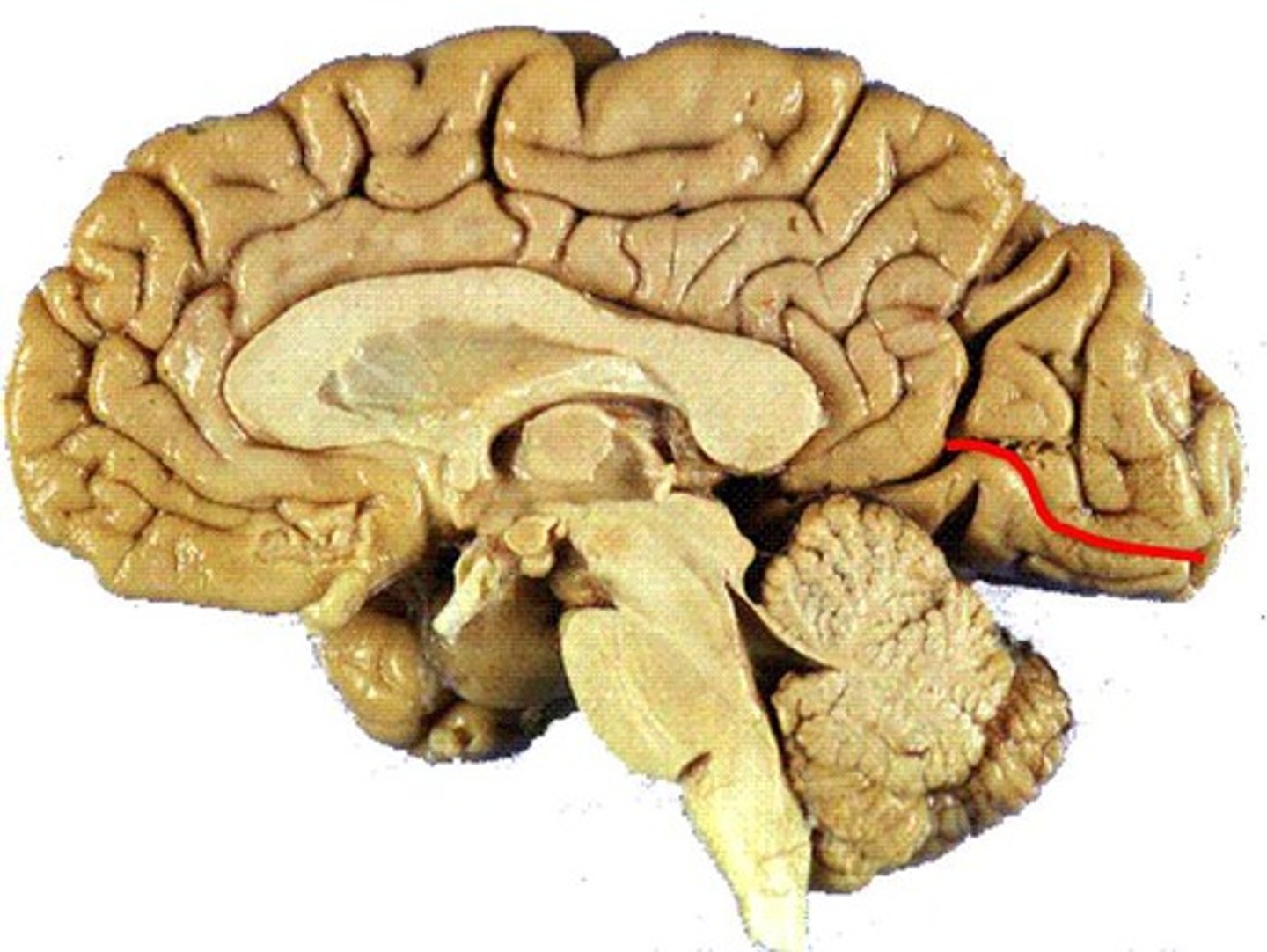
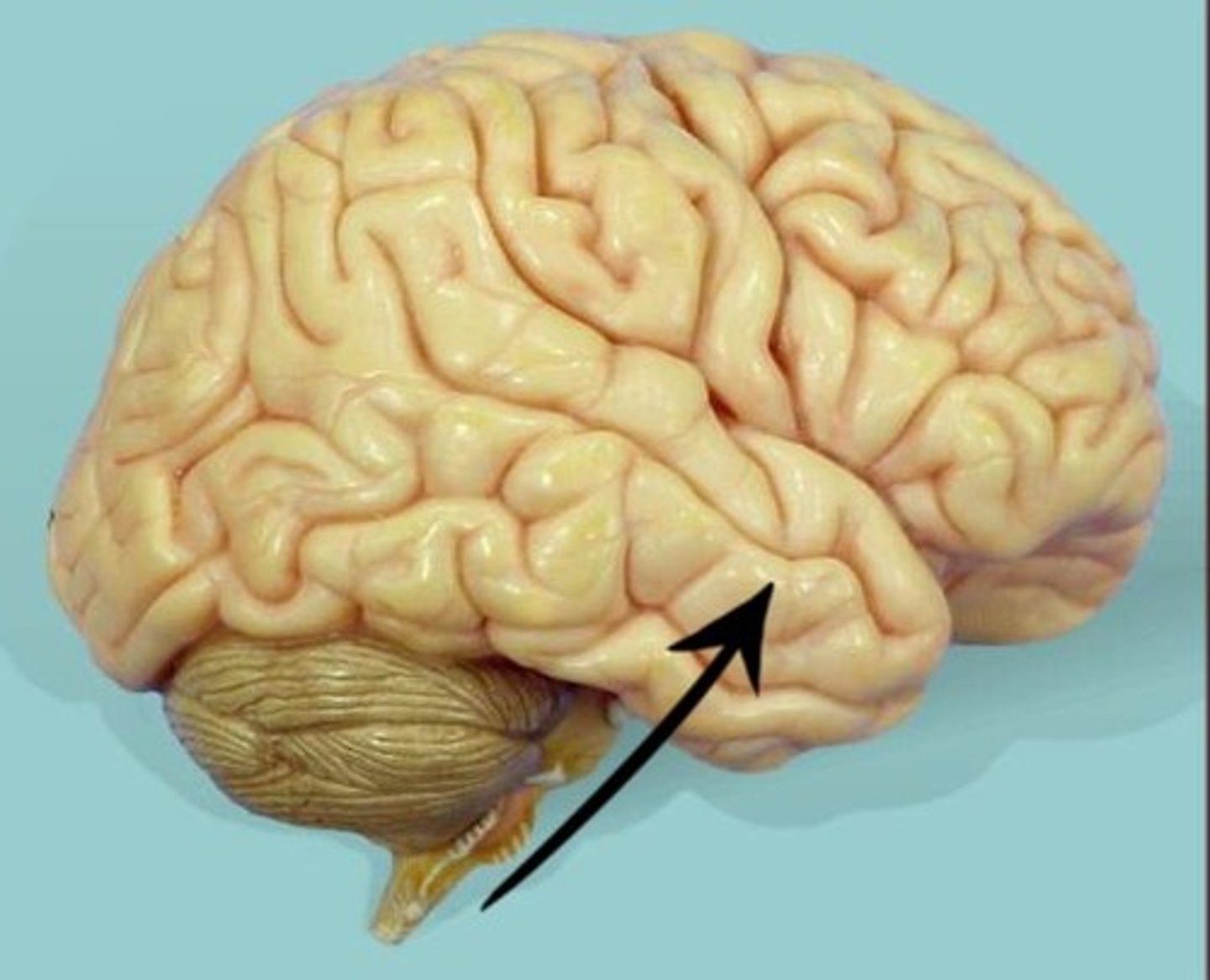
lateral fissure
The boundary between the frontal and temporal lobe.
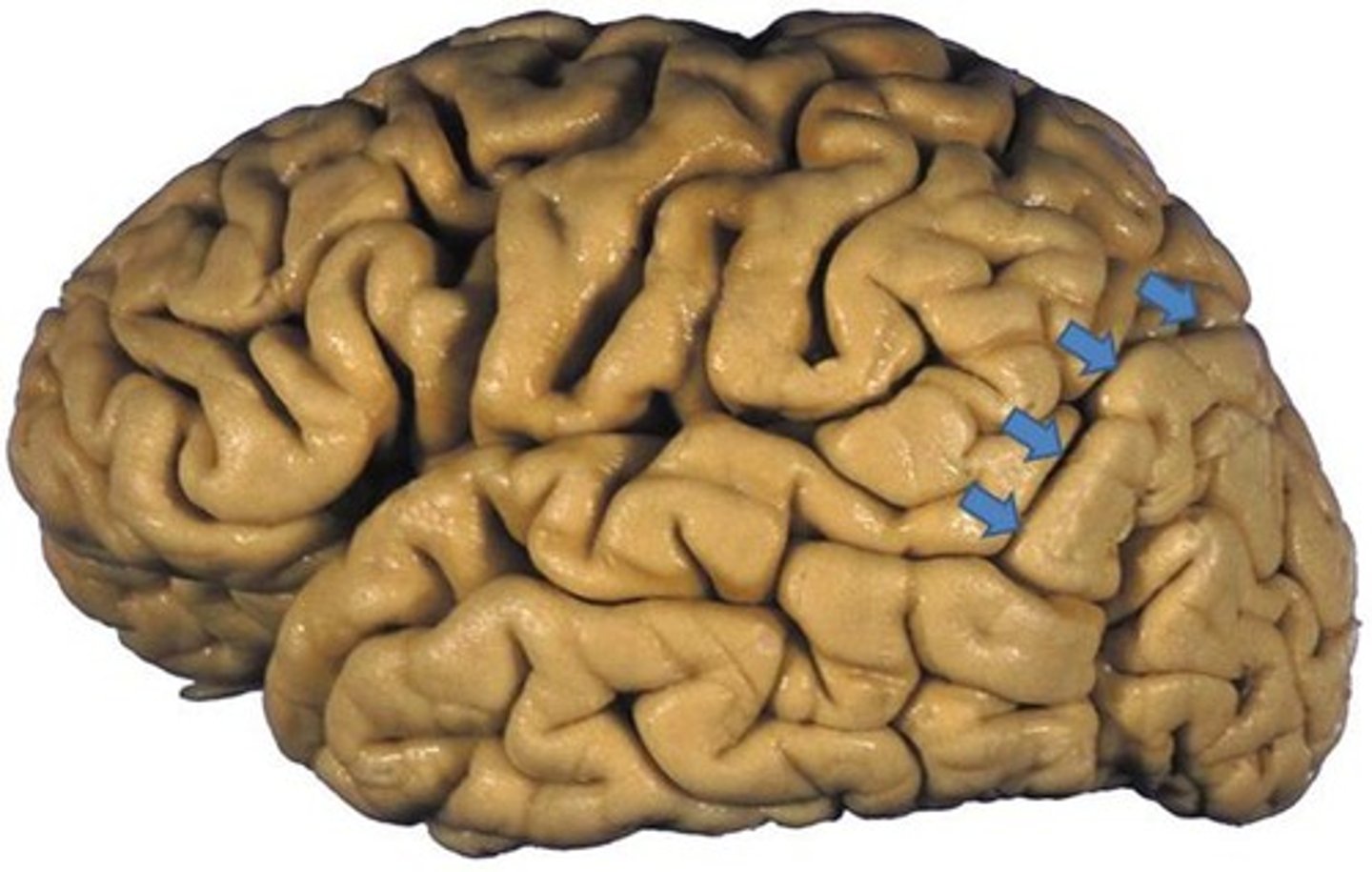
parieto-occipital sulcus
separates the parietal lobe from the occipital lobe
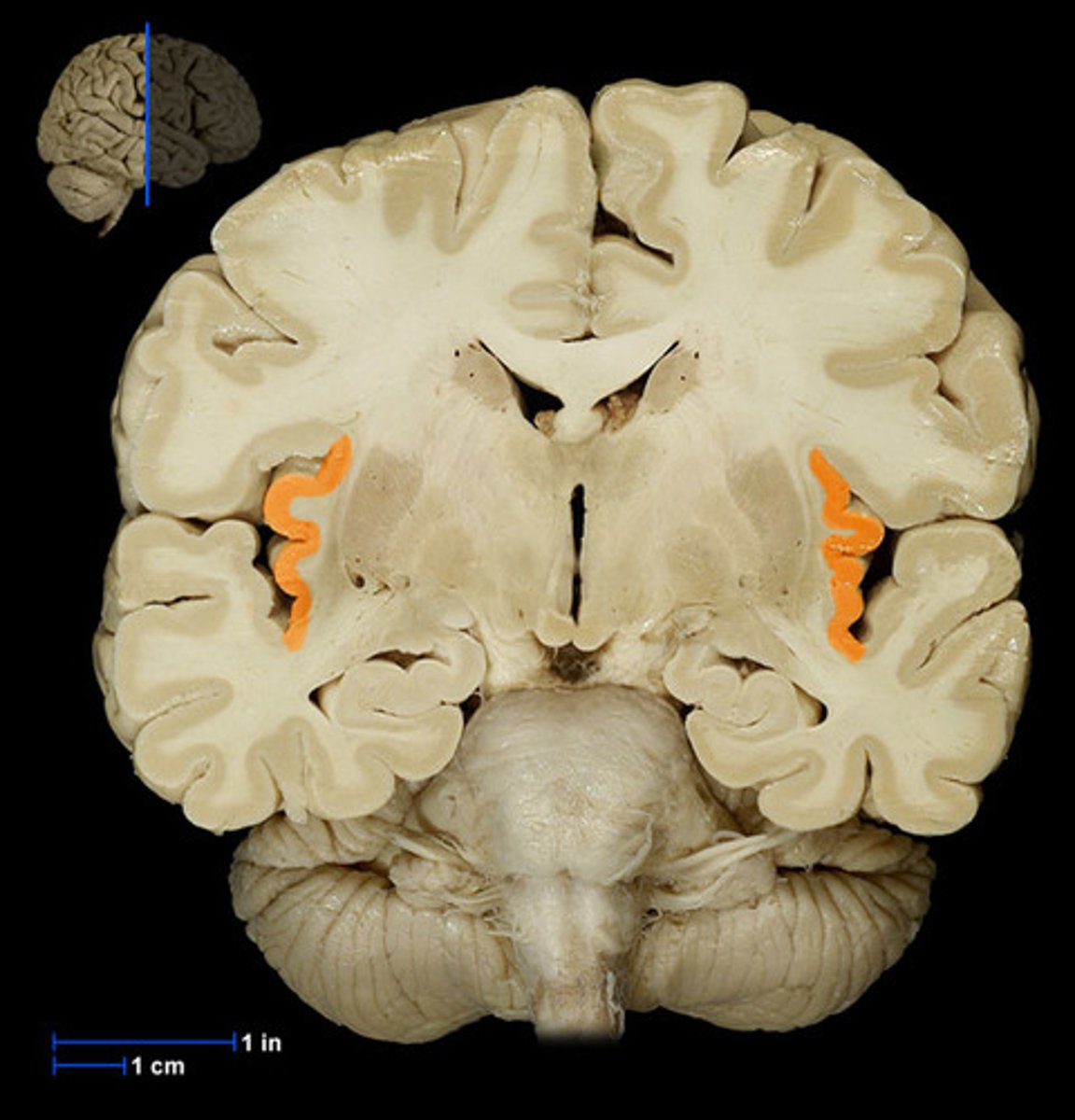
insula
located deep within the lateral fissure between the parietal + temporal lobe. perpendicular to lateral fissure.
thalamus
heart shaped, deep in the brain, hugs the third ventricle. Referred to as the relay center.
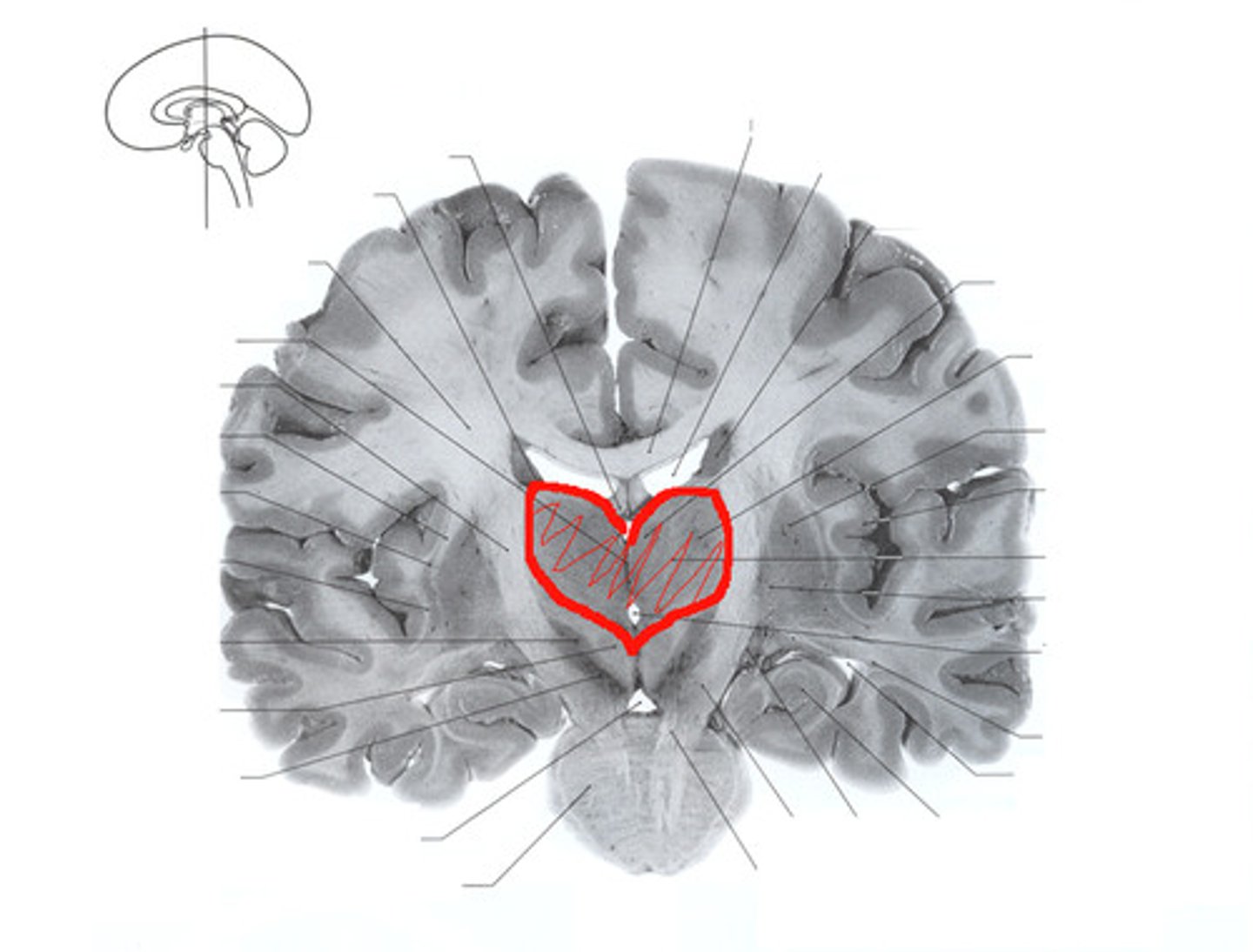
hypothalamus
anterior+inferior to the thalamus, U-shape below the third ventricle, medial to globus pallidus. maintains homeostasis.
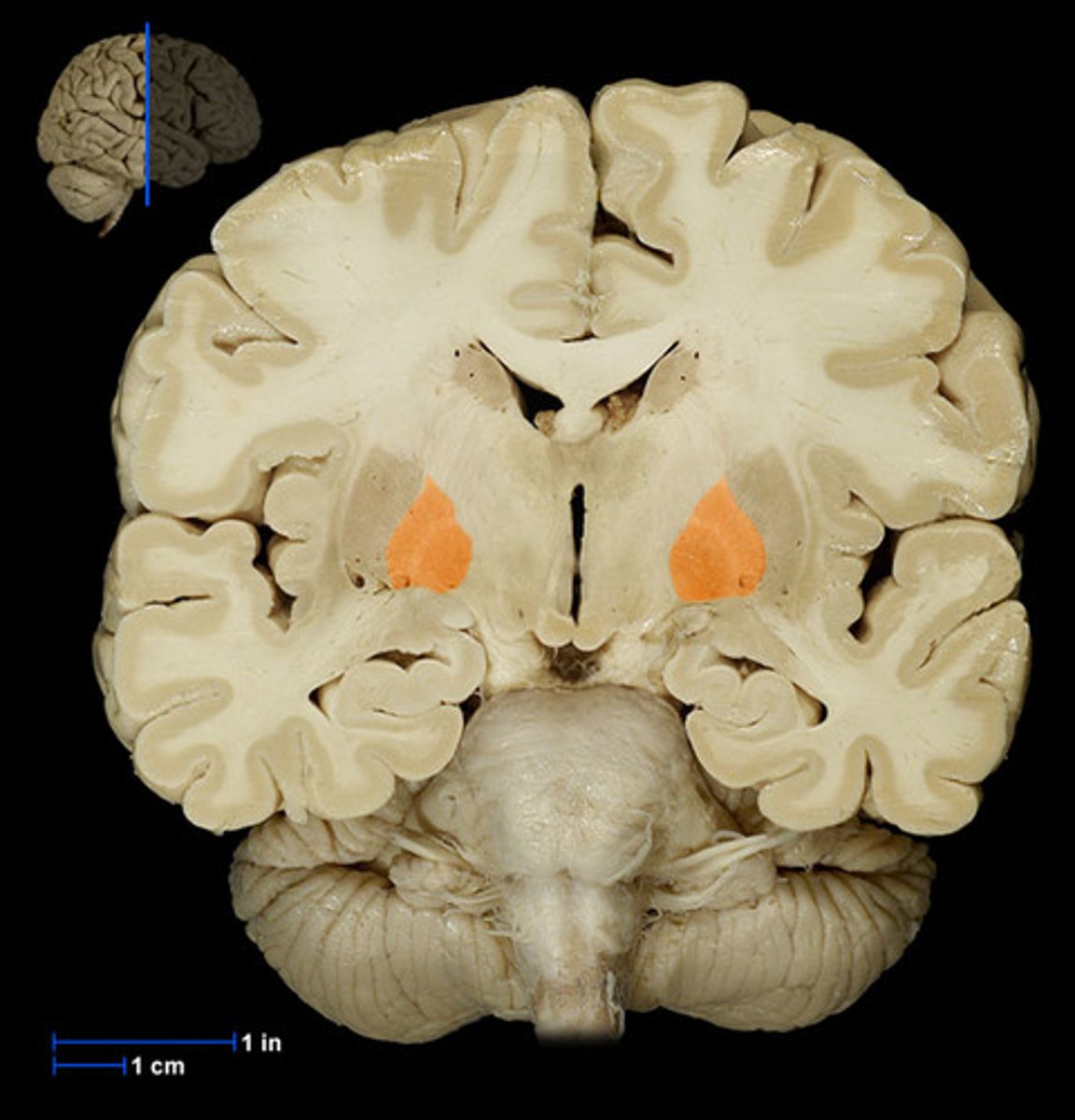
Basal Ganglia
structures in the forebrain that help to control movement. Composed of three main parts: the caudate nucleus, the putamen, and the globus pallidus
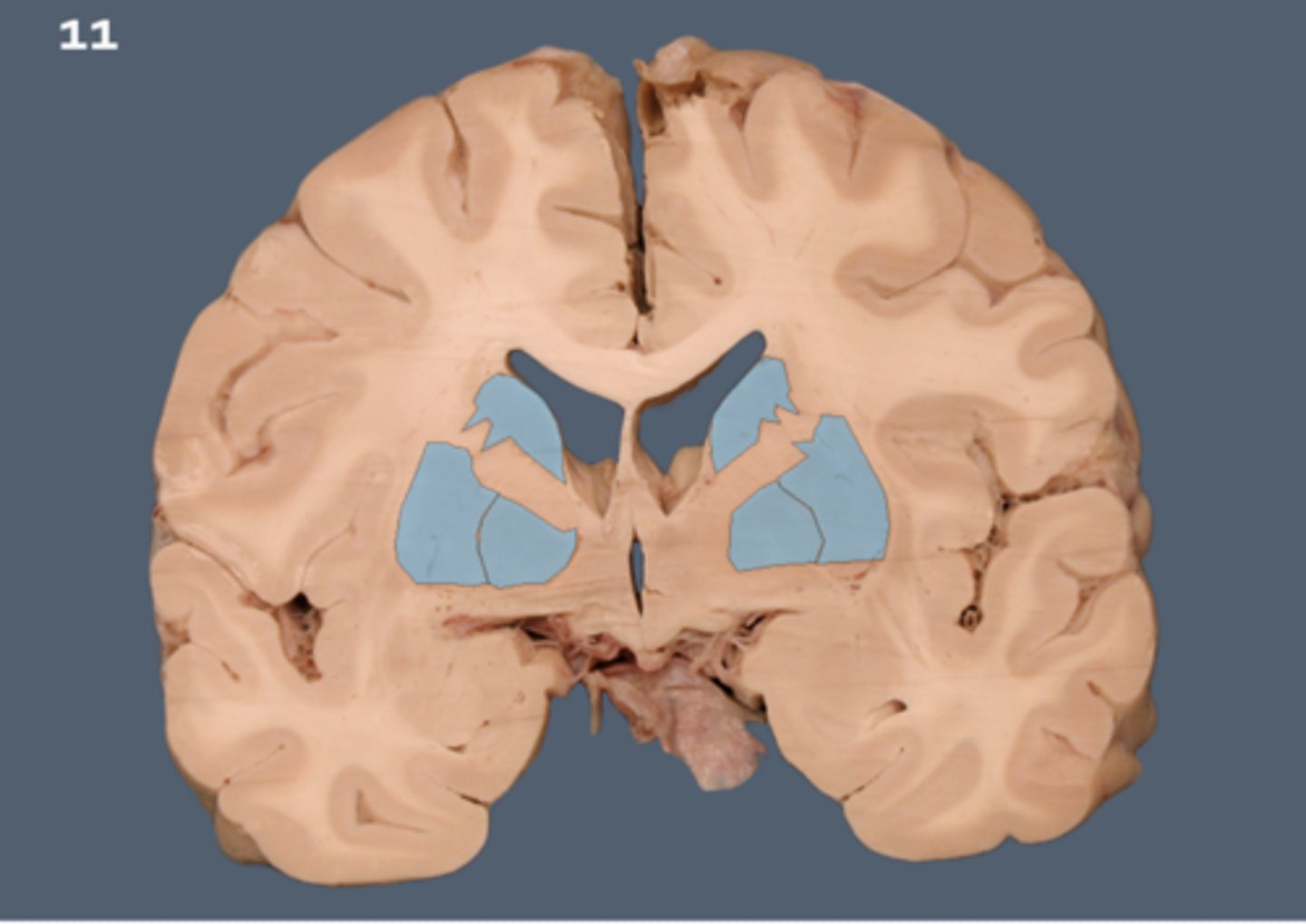
Caudate nucleus
One of the major nuclei that make up the basal ganglia. Head: Anterior to the thalamus, forming the lateral wall of the lateral ventricle.
Body: Extends posteriorly and laterally from the head, parallel to the thalamus.
Tail: Curves inferiorly and medially, lying above the temporal horn of the lateral ventricle.
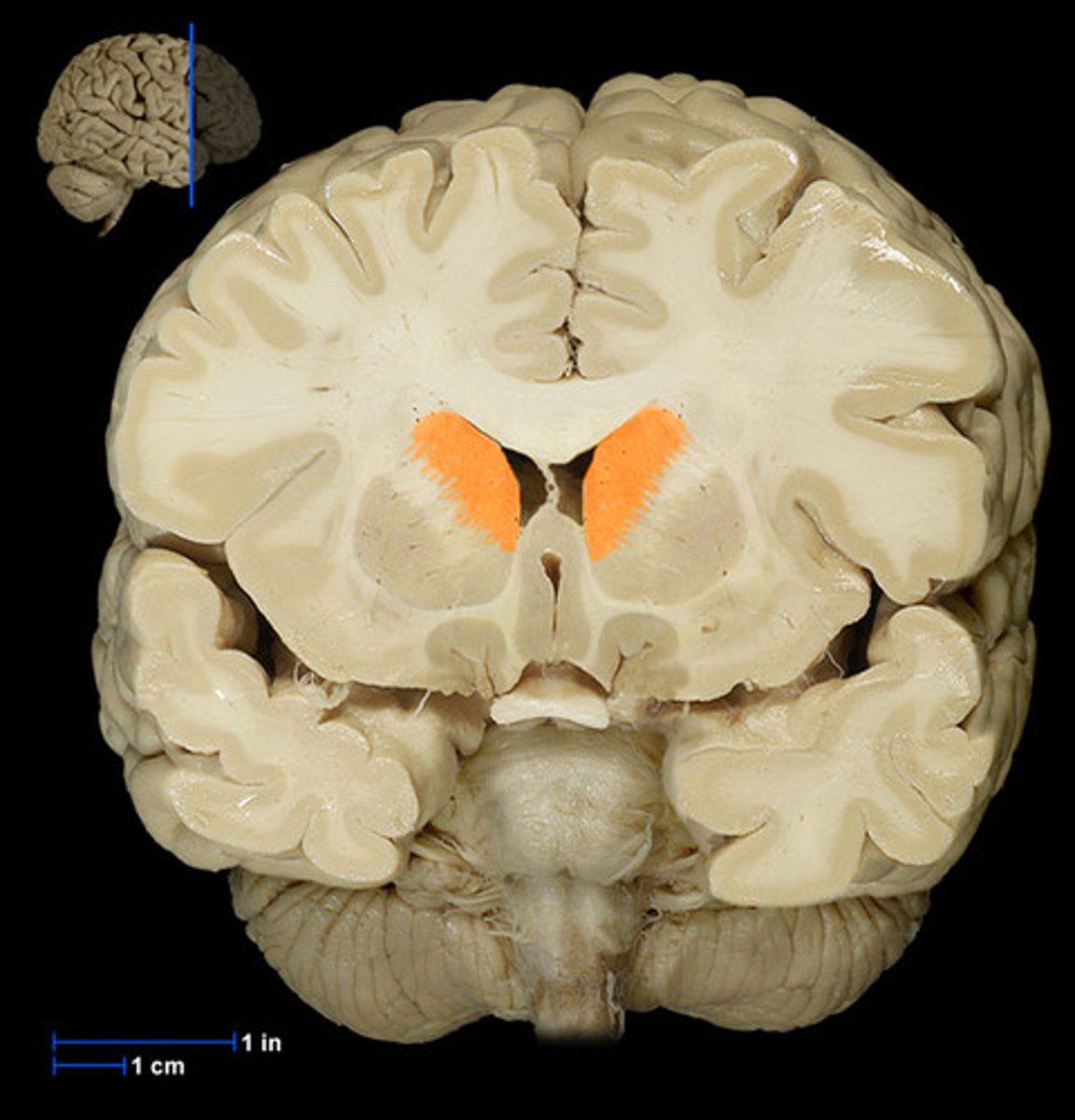
Putamen
involved in motor control and learning
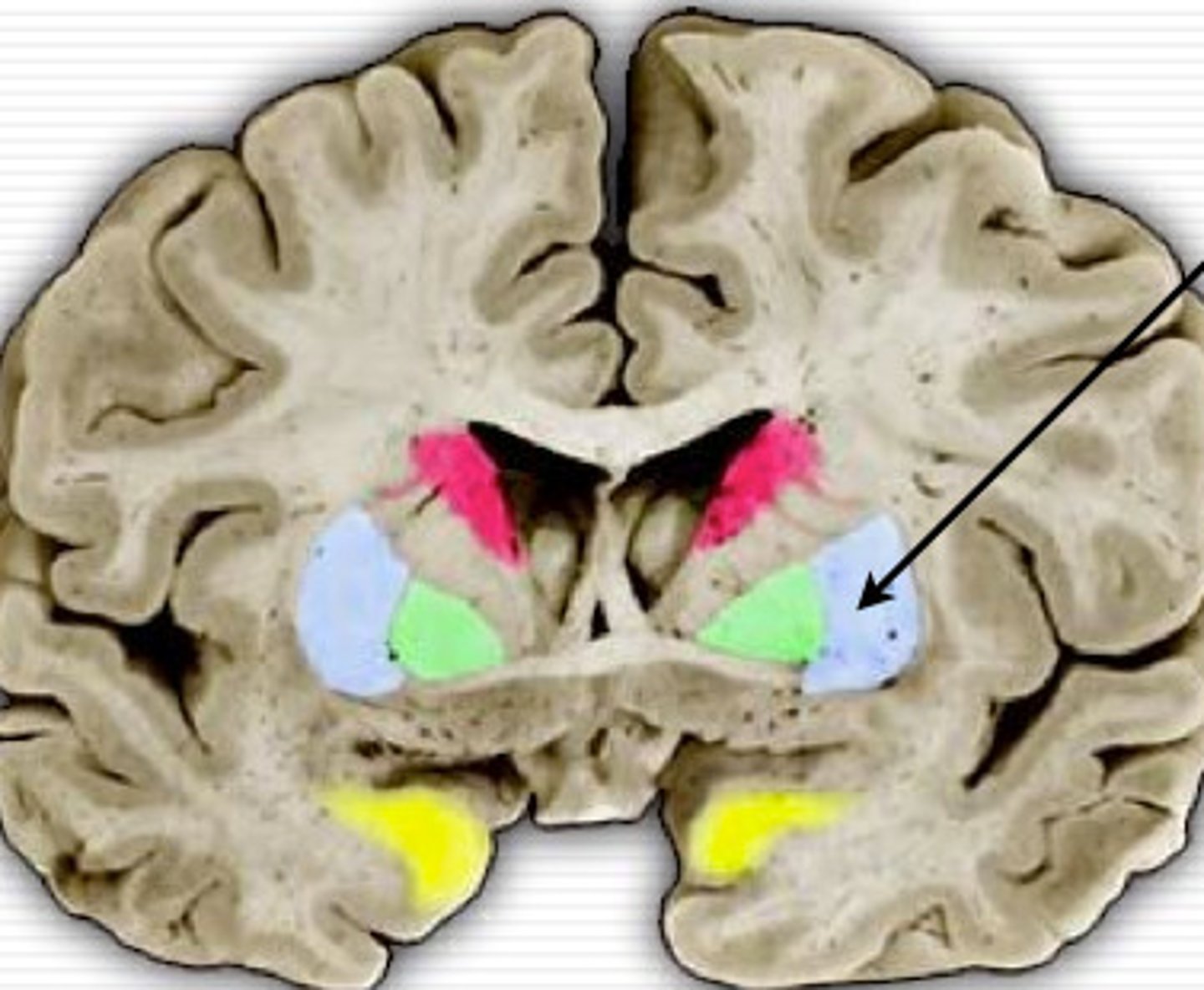
Globus Pallidus
more medial than putamen, appears with the third ventricle.
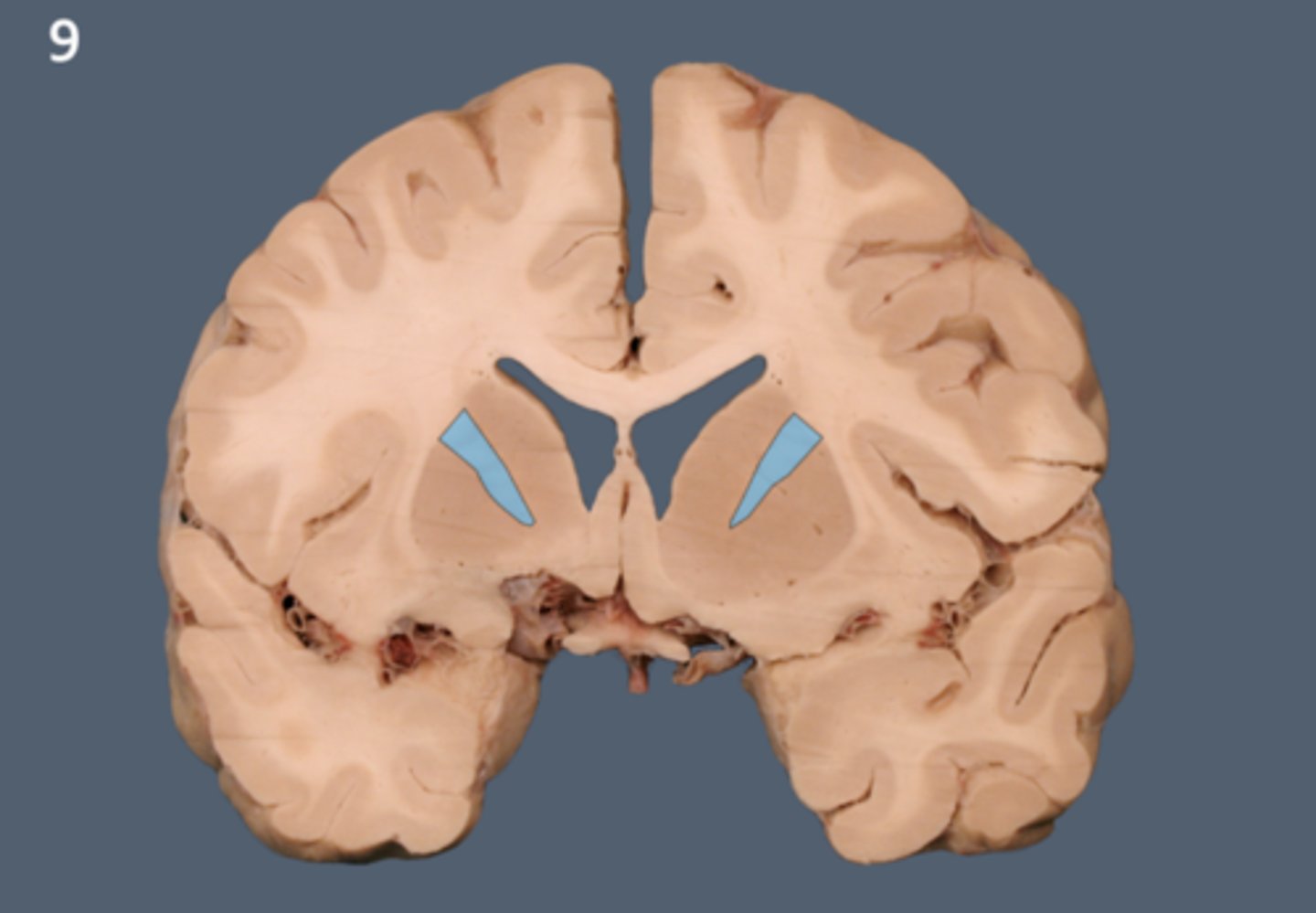
internal capsule
White matter pathway is lateral to the caudate nucleus, between the caudate and the putamen (and globus pallidus). It carries primarily motor fibers, including corticospinal tract fibers.
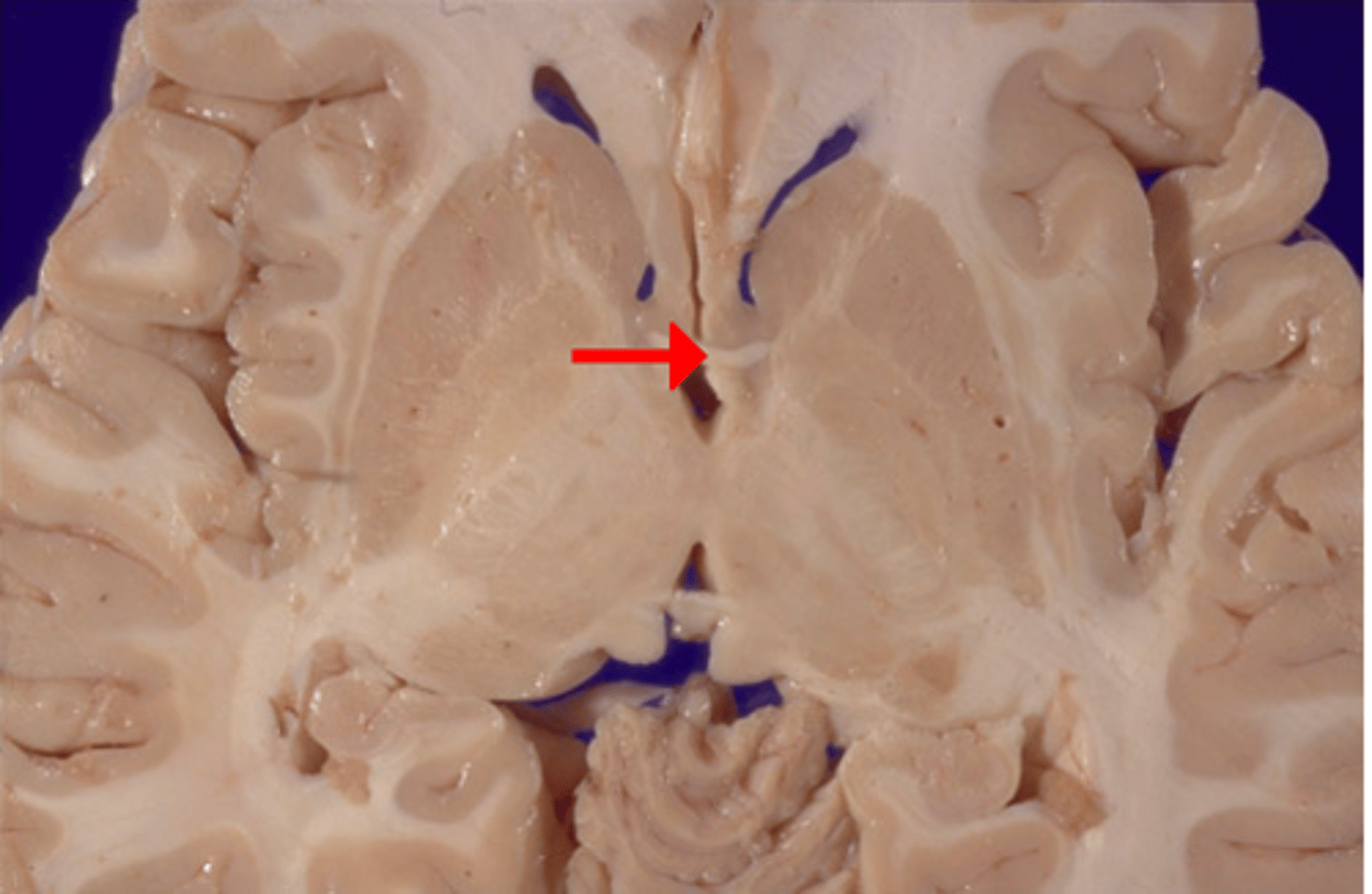
anterior commissure
White matter tract that crosses the third ventricle. Located just anterior to the thalamus. connects parts of the frontal+temporal lobes of the 2 hemispheres.
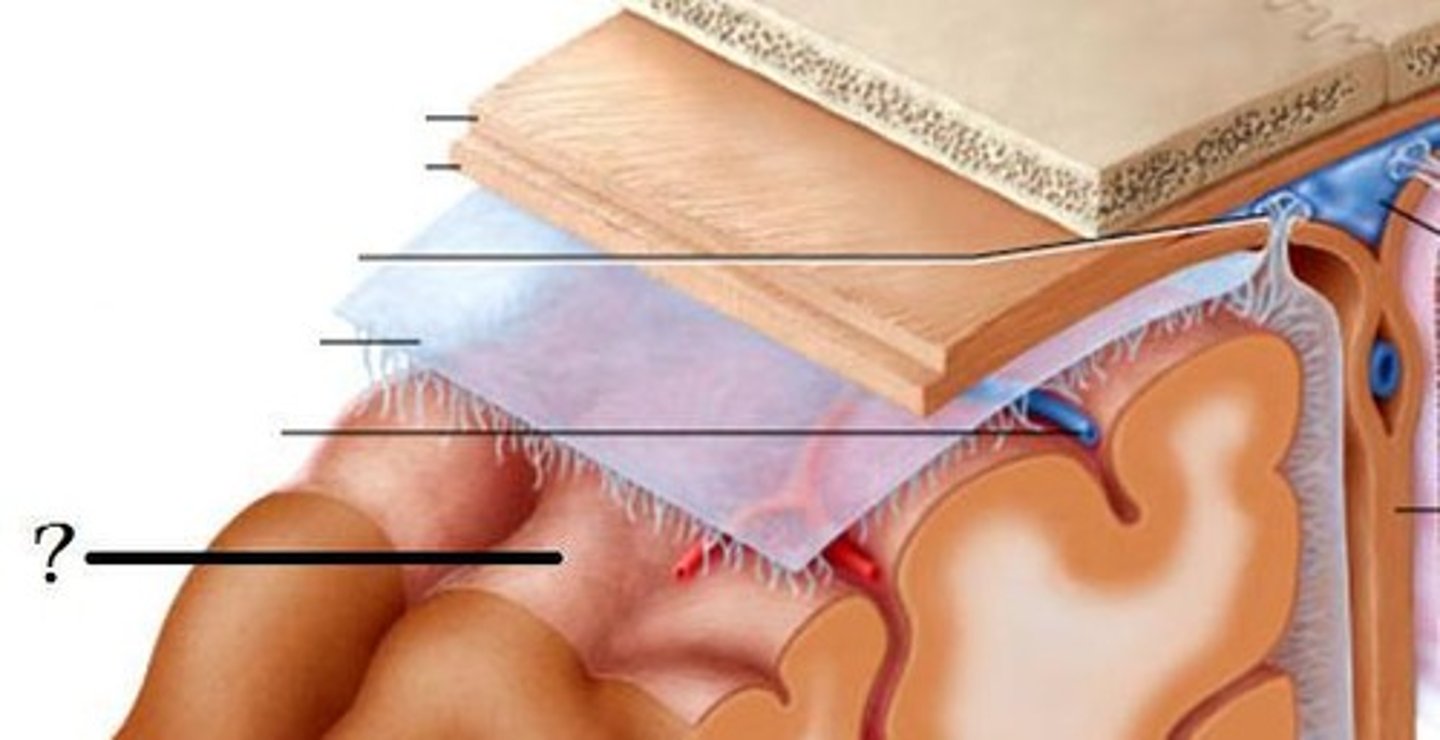
Dura mater
thickest layer of meninges, follows contours of brain but does not divide sulci.
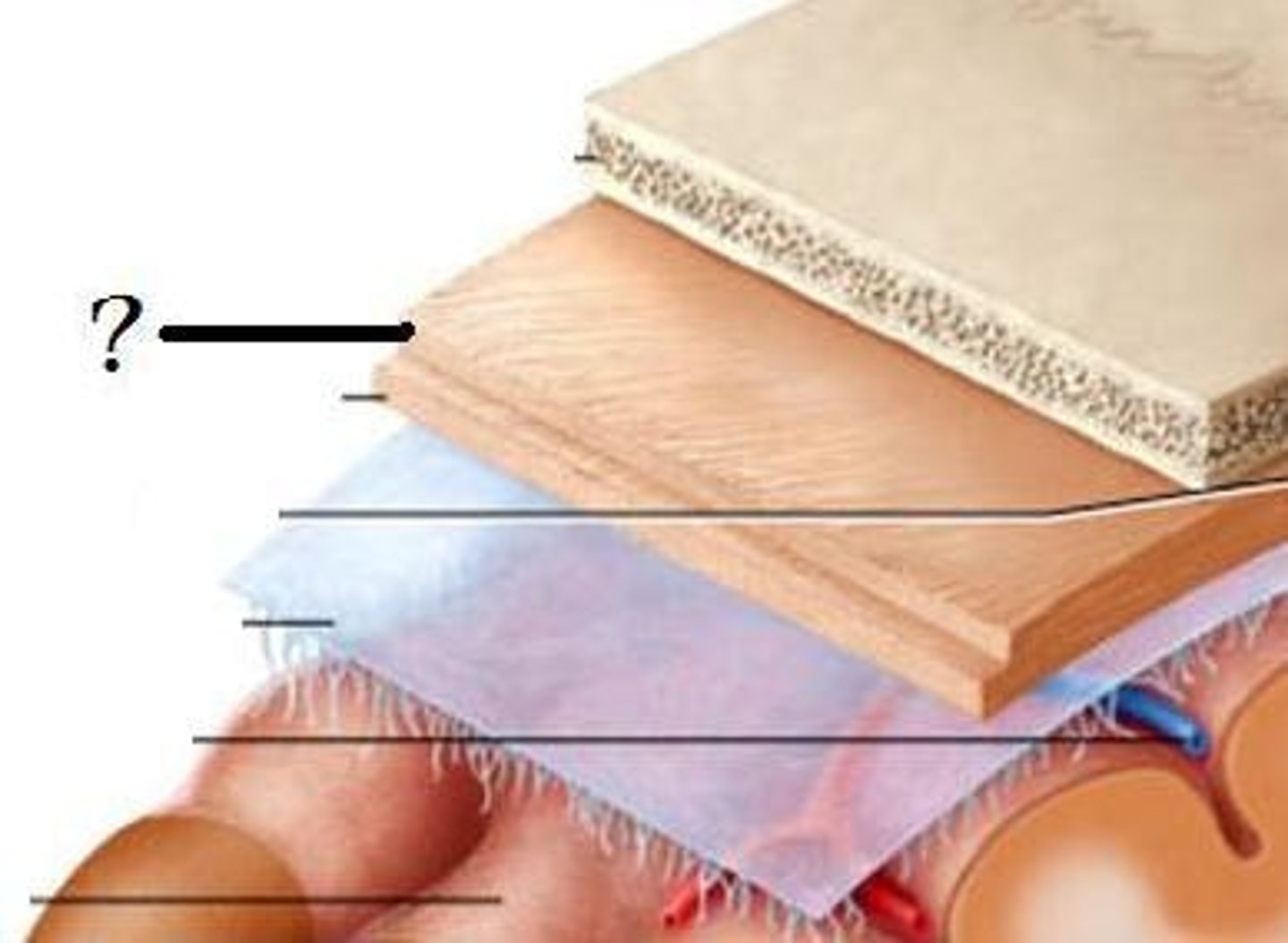
Dural reflections
the area where dura mater folds + dives into spaces between parts of the brain. Two areas: falx cerebri and tentorium cerebelli.
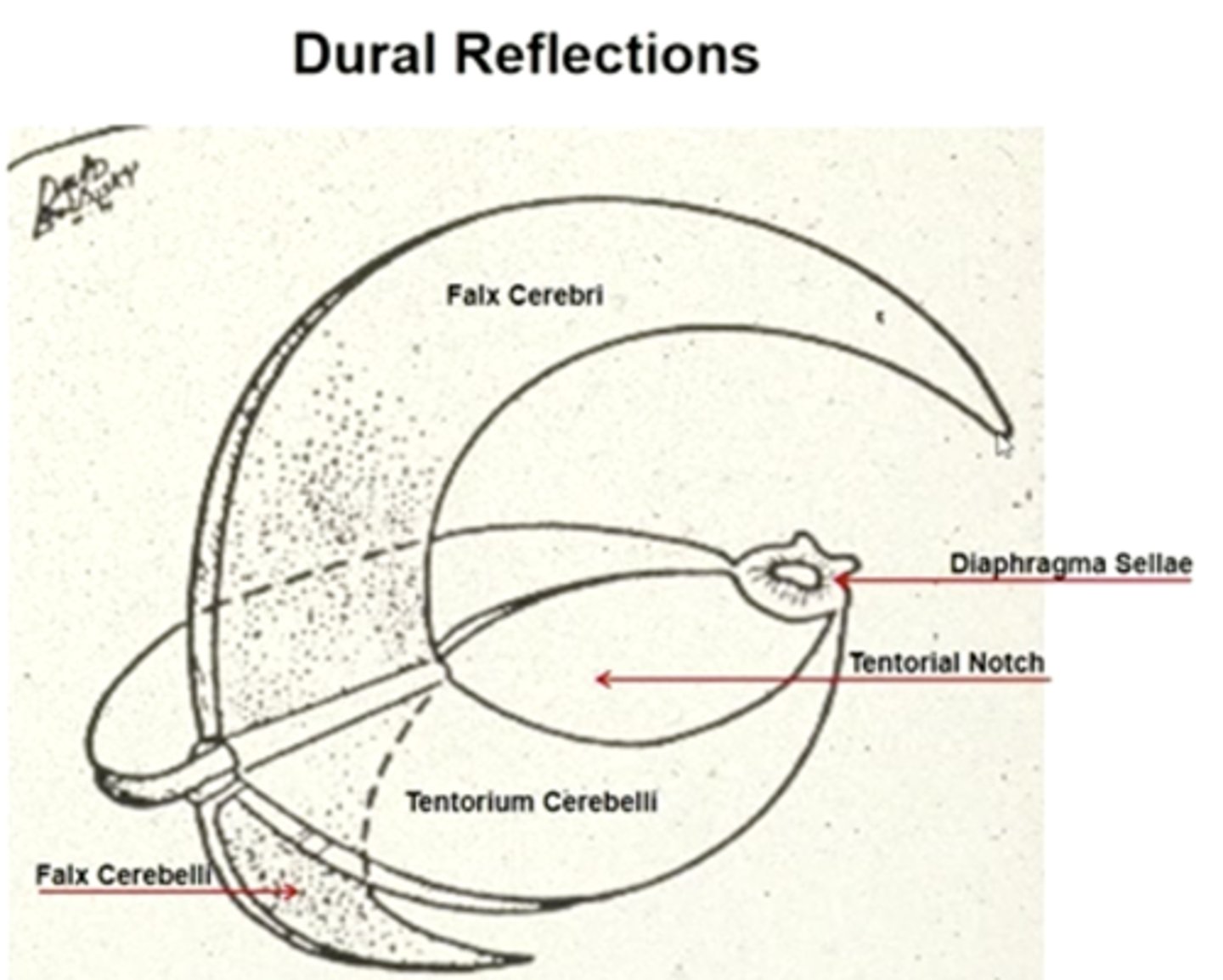
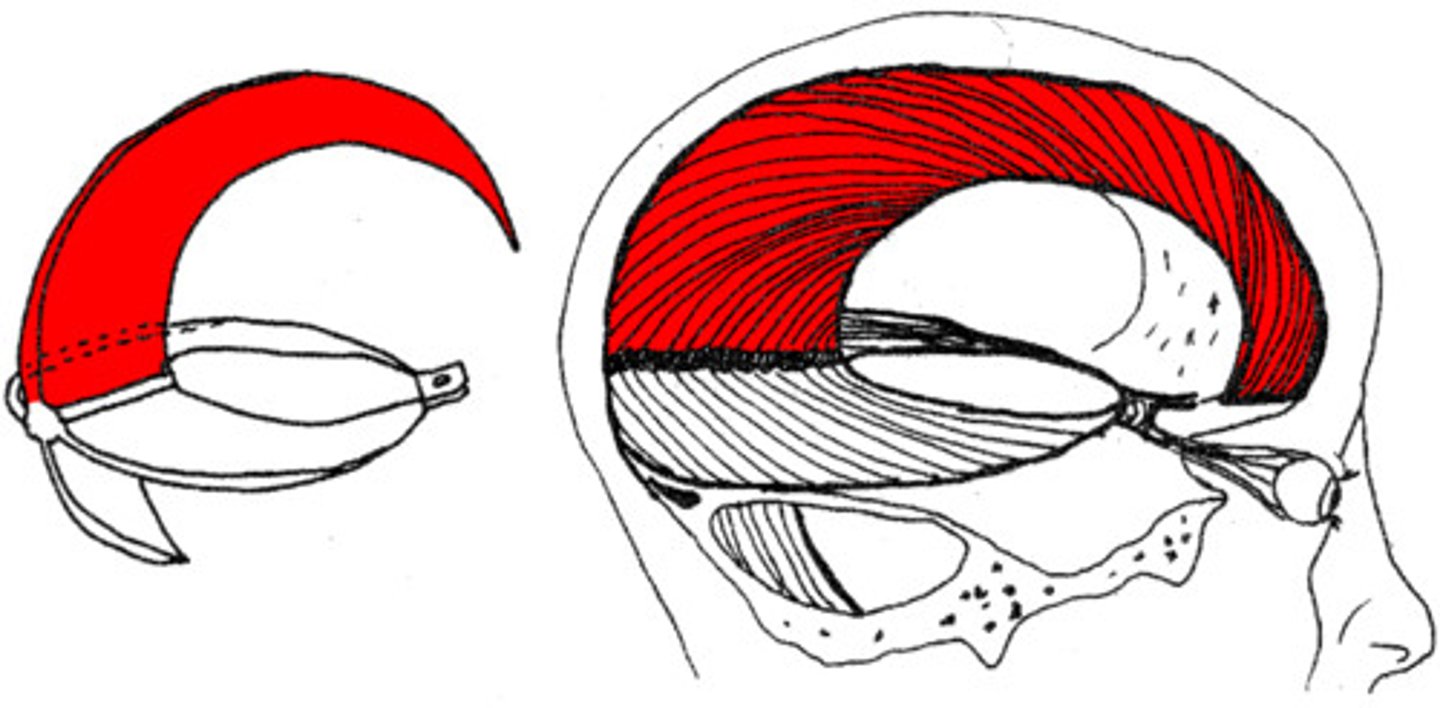
falx cerebri
the dura mater in the sagittal (median longitudinal) fissure, separates R+L hemispheres.
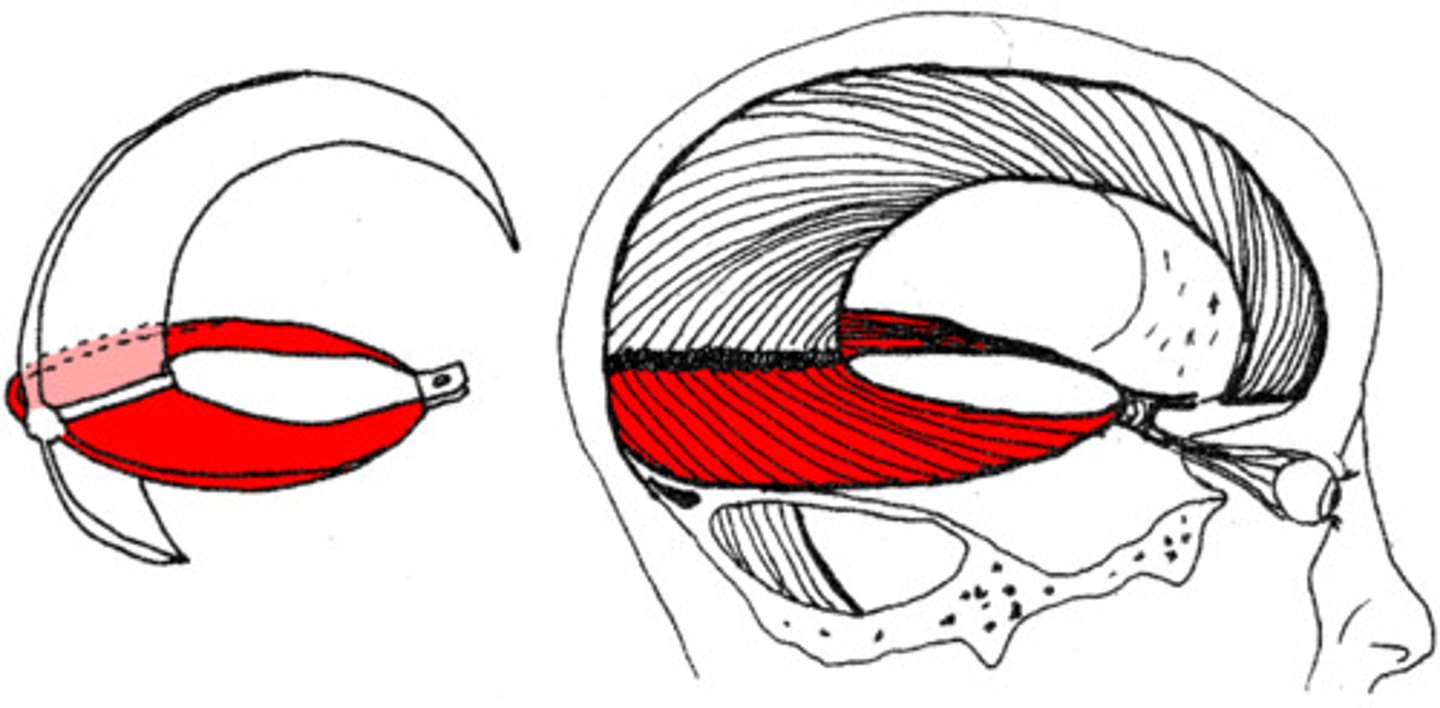
tentorium cerebelli
the dura mater between the cerebellum and cerebrum.
Arachnoid mater
delicate, transparent layer of meninges, can be seen on the surface, follows form of overlying dura
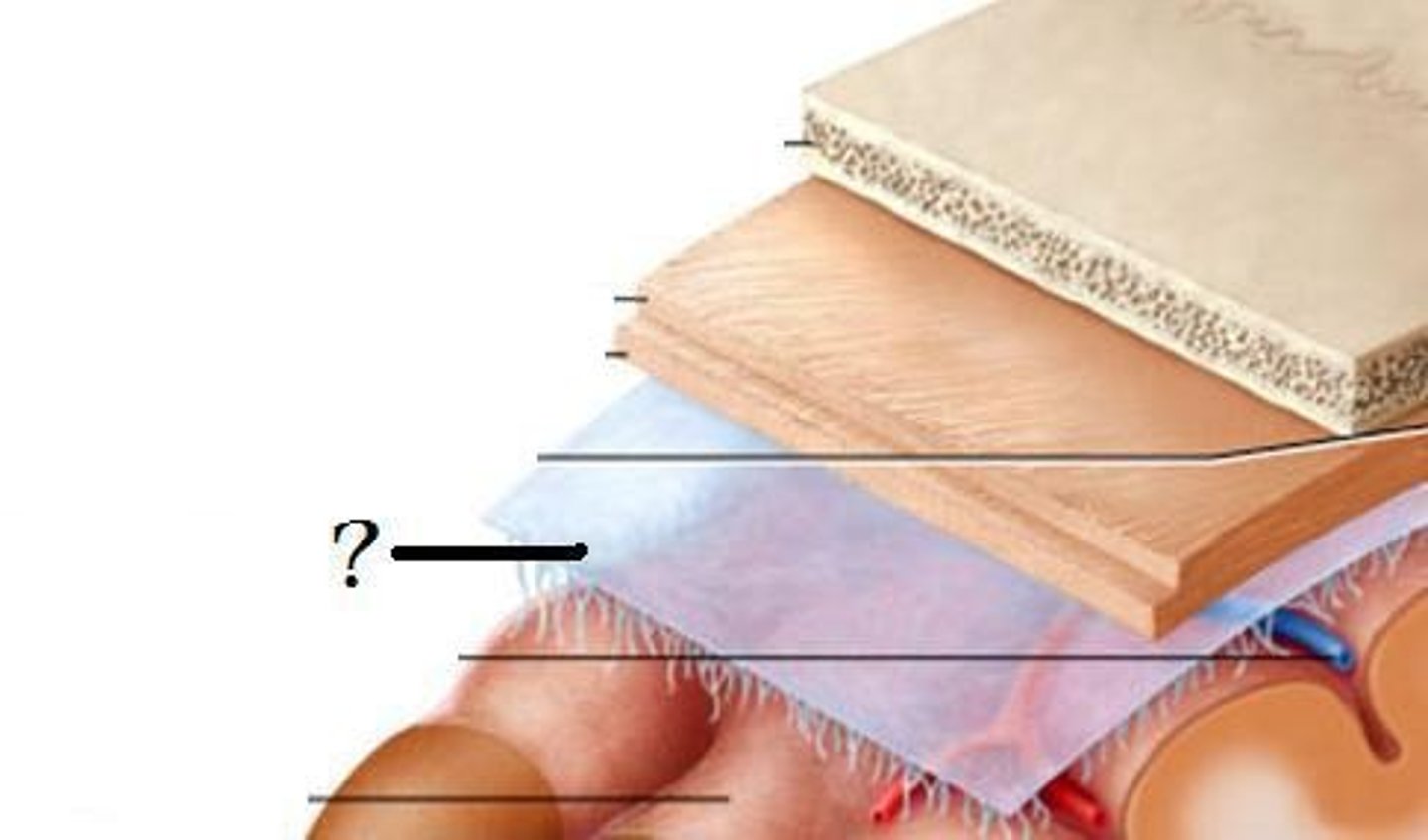
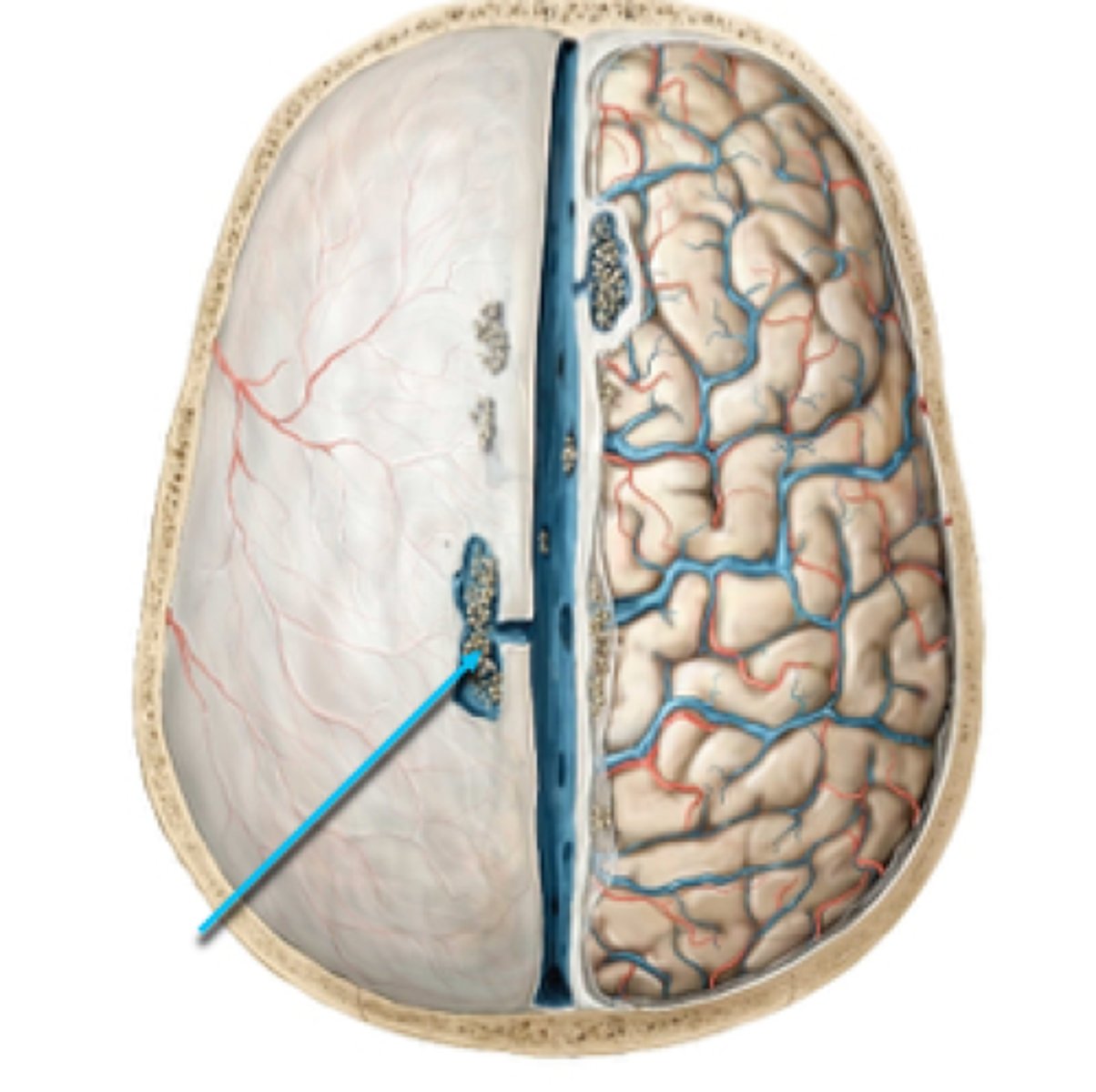
arachnoid granulations
Extensions of the arachnoid mater that allow excess CSF to be absorbed by the dural sinuses. Stringy, located in sulci
pia mater
innermost membrane, covers brain tissue, sulci, and gyri.
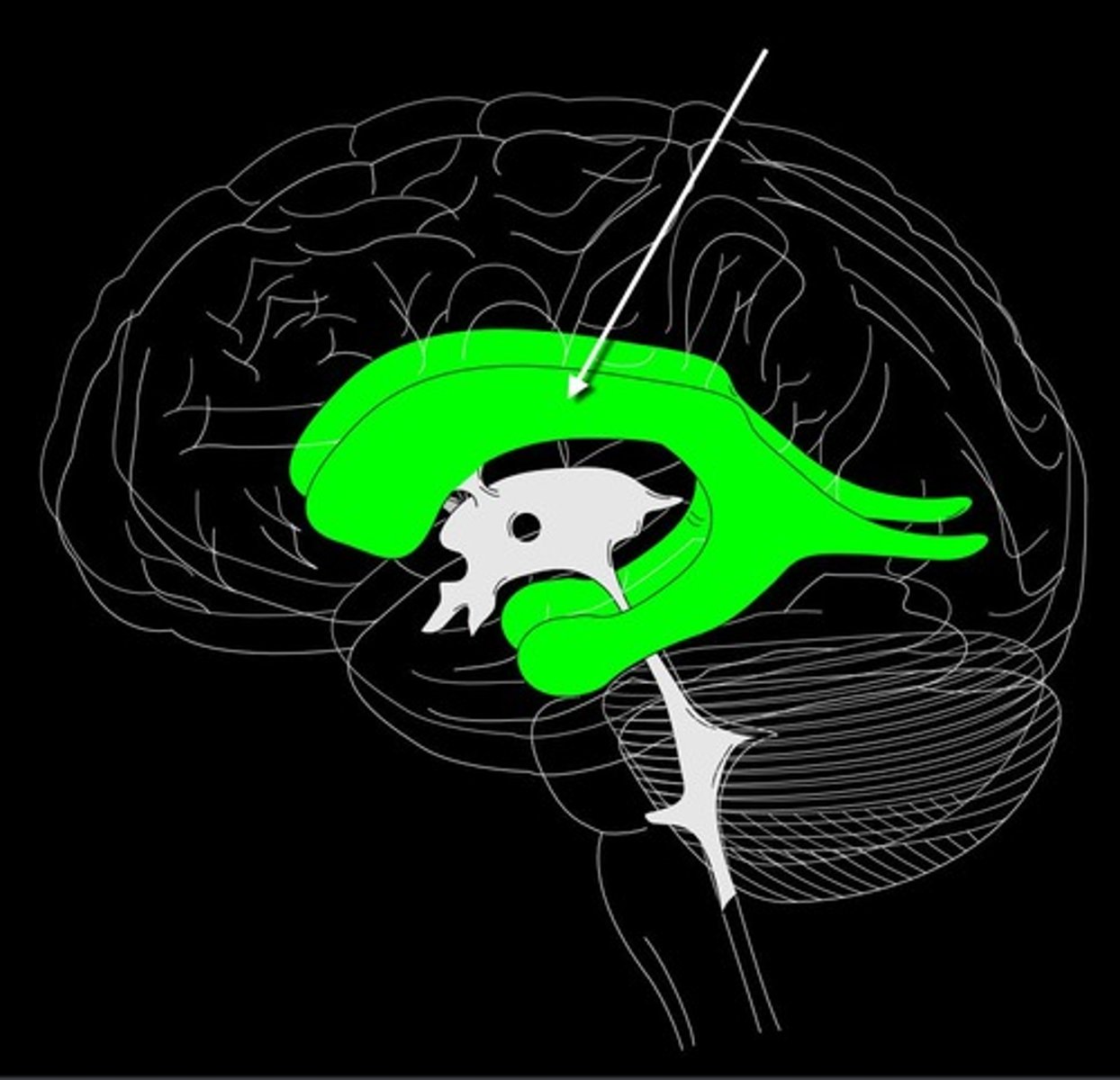
lateral ventricle
A complexly shaped lateral portion of the ventricular system within each hemisphere of the brain.
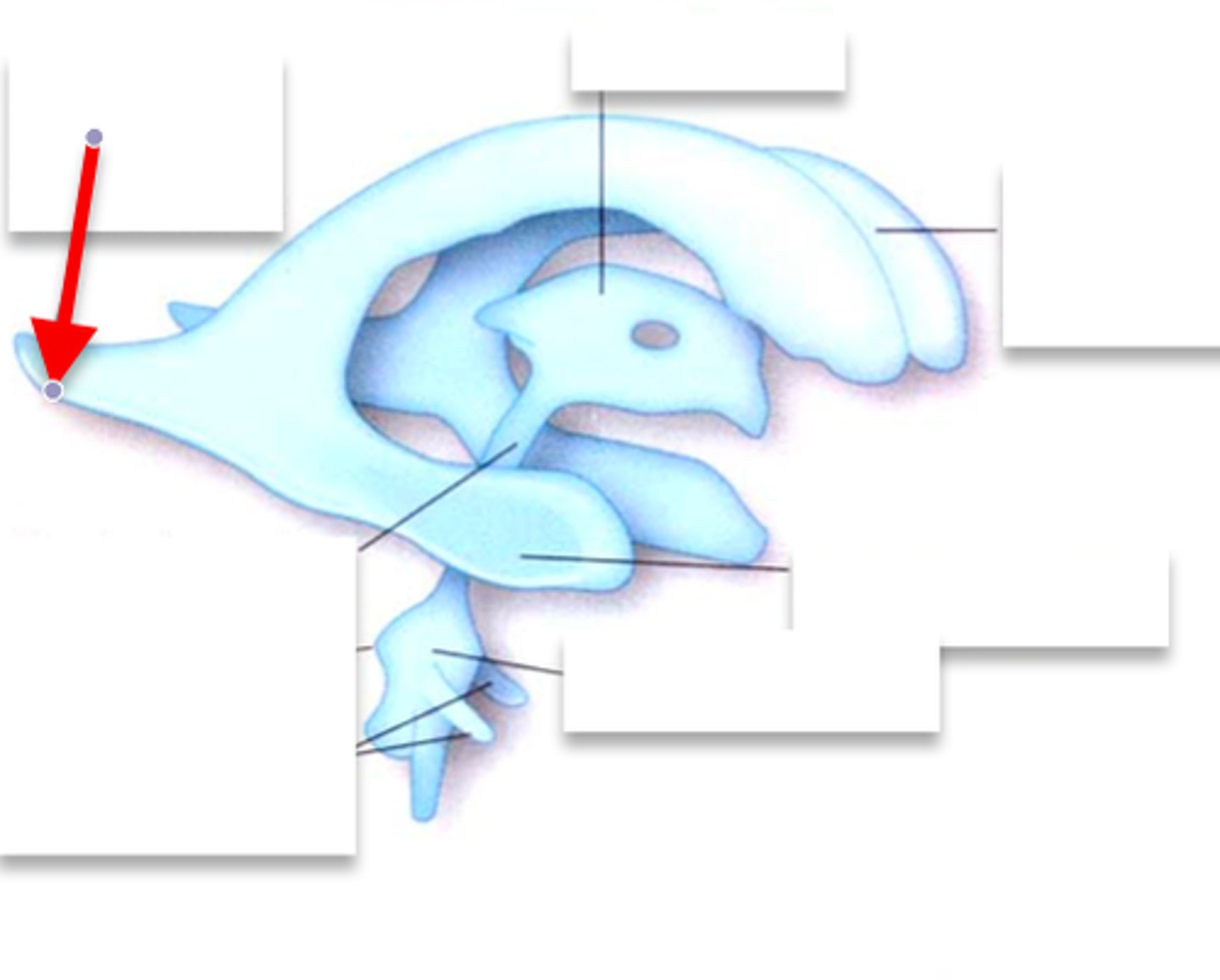
anterior horn of lateral ventricle
located in the frontal lobe and is the part of the lateral ventricle that lies in front of the interventricular foramen
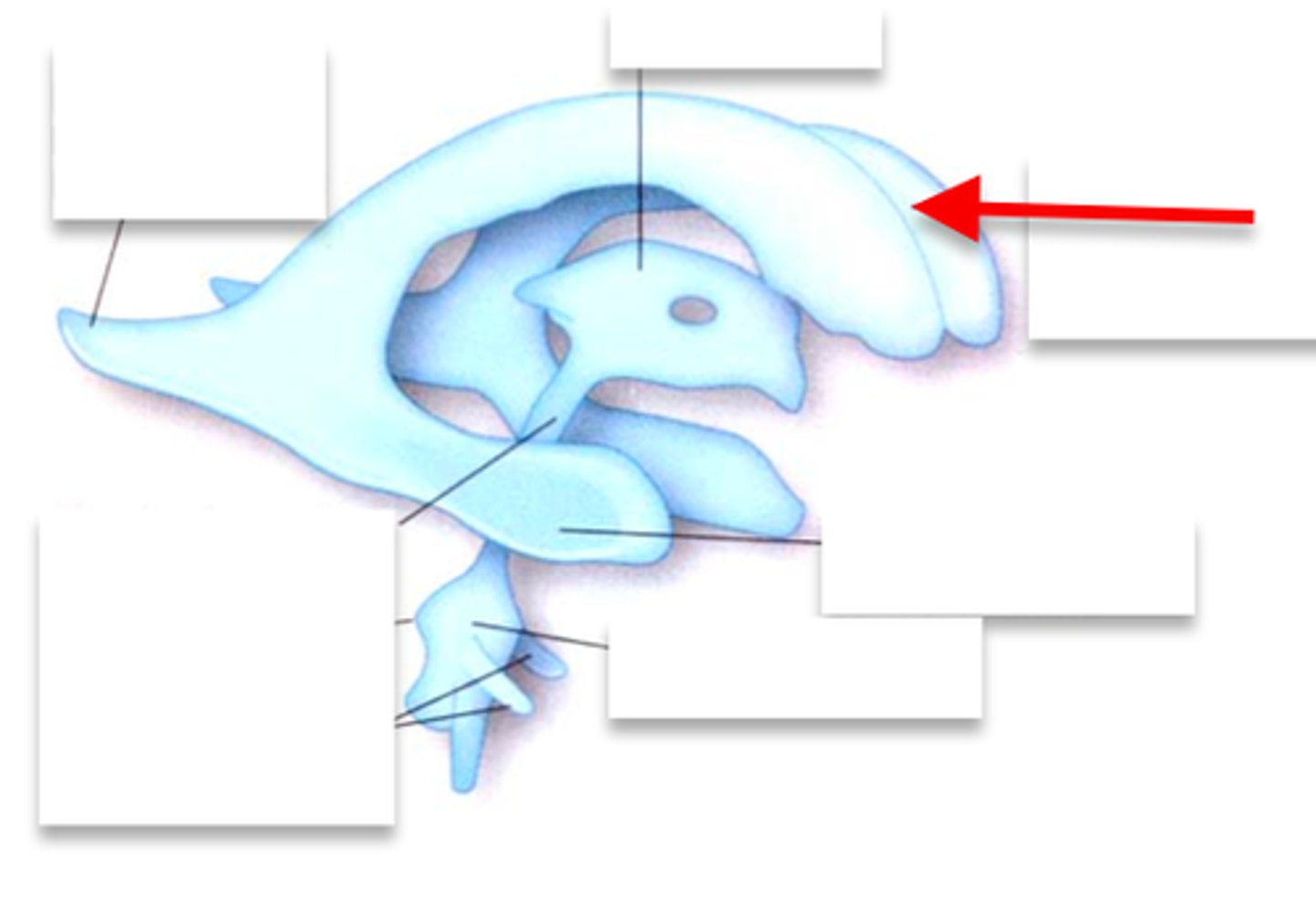
body of lateral ventricles
located in the parietal lobe, situated between the anterior and posterior horns.
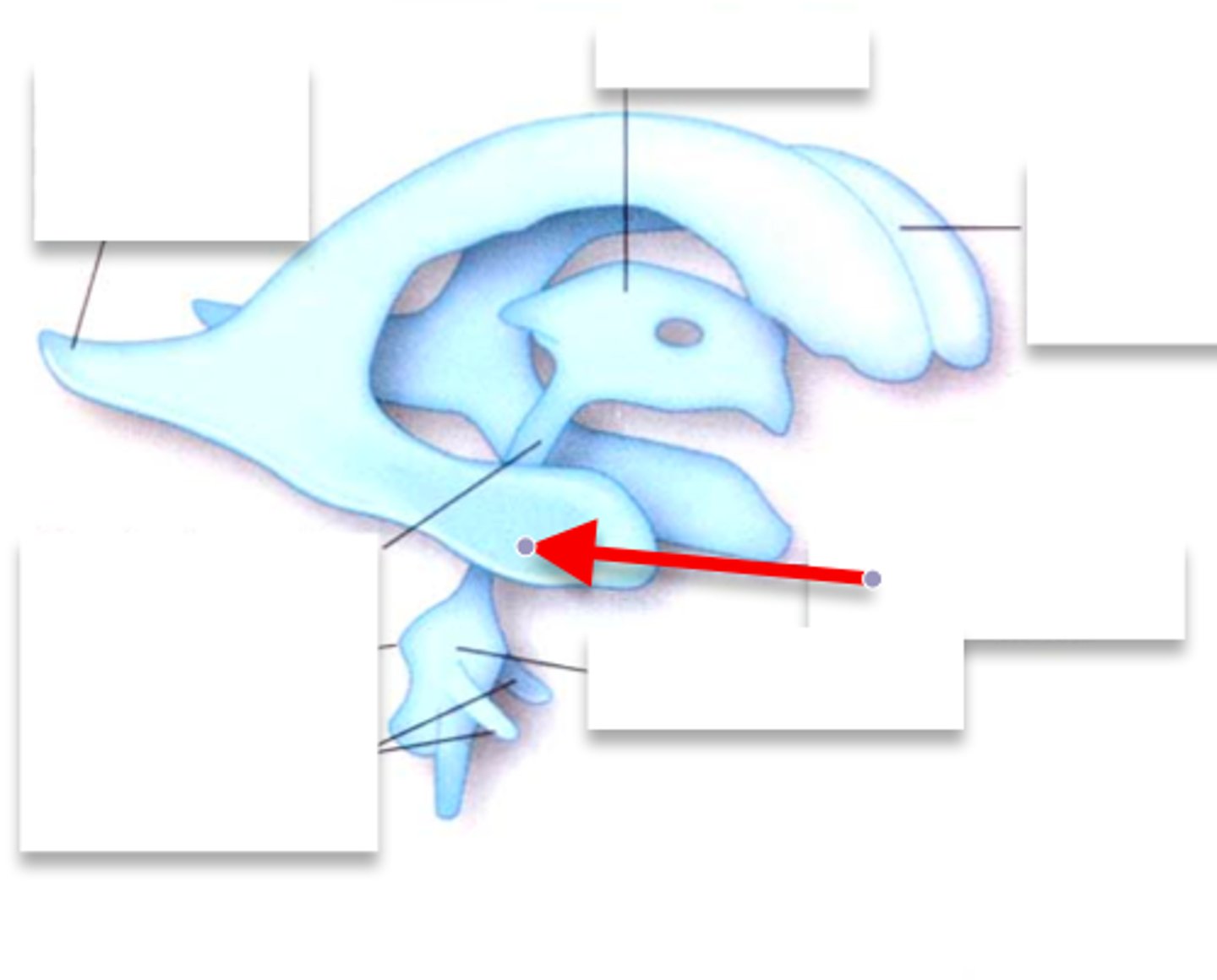
inferior horn of lateral ventricle
located in the temporal lobe of the brain. It is the largest of the three horns and extends from the atrium, curving anteriorly and inferiorly to go under the thalamus and into the temporal lobe
posterior horn of lateral ventricle
located in the occipital lobe of the brain, projecting backward. It is the most posterior part of the C-shaped lateral ventricle and lies deep within the occipital lobe.

interventricular foramen (of monro)
connects lateral ventricles to third ventricle
third ventricle
thin midline space that separates the left and right thalami.
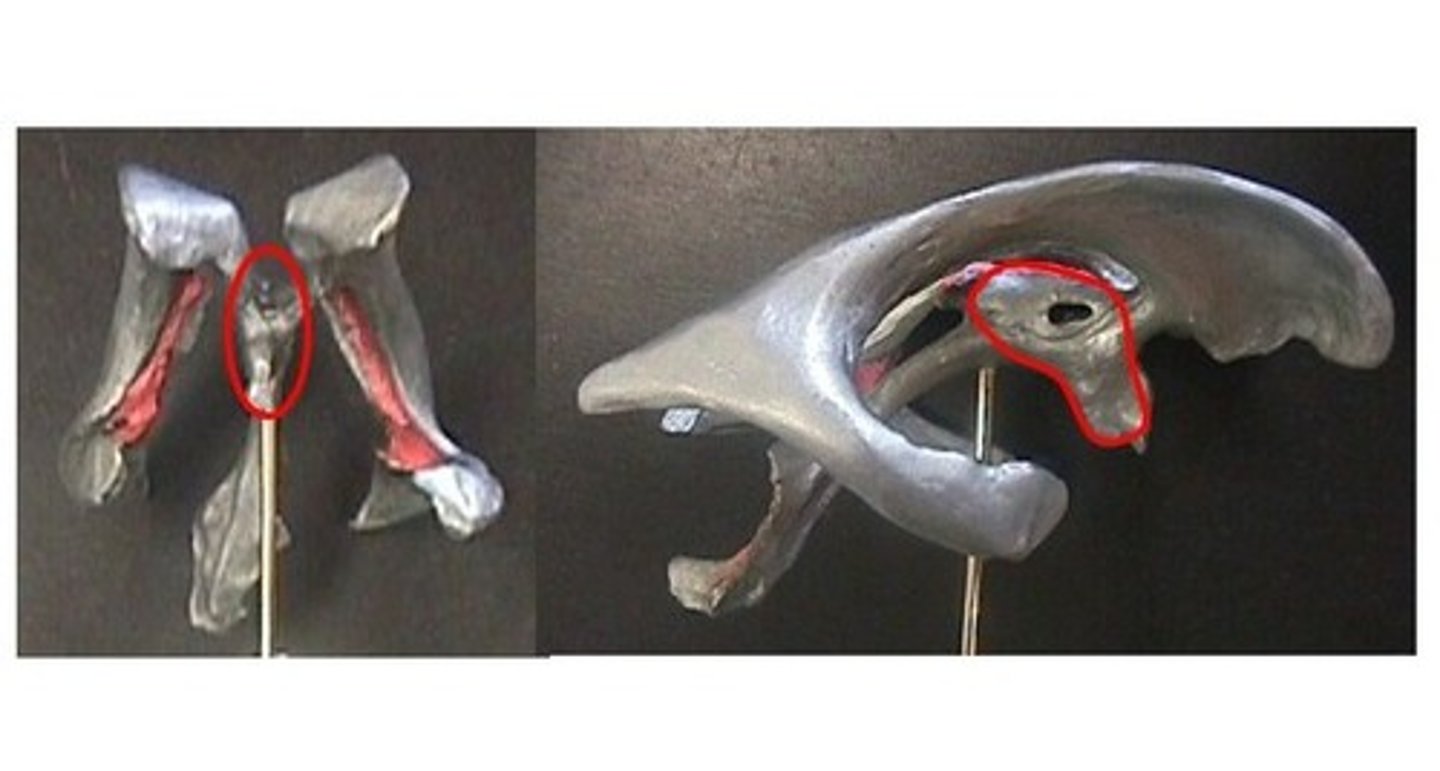
interthalamic adhesion
Connects the two thalami and passes through the third ventricle.
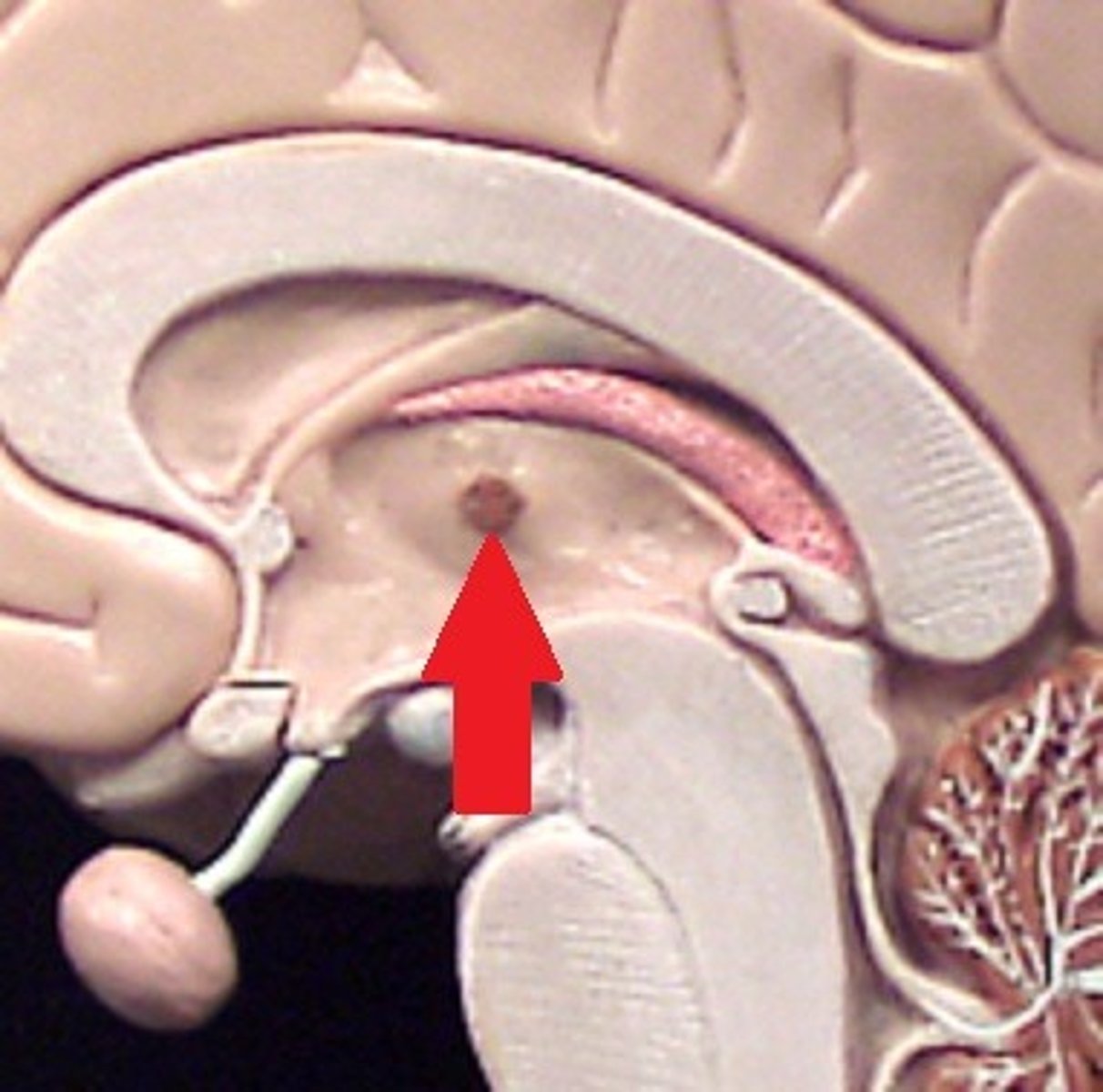
cerebral aqueduct
connects the third and fourth ventricles
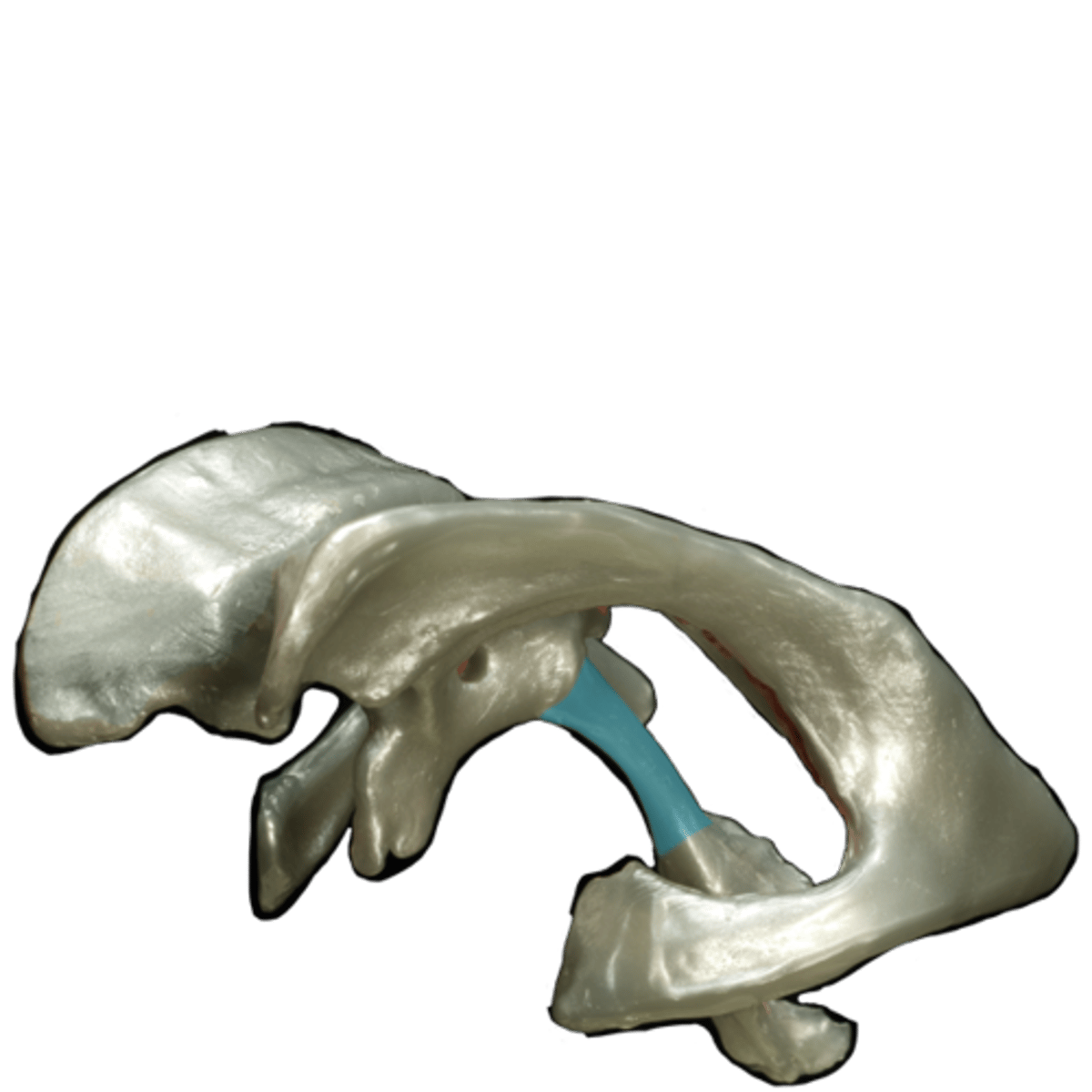

fourth ventricle
the ventricle located between the cerebellum and the pons
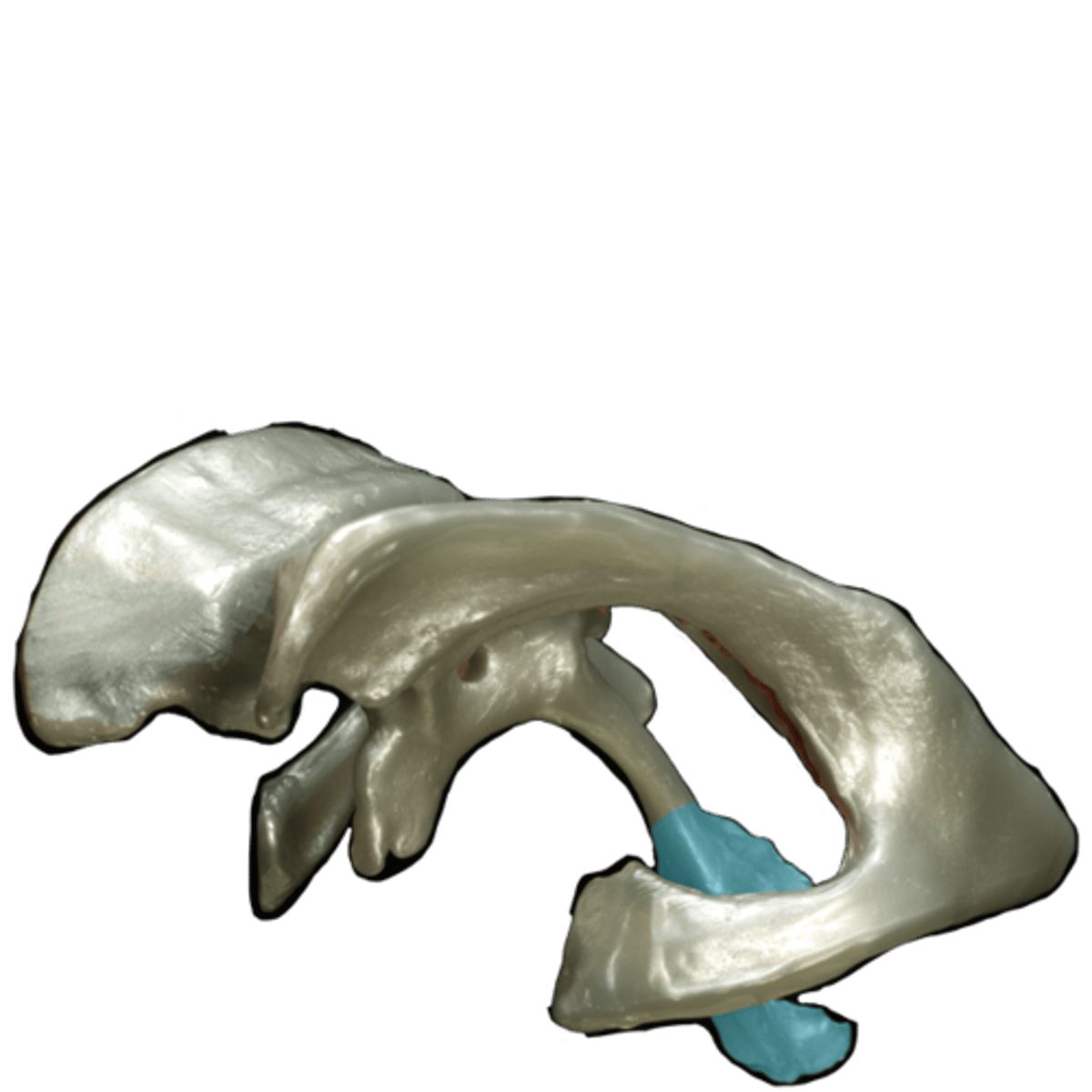

Flow of CSF
1. Lateral ventricle
2. Interventricular foramen (of Monro)
3. Third ventricle
4. Cerebral aqueduct
5. Fourth ventricle
6. CSF can escape via the lateral apertures, median aperture, or central canal.
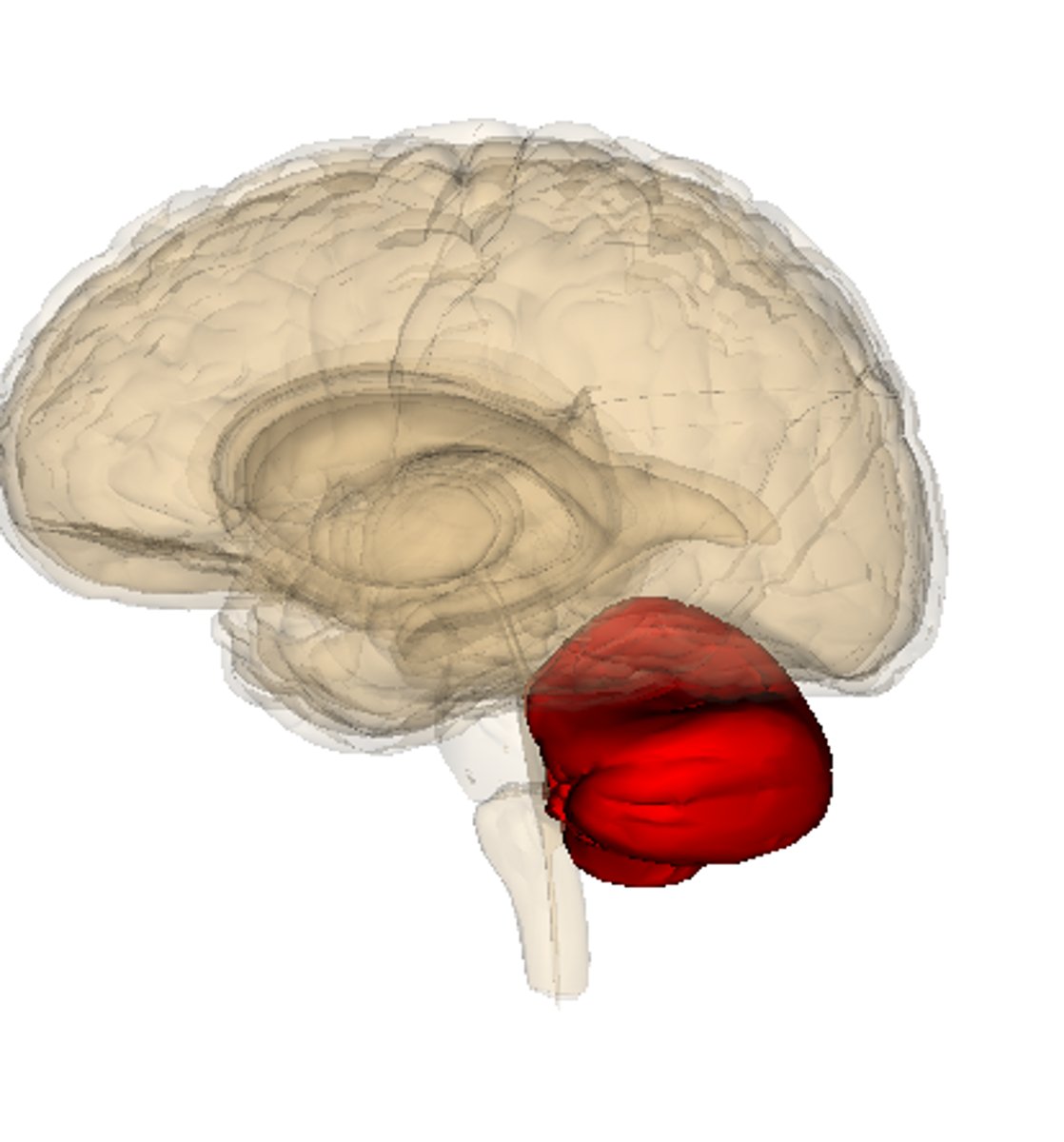
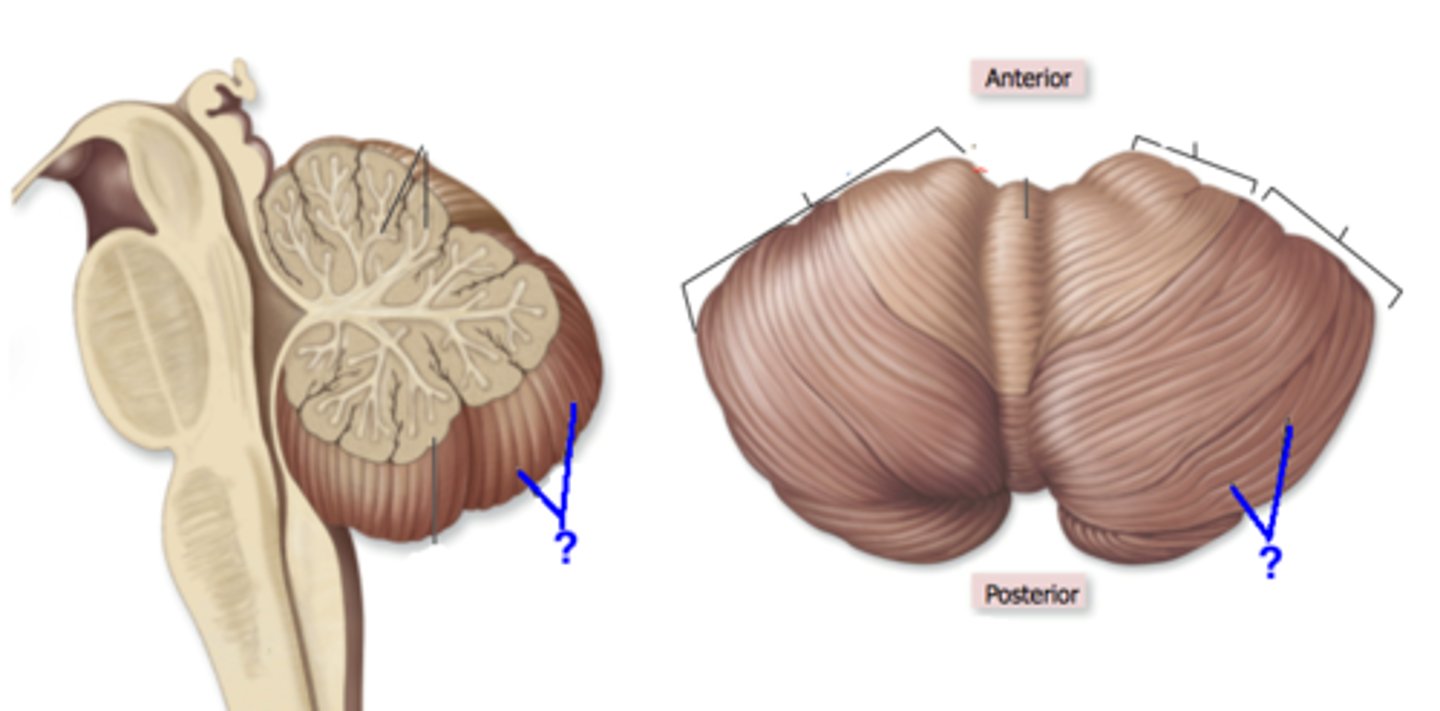
cerebellum
the "little brain" at the rear of the brainstem; functions include processing sensory input and coordinating movement output and balance
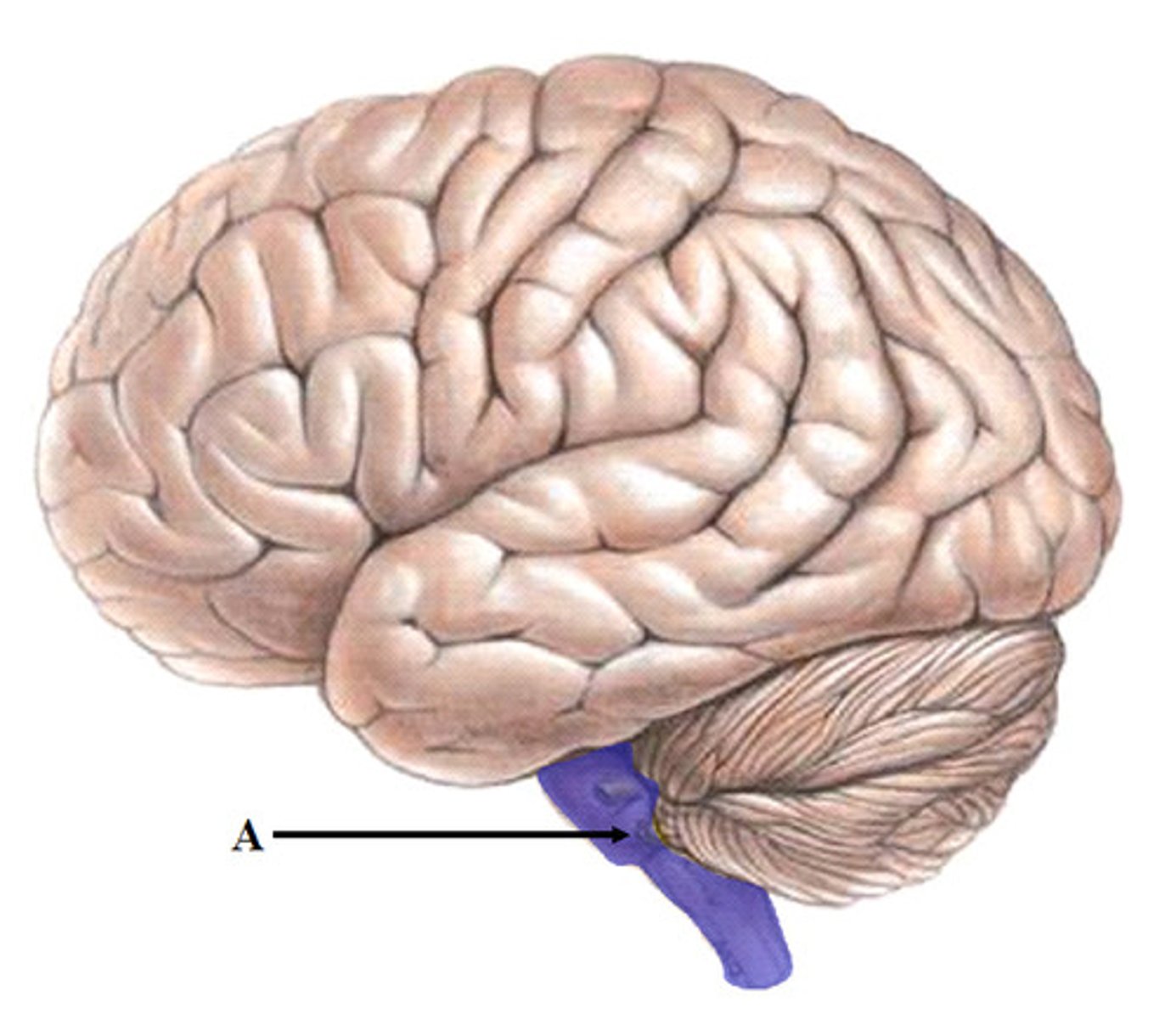
brainstem
responsible for automatic survival functions
medulla oblongata
Most inferior part of the brainstem that controls vital life-sustaining functions such as heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, and digestion.
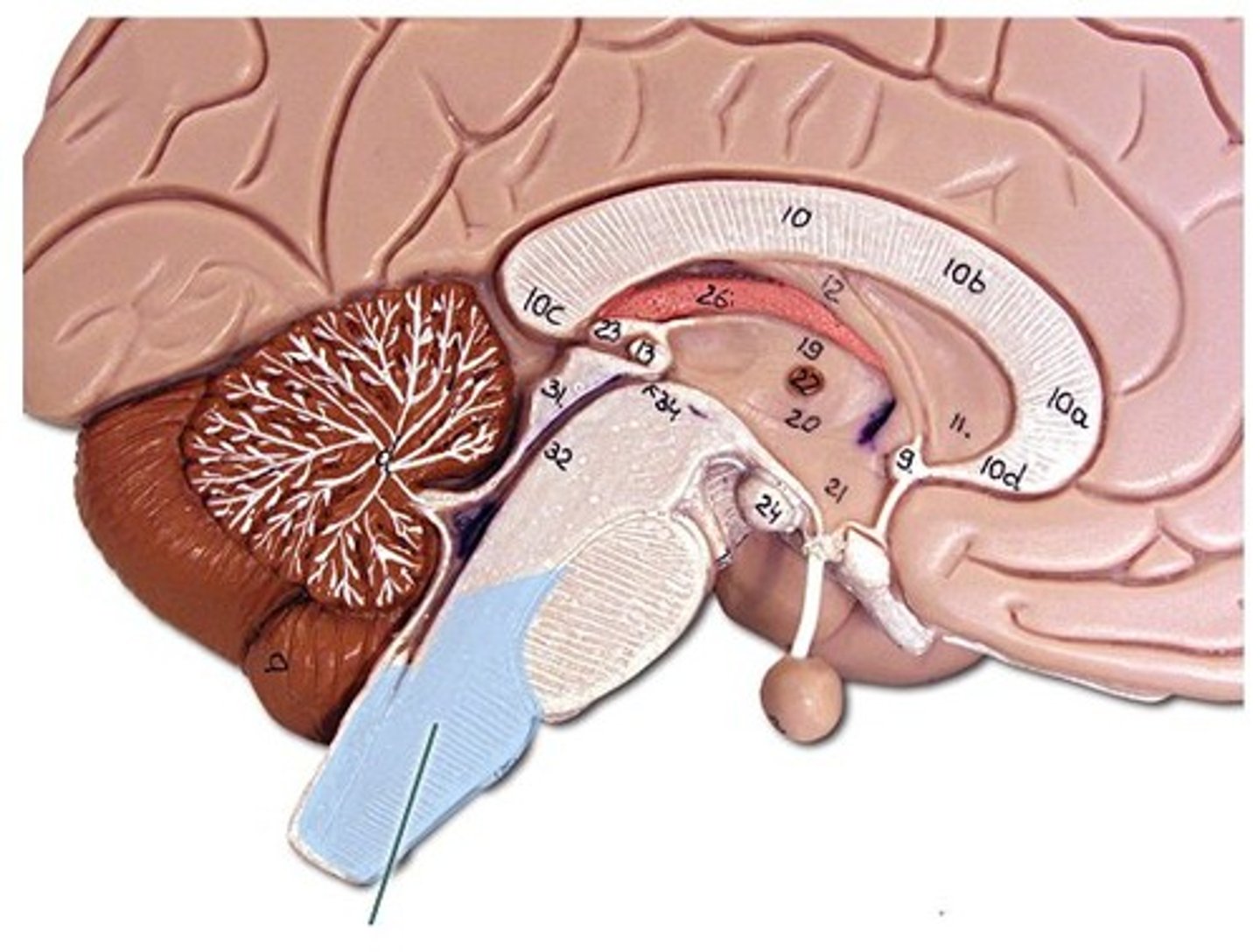
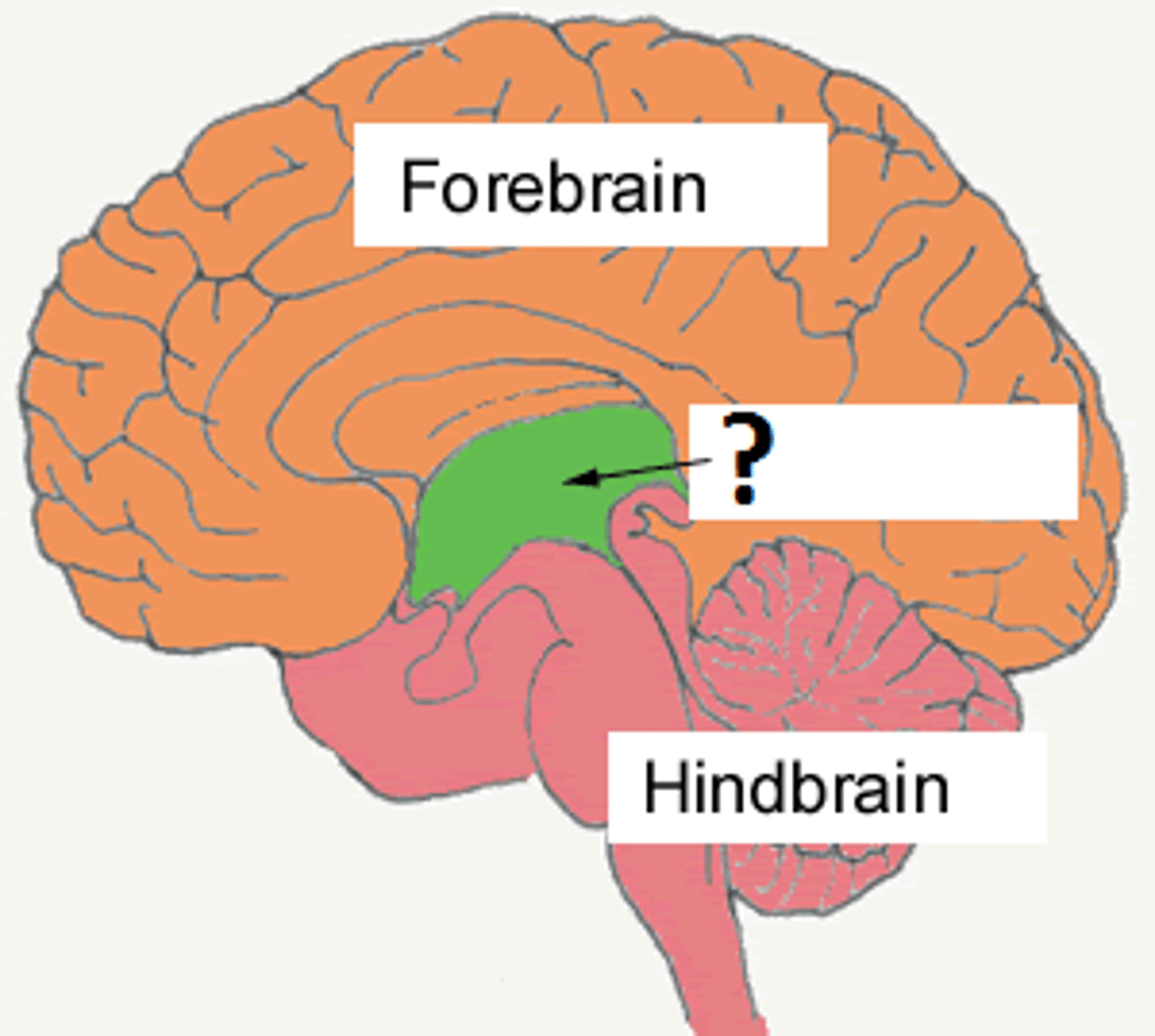
pons
A brain structure that relays information from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain. Has a "belly" on anterior surface
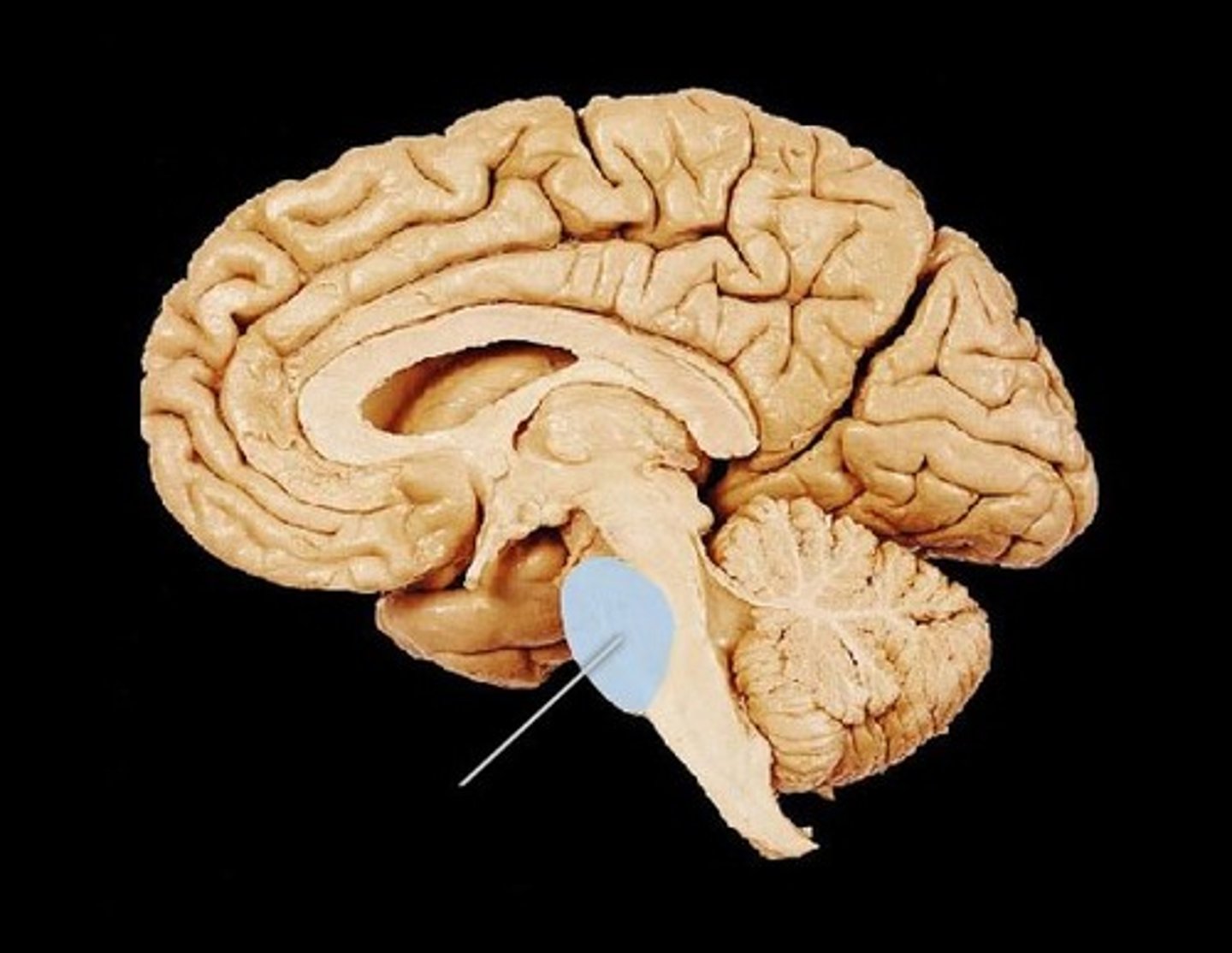
midbrain
A small part of the brain above the pons and below the thalamus that integrates sensory information and relays it upward. Surrounds the cerebral aqueduct.
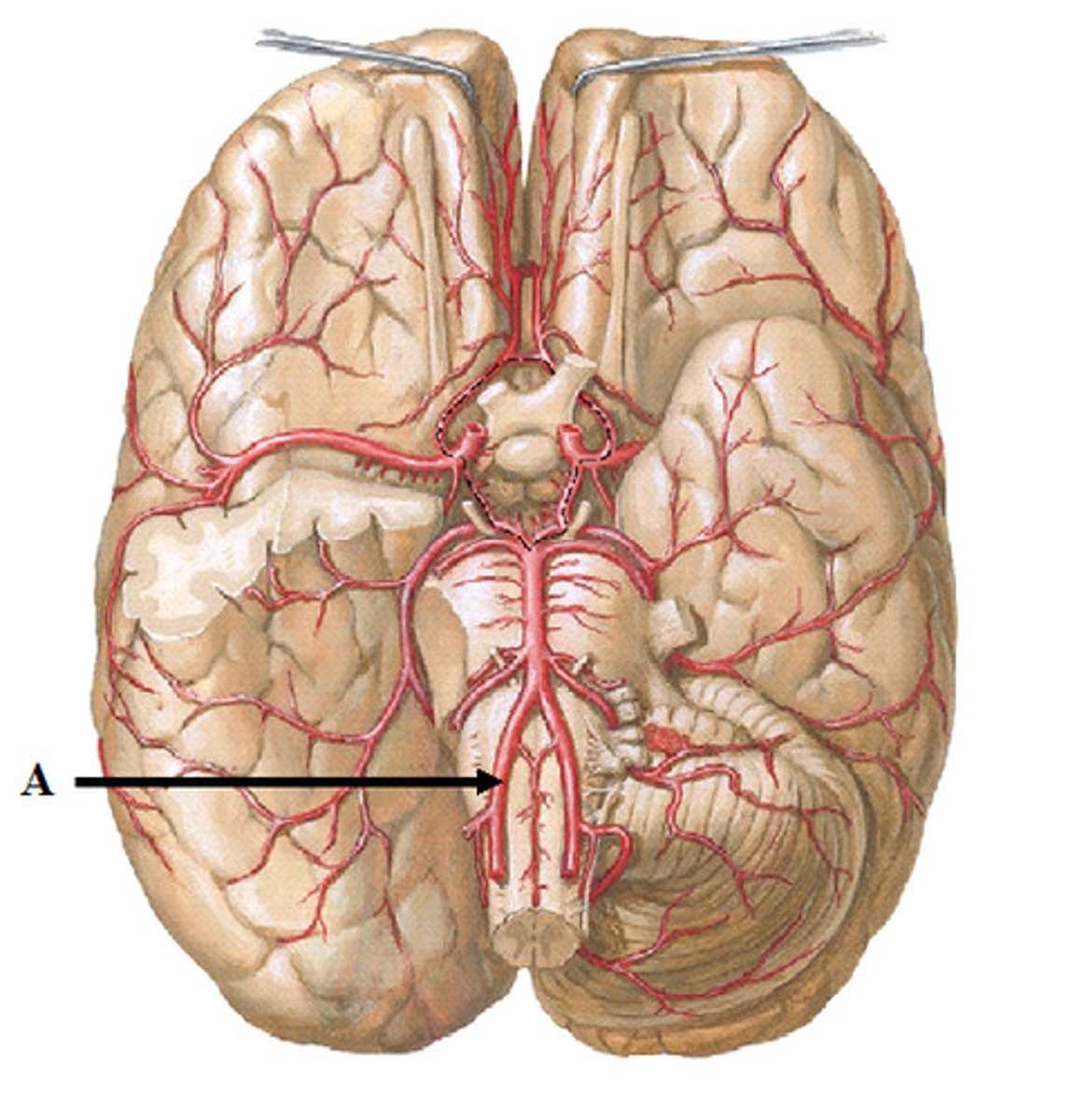
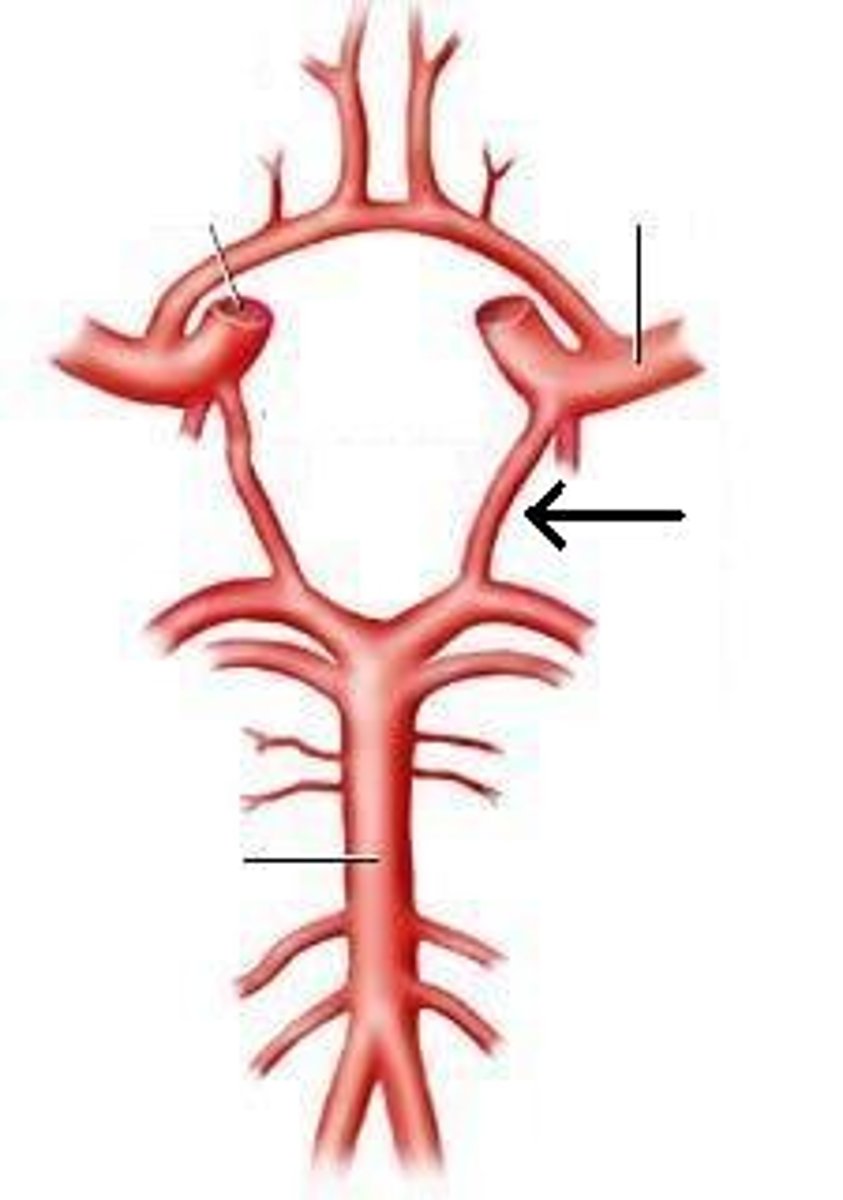
vertebral arteries
Arteries that ascend the vertebrae, enter the base of the skull, and join together to form the basilar artery. Travel through foramen magnum to reach the pons.
internal carotid arteries
this artery branches off the common carotid arteries, travel up into the skull through the carotid canal, and then divide to form the anterior and middle cerebral arteries.
anterior cerebral arteries
two large arteries, arising from the internal carotid arteries. Travels anteromedially to the median longitudinal fissure where it supplies the superior and medial aspects of the frontal and parietal lobes.
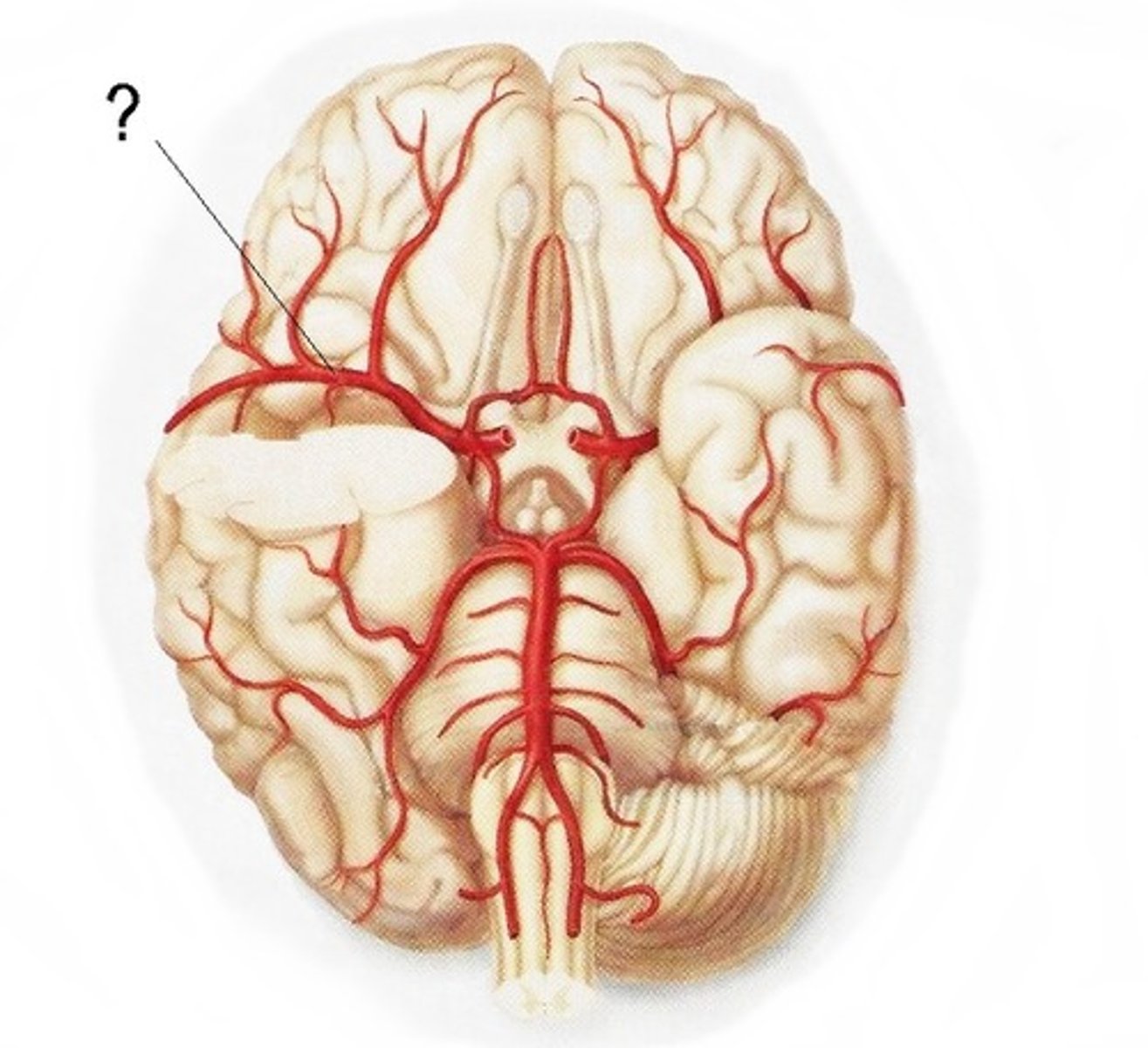
middle cerebral arteries
two large arteries, arising from the internal carotid arteries. Dives into the lateral fissure to travel to the lateral aspect of the brain, where it supplies the majority of the temporal lobe and a large portion of the frontal and parietal lobes.
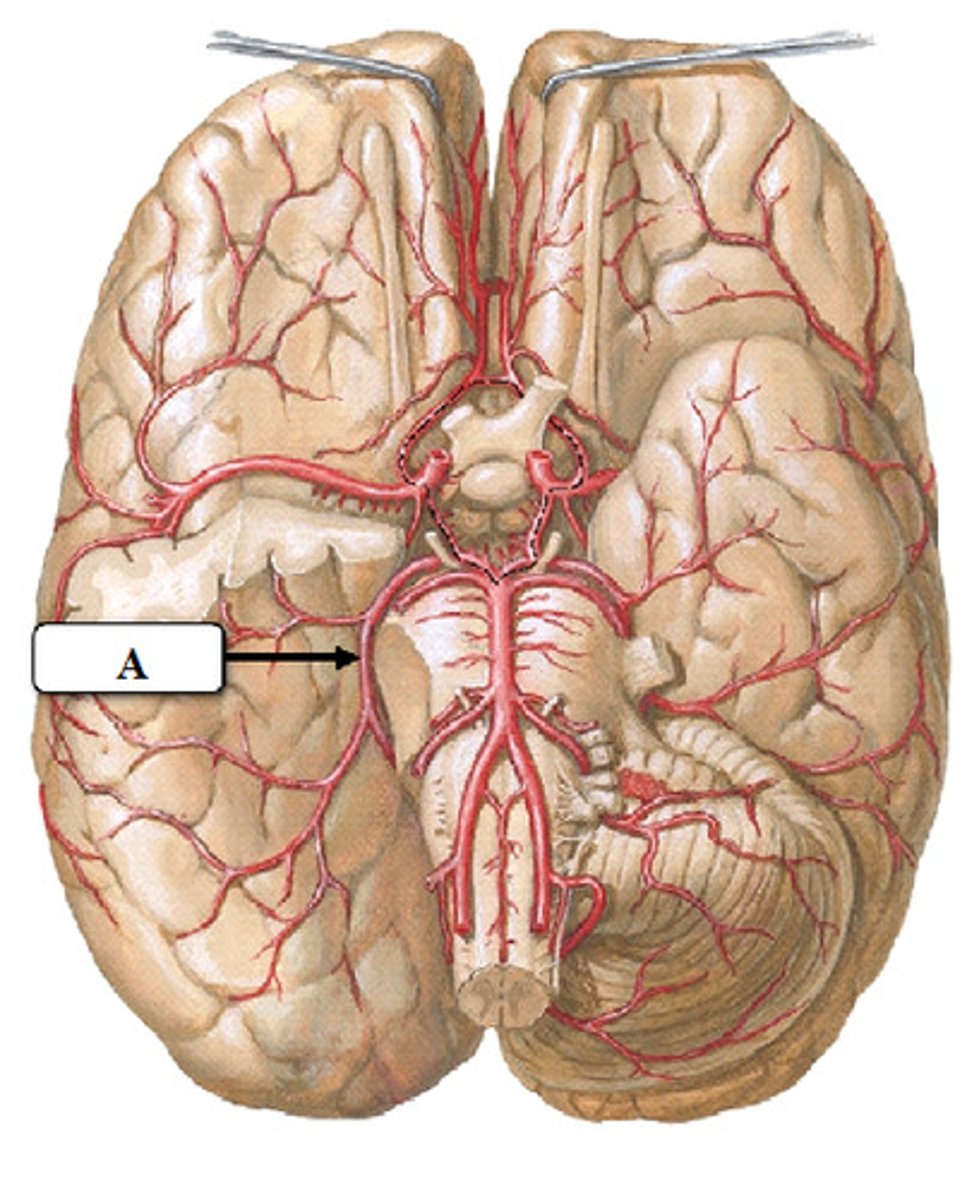
posterior cerebral arteries
Two large arteries, arising from the basilar artery, that supply the posterior aspect of the brain, including the occipital lobes, as well as the inferior portion of the temporal lobes.
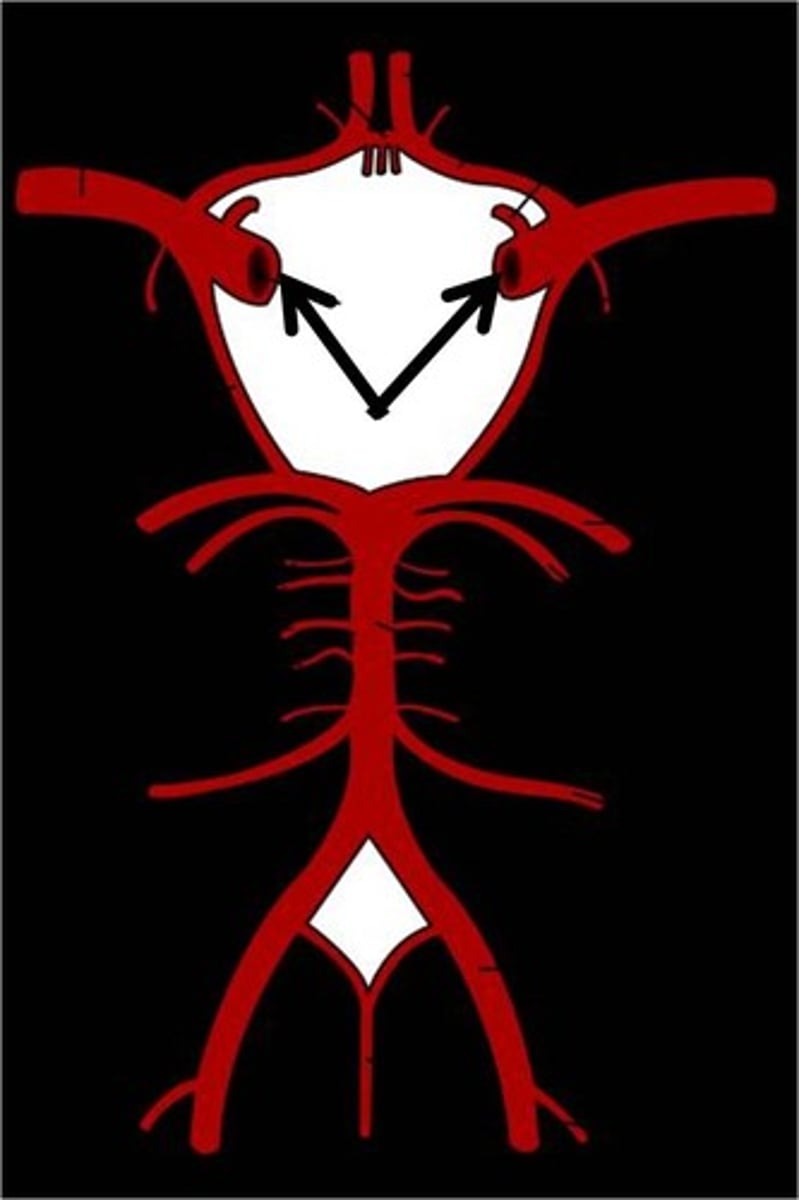
anterior communicating artery
Connects the two anterior cerebral arteries before they enter the median longitudinal fissure
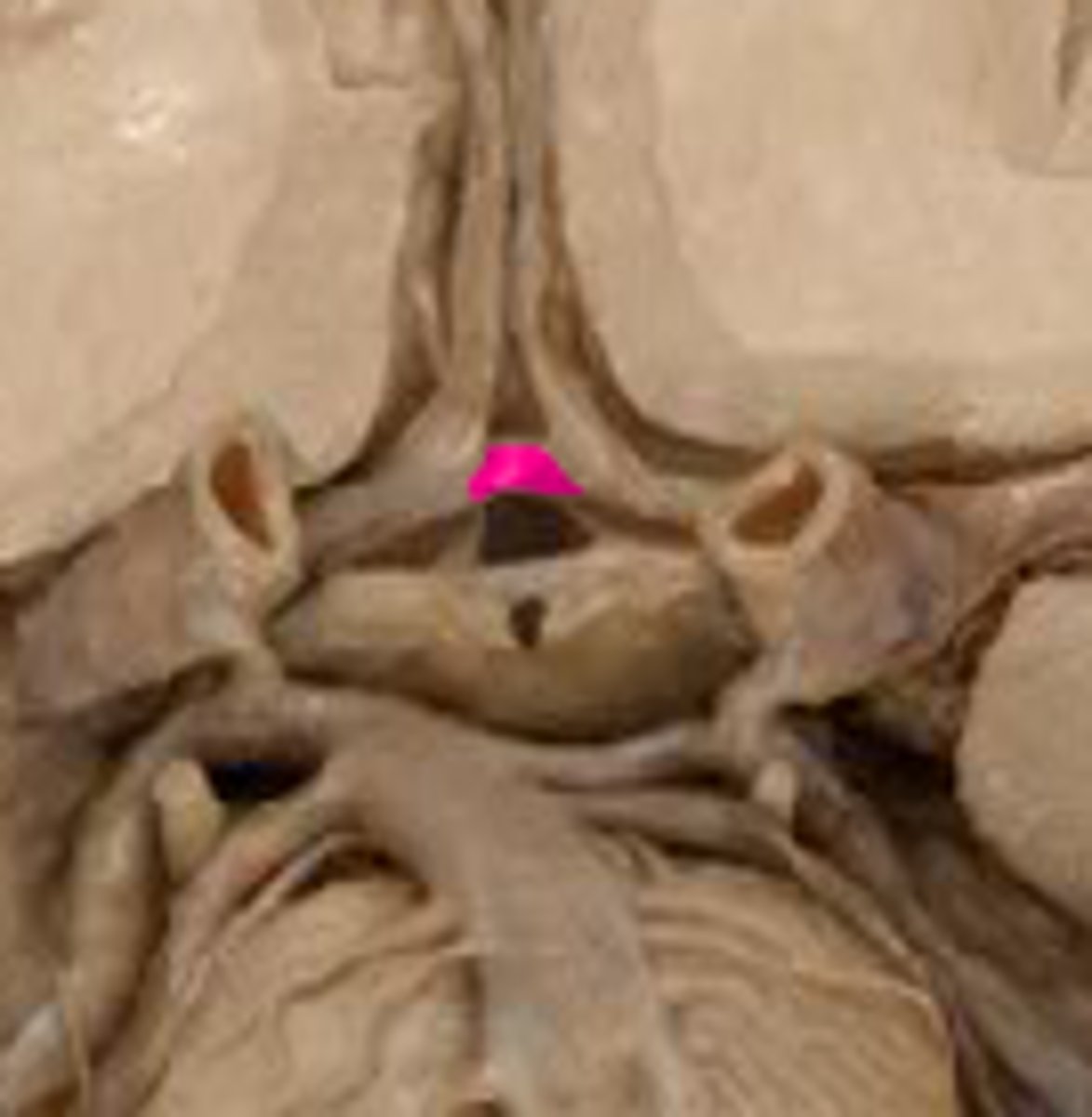
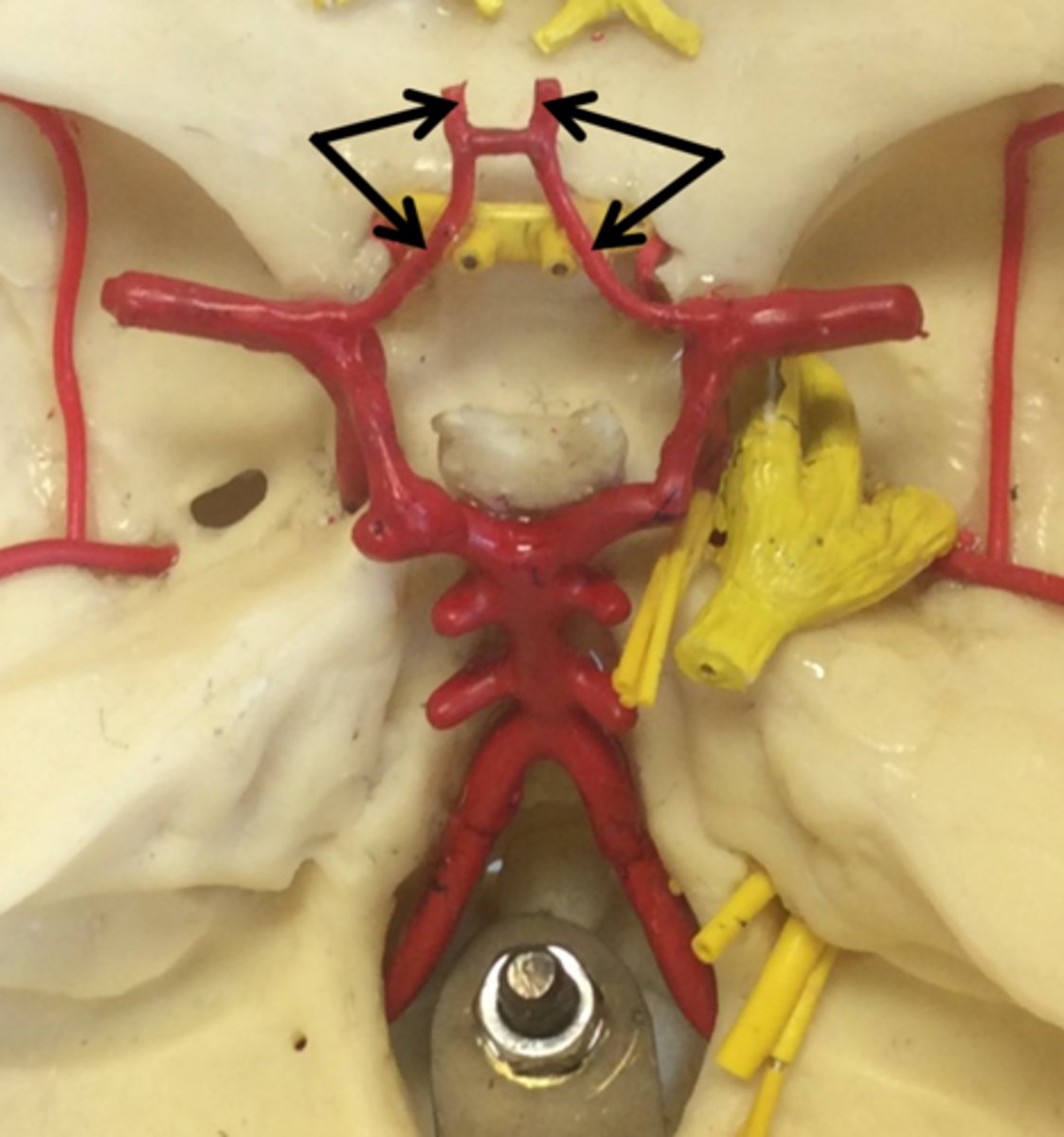
posterior communicating artery
small arteries that connect the posterior cerebral and internal carotid arteries.
basilar artery
arises from the vertebral arteries and runs along the pons before dividing into posterior cerebral arteries.
Folia
folds of the cerebellum
pyramids
tube-like bulges on the sides of the medulla
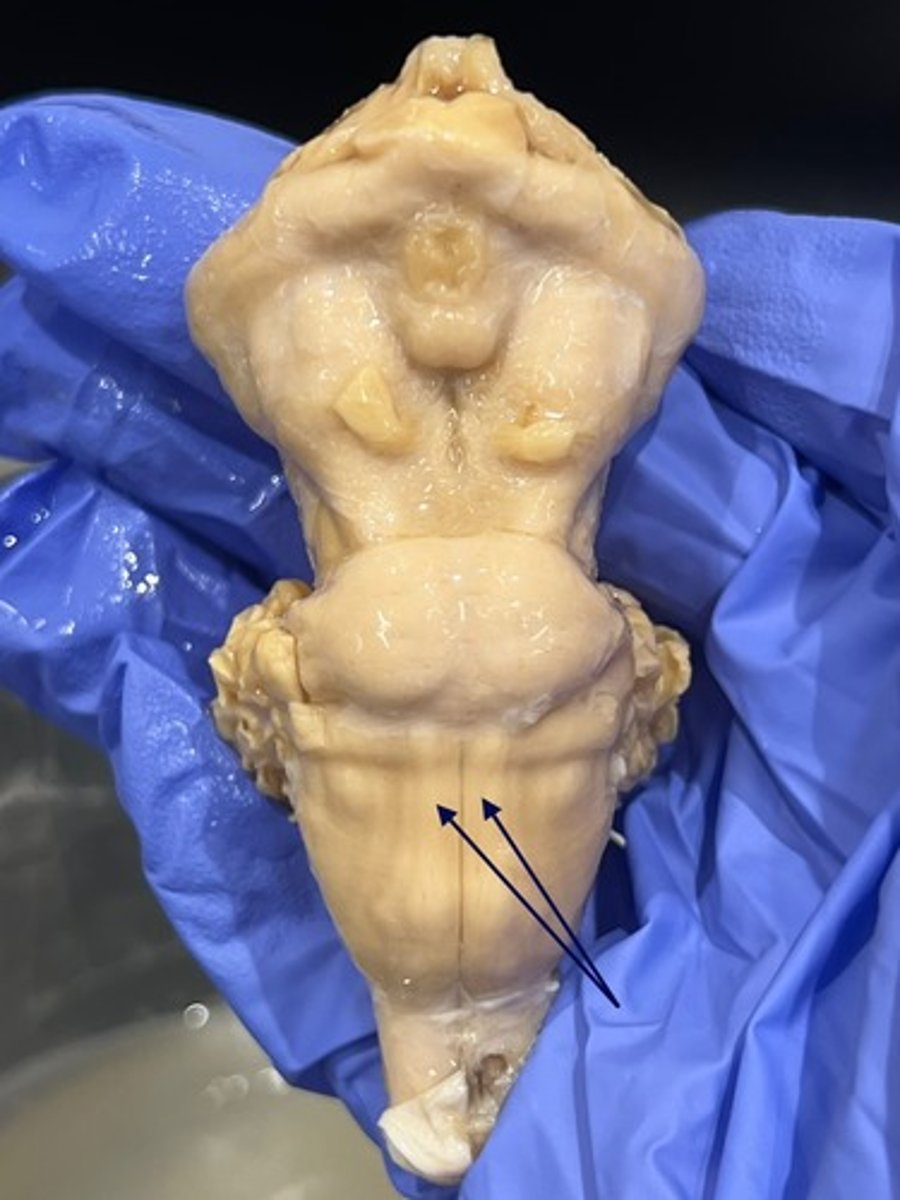
pyramidal decussation
location at which corticospinal tract fibers cross the midline and the sulcus disappears briefly
Cerebral peduncles
located on the ventral side of the midbrain. These white matter pathways carry fibers of the corticospinal tract, originating in the primary motor cortex and descending fibers from other cortical regions. bunny ear appearance off the pons
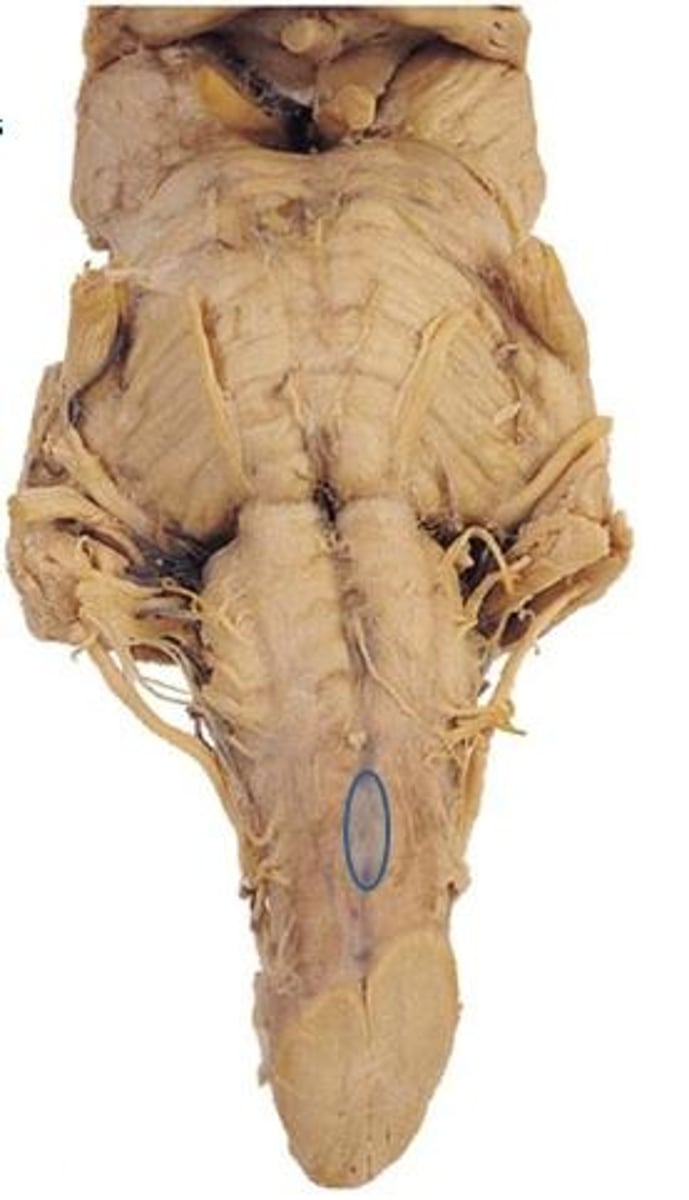
interpeduncular fossa
space between cerebral peduncles
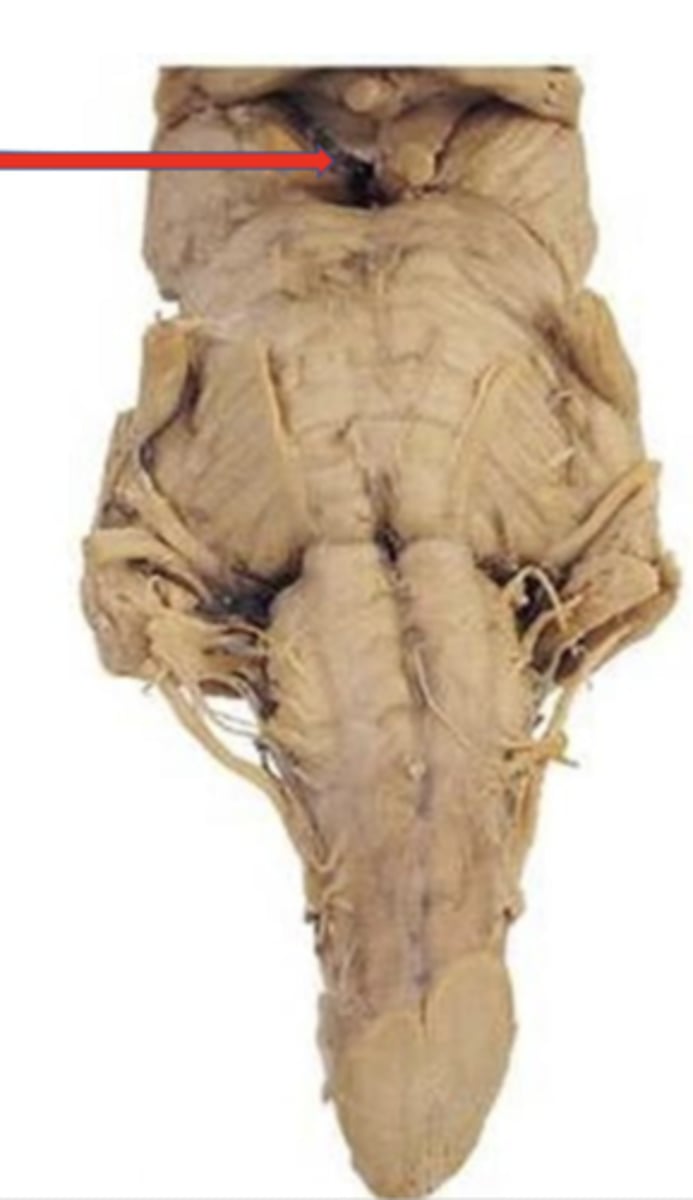
substantia nigra
a dark pigmented line in the midbrain
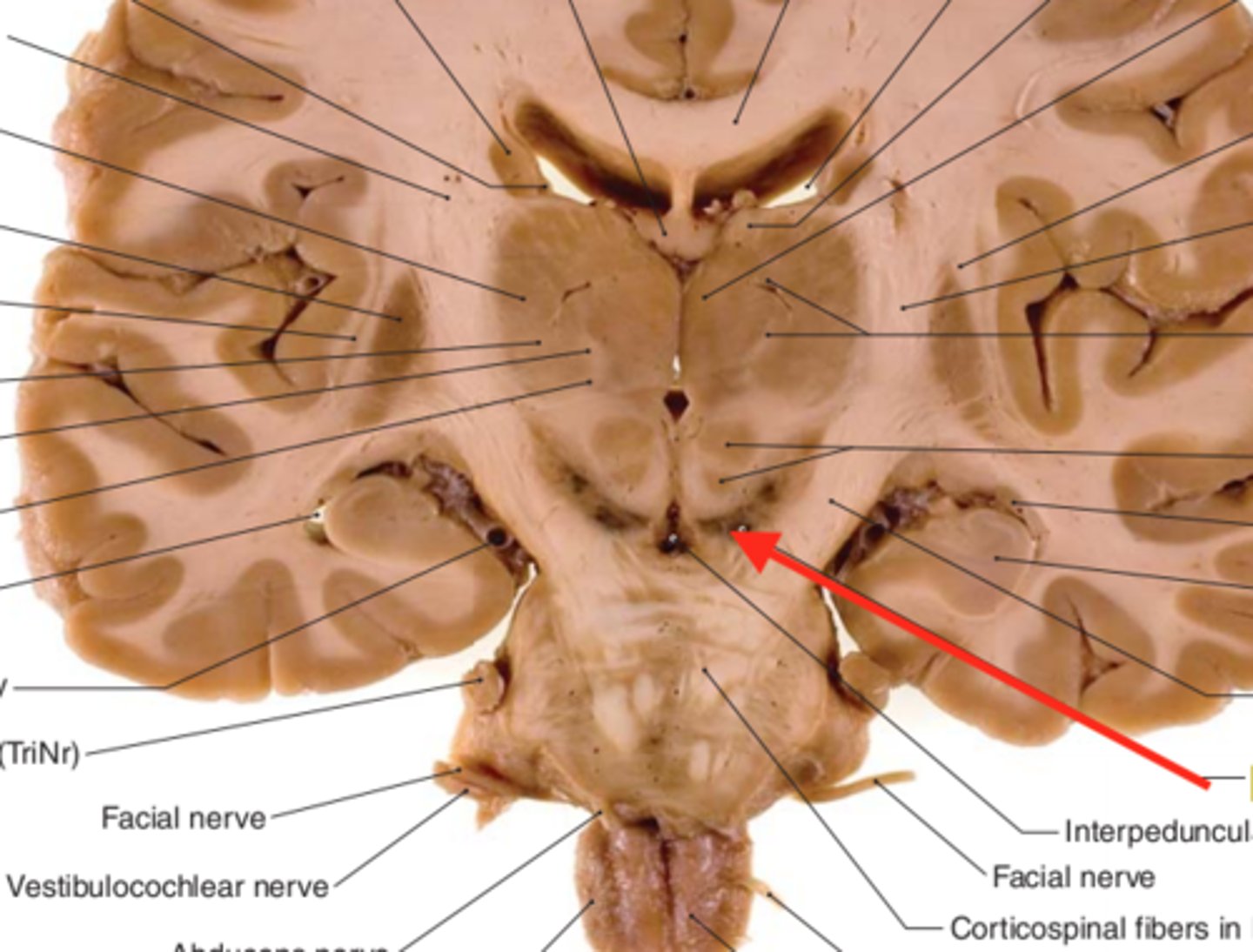
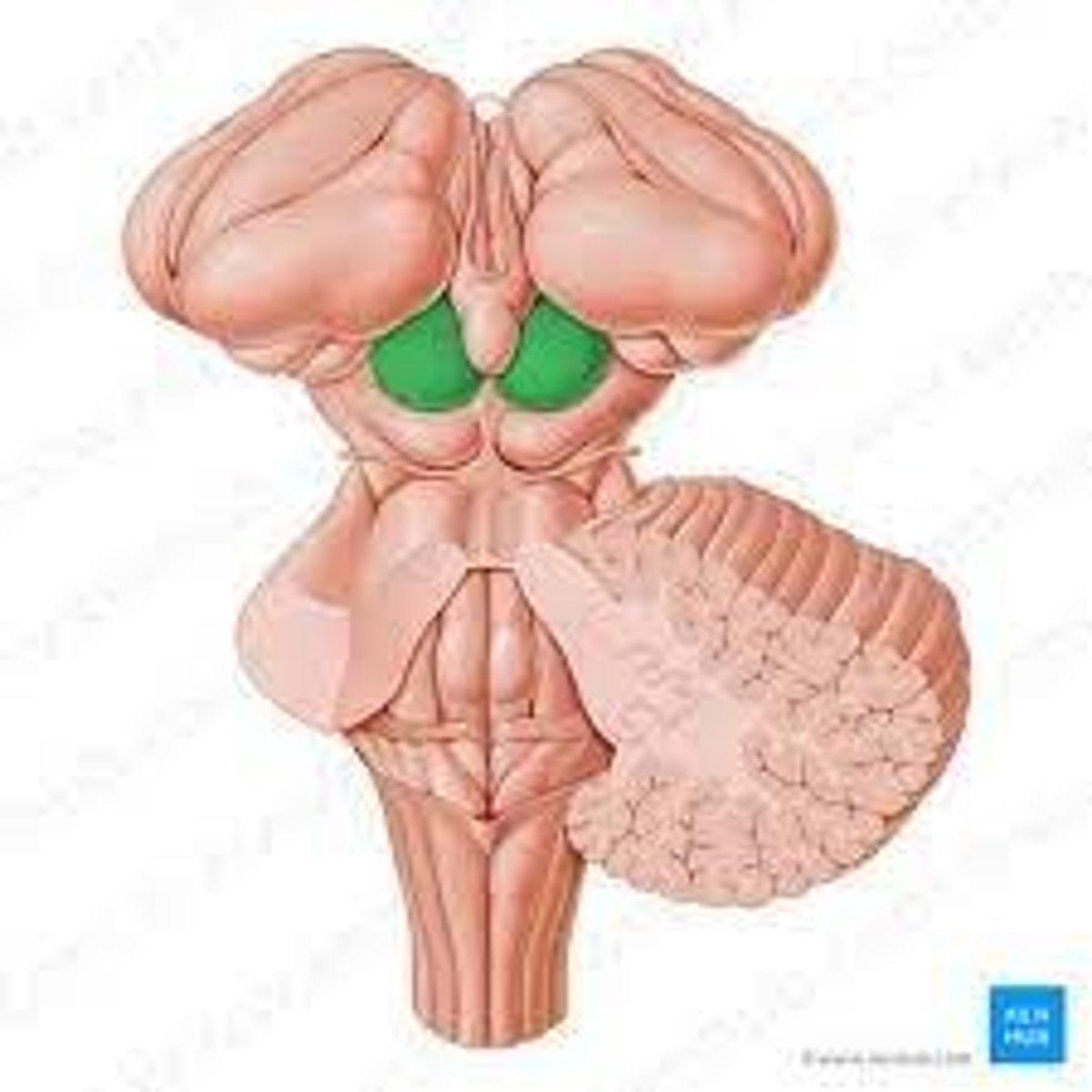
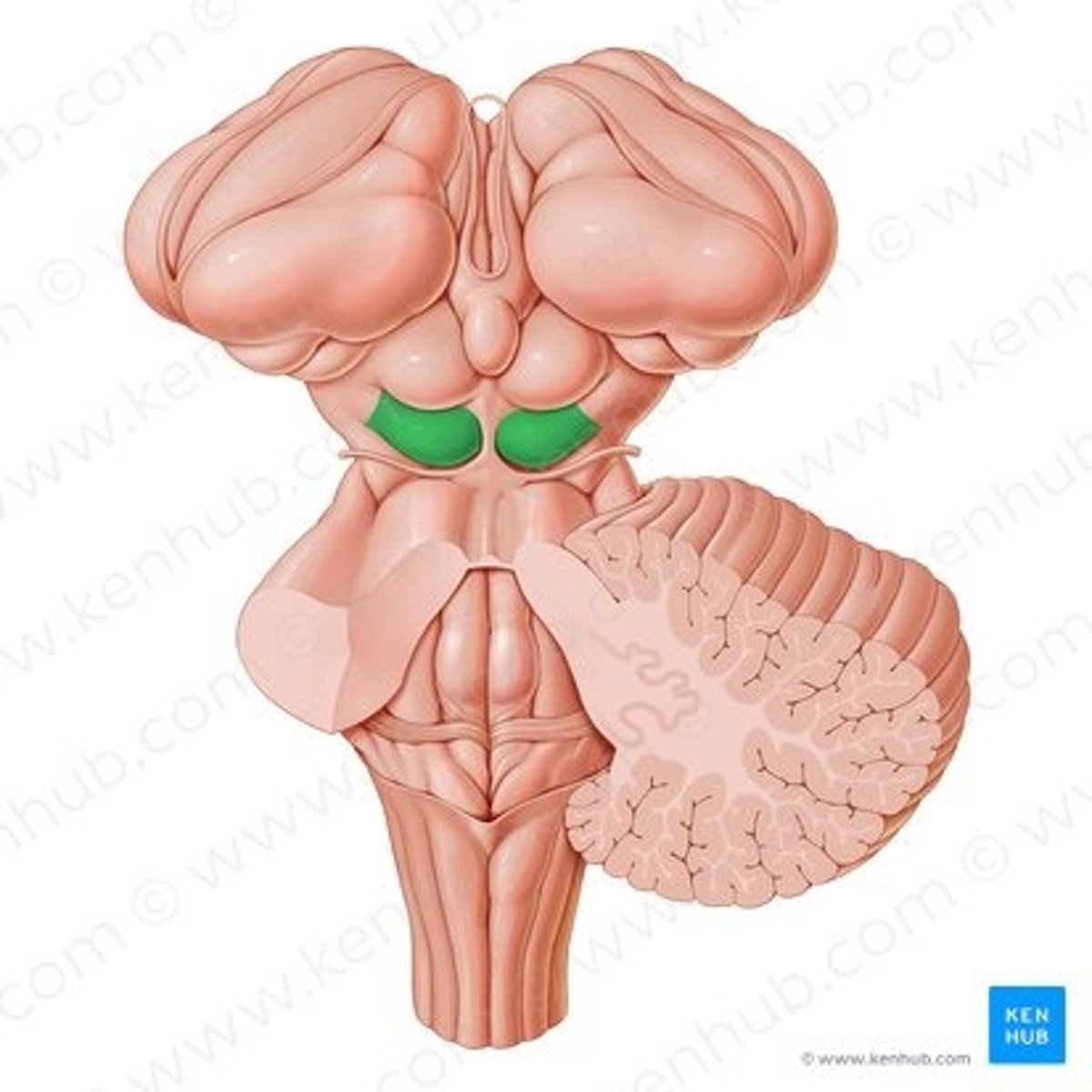
Tectum
the four bumps located on the dorsal side of the midbrain. Very caudal.
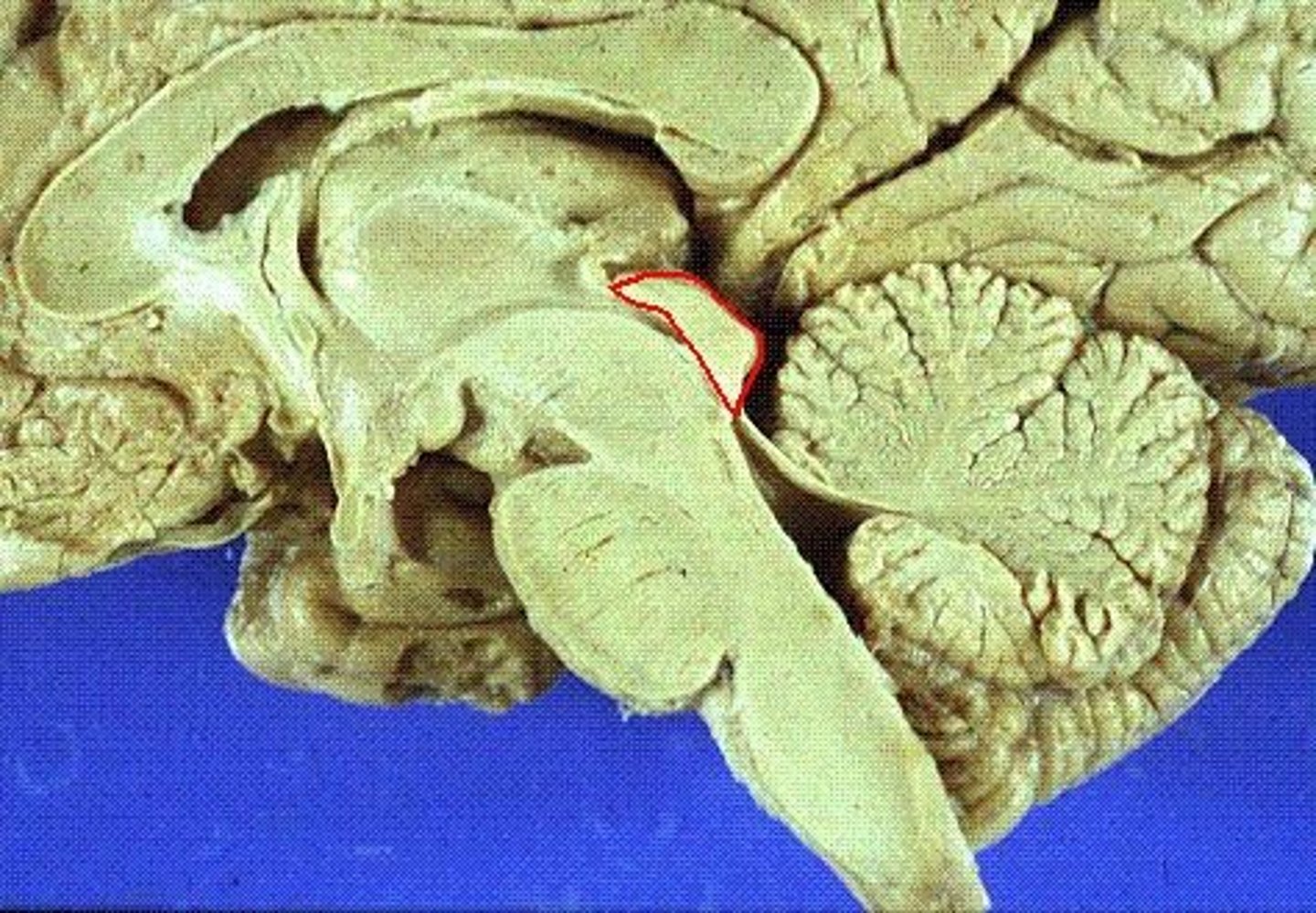
superior colliculi
the two superior bumps of the tectum. Responsible for visual reflexes.
inferior colliculi
the two inferior bumps of the tectum. Responsible for auditory reflexes
CNI
olfactory nerve: smell, sensory, arise in the olfactory epithelium of the nasal cavity and course dorsally to the olfactory bulb. Associated with the cerebrum. Exit at the foramina in cribriform plate of ethmoid bone.
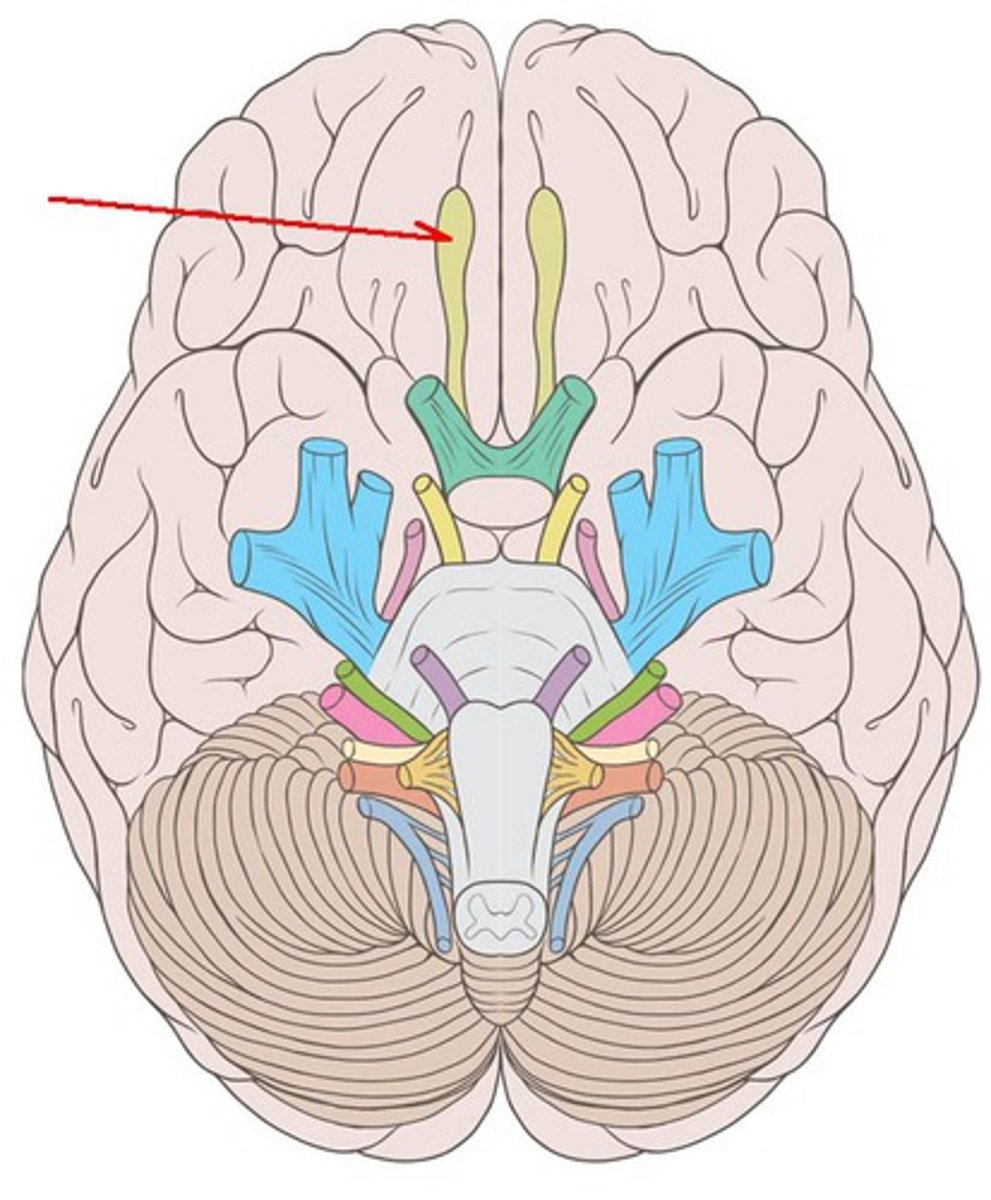
olfactory nerve
innervates the sensory function of smell
olfactory bulb
inferior to the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere. Where the olfactory nerves synapse.
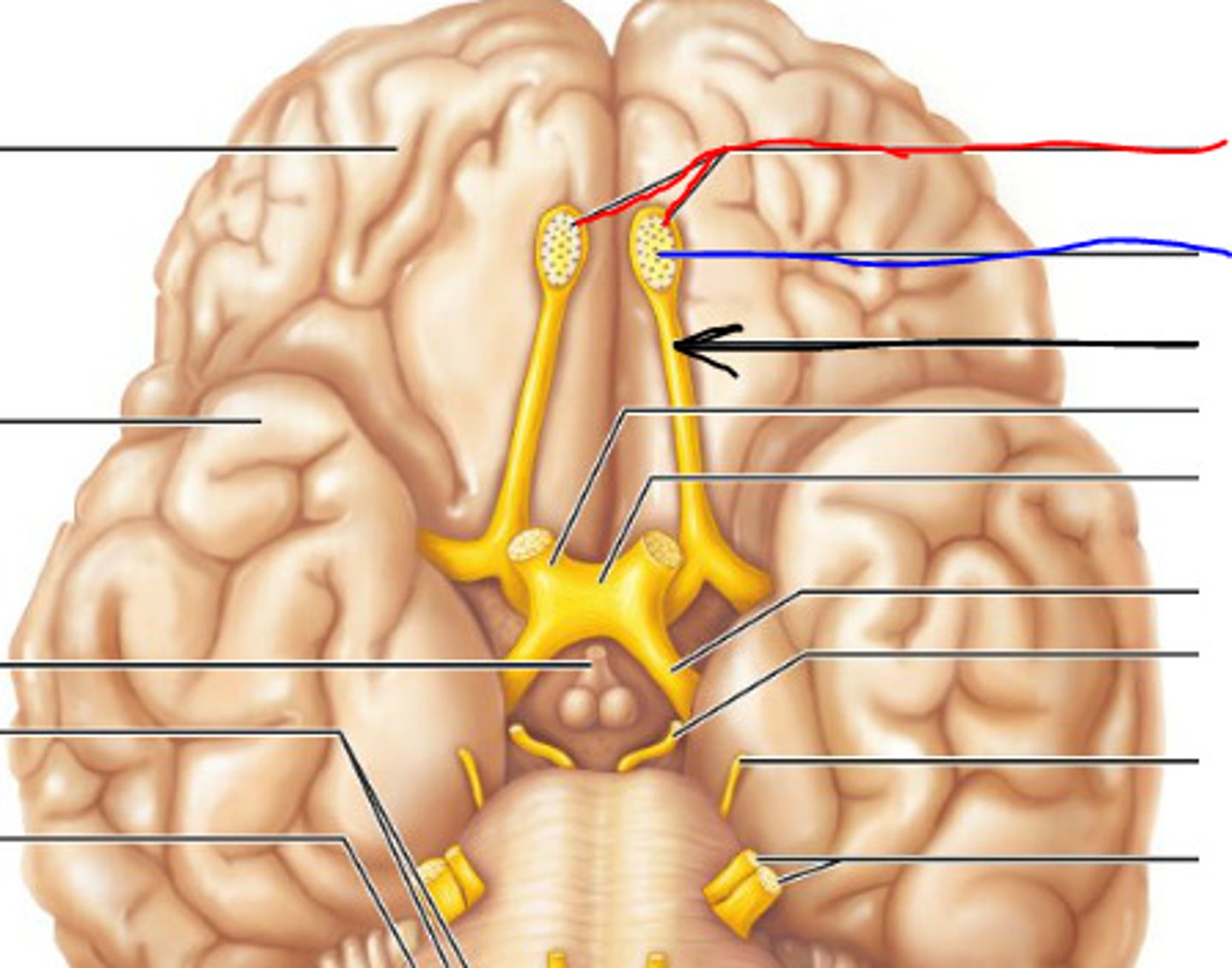
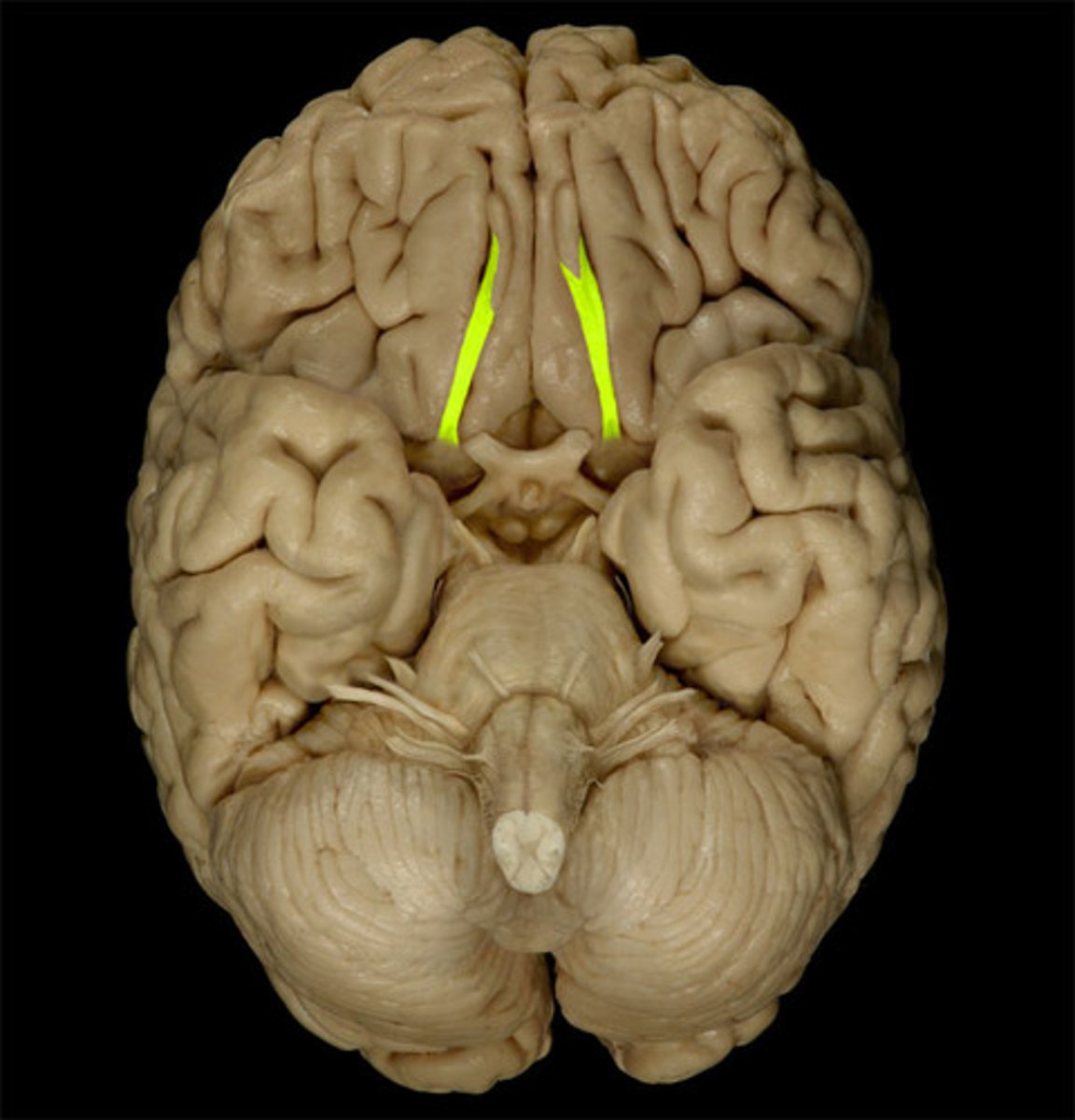
olfactory tract
originates in the olfactory bulb and runs caudally on the ventral aspect of the frontal lobe
CNII
Optic nerve: vision, sensory, begin in the retina of each eye. These nerves course posteriorly and are united in the optic chiasm. The fibers split again immediately posterior to the optic chiasm and extend posteriorly as the optic tracts. Associated with the thalamus. Exit at the optic canal.
optic nerve
innervates the sensory ability to see using the retina
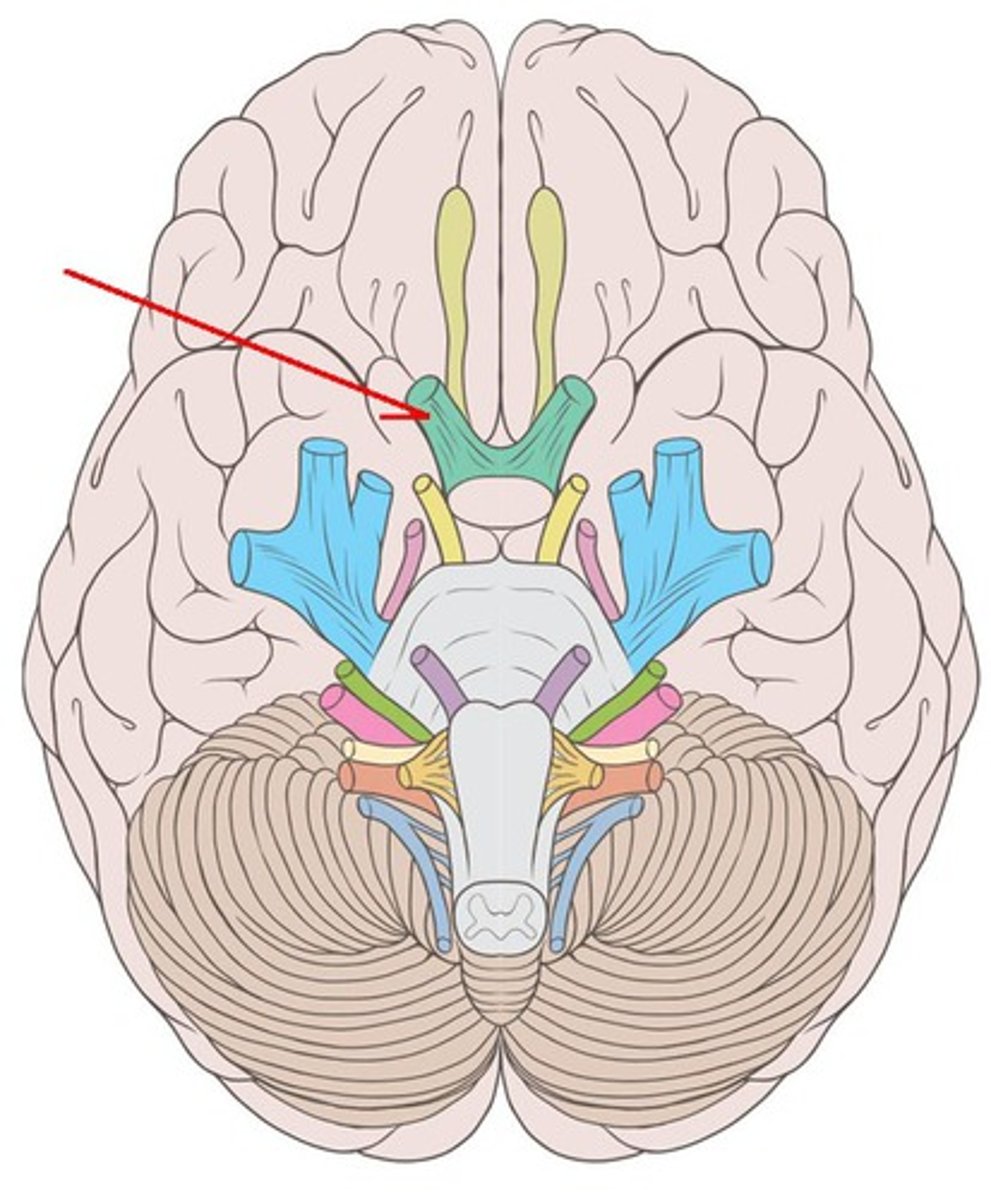
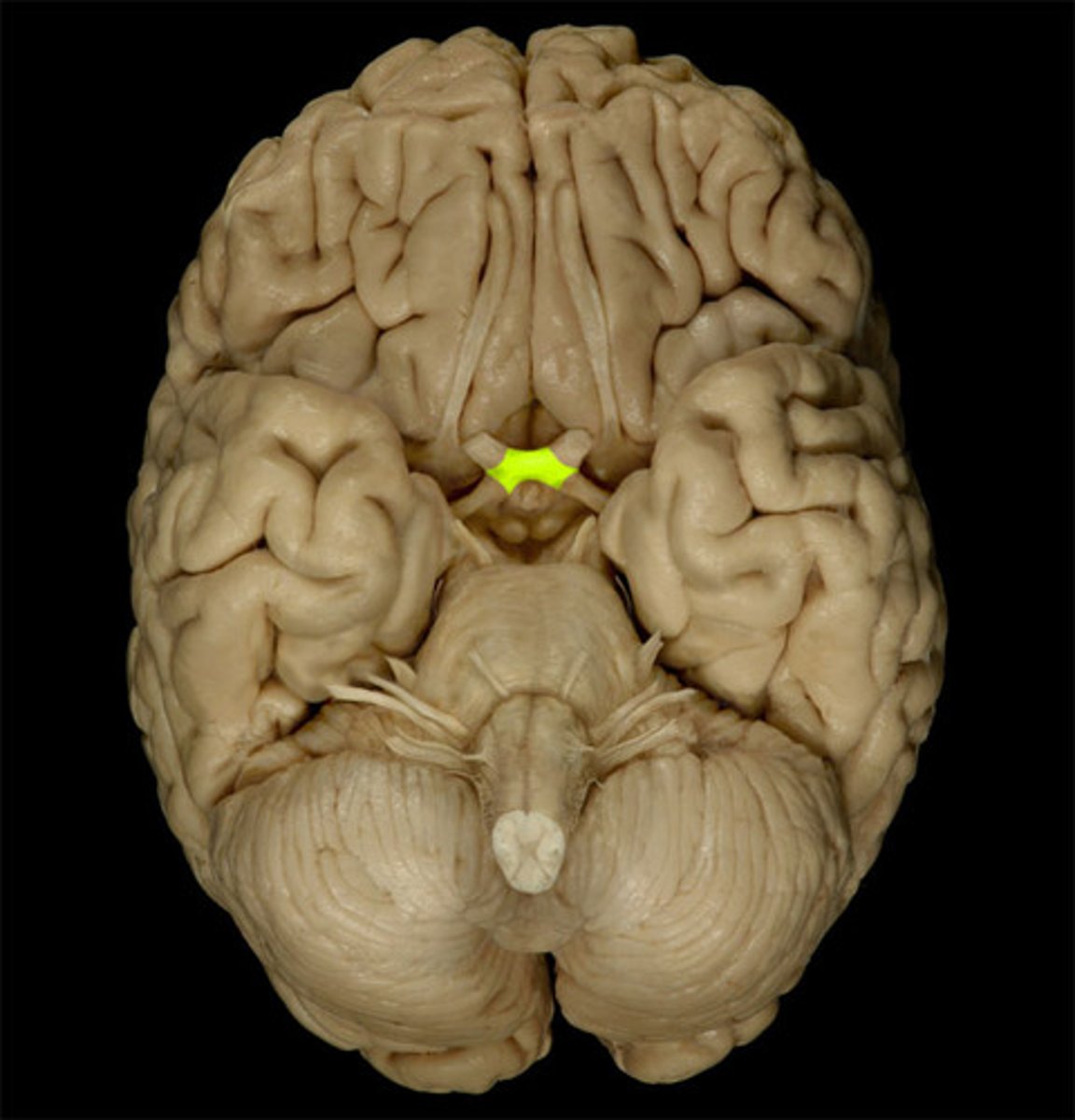
Optic chiasm
where the R+L optic nerves join at an "X"
Optic tract
arises from optic chiasma to terminate posteriorly
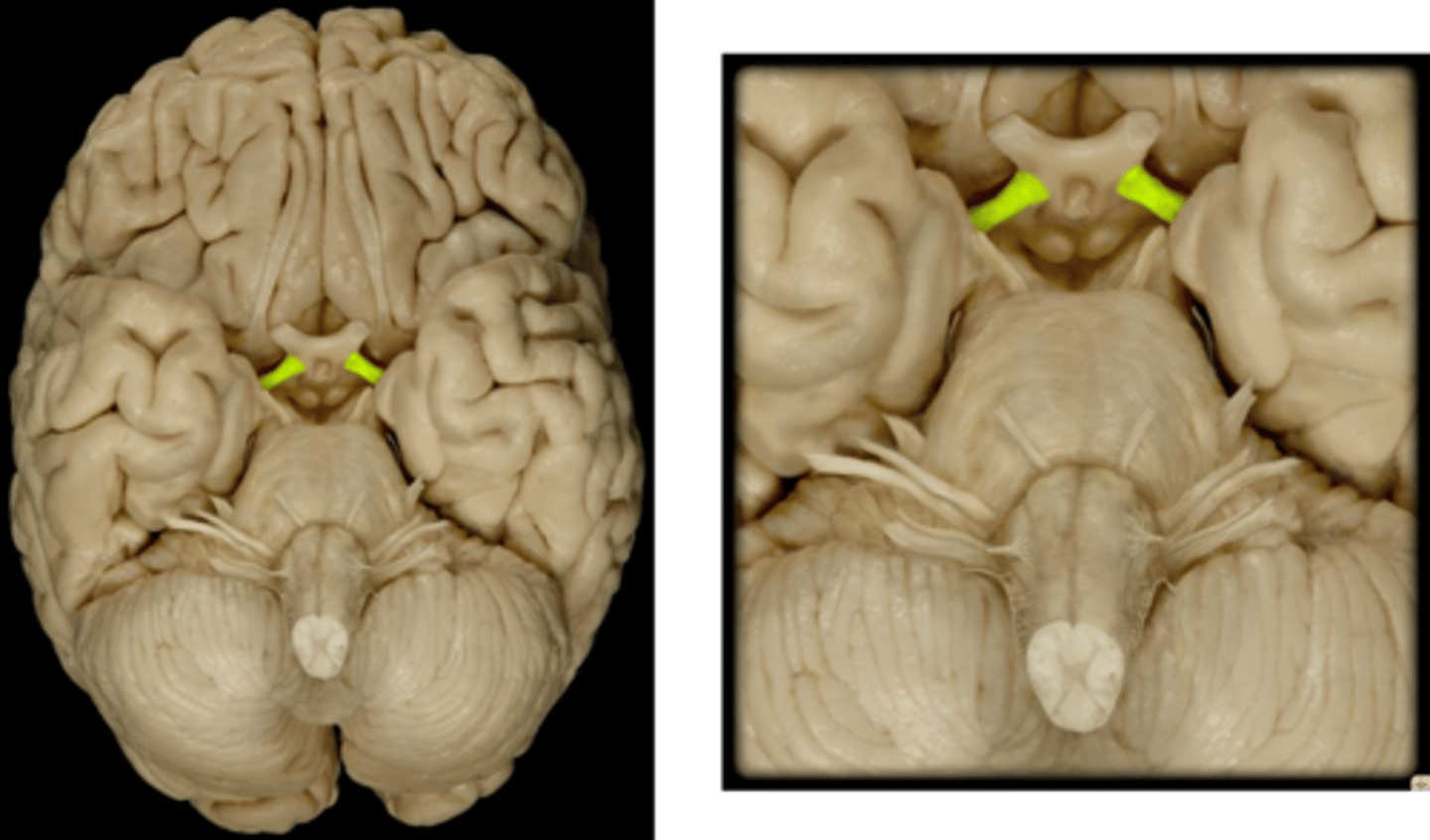
CNIII
Oculomotor nerve: movement of the eyes+pupils, motor, emerge in the interpeduncular fossa and innervate 4 of the 6 extraocular muscles: the medial rectus, superior rectus, inferior rectus, and inferior oblique. exit at the superior orbital fissure.
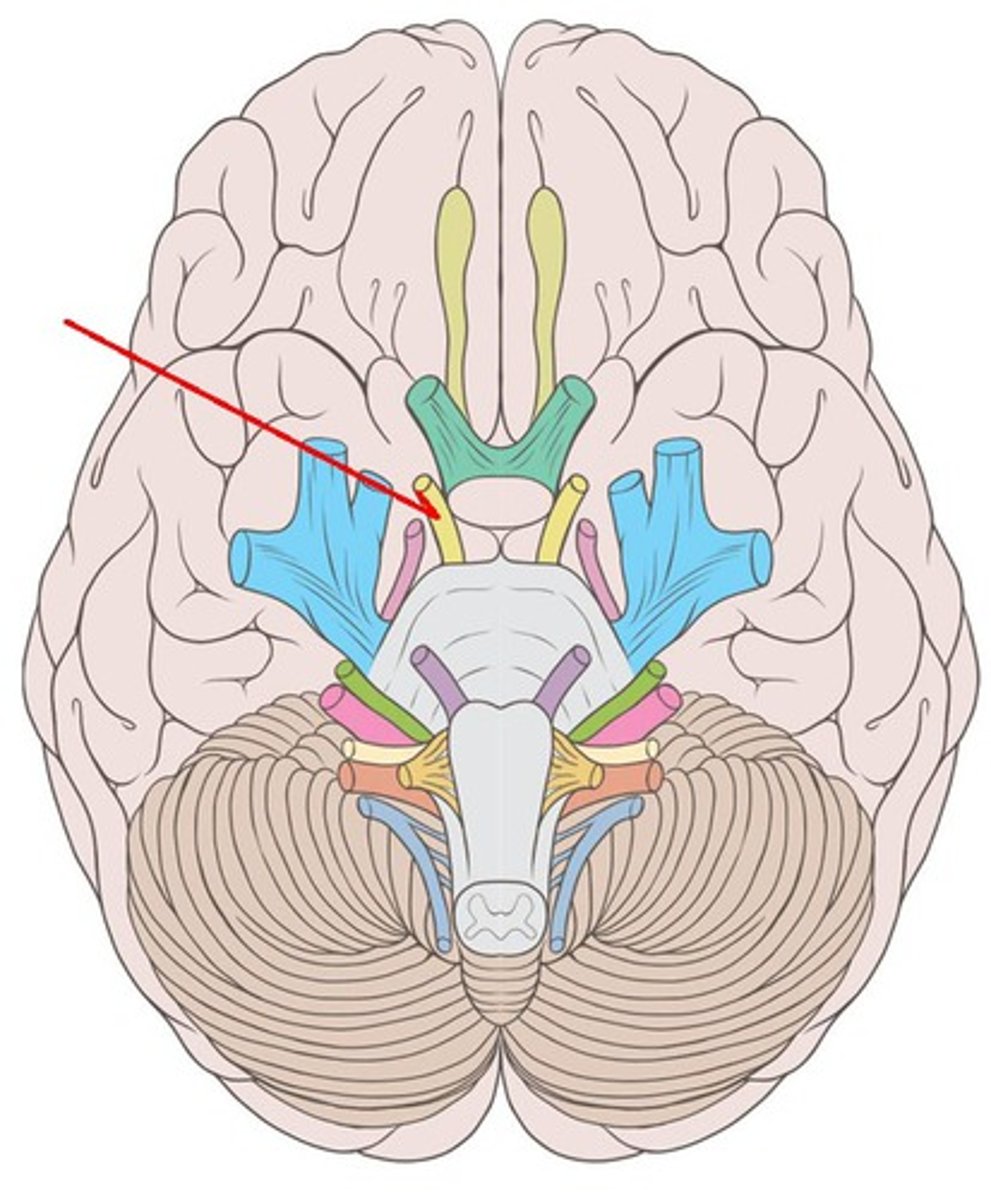
Oculomotor nerve
innervates medial rectus (adducts), superior rectus (look up), inferior rectus (look down), and inferior oblique (Elevates eye and turns it laterally)
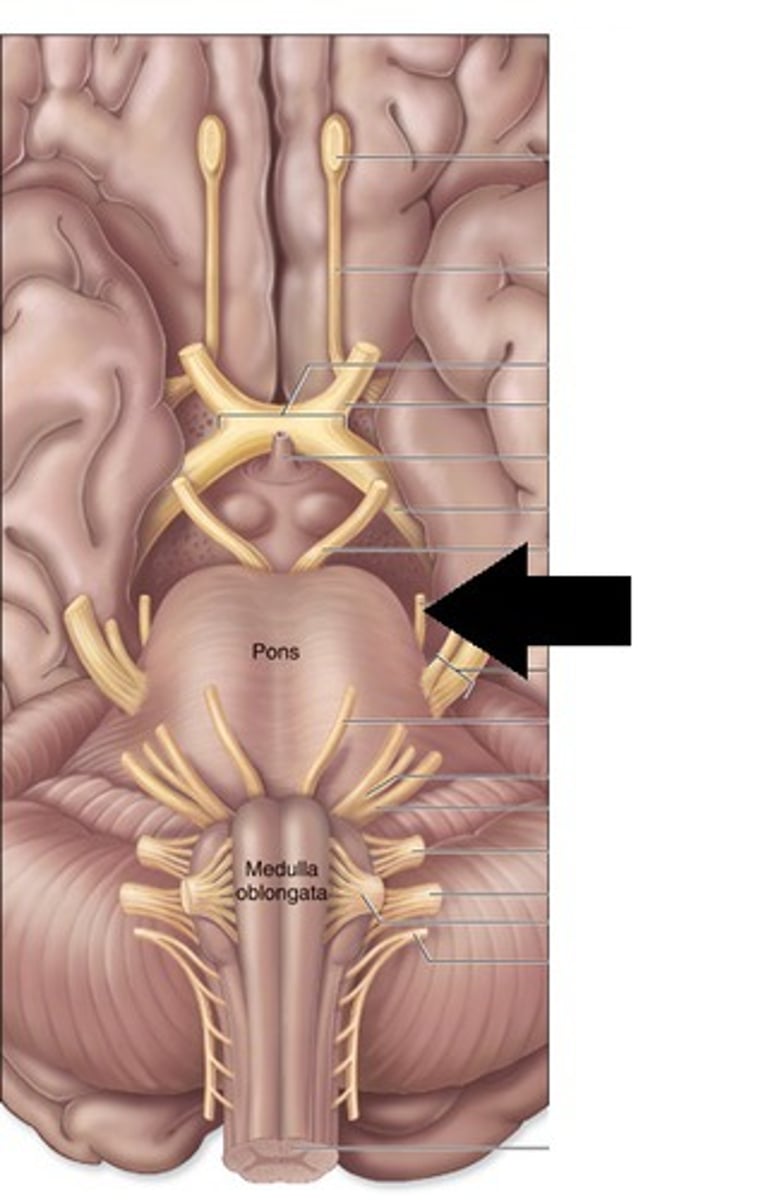
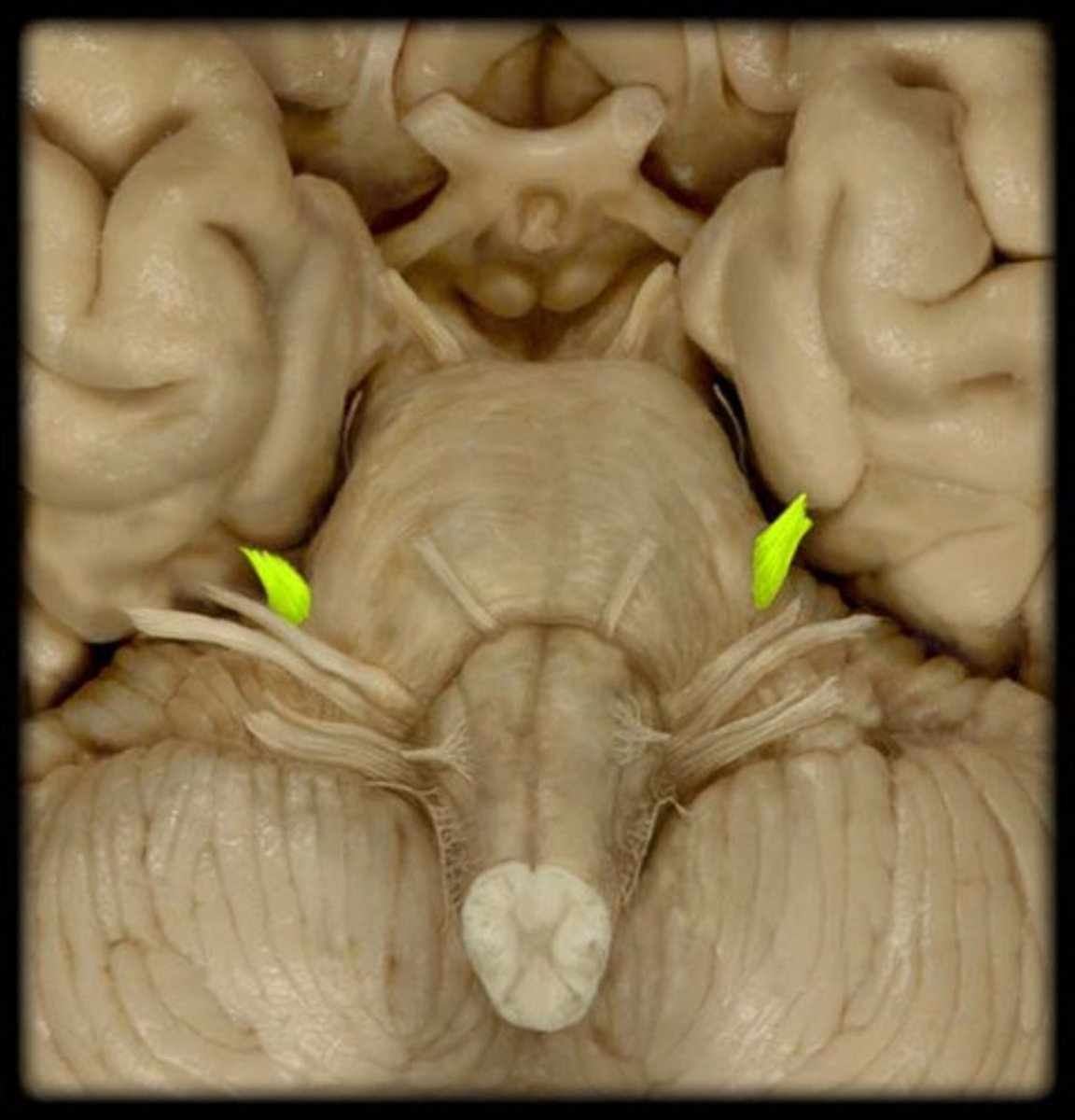
CNIV
trochlear nerve: movement of the eyes, motor, emerge on the brainstem’s dorsal aspect. They travel around the sides of the midbrain and pons to innervate the superior oblique. exit at the superior orbital fissure.
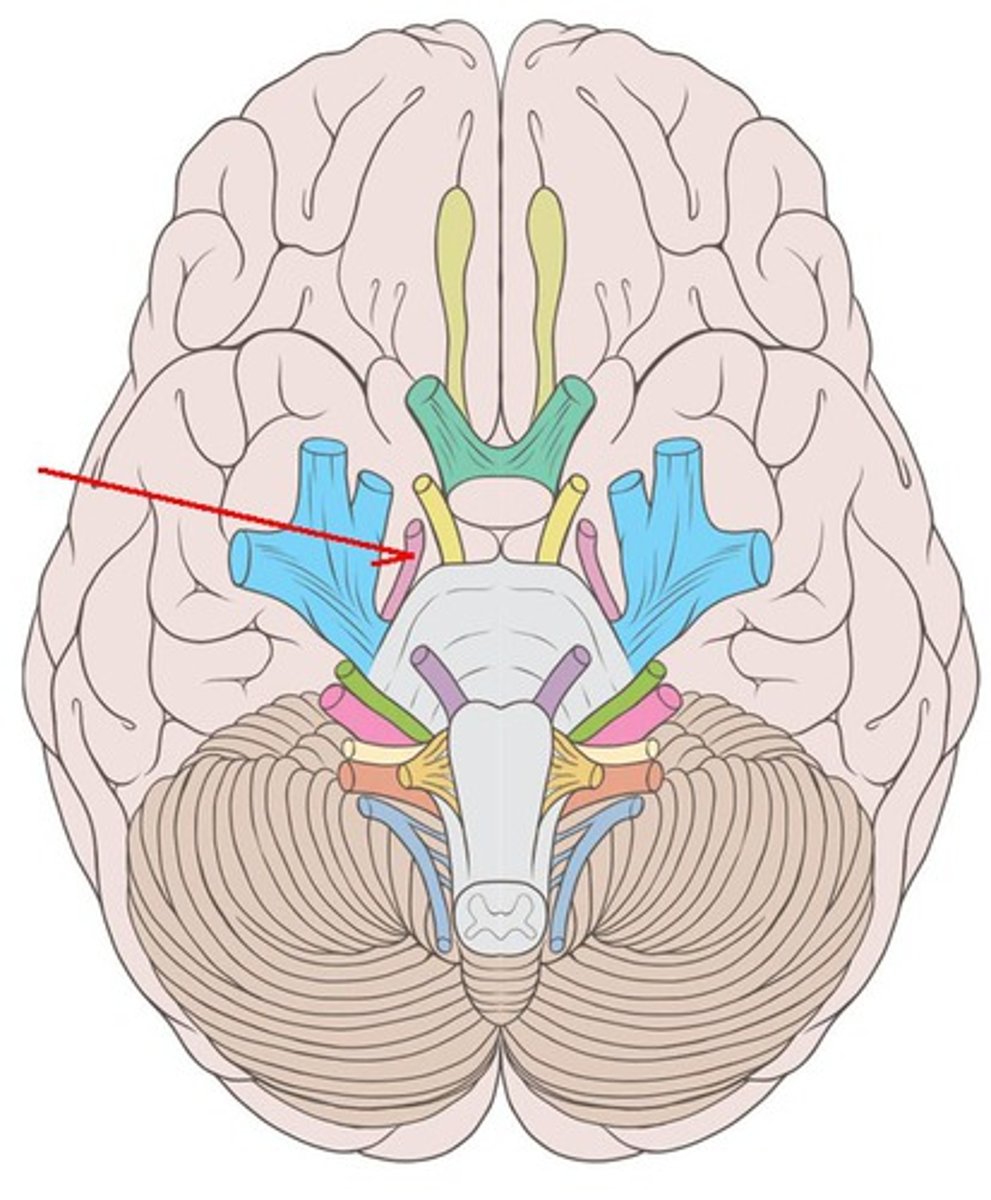
Trochlear nerve
innervates superior oblique muscle (Depresses eye and turns it laterally)
CNV
trigeminal nerve: sensation of the face, sinuses, and teeth, movement of the jaw, muscles of mastication, both, emerge from the lateral aspect of the pons. exit: ophthalmic branch-superior orbital fissure, maxillary branch-foramen rotundum, mandibular branch-foramen ovale
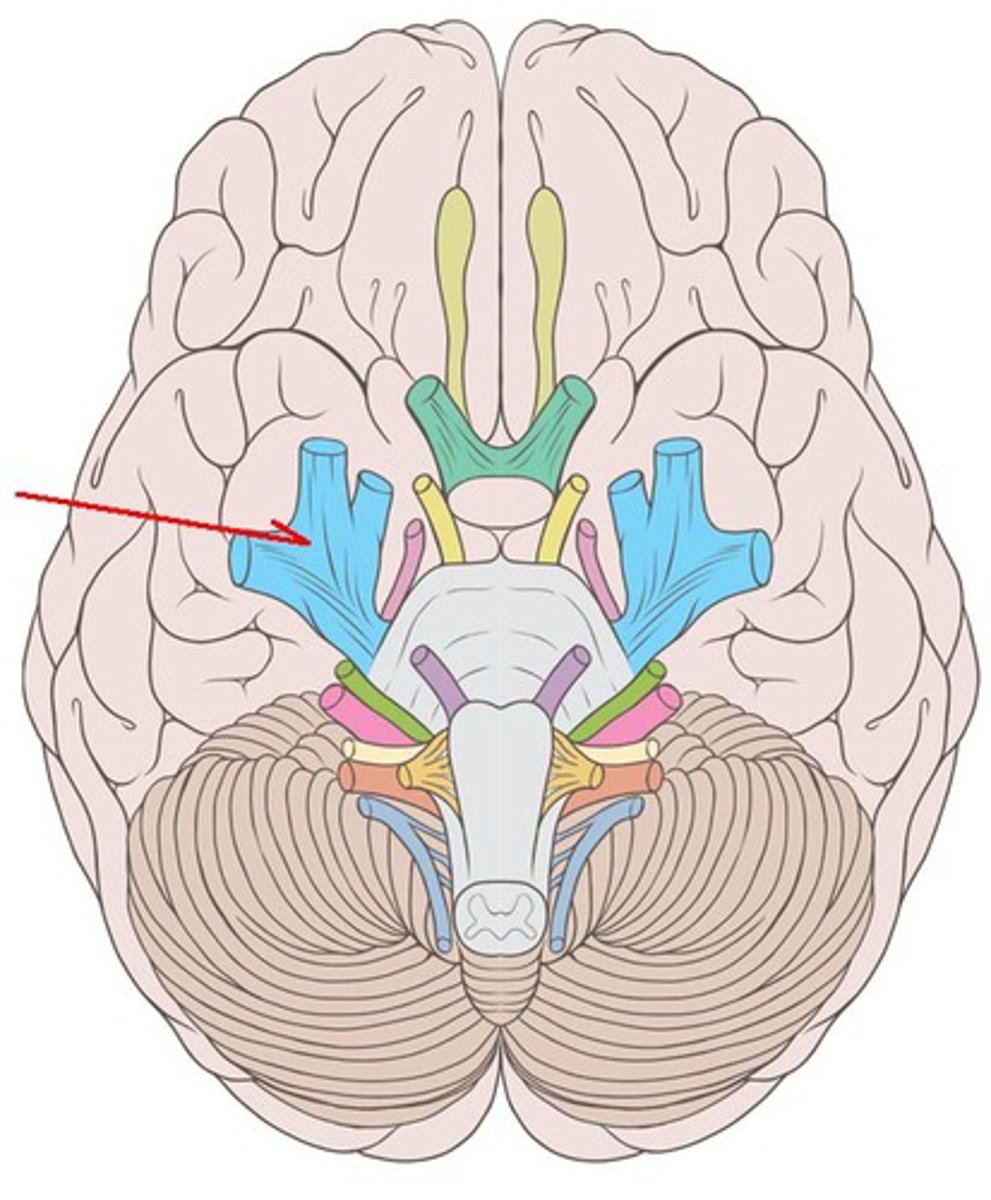
Trigeminal nerve
innervates the sensation of the whole face (all three branches) and muscles of mastication (mandibular branch: temporalis, masseter, medial and lateral pterygoid)
ophthalmic branch
exits at superior orbital fissure, branch of trigeminal nerve that provides sensory innervation for the upper face
maxillary branch
exit at foramen rotundum
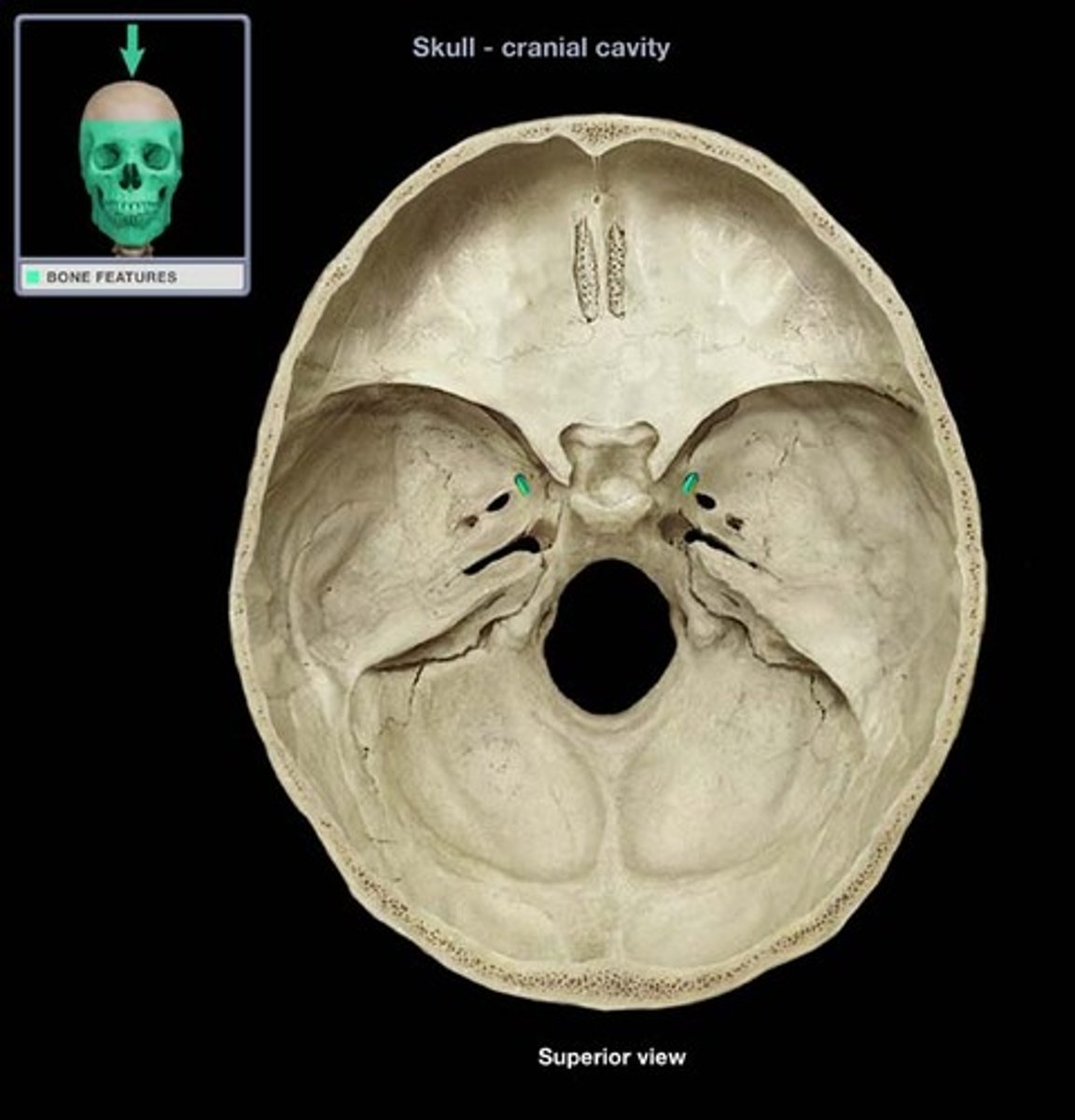
mandibular branch
exit at foramen ovale to innervate the muscles of mastication
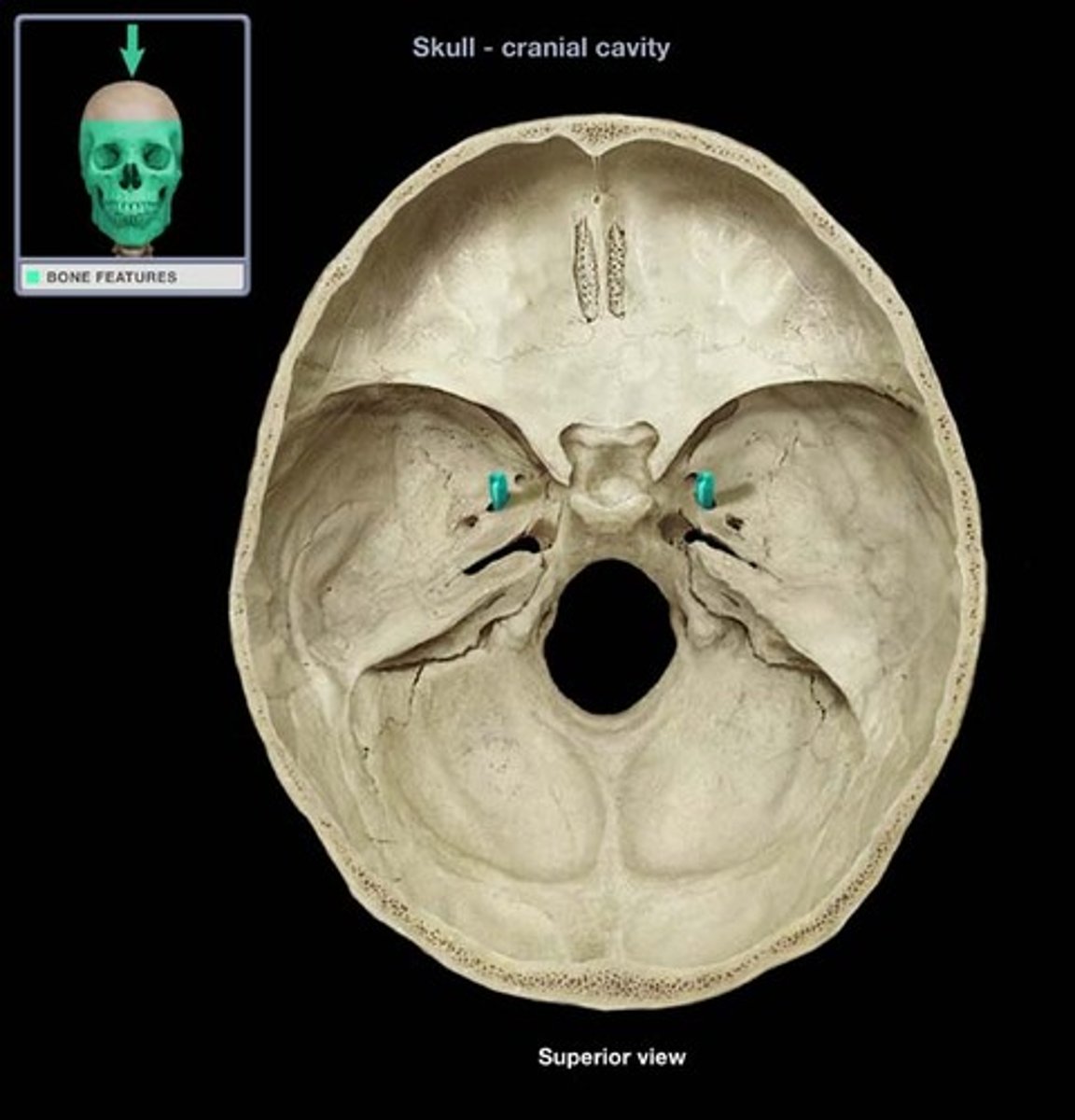
CNVI
abducens nerve: movement of the eyes laterally. Innervates the lateral rectus muscle. motor. emerge near the midline at the border of the pons and medulla, runs up the pons, exit at superior orbital fissure.
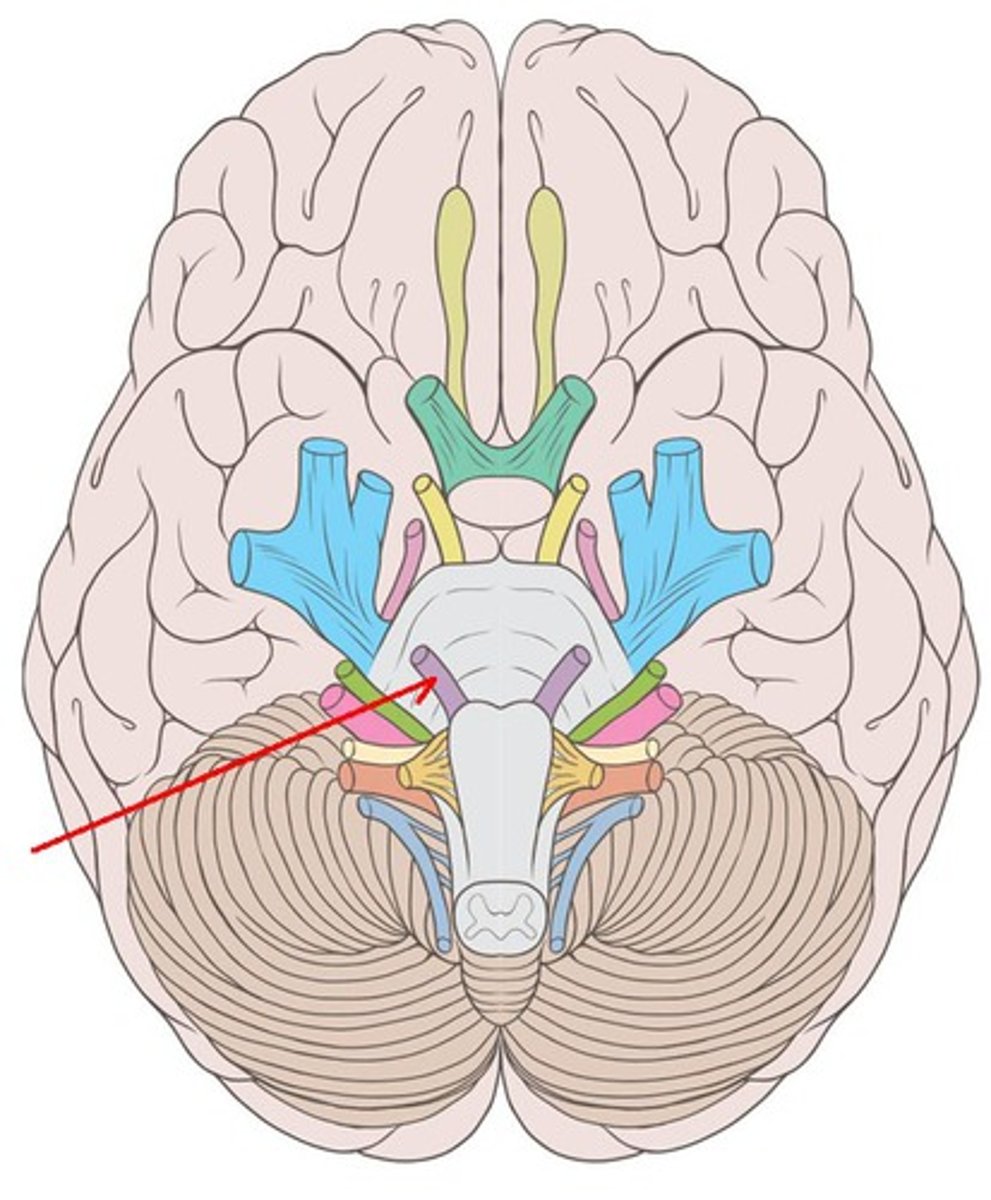
abducens nerve
innervates the lateral rectus, exits at superior orbital fissure
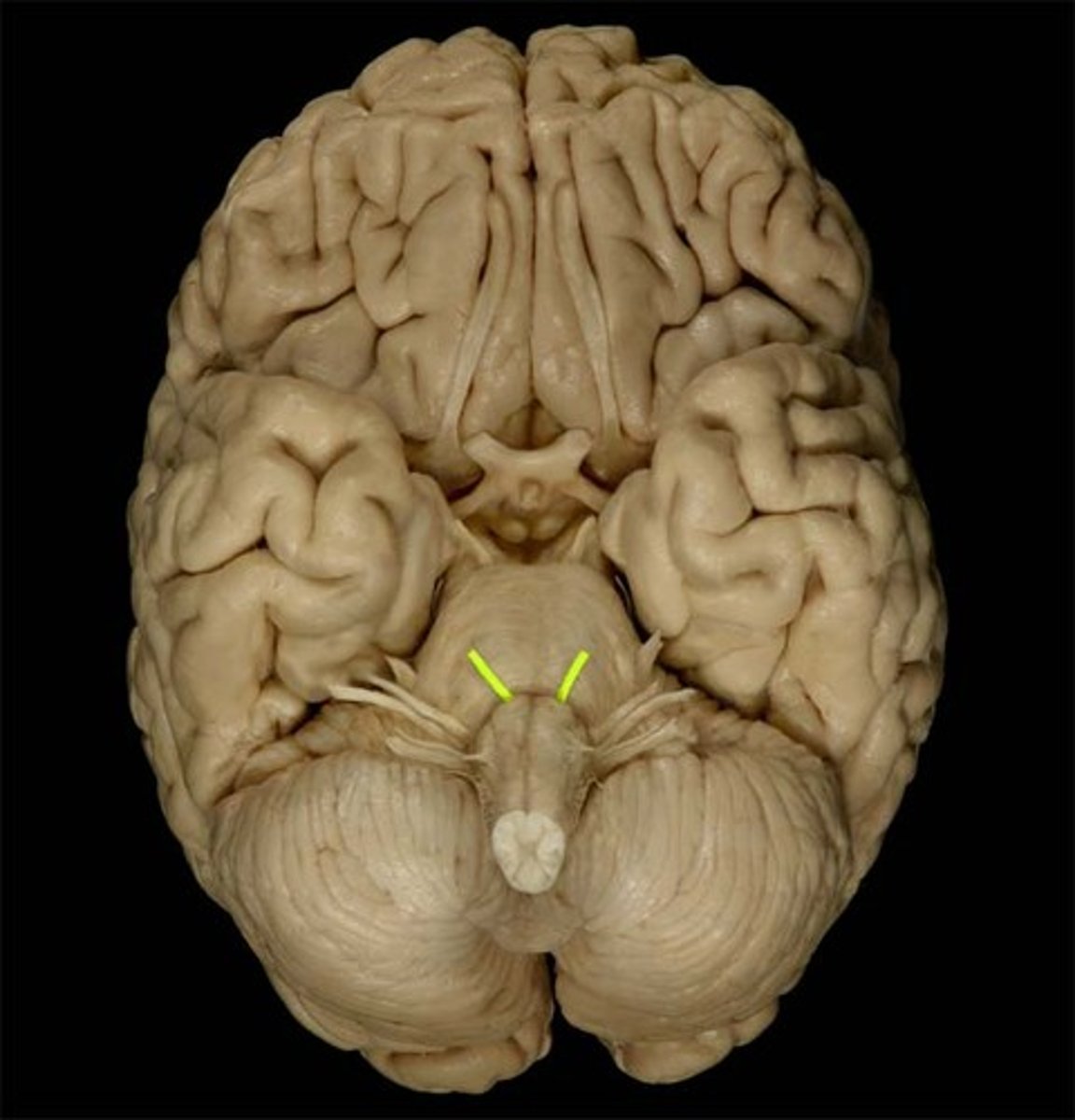
CNVII
Facial nerve: taste (anterior 2/3 of tongue), muscles of facial expression, innervation of most salivary glands. Both. Emerge near junction of pons and medulla lateral to emergence of abducens nerves. exit at internal acoustic meatus and stylomastoid foramen.
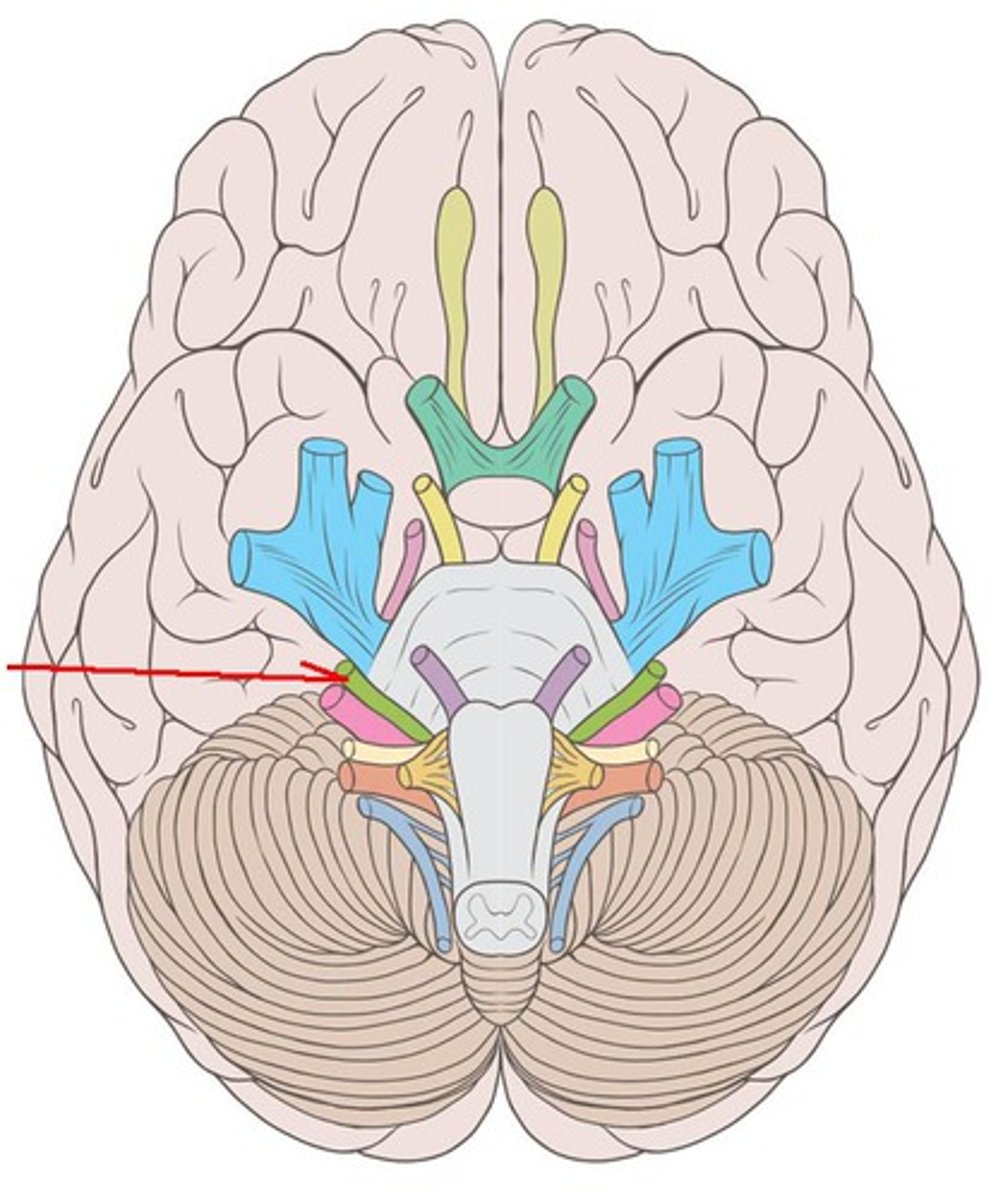
facial nerve
innervates the anterior 2/3 tongue taste and facial expression muscles, exit at internal acoustic meatus
CNVIII
vestibulocochlear nerve: hearing, balance, and orientation. sensory. Enter the brainstem lateral to (right next to) the facial nerves. Exit at internal acoustic meatus.
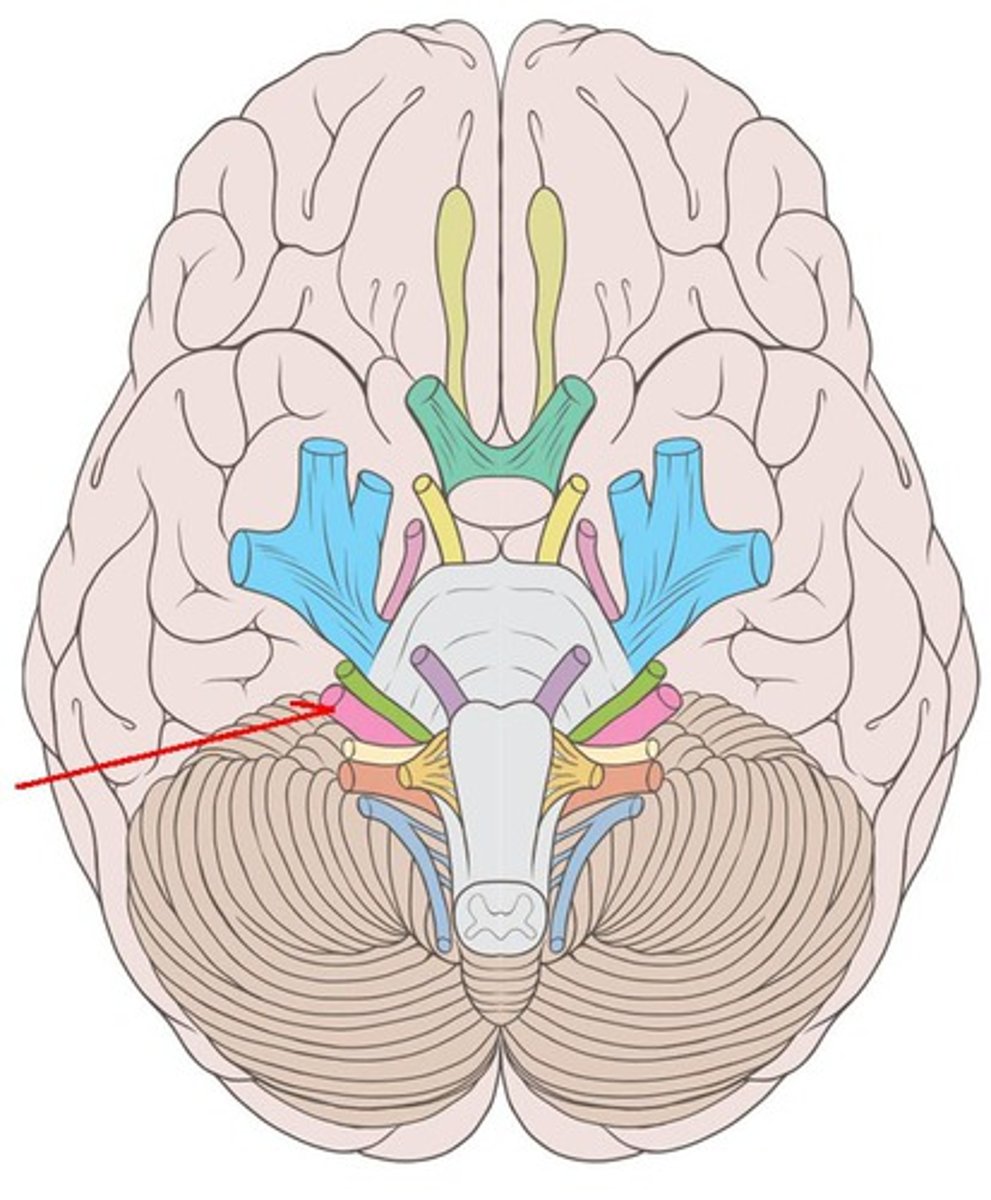
vestibulocochlear nerve
sensory innervation to the ears, exit at internal acoustic meatus
CNIX
Glossopharyngeal nerve: receive sensory information from the tonsils, pharynx, middle ear, and posterior tongue and innervates the stylopharyngeus muscle and parotid gland. Both. Emerge posterior to the olive on the lateral aspect of the medulla oblongata. Exit at jugular foramen.
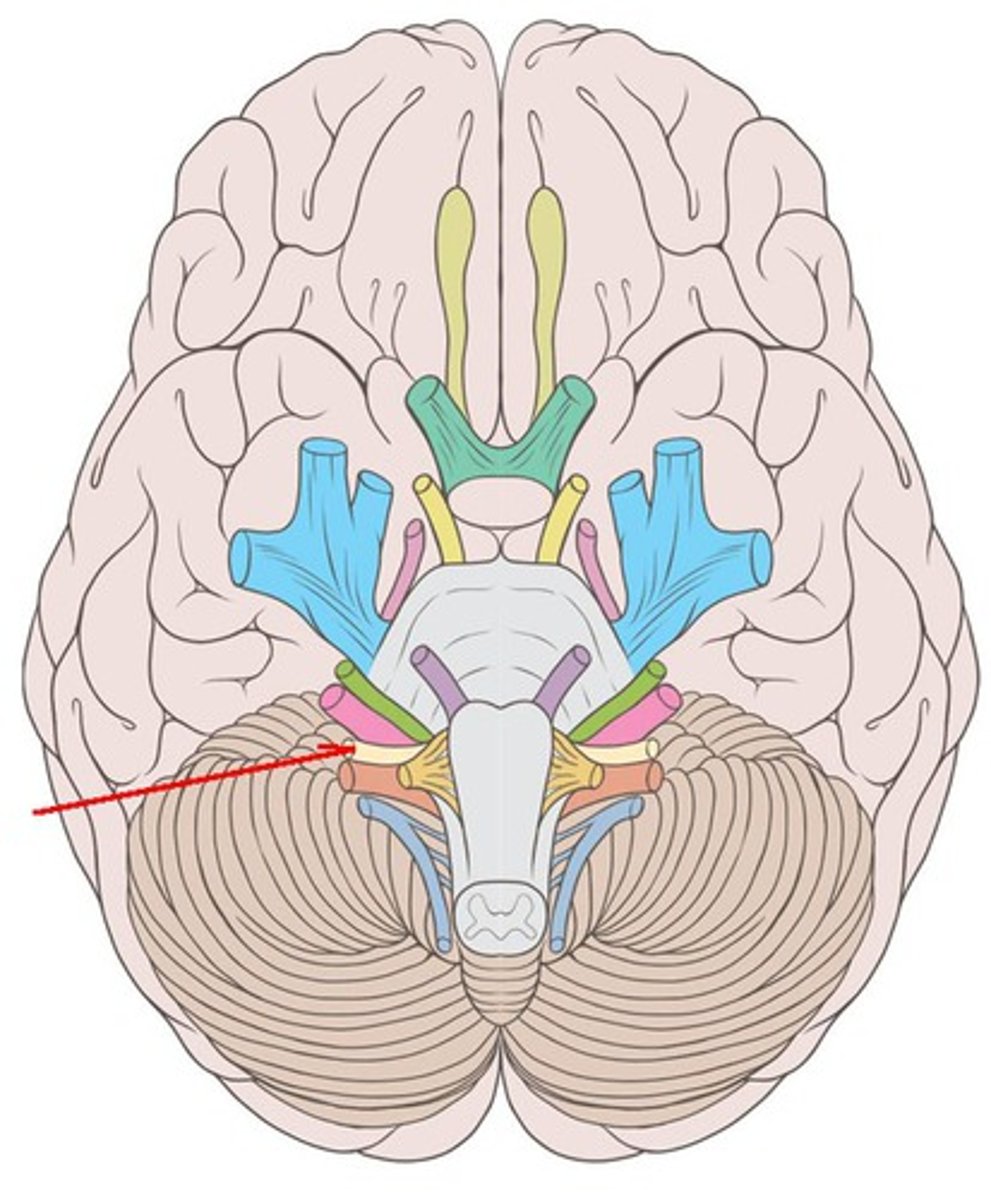
glossopharyngeal nerve
sensory: tonsils, pharynx, middle ear, posterior 1/3 of tongue taste
motor: stylopharyngeus
parotid gland innervation
exit: jugular foramen
CNX
Vagus nerve: provides parasympathetic innervation to organs of the thorax and part of the abdomen and the innervation of muscles of the larynx and pharynx. Both. Emerge caudal to the glossopharyngeal nerves in the same series of rootlets. Exit at jugular formaen.
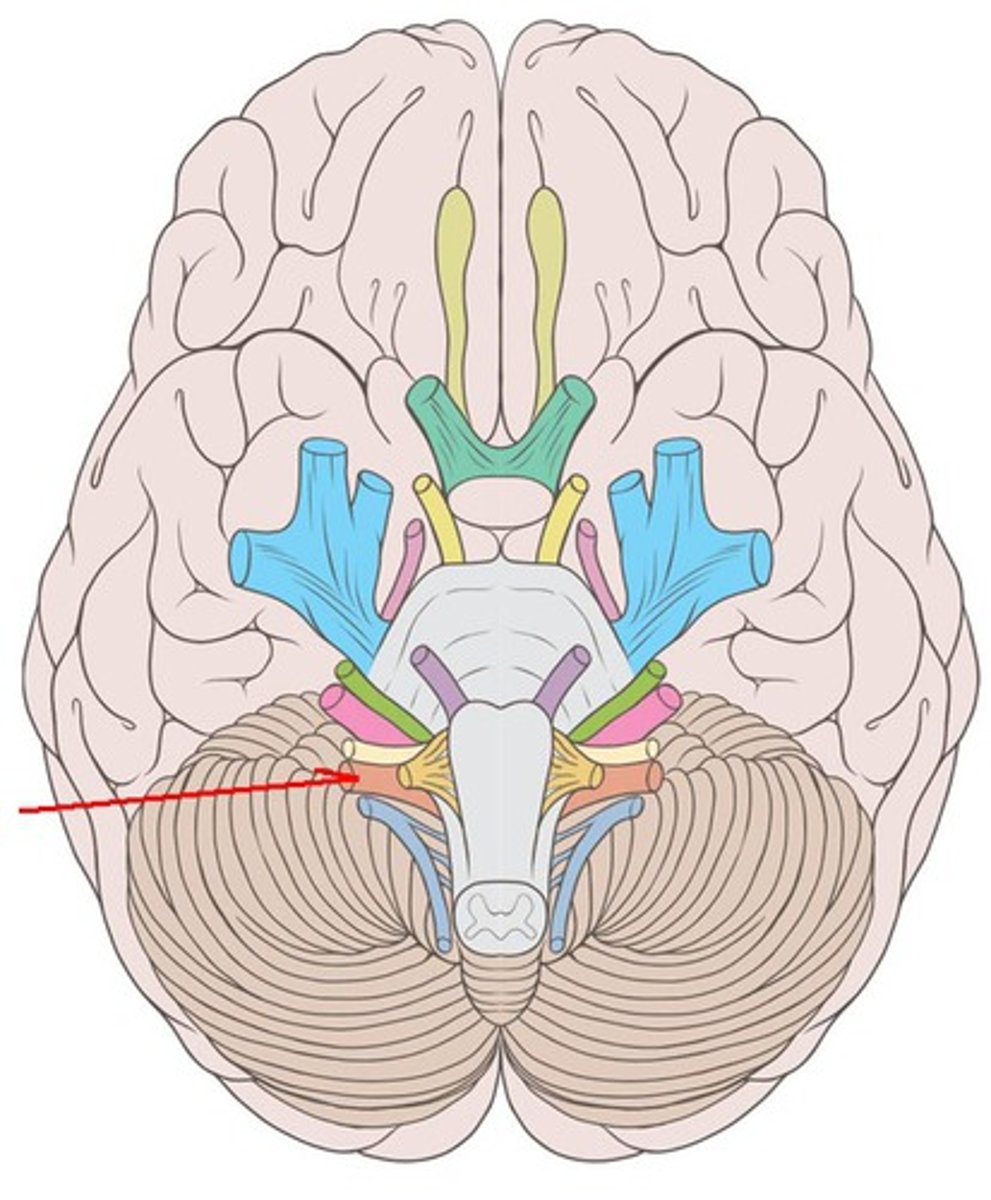
vagus nerve
innervates digestive organs, heart and other areas
innervates muscles of larynx and pharynx
exit: jugular foramen