CHEM 1130 FINAL EXAM DUTTA
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
149 Terms
When pKa > pH
the R group will form an ion
When pH > pKa
the structure is deprotonated (more basic)
When pH < pKa
the structure is protonated (more acidic)
When there are more negative charges
the pH will be higher
When there are more positive charges
the pH will be lower
When HCL is present
-it is there to increase solubility and to help eliminate the bad smell of the amine group
-It is now soluble in water and alcohol
-HCL makes it a salt.
Salts
soluble
Neutral compounds
not soluble
Primary protein
sequence of amino acids in a amino acid chain
Secondary protein
alpha helix, or beta plated sheet (H-bonds are present in the backbone)
Tertiary protein
Overall 3D structure of the protein (H-phobic, Disulfide, Salt bridge, H-bond)
Quaternary protein
More than 1 polypeptide chain
Hydrogen bonds
occur in the backbone. Create a fold in structure. Typically, _________ side chains are present on the surface of a folded protein, where they can form __________ with surrounding water molecules
Salt Bridges
Attractions between the positive and negative charges in side chains create salt bridges.
Hydrophobic
Mostly CH3 groups
Disulfide
Sulfide sulfide bonds
Hemiacetal
hydrogen OH-C-OR
Acetal
has 2 -OR groups (ethers) OR-C-OR
Denature
Heating, pH, adding acid/base (effects the secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure)
Inhibition
any process that stops or slows down the action of an enzyme
Feedback control
regulation of enzymes activity by the product later on in the pathway
Allosteric Control
interaction where binding at the one site affects the proteins ability to bind another molecule at a different site.
Covalent Modification
adding or removing a covalent portion or group to an enzyme
Genetic Control
makes enzymes only when needed
Irreversible inhibition
permanently bonds to active site, kills the enzyme
Reversible inhibition
inhibitor can leave the active site resuming enzyme activity
Competitive
Competes to bond at active site, is very similar to the substrate
Noncompetitive
binds to the allosteric site and closes off the active site
Agonist
binds to the receptor and activates
Antagonist
binds to the receptor and inhibits/blocks
Oxidoreductases
catalyze oxidation-reduction reactions
Transferases
catalyze the transfer of a group from one molecule to another molecule
Hydrolases
catalyze the hydrolysis of substrates (breaking of water)
A-B +H2O > A-OH + B-H
Isomerases
catalyze the isomerization of substrate. (typically one substrate and one product)
Lyases
catalyze the bonding together of 2 substrate molecules (involves conversion of ATP>ADP)
Neurotransmitters
travel through the nervous system
Hormones
travel through the endocrine system
Amino-Acid derivatives
require 2nd messenger system
Polypeptides
require 2nd messenger system
Steroids
do not require 2nd messenger system
Epinephrine
a hormone and a neurotransmitter (fight or flight) releases glucose to use right away
Acetylcholine
responsible for all skeletal muscle movements
Insulin
lowers our blood sugar - hydrogenesis
Glucagon
raises your blood sugar, break down glycogen stores
Type 1 diabetes
insulin dependent
Type 2 diabetes
insulin independent; insulin receptors aren't working properly
Step 1 of chemical response of a cell to epinephrine
Activation of G protein in a cell membrane
Step 2 of chemical response of a cell to epinephrine
Production of GTP from GDP
Step 3 of chemical response of a cell to epinephrine
Activation of adentiate cylase
Step 4 of chemical response of a cell to epinephrine
Conversion of ATP > cAMP
Step 5 of chemical response of a cell to epinephrine
Release of glucose to the bloodstream
Step 6 of chemical response of a cell to epinephrine
Conversion of cAMP > ATP
When determining if the cyclic structures are reducing sugars
you must have a hemiacetal
When a cyclic structure is formed
the chiral carbon is considered the anomeric carbon
B-linkage
more stable than A-linkage.
cellulose
Our body cannot digest ________ because we do not have the necessary enzymes to break the beta-linkages
Chiral carbons
all four groups attached are different
Racemate
an equal number of positive and negative chiral carbons
Phospholipid
Has a charged phosphate group attached
Glycolipid
Contain a backbone that have an NH. Have an attached carbohydrate. Can be identified by an anomeric ring
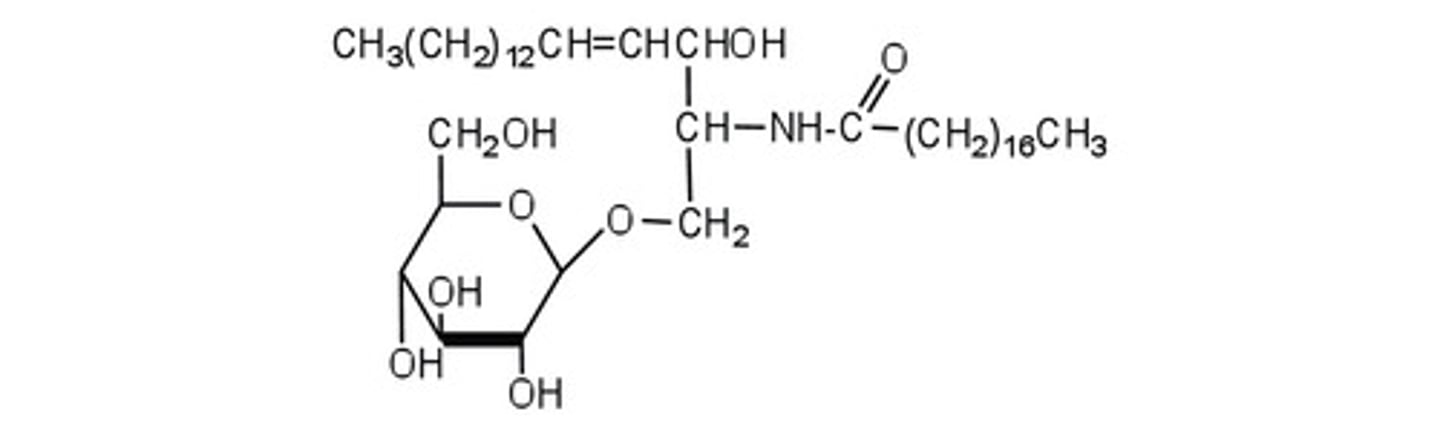
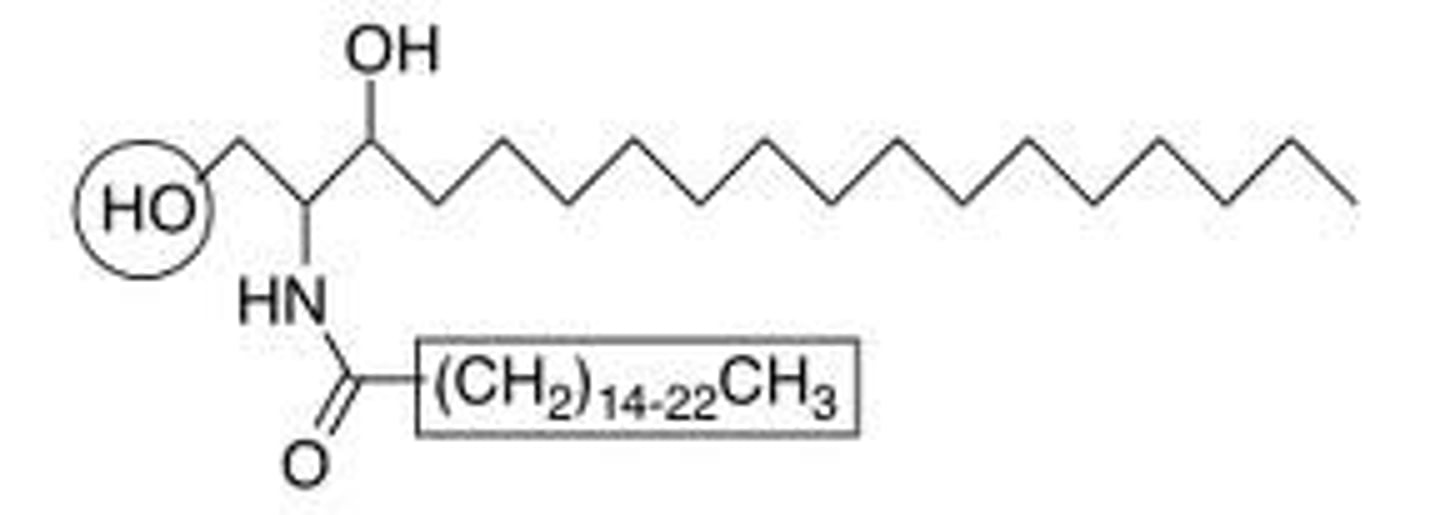
Sphingolipid
contain sphingosine which is a backbone containing NH. Also include a sphingomyelin which a phosphate group is attached as well as an additional H2N.
Carbohydrates
-digested in the mouth
-broken down by hydrolysis
Fatty acids
-digested in the small intestines
-broken down by the B-Oxidation pathway
Lipids
-digested in the small intestines
Citric Acid Cycle
- to reduce coenzymes that go to the electron transport chain and produce CO2
- Requires oxygen
- Acetyl CoA is oxidized to Co2 which is eventually made into water in the ETC
Electron Transport Chain
carries NADH and FADH2 and uses the energy from those to pump H+ ions
B-Oxidation pathway
Oxidize fatty acids. Cuts fatty acids into 2-carbon molecules (Acetyl-CoA)
Cori Cycle
Converts lactate back to glucose
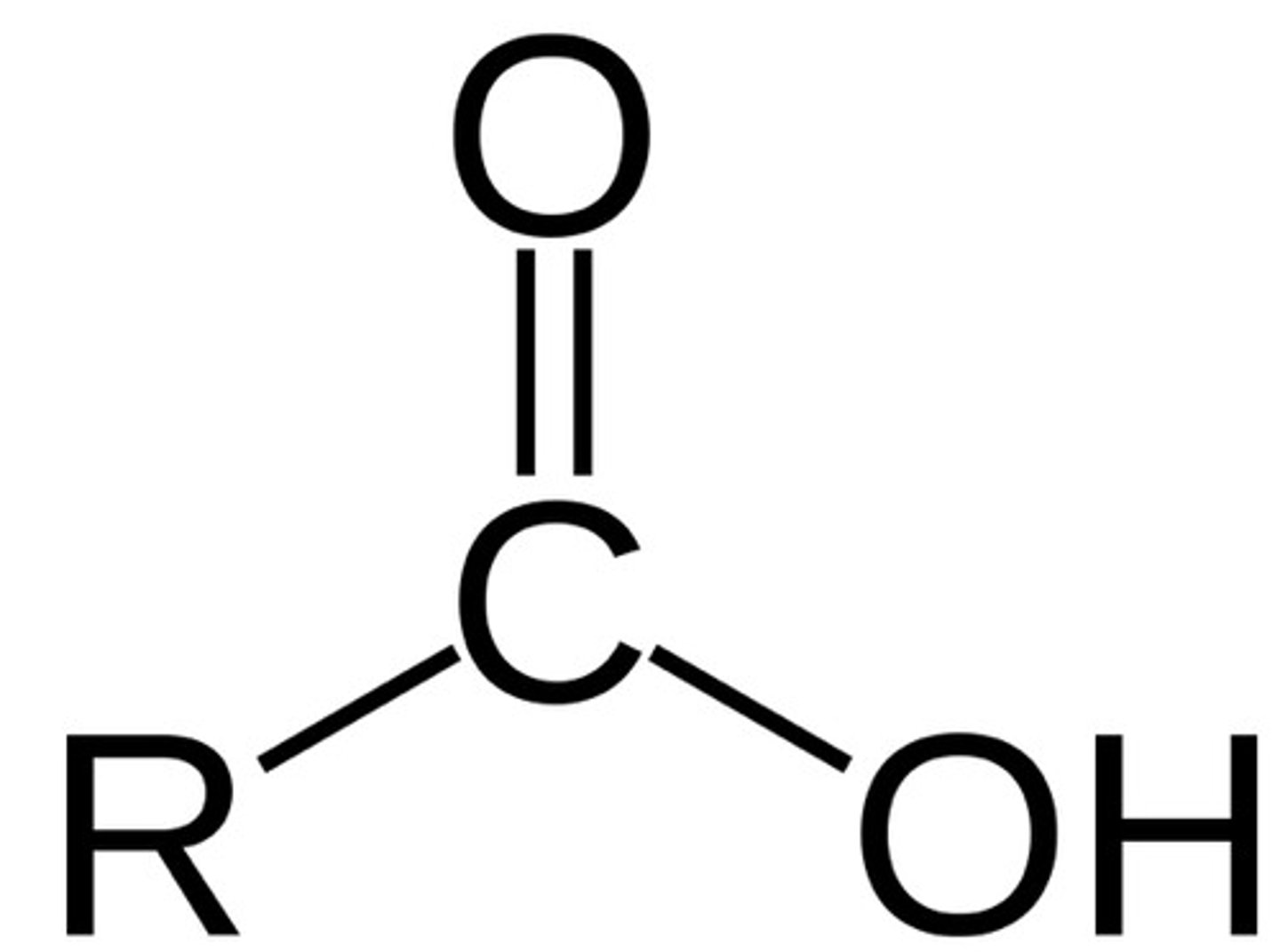
Carboxylic Acid
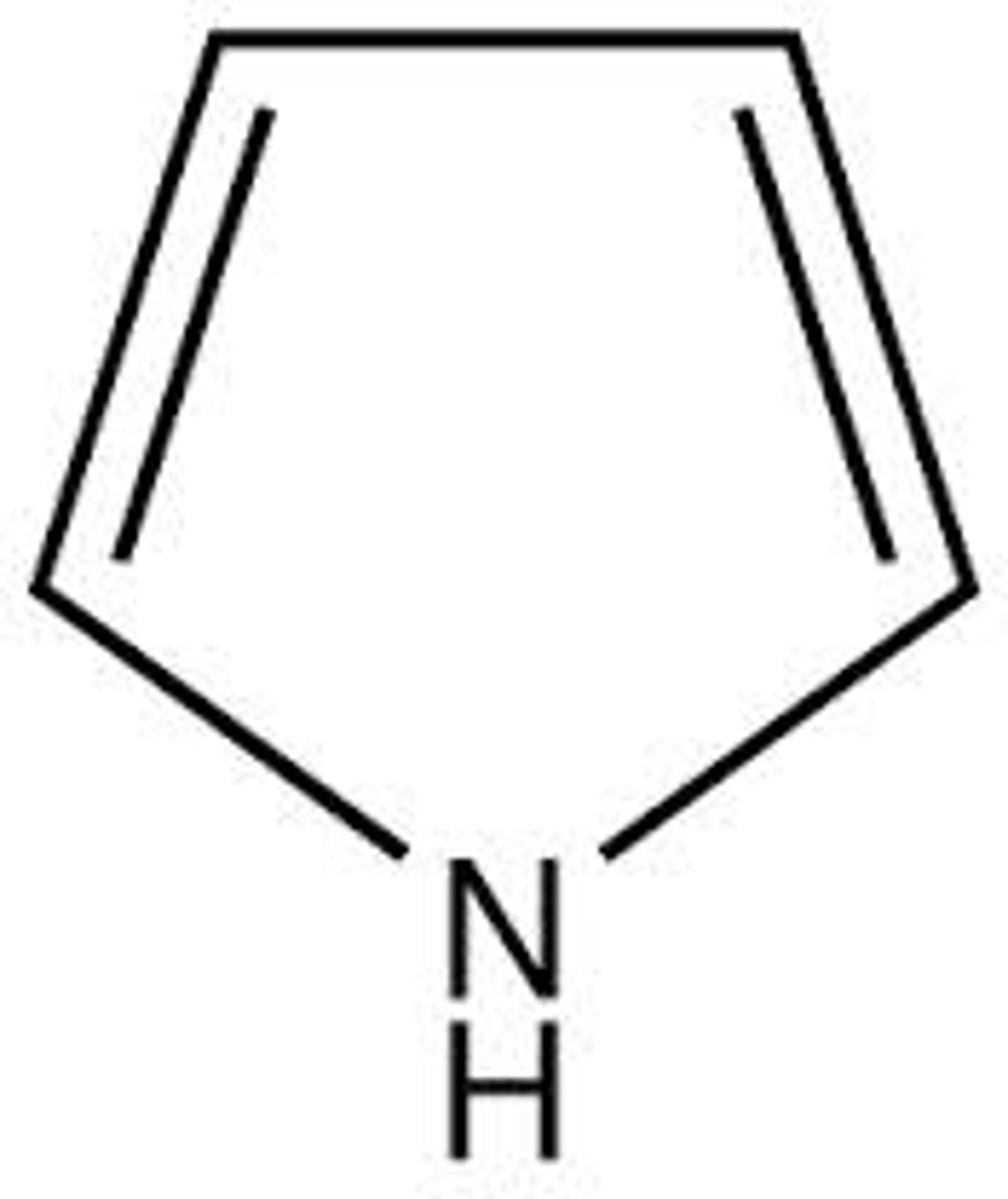
Heterocyclic
Something other than carbon in the ACTUAL ring
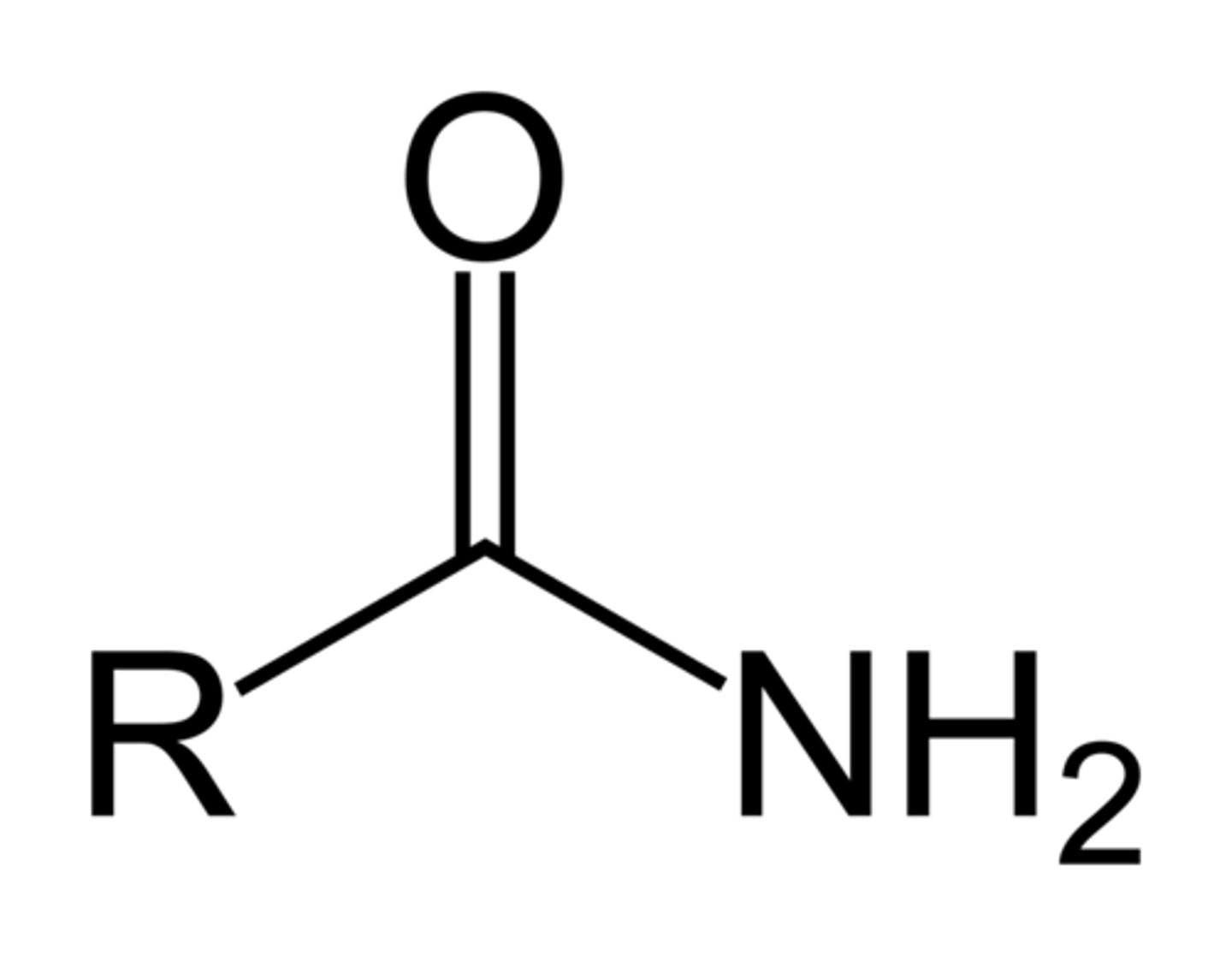
Amide
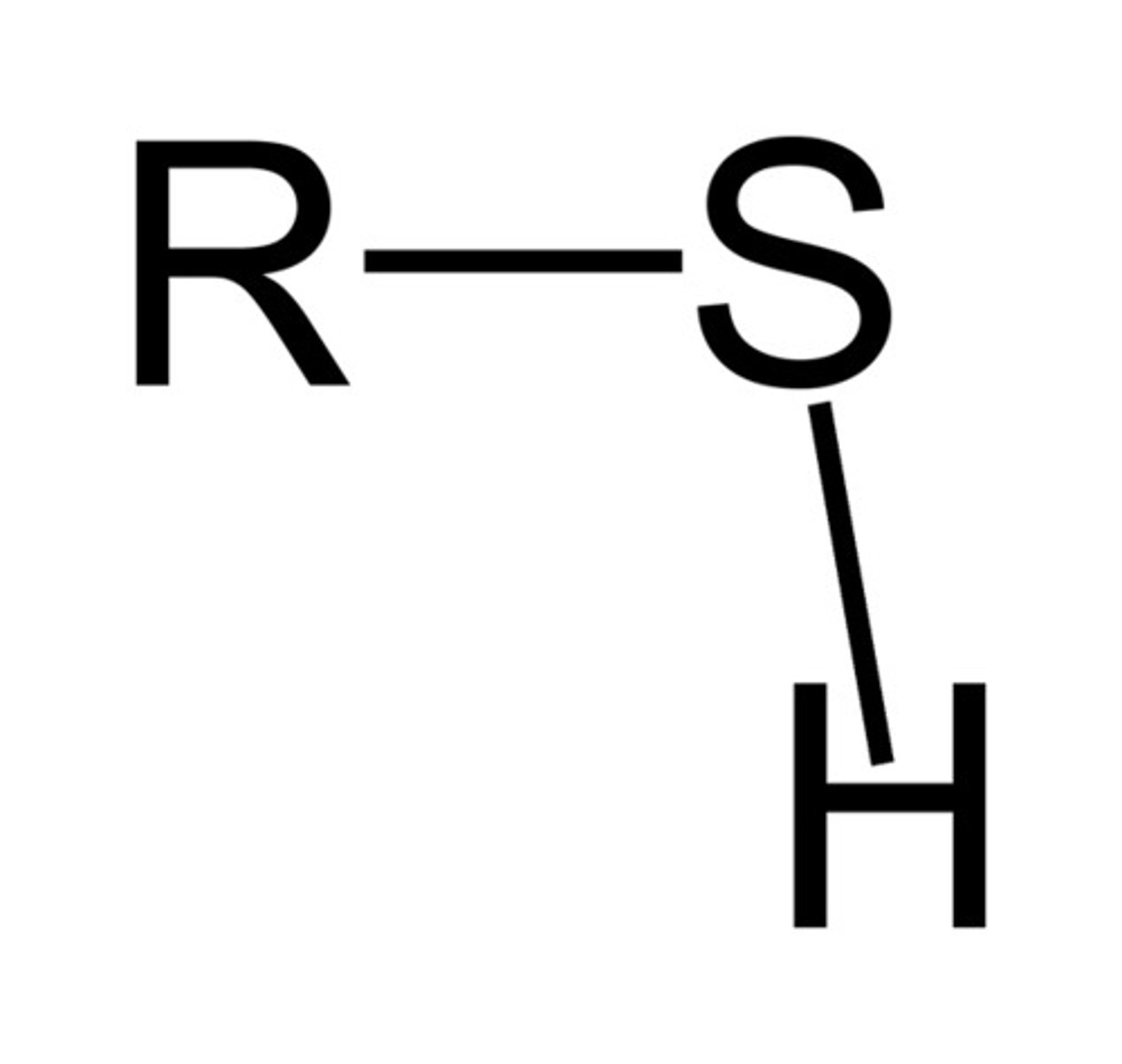
Thiols
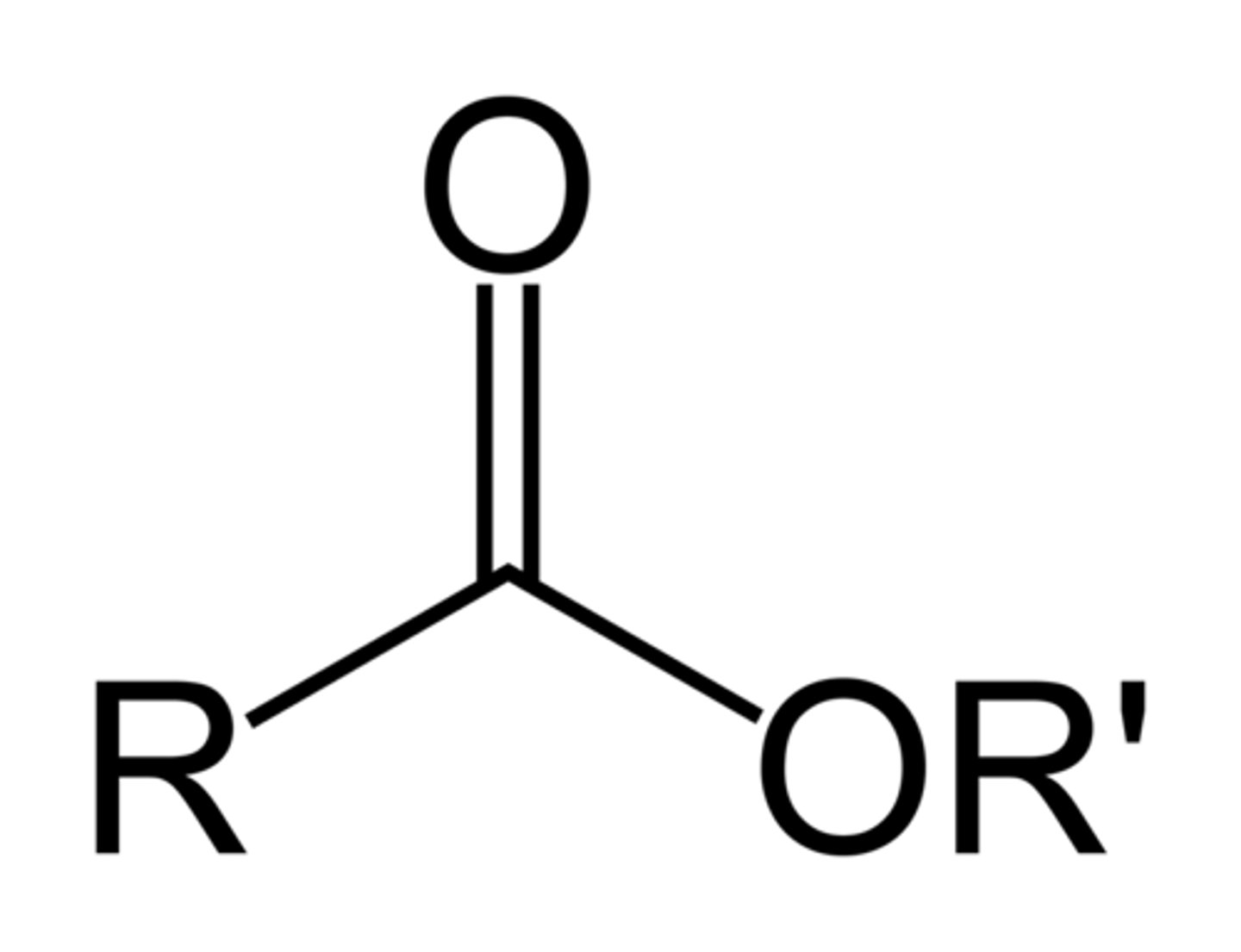
Ester
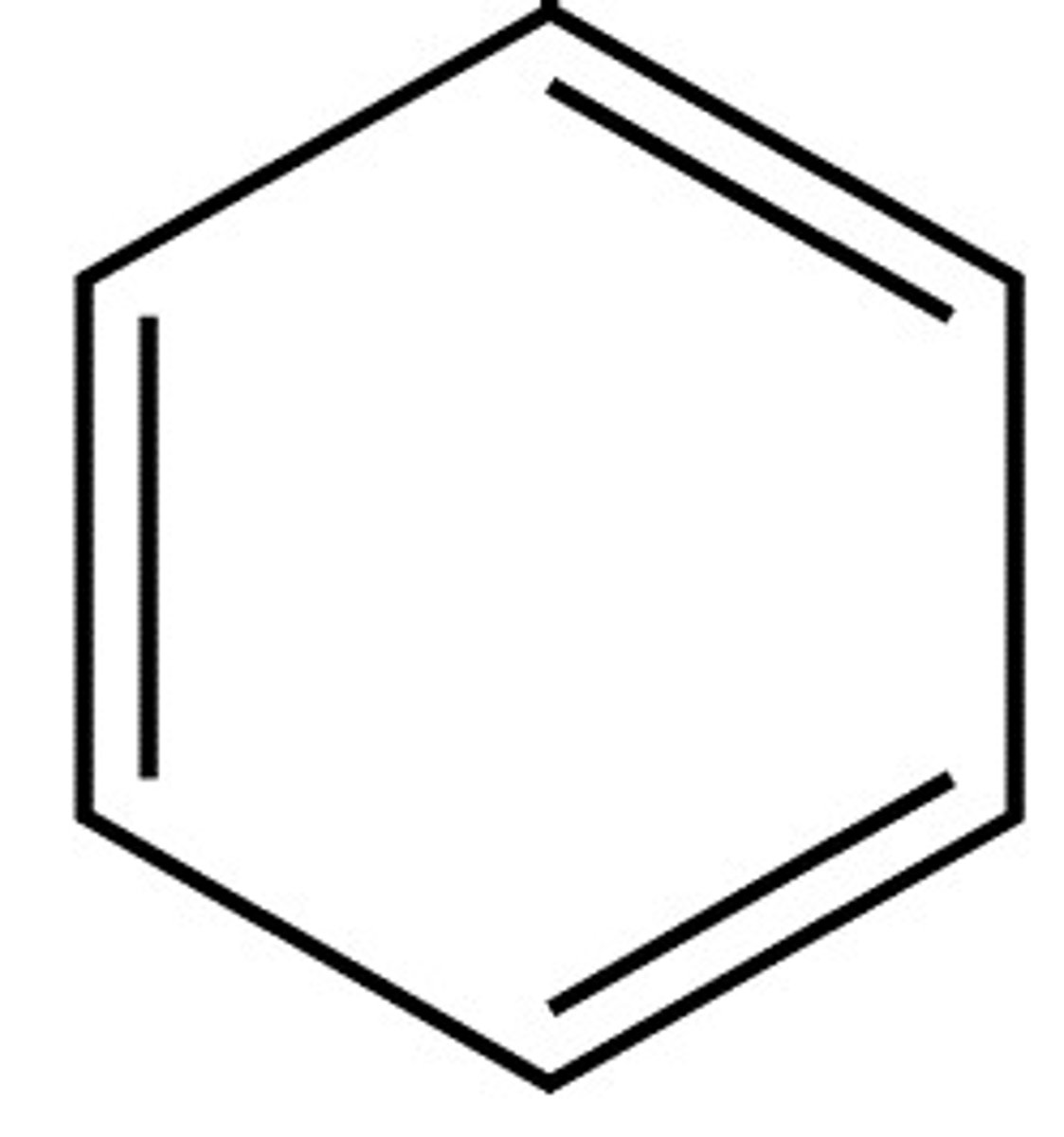
Aromatic
Hemiacetals
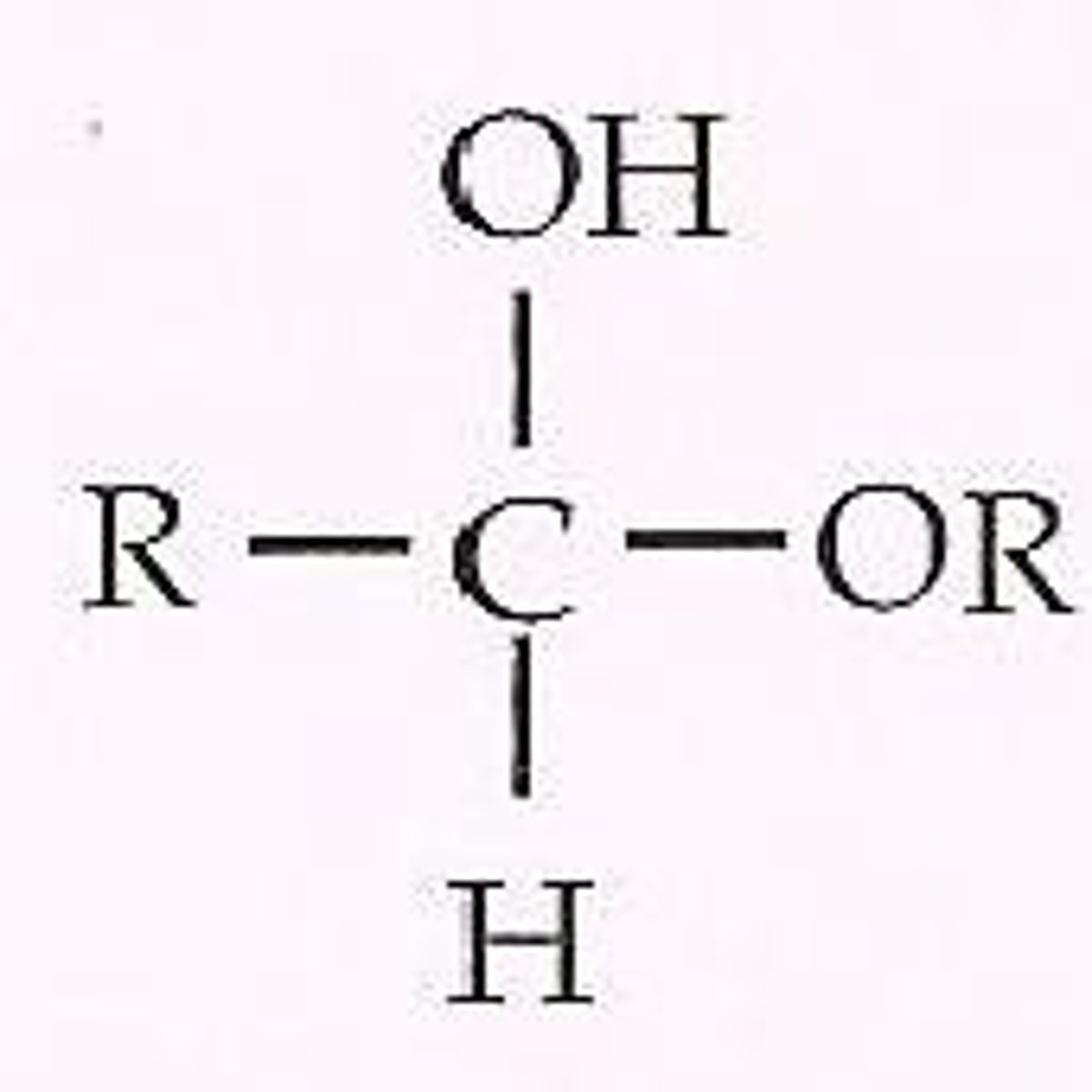
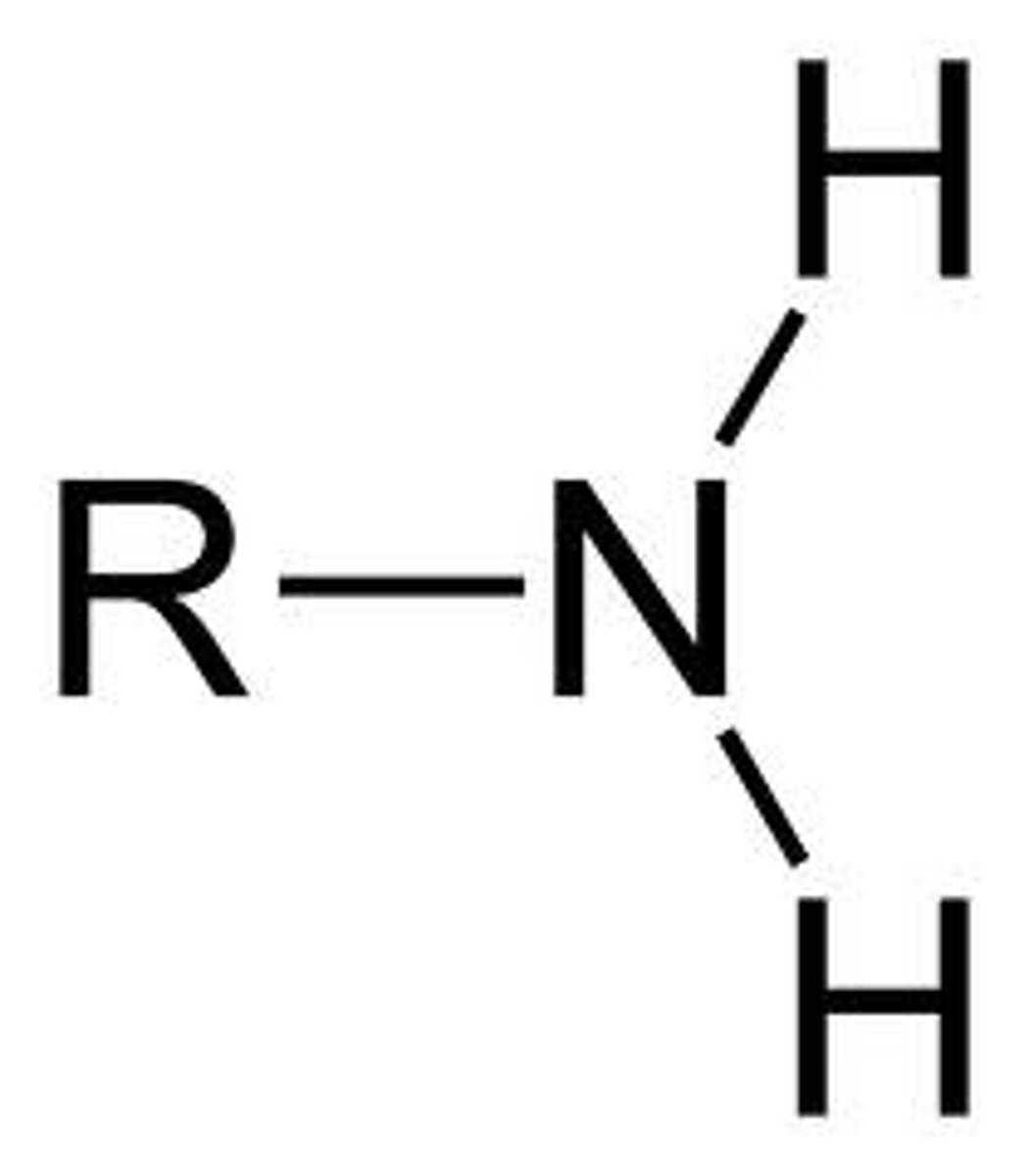
Amine
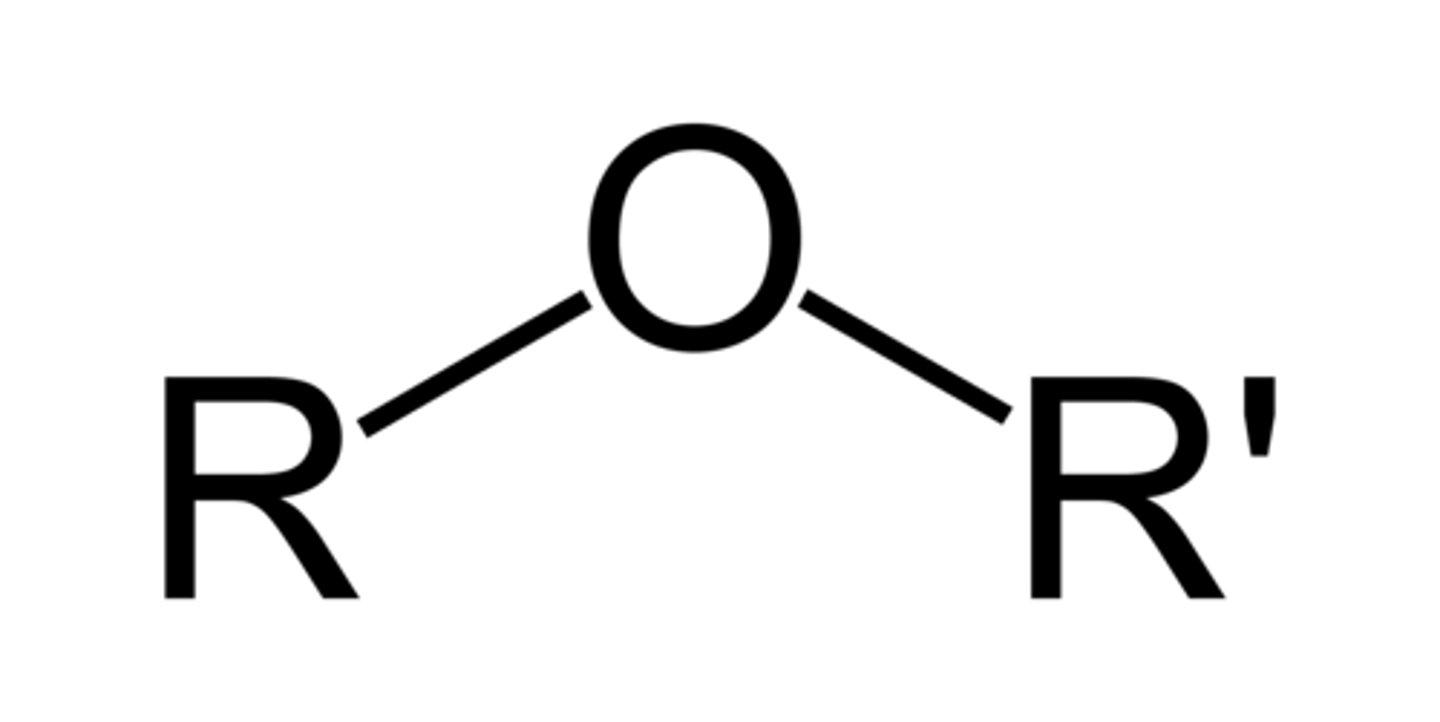
Ether
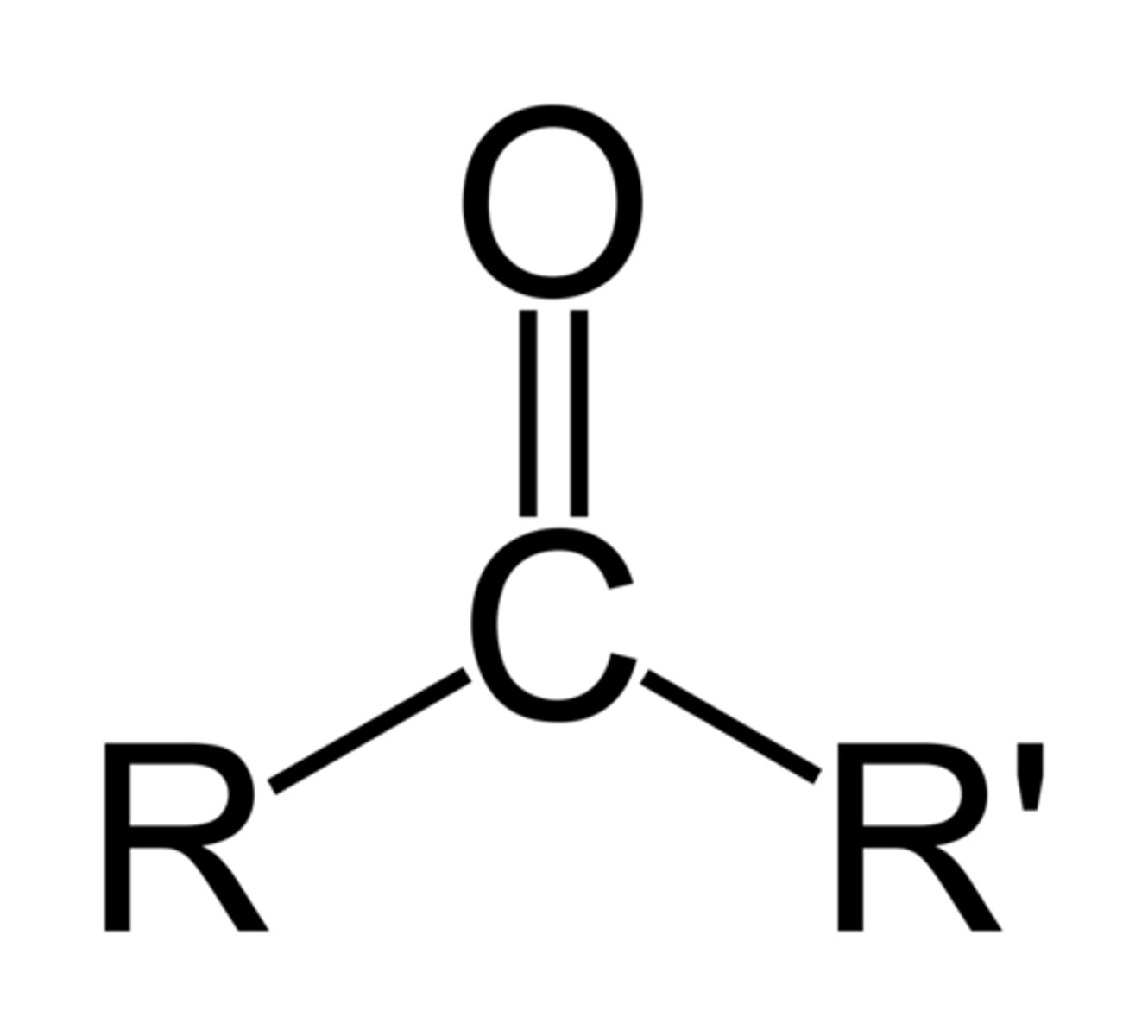
Ketone
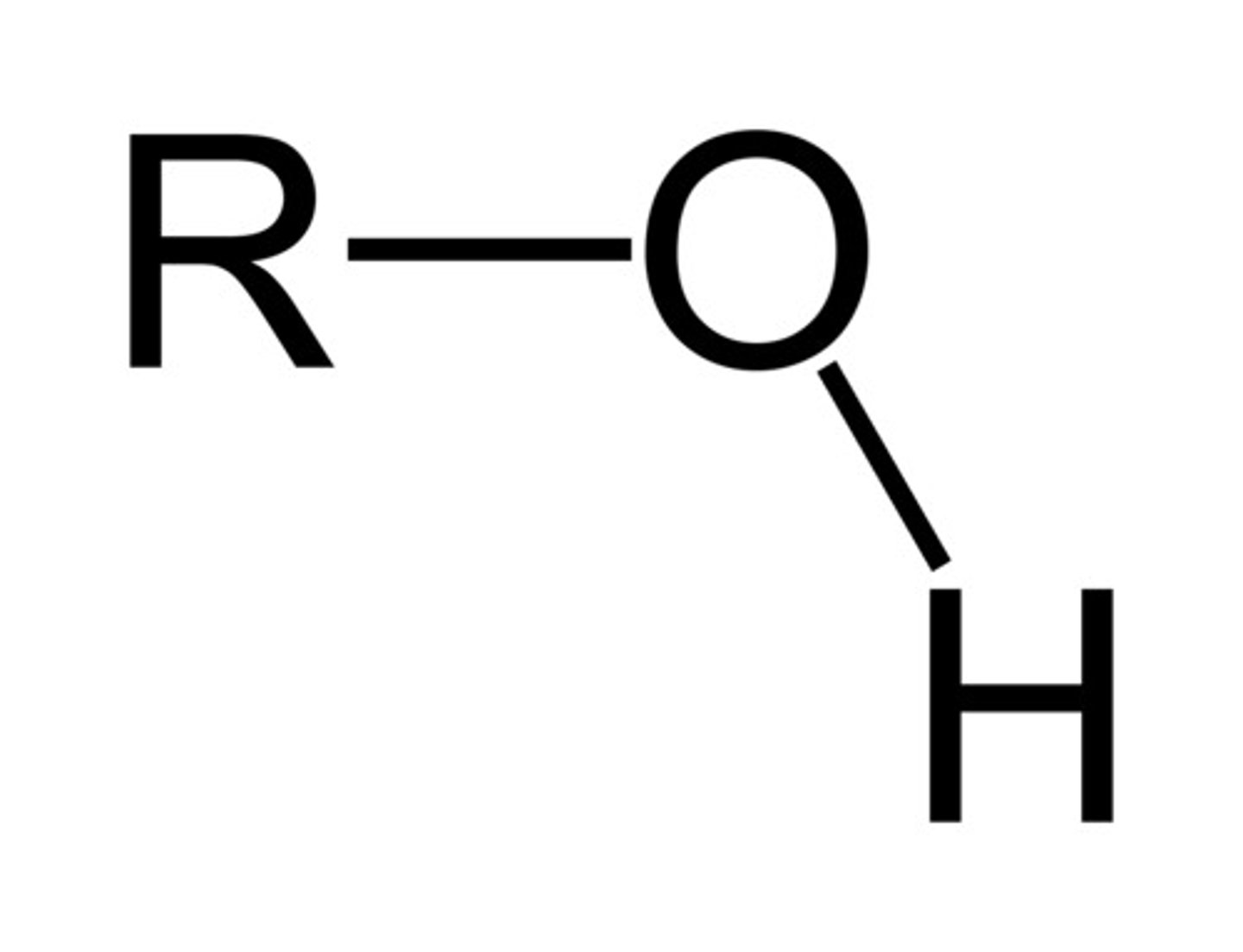
Alcohol
Disulfides

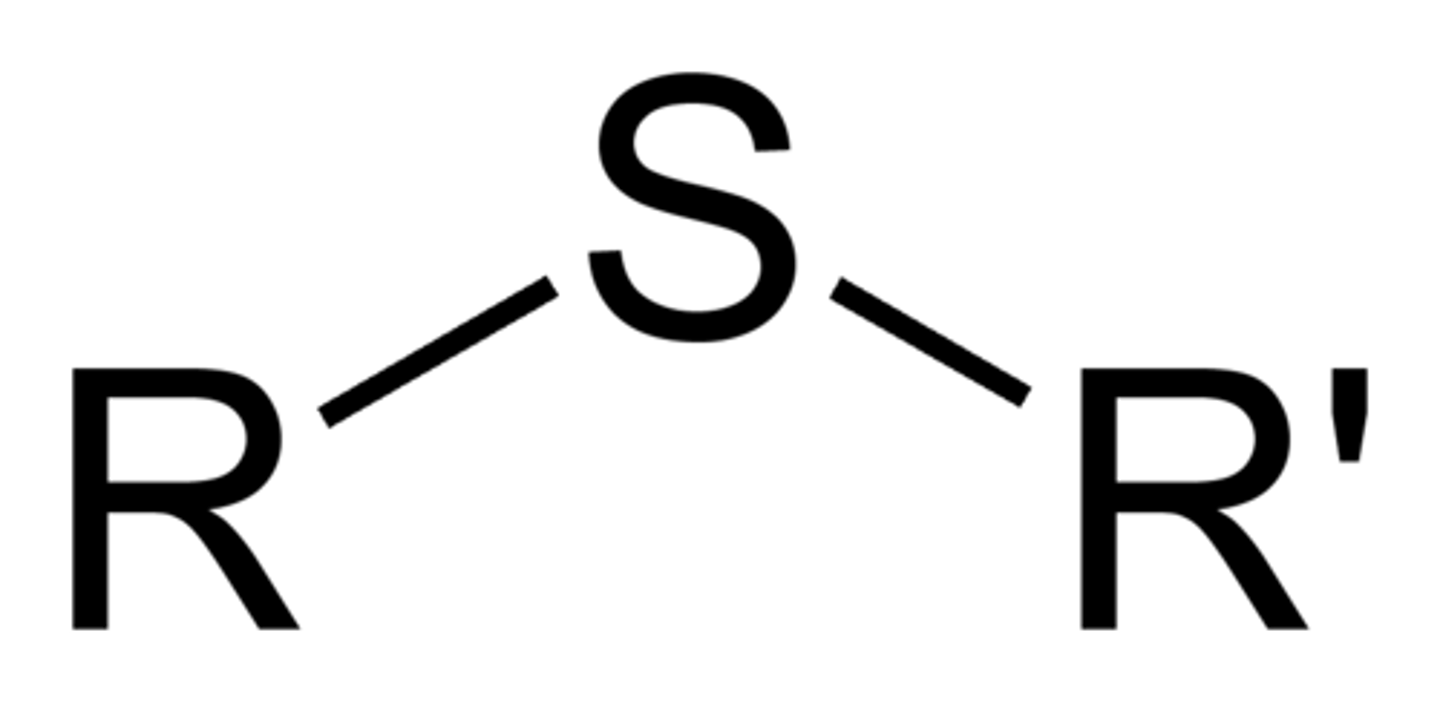
Sulfides
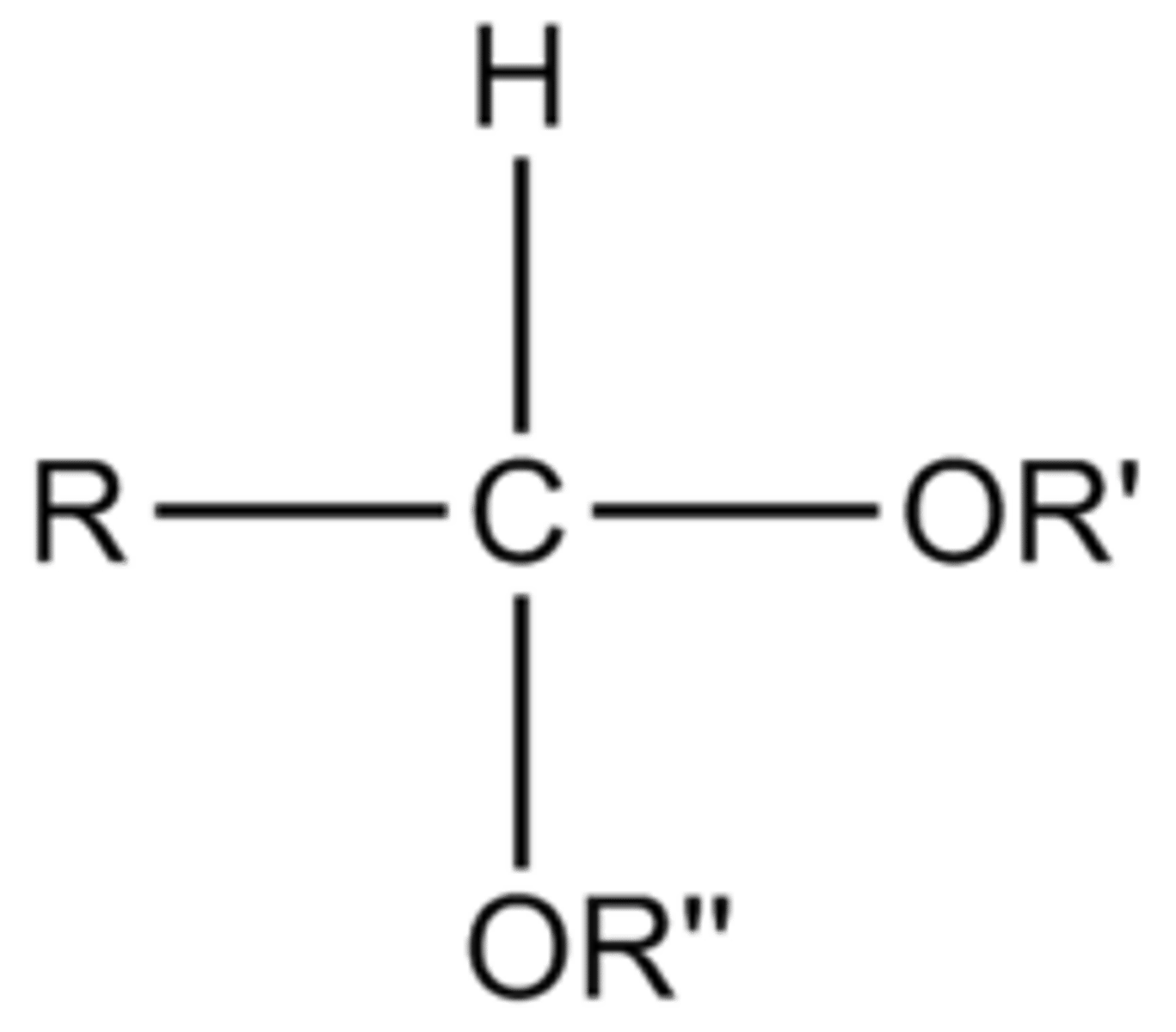
Acetals
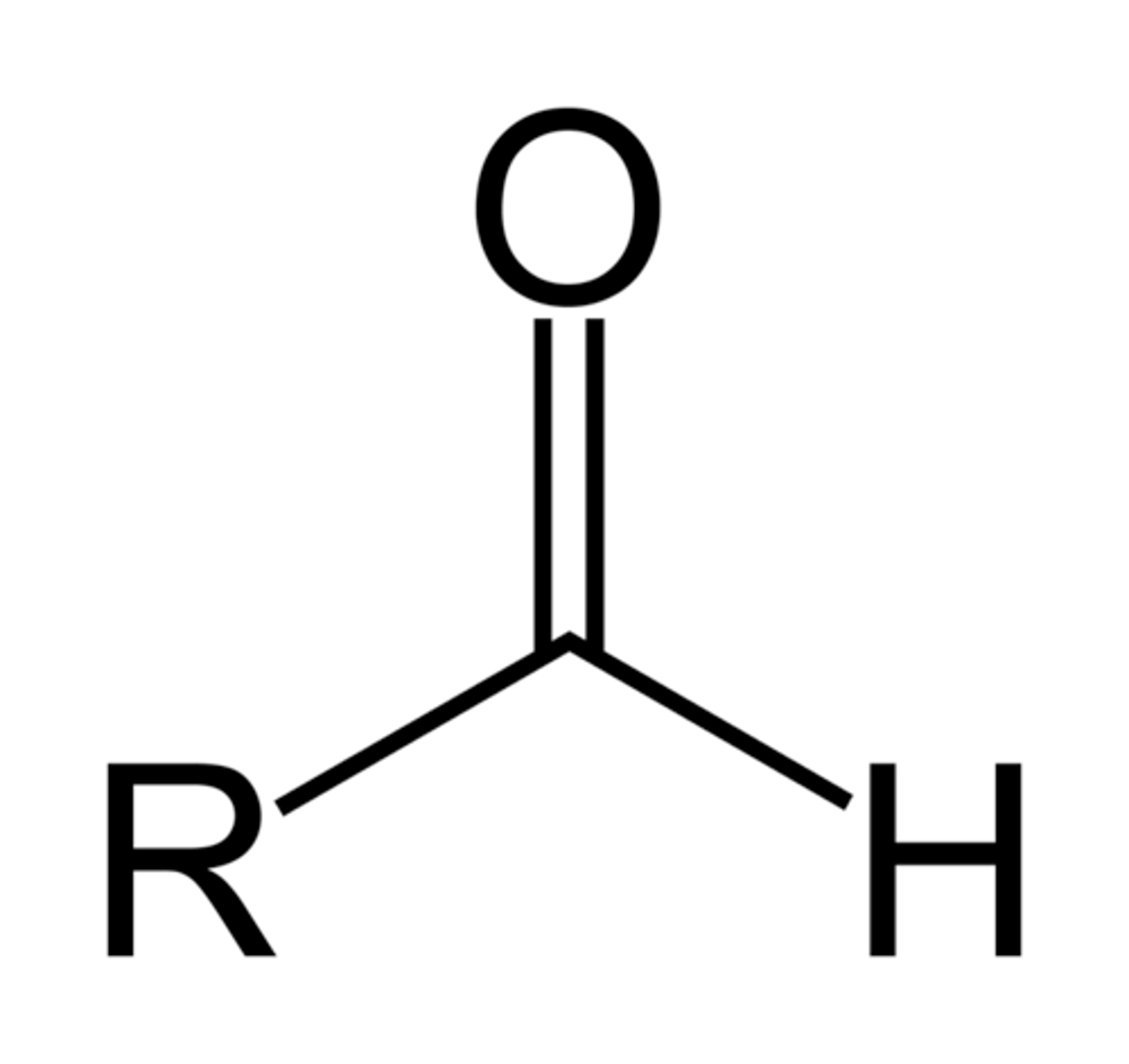
Aldehyde
Phosphates
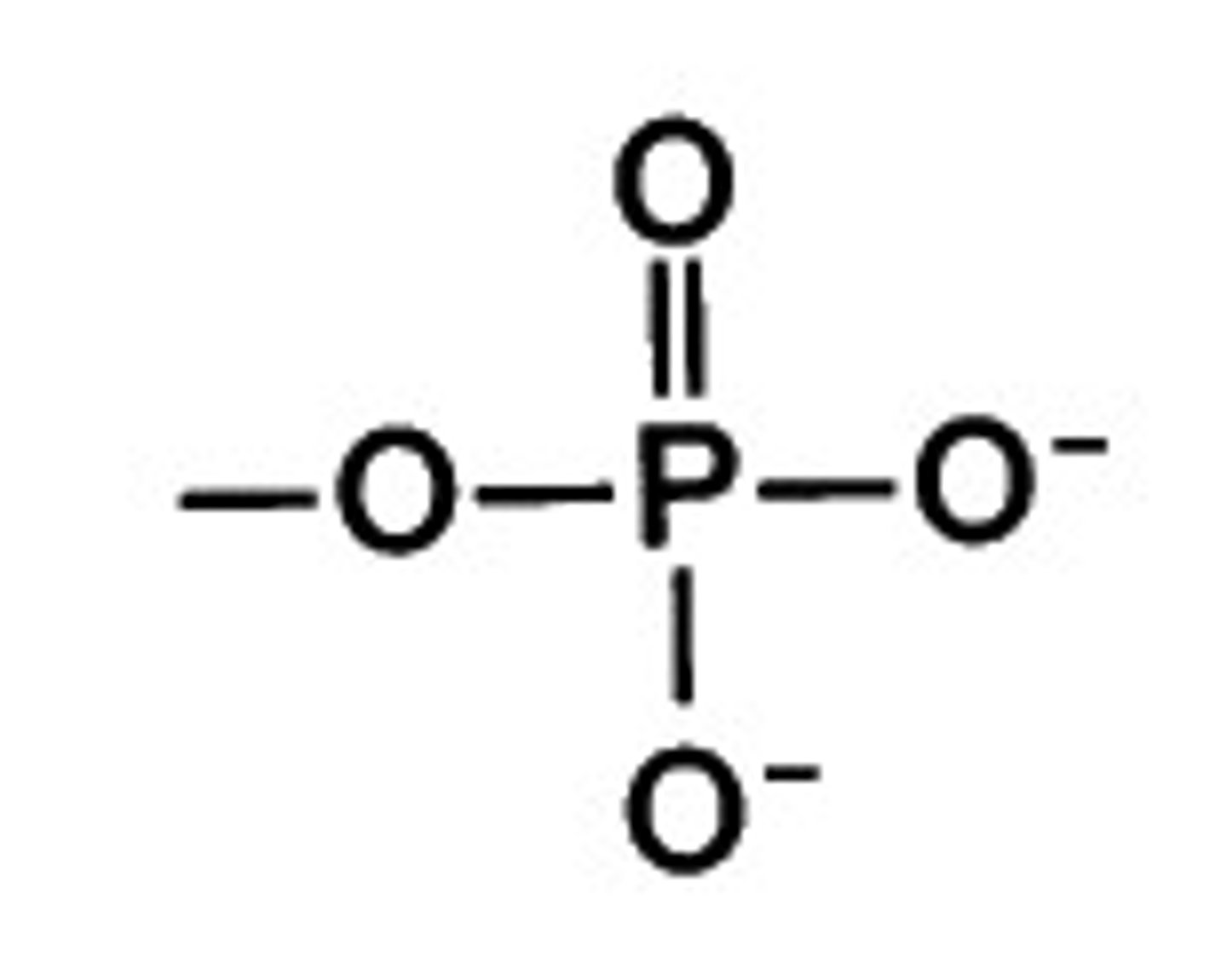
glycolysis
-breaks down carbohydrates and sugars through a series of reactions to either pyruvic acid or lactic acid and release energy for the body in the form of ATP
-Anaerobic
-occurs in mitochondria
Gluconeogenesis
the formation of glucose from noncarbohydrate sources, such as amino acids
Chemical process that converts lactate and pyruvate back into glucose.
Within the liver
Glycogenesis
formation of glycogen from glucose-- by insulin or anabolic conditions
Glycogenolysis
breakdown of glycogen to glucose
Glygoneogensis
glucose form non-carbohydrates
Outside and inside layer cell membrane
Hydrophillic
Middle layer of cell membrane
Hydrophobic
mitochondrion
Cell organelle that converts the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work
ADP
Adenosine Diphosphate is a chemical that plays an important role in energy transfer
Metabolism
All of the chemical reactions that occur within an organism
Catabolism
Metabolic pathways that break down molecules, releasing energy.
Anabolism
Metabolic pathways that construct molecules, requiring energy.
Oxidation
Loss of electrons
Reduction
Gain of electrons
stage 1 of
metabolism
Digestion - enzymes in the saliva, stomach, and small intestine