T4 - RBC Disorders (RBC Variations)
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Reticulocyte Count
ANEMIA EVALUATION:
Indicates bone marrow response (effective or ineffective)
Peripheral Blood Smear
ANEMIA EVALUATION:
classify anemia by RBC morphology (micro/macrocytic, normo/hyper/hypochromic)
MEAN CELL VOLUME
LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS FOR ANEMIA:
Most important
Key in the morphologic classifications of anemia
Red Cell Distribution Width (RDW)
LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS FOR ANEMIA:
Index of vartiations of cell volume in a red blood cell population
The coefficient of variations of RBC volume expressed in percentage
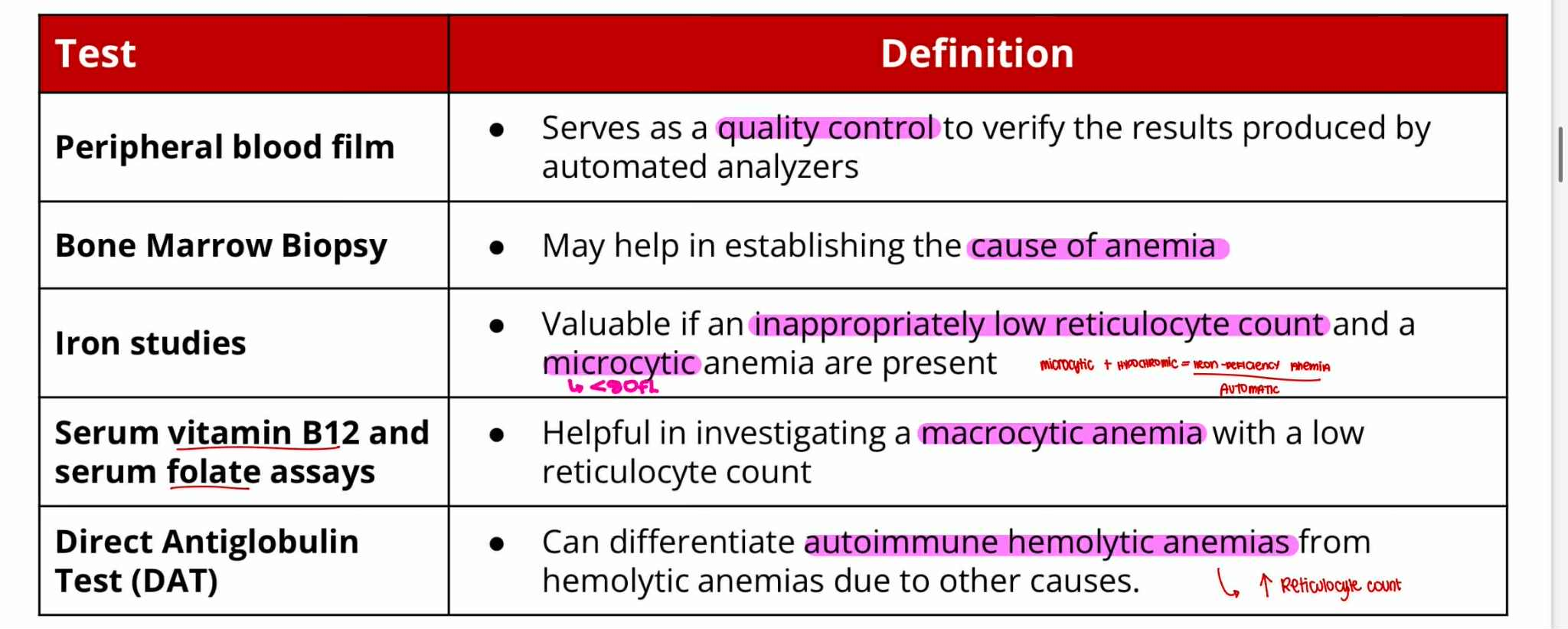
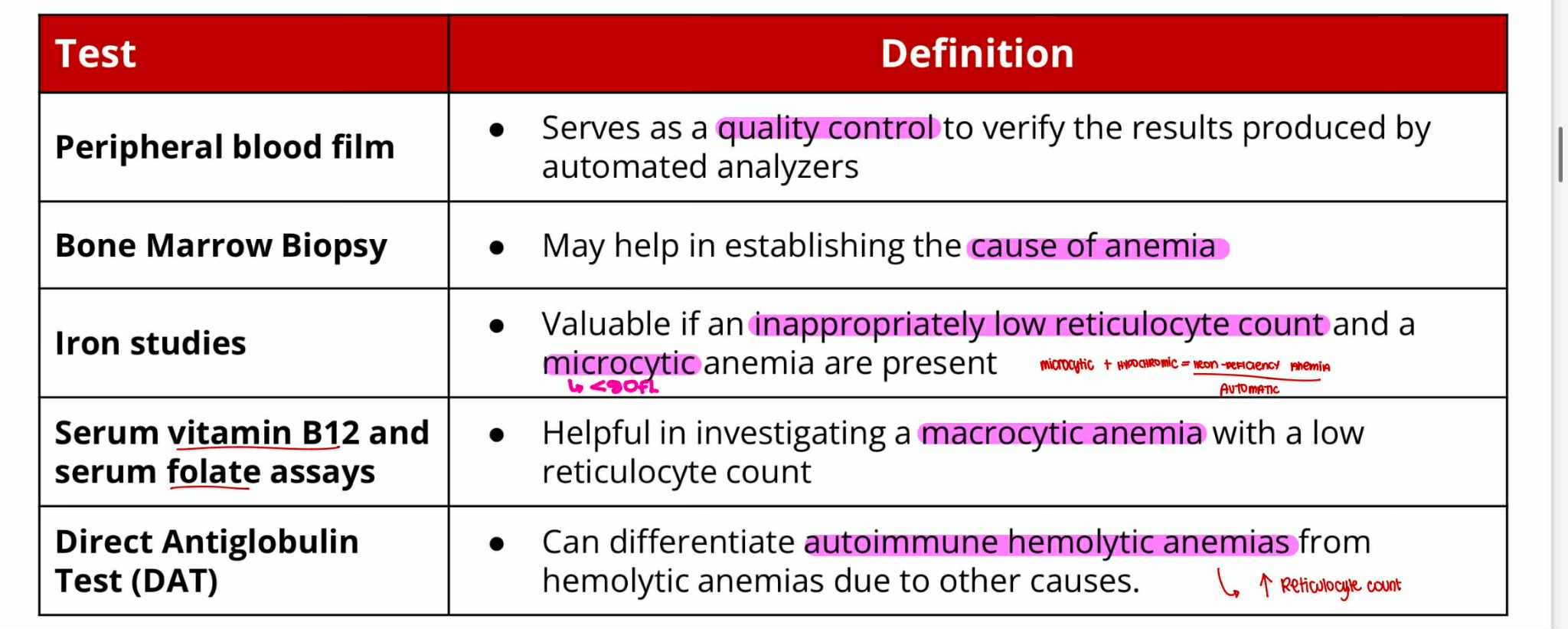
Peripheral Blood Film —quality control
Bone Marrow Biopsy —cause of anemia
Iron Studies —microcytic
Serum Vit B12 and Folate assays —macrocytic
Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT) —autoimmune hemolytic
LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS FOR ANEMIA:
Serves as quality control to verify the result produced by automated analyzers
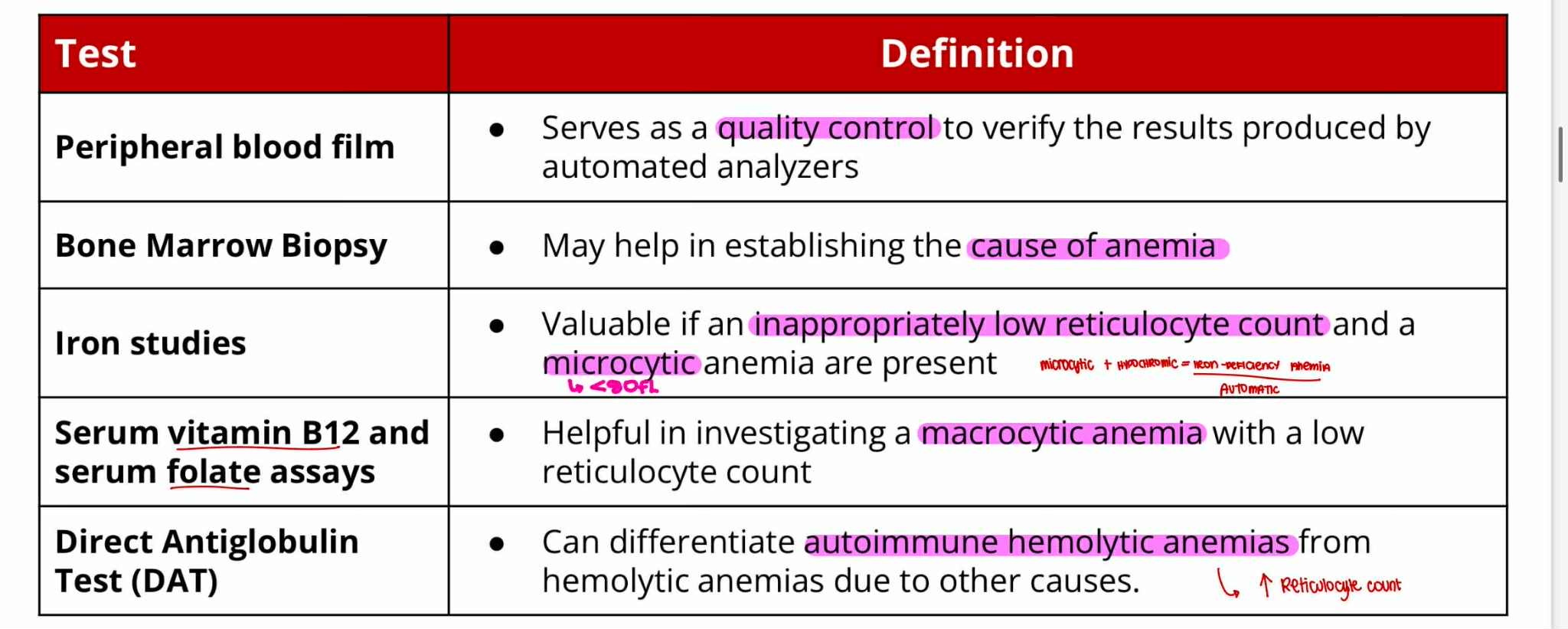
Peripheral Blood Film —quality control
Bone Marrow Biopsy —cause of anemia
Iron Studies —microcytic
Serum Vit B12 and Folate assays —macrocytic
Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT) —autoimmune hemolytic
LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS FOR ANEMIA:
May help in establishing the cause of anemia
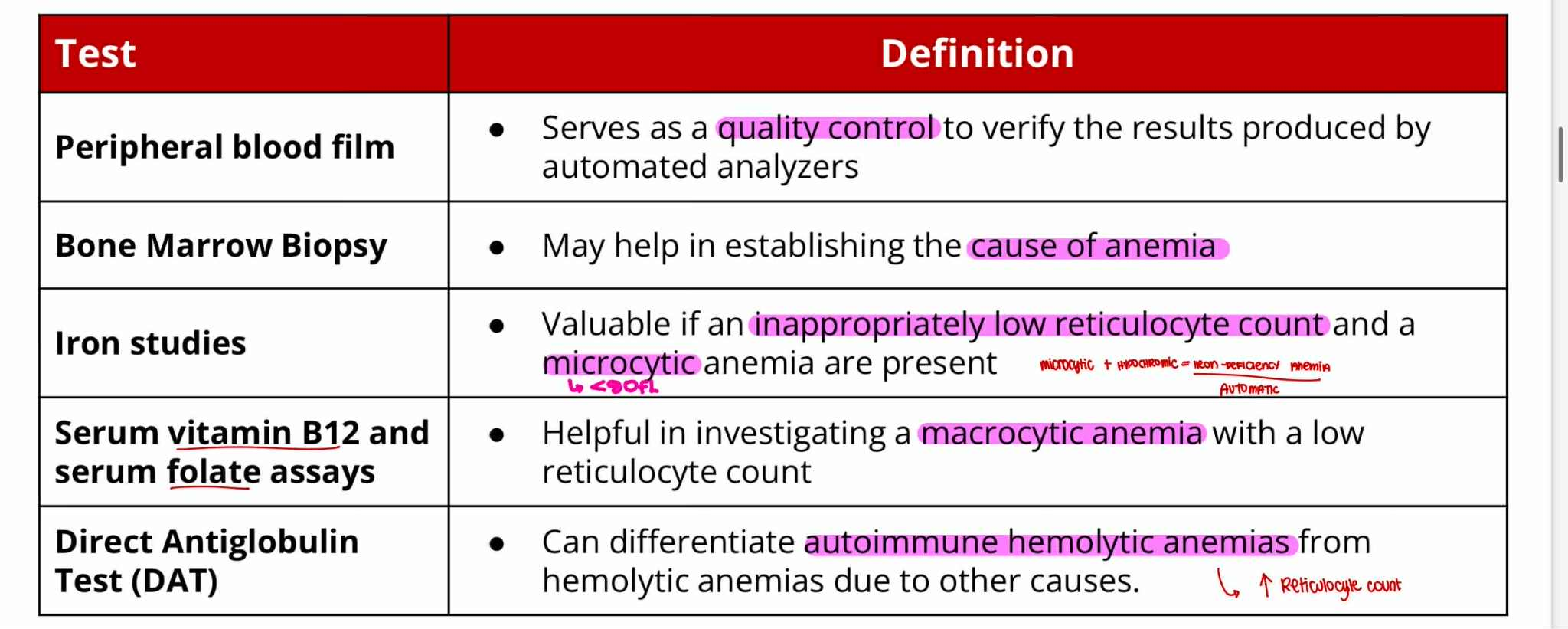
Peripheral Blood Film —quality control
Bone Marrow Biopsy —cause of anemia
Iron Studies —microcytic
Serum Vit B12 and Folate assays —macrocytic
Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT) —autoimmune hemolytic
LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS FOR ANEMIA:
Valuable if an inappropriately low reticulocyte count and a microcytic anemia are present
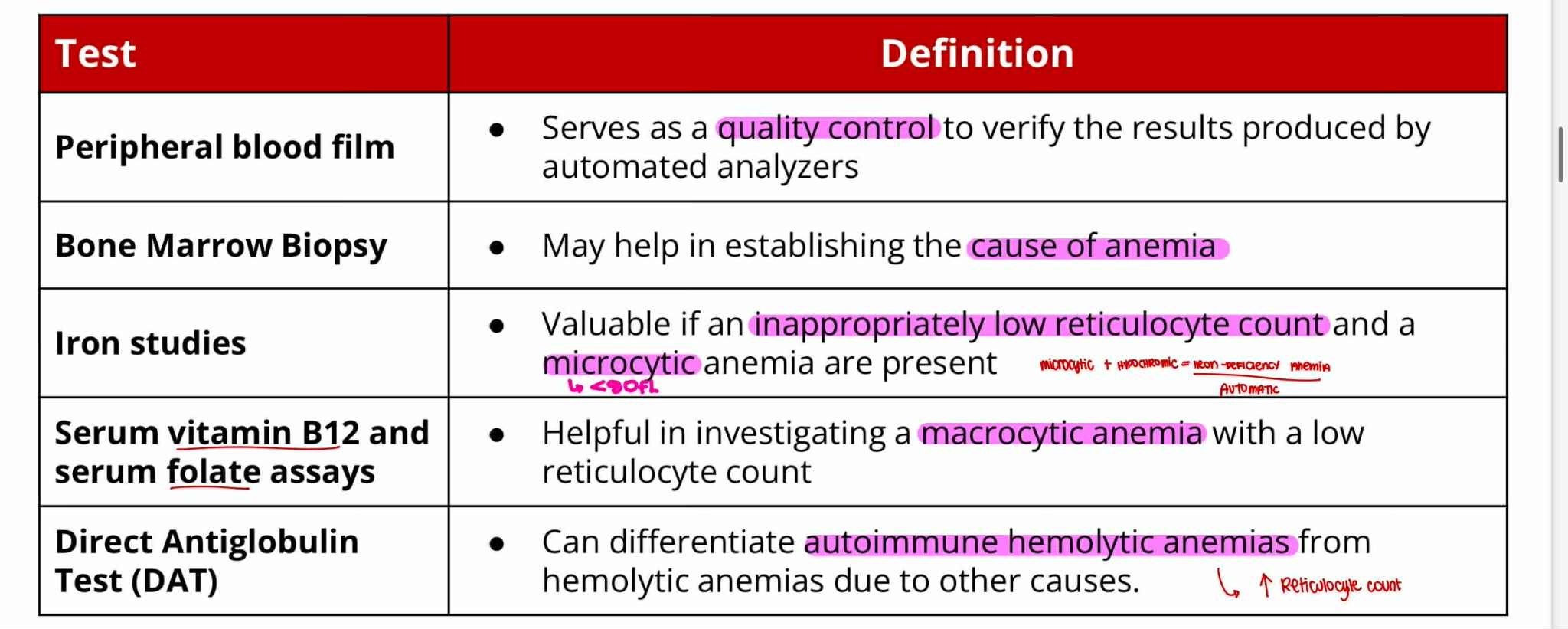
Peripheral Blood Film —quality control
Bone Marrow Biopsy —cause of anemia
Iron Studies —microcytic
Serum Vit B12 and Folate assays —macrocytic
Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT) —autoimmune hemolytic
LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS FOR ANEMIA:
Helpful in investigating a macrocytic anemia with a low reticulocyte count
Peripheral Blood Film —quality control
Bone Marrow Biopsy —cause of anemia
Iron Studies —microcytic
Serum Vit B12 and Folate assays —macrocytic
Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT) —autoimmune hemolytic
LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS FOR ANEMIA:
Can differentiate autoimmune hemolytic anemias from hemolytic anemias due to other causes
Ineffective Erythropoiesis —defective
Insufficient Erythropoiesis —↓ precursor
Effective Erythropoiesis —adequate, ↑Reticulocyte
MECHANISM OF ANEMIA:
Production of defective precursor erythroid cells
# of precursor cells are normal
Defective in function
Ineffective Erythropoiesis —defective
Insufficient Erythropoiesis —↓ precursor
Effective Erythropoiesis —adequate, ↑Reticulocyte
MECHANISM OF ANEMIA:
Decrease number of erythroid precursor cells
Ineffective Erythropoiesis —defective
Insufficient Erythropoiesis —↓ precursor
Effective Erythropoiesis —adequate, ↑Reticulocyte
MECHANISM OF ANEMIA:
Adequate bone marrow response
Reticulocyte count is eleveated due to increased RBC production
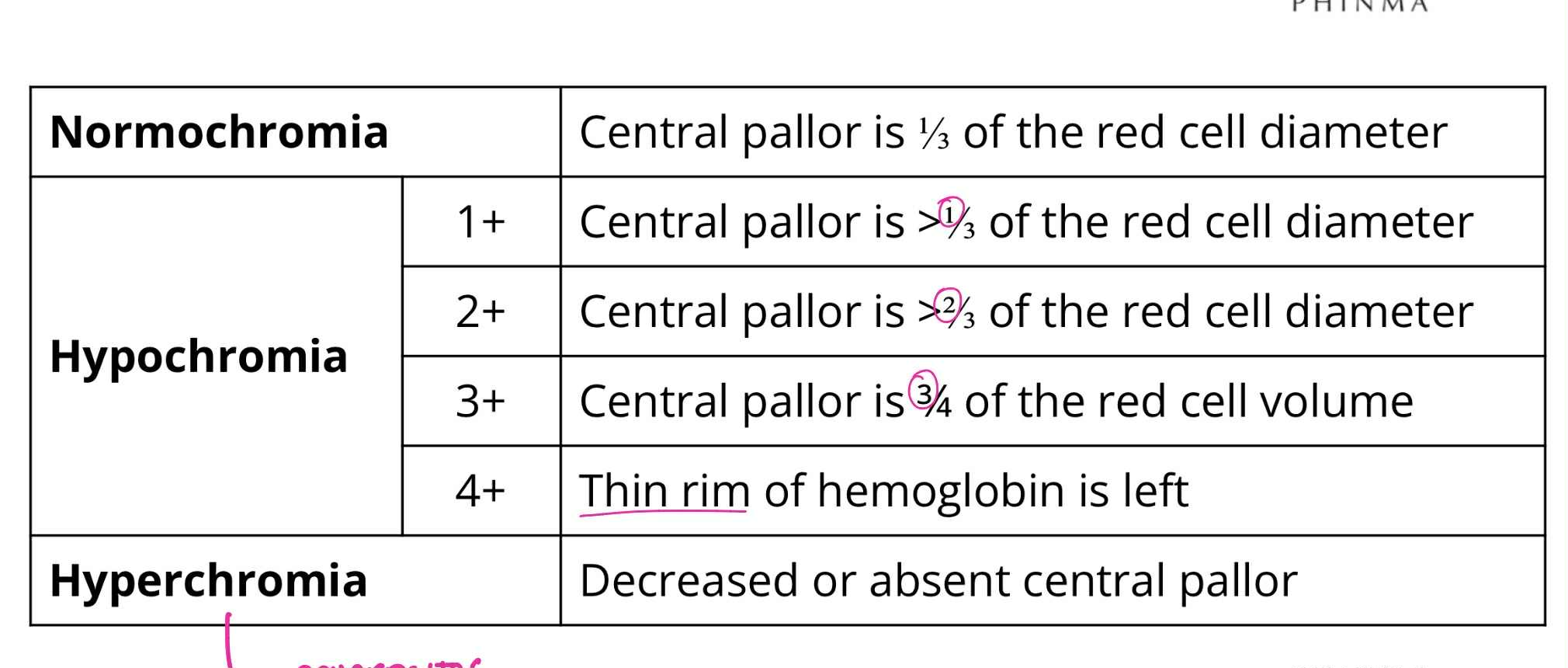
Normochromia
QUALITATIVE RBC ABNORMALITIES:
Central pallor is 1/3 of RBC diameter
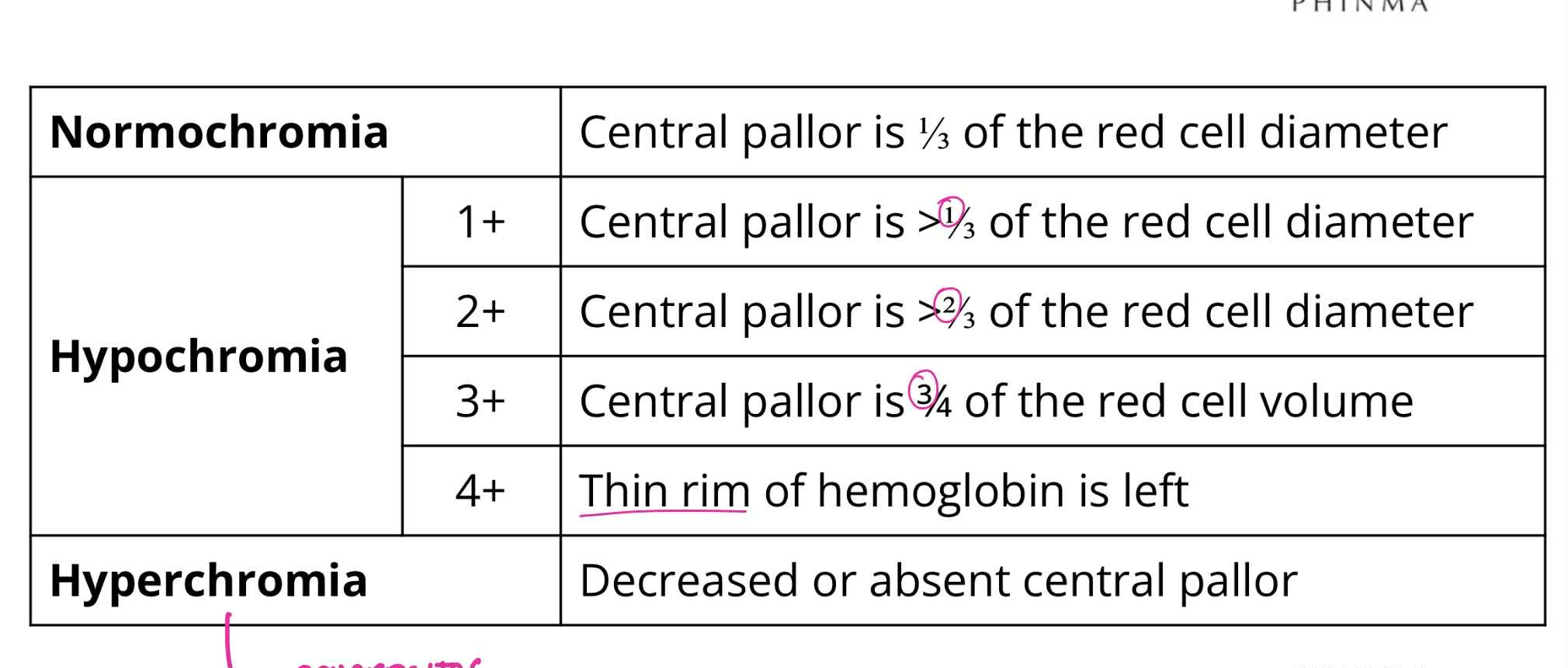
Hypochromia (1+)
QUALITATIVE RBC ABNORMALITIES:
Central pallor is >1/3 of RBC diameter
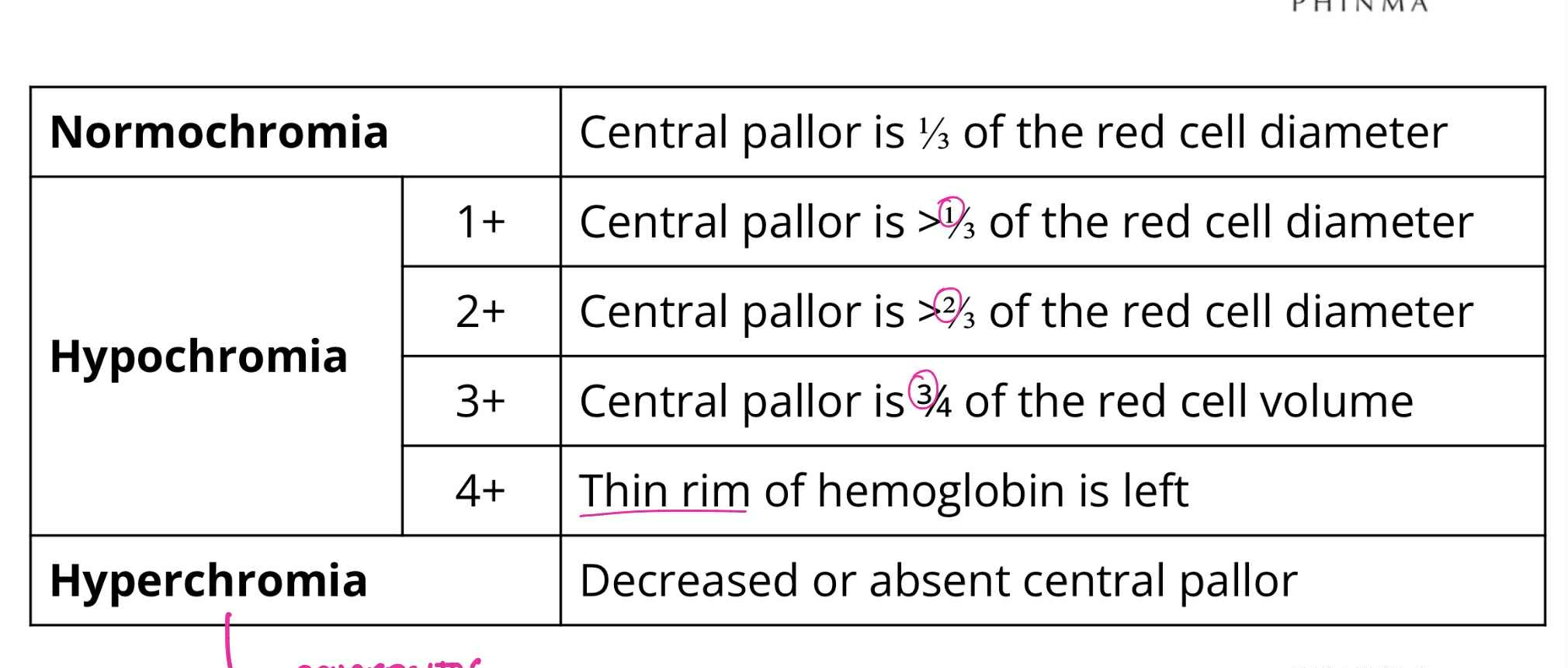
Hypochromia (2+)
QUALITATIVE RBC ABNORMALITIES:
Central pallor is >2/3 of RBC diameter
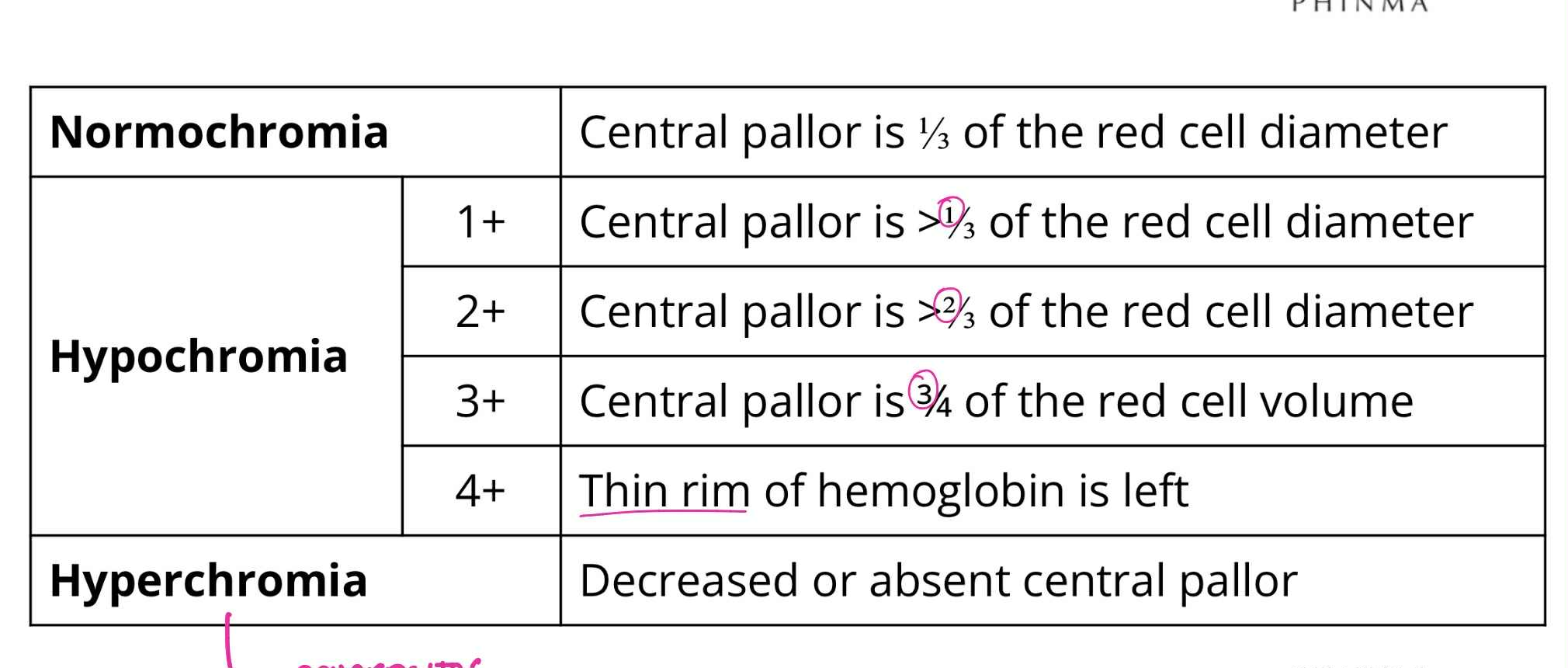
Hypochromia (3+)
QUALITATIVE RBC ABNORMALITIES:
Central pallor is 3/4 of RBC diameter
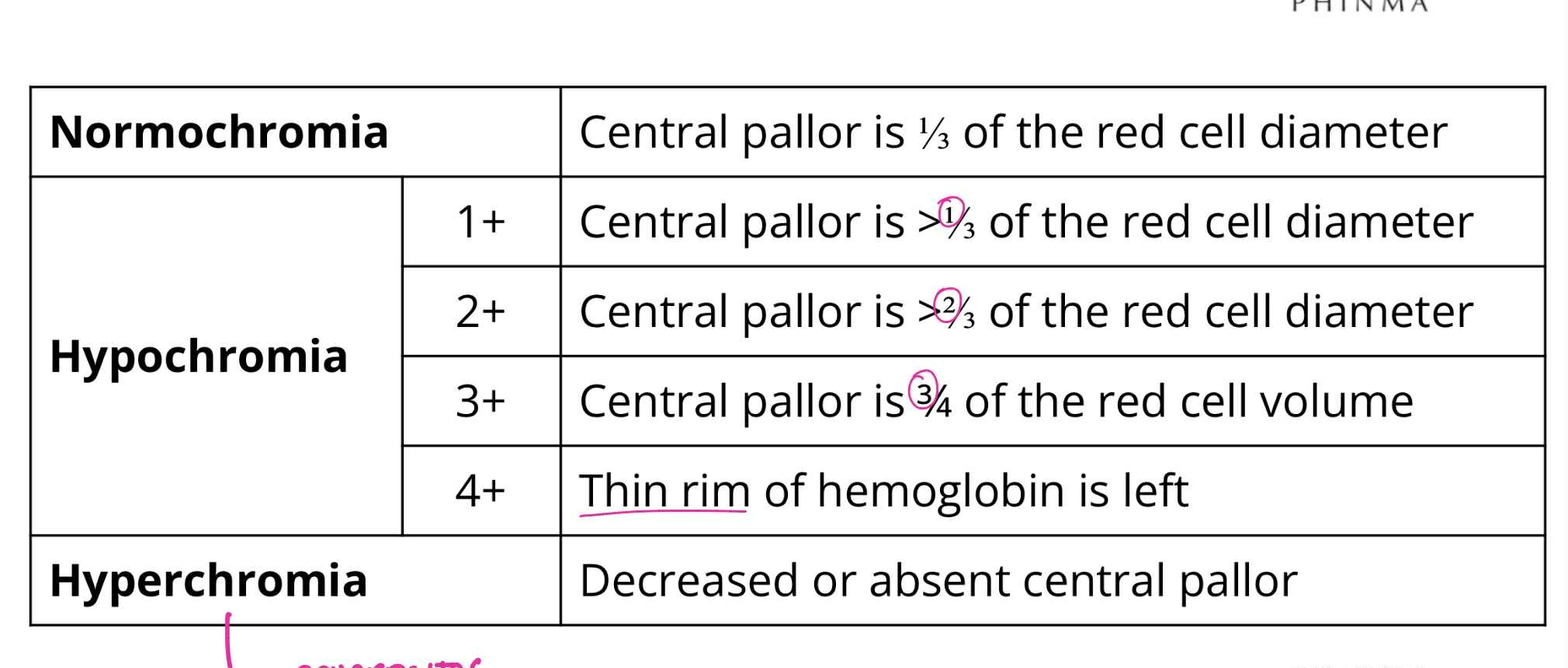
Hypochromia (4+)
QUALITATIVE RBC ABNORMALITIES:
Thin rim of hemoglobin is left
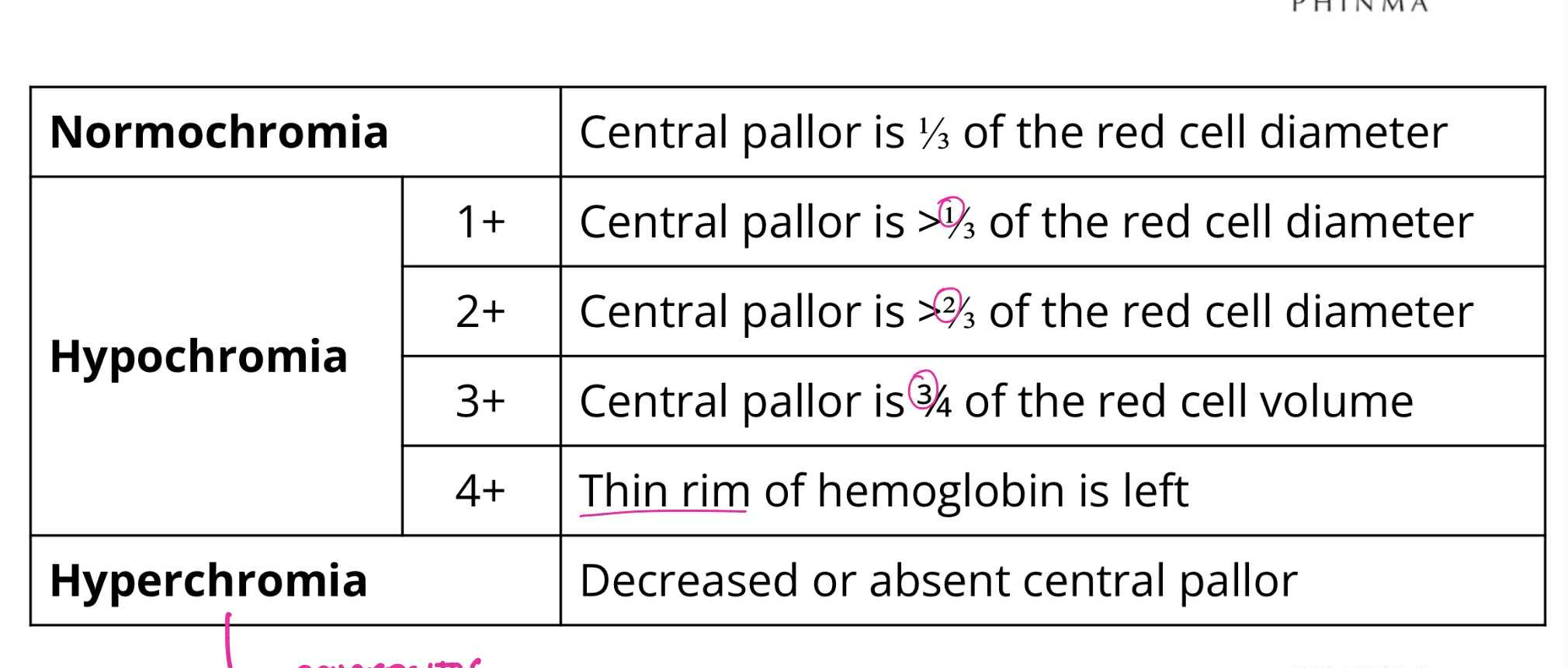
Hyperchromia
QUALITATIVE RBC ABNORMALITIES:
Decreased or absent central pallor
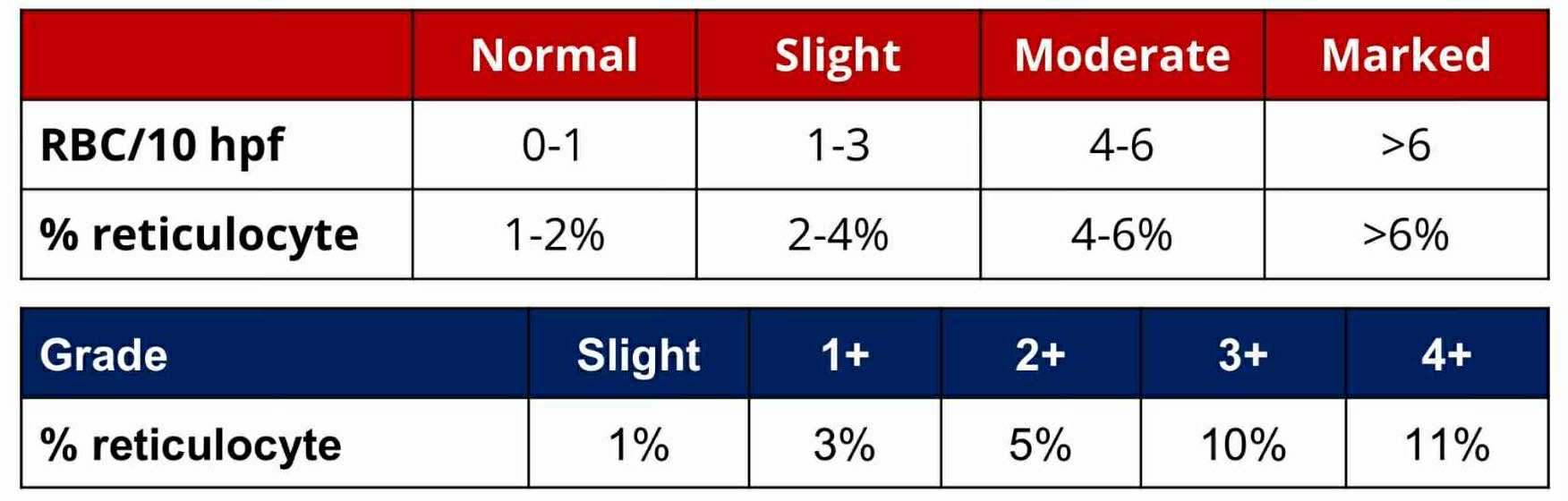
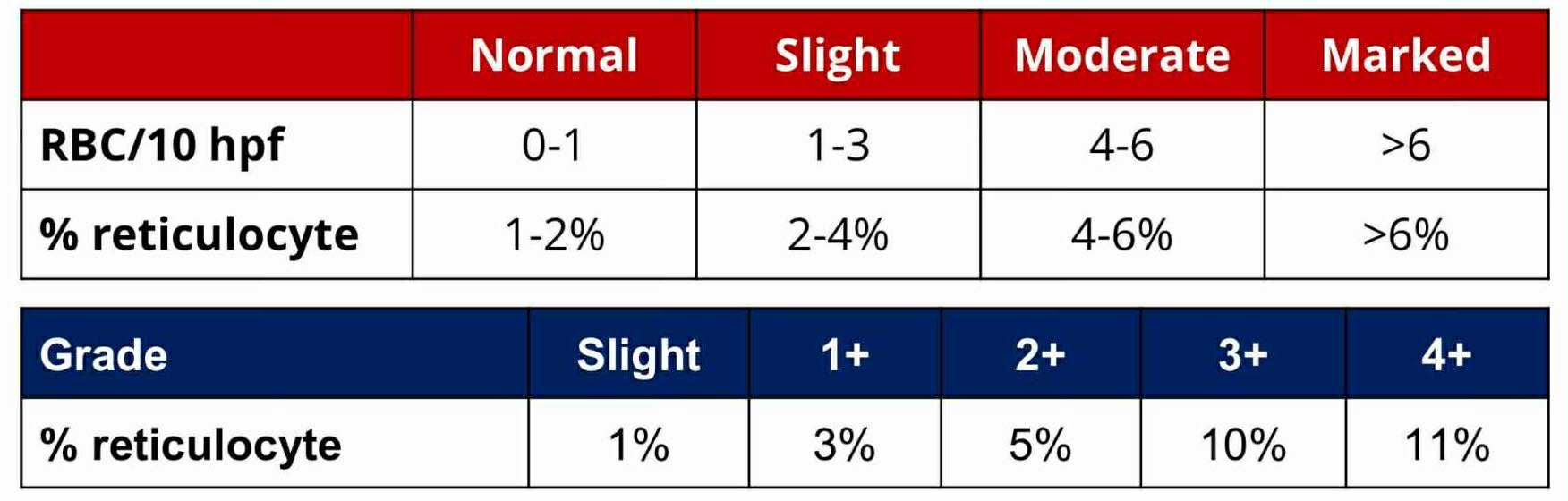
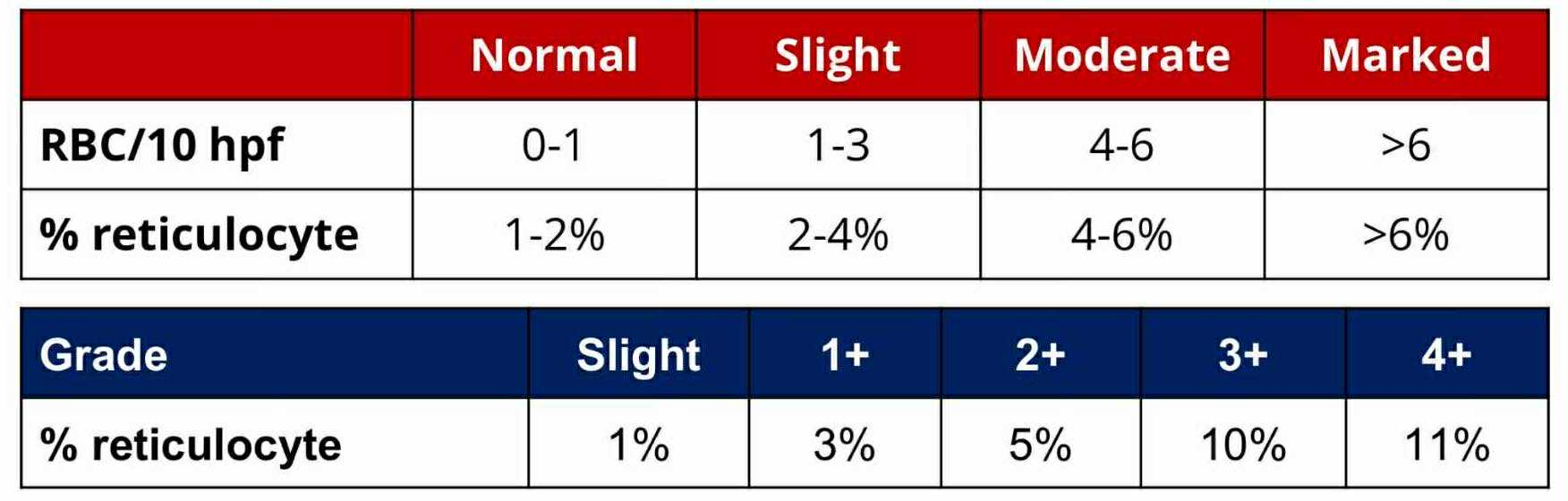
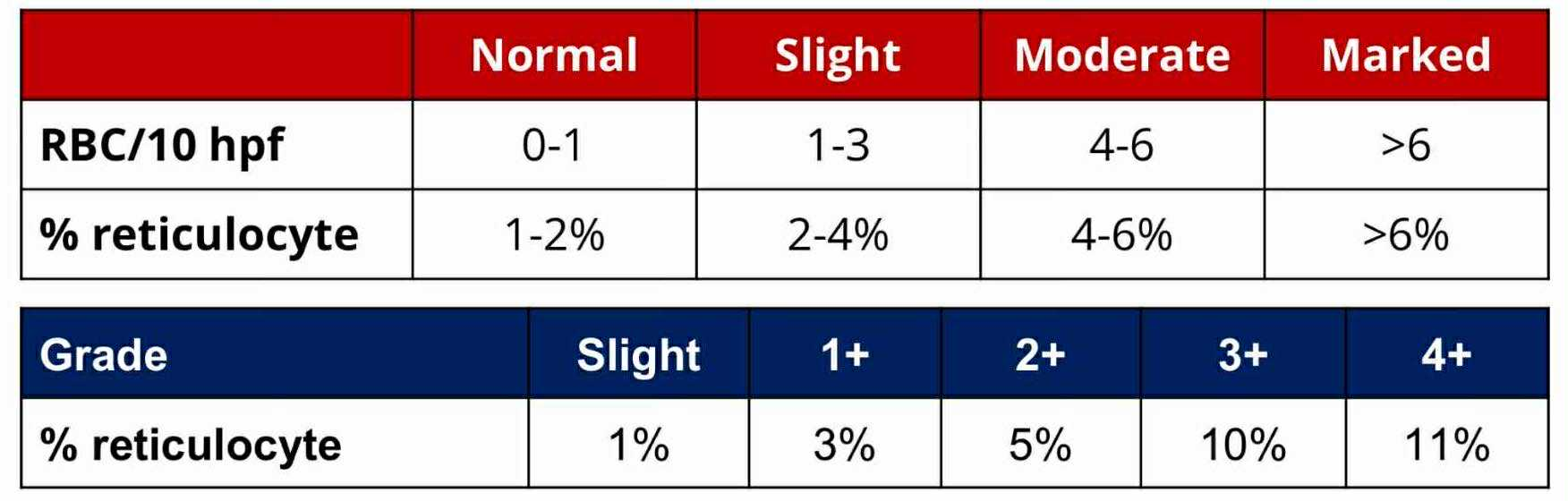
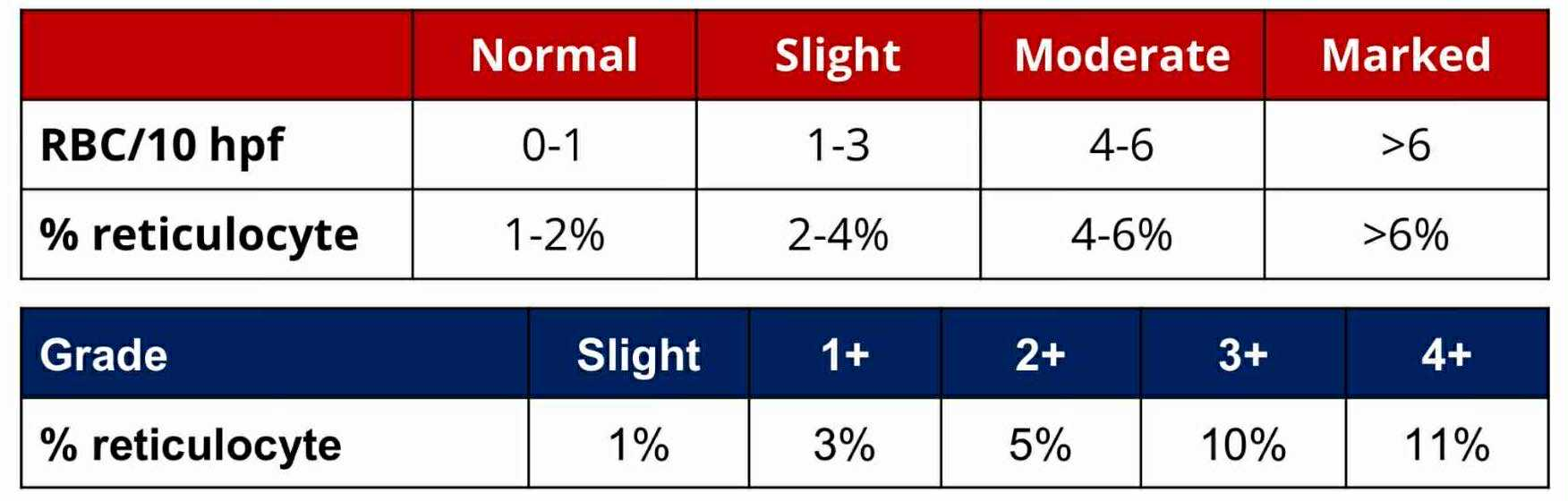
Slight
RETICULOCYTE GRADE:
1%
1+
RETICULOCYTE GRADE:
3%
2+
RETICULOCYTE GRADE:
5%
3+
RETICULOCYTE GRADE:
10%
4+
RETICULOCYTE GRADE:
11%
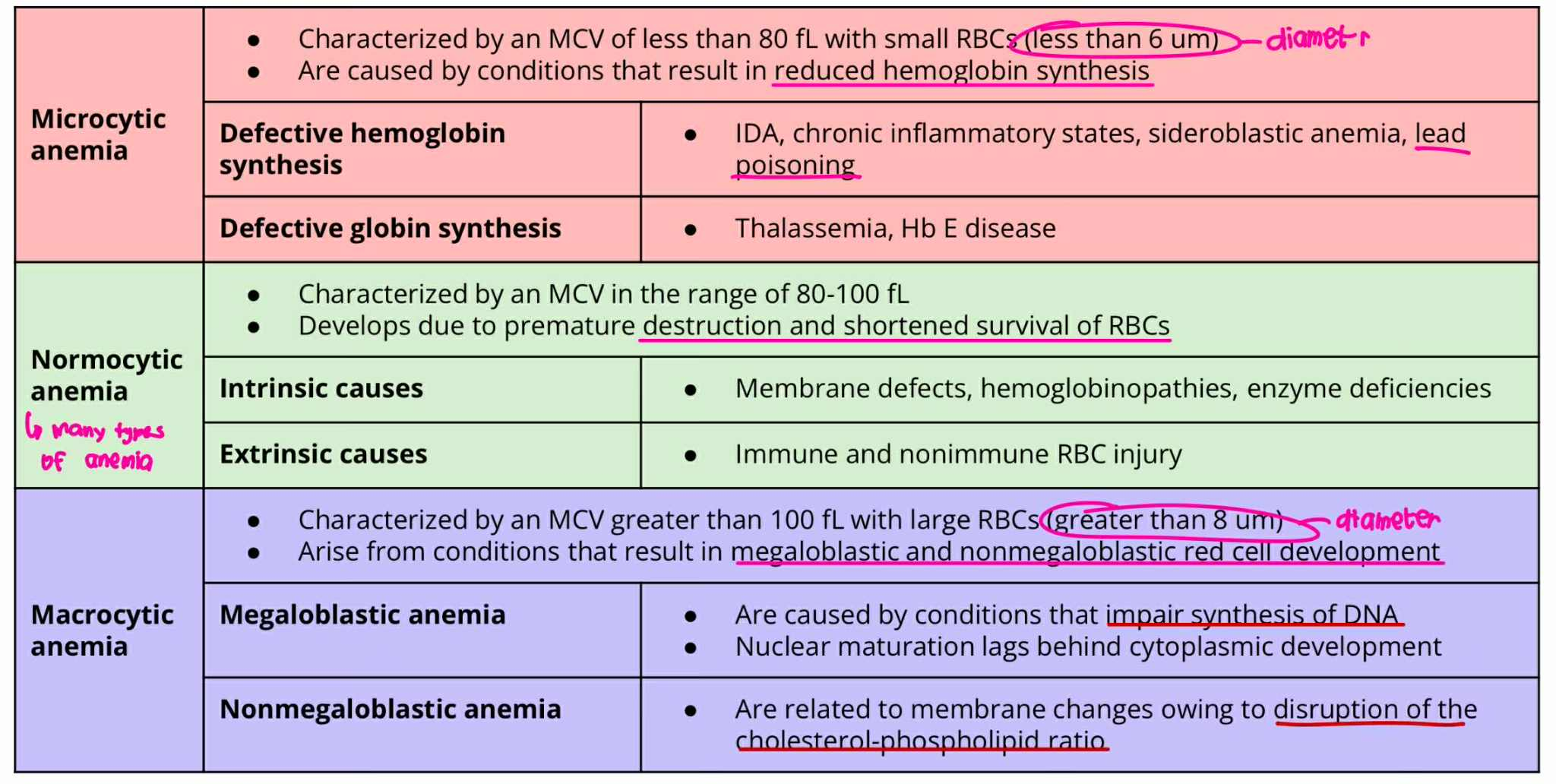
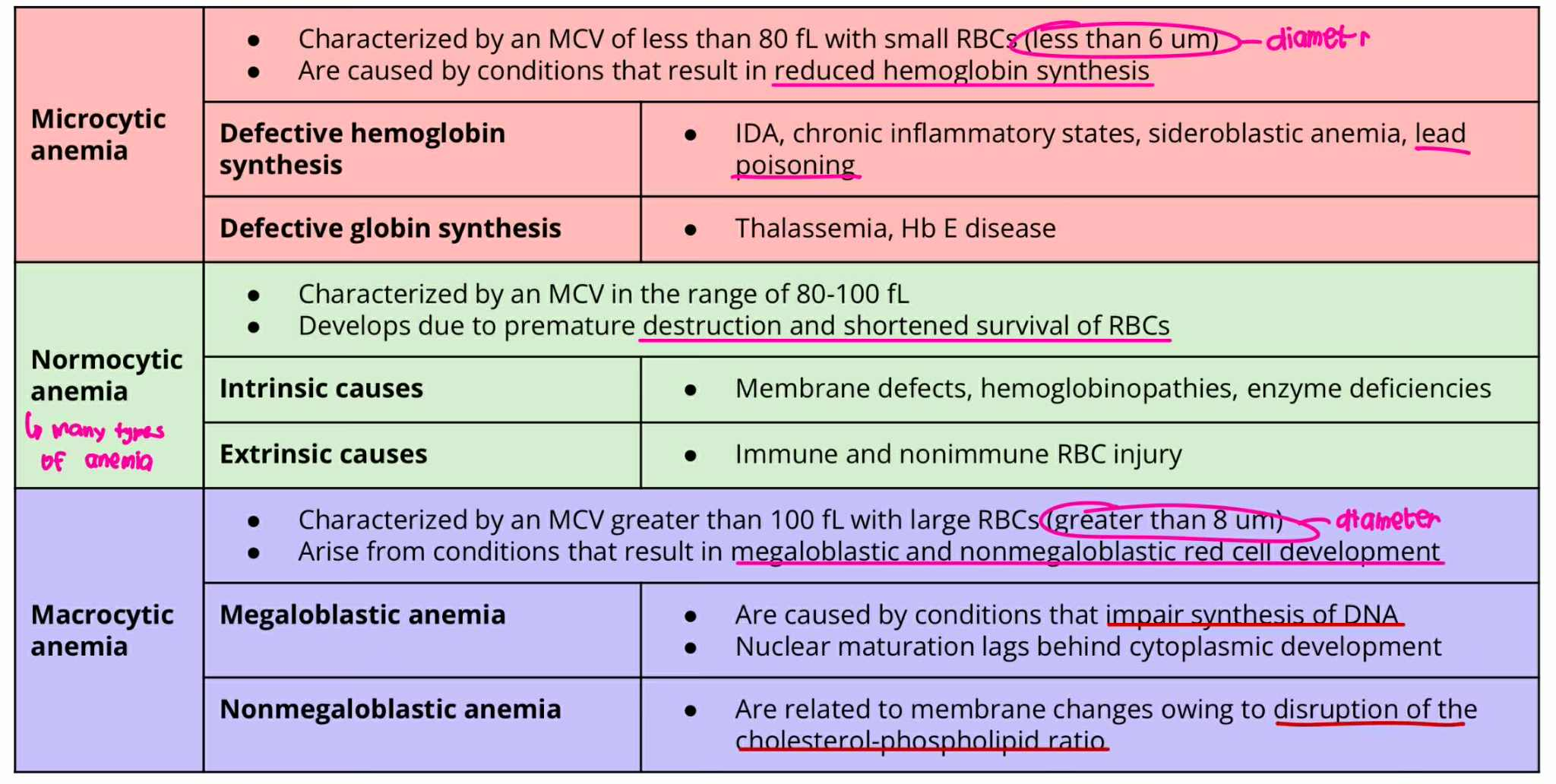
Microcytic anemia
MCV = less 80 fL
RBC size = less 6um
ANICOCYTOSIS (Type of Anemia)
result in reduced hemoglobin synthesis
Defective hemoglobin synthesis
Defective globin synthesis
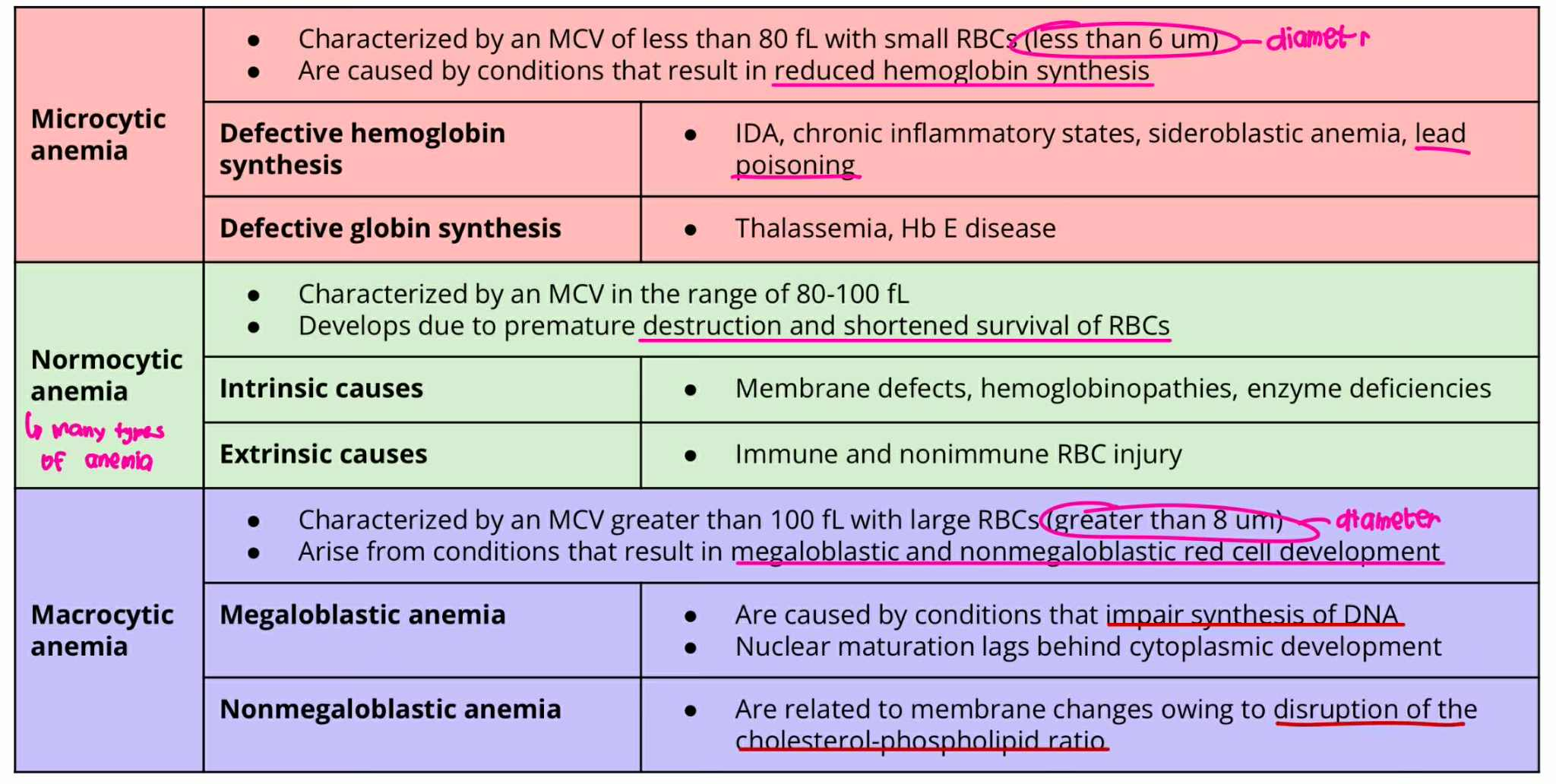
Normocytic Anemia
MCV = 80-100 fL
ANICOCYTOSIS (Type of Anemia)
Develops due to premature destruction and shortened survival of RBCs
Intrinsic causes
Extrinsic causes
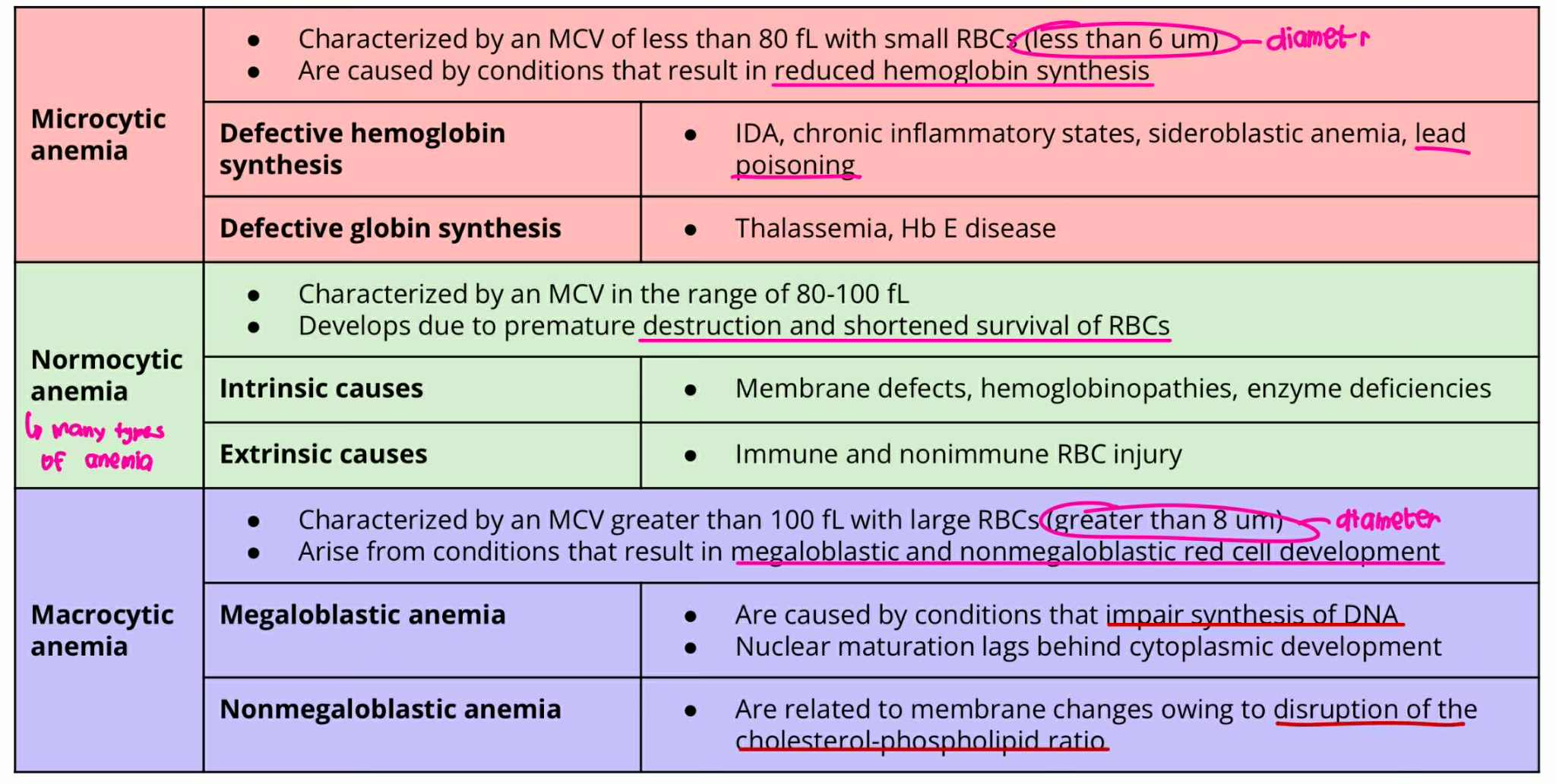
Macrocytic Anemia
MCV = more 100fL
RBC Size = greater 8um
ANICOCYTOSIS (Type of Anemia)
result in megaloblastic and non-megaloblastic cell development
Megaloblastic Anemia
Non-Megaloblastic Anemia
Microcytic Anemia + Defective Hemoglobin synthesis
ANICOCYTOSIS (Type of Anemia)
Iron-Deficiency Anemia
Chrocnic inflammatory state
Sideroblastic anemia
LEAD POISIONING
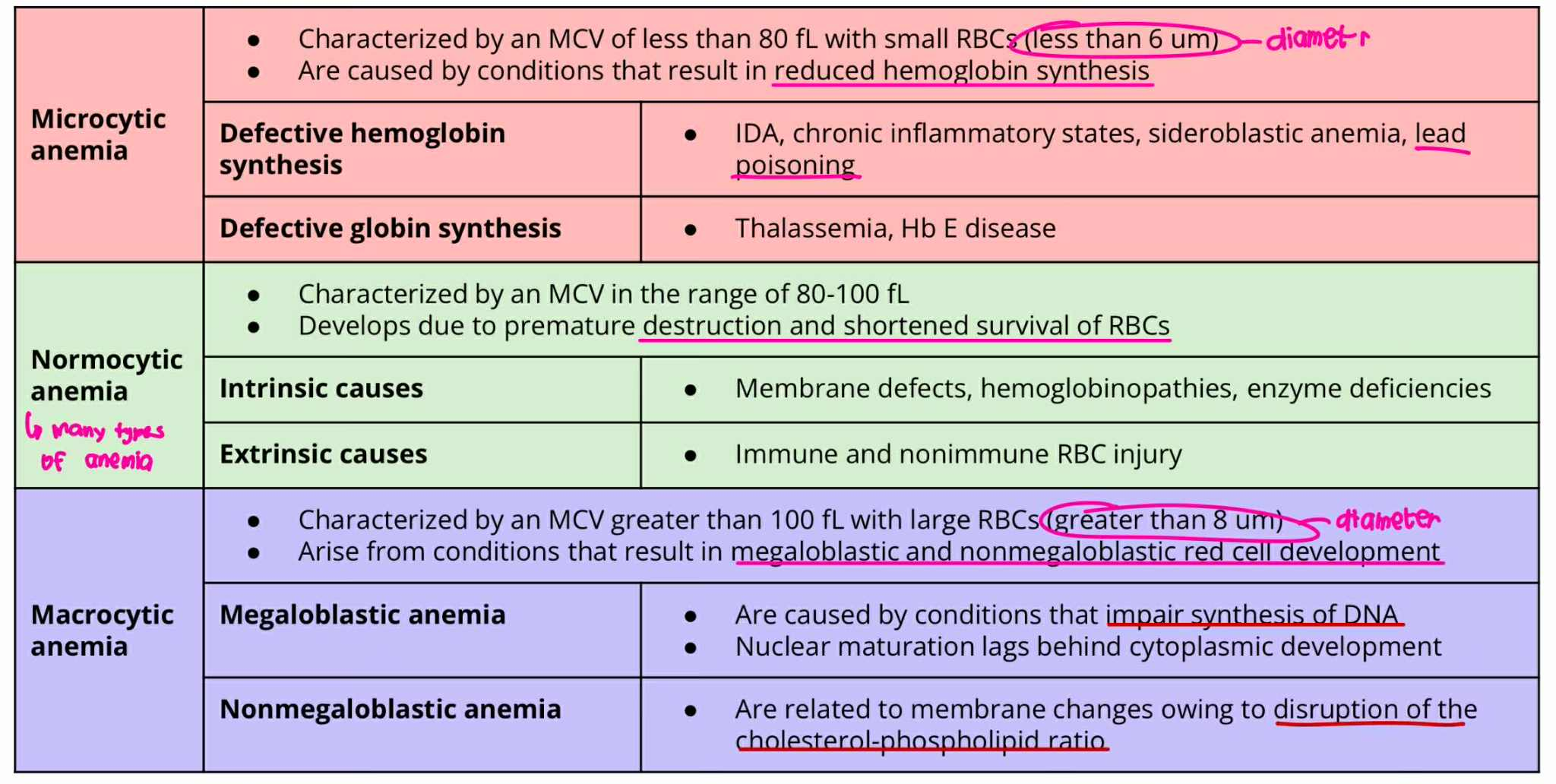
Microcytic Anemia + Defective Globin synthesis
ANICOCYTOSIS (Type of Anemia)
Thalasemmia
Hb E disease
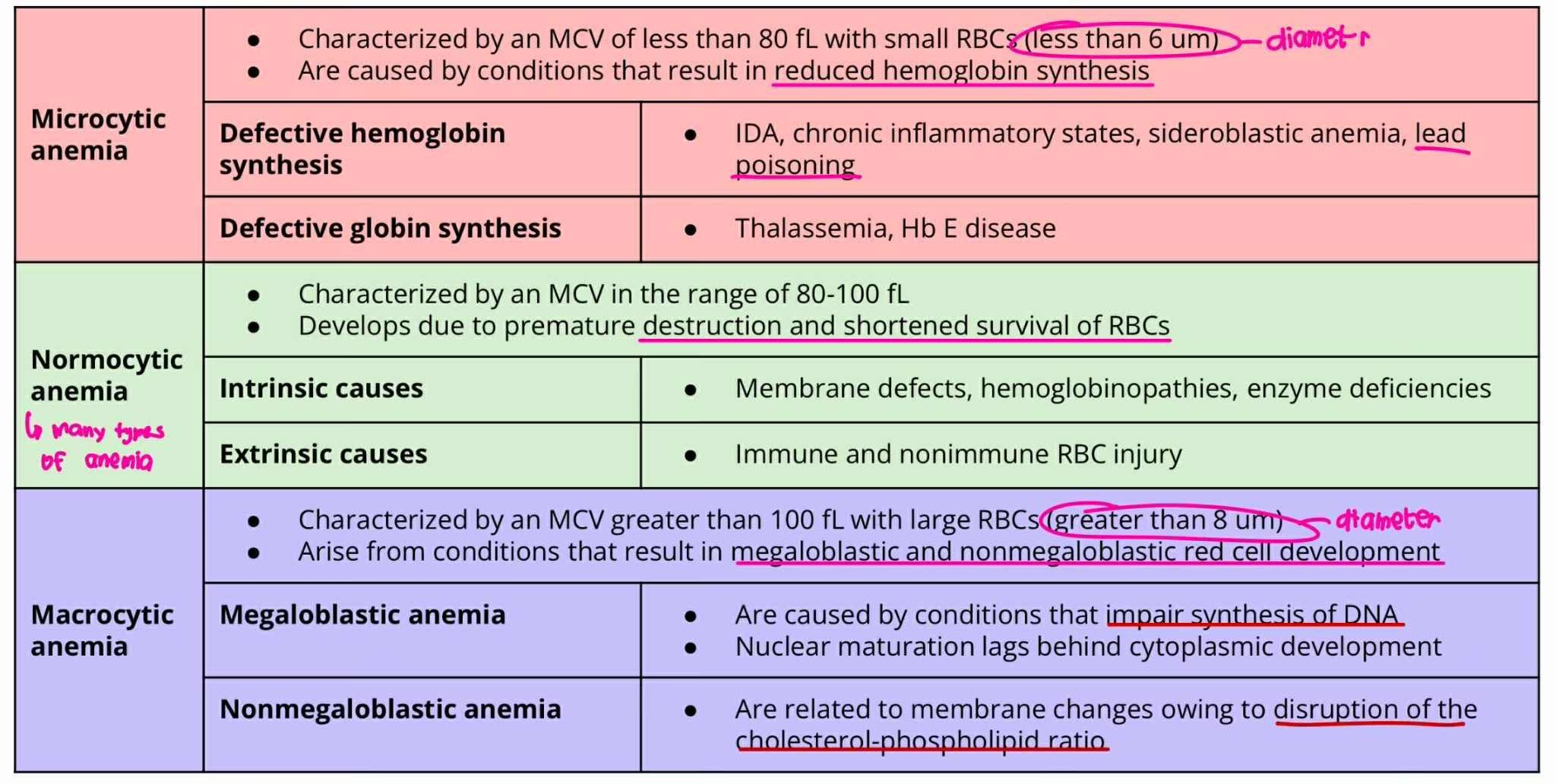
Normocytic Anemia + Intrinsic cause
ANICOCYTOSIS (Type of Anemia)
Membrane defect
Hemoglobinopathies
Enzyme deficiencies
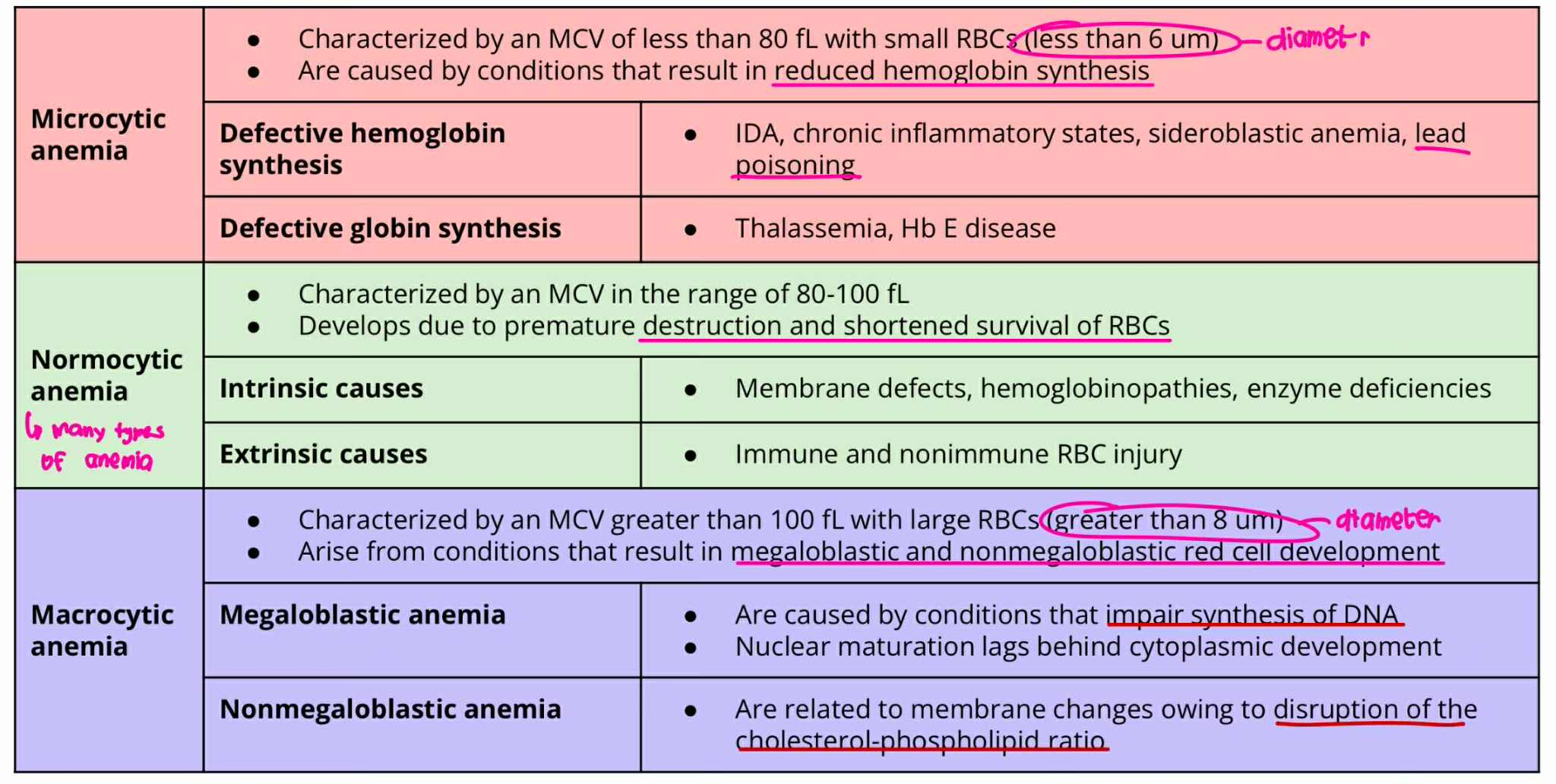
Normocytic Anemia + Extrinsic cause
ANICOCYTOSIS (Type of Anemia)
Immune and nonimmune RBC injury
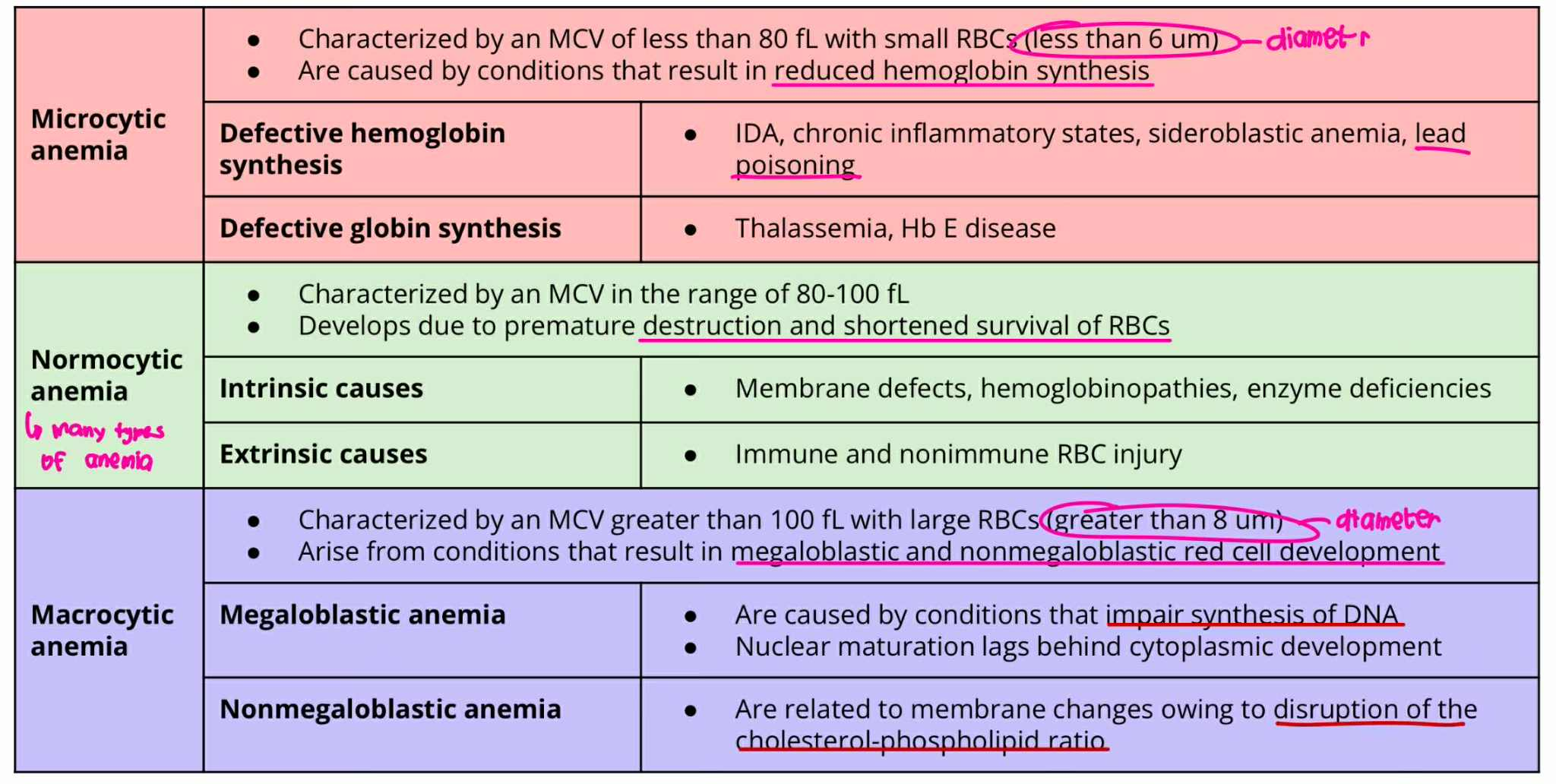
Macrocytic Anemia + Megaloblastic Anemia
ANICOCYTOSIS (Type of Anemia)
Caused by impair synthesis of DNA
Nuclear maturation lags behind cytoplasmic development
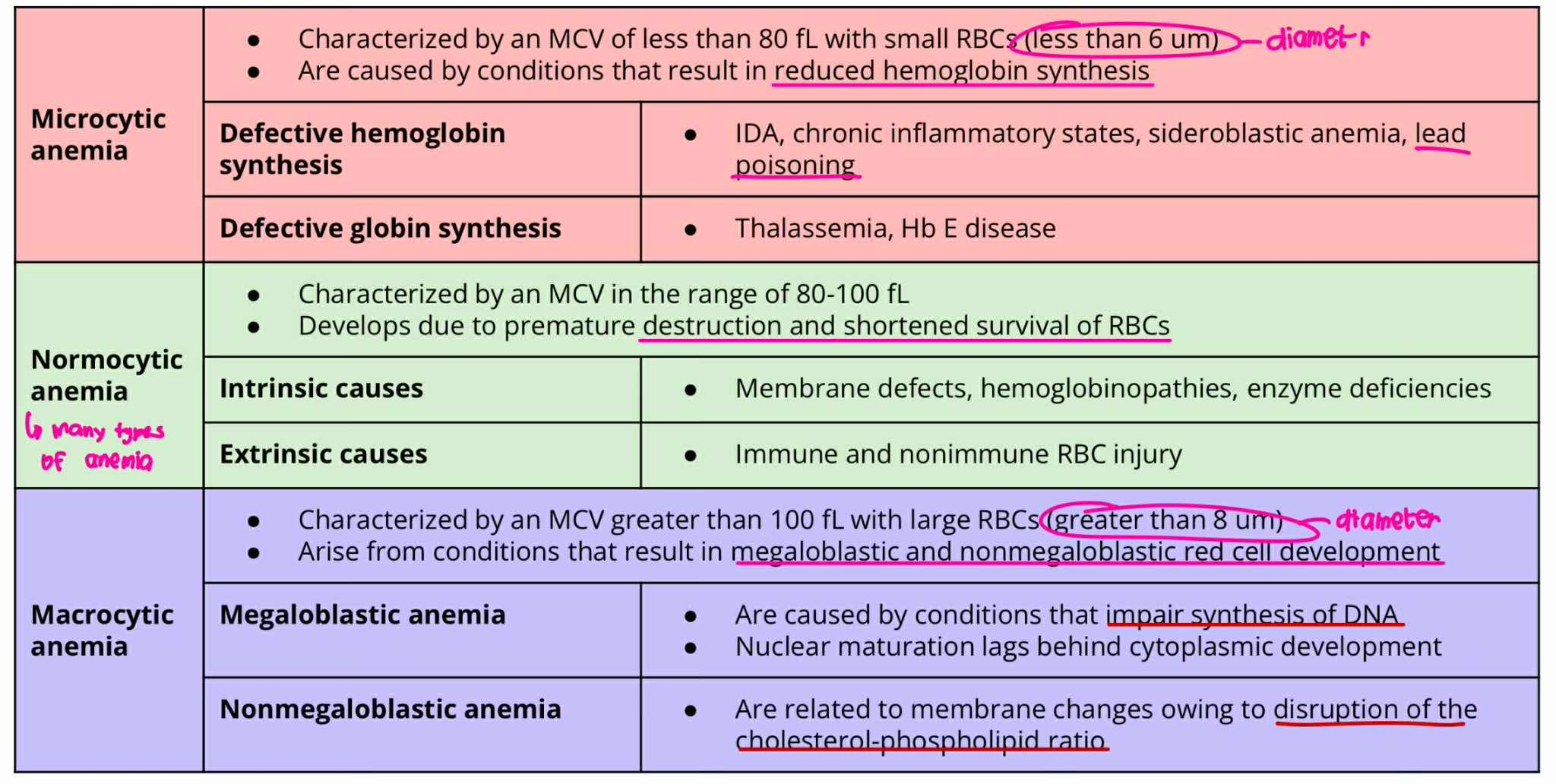
Macrocytic Anemia + NonMegaloblastic Anemia
ANICOCYTOSIS (Type of Anemia)
Are related to membrane changes owing to disruption of cholesterol-phospholipid ratio