Solar System Full Notes
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
Nucleosynthesis
The process by which atomic nuclei are formed from protons and neutrons, primarily during the early universe and within stars.
Isotope Stability
Refers to the stability of isotopes, which is related to the neutron-to-proton ratio.
Half-life
The time required for half of the unstable isotopes in a sample to decay into a more stable form.
Principles of Nucleosynthesis
Atom stability, conditions must be high T and P, stars have these conditions
Atom Stability
The tendency of atoms to remain unchanged, or decay into new nuclei if they are unstable.
Nuclear Fusion
A reaction where atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus, requiring high temperature and pressure.
Stellar Formation
The process in which gas clouds collapse under gravity to form stars.
Conditions After the Big Bang
The state of the universe post-Big Bang, characterized by extreme temperatures and densities.
Stellar Nucleosynthesis
The formation of heavier elements from hydrogen through fusion processes in stars.
Fusion of Hydrogen
The primary nuclear reaction powering stars, converting hydrogen into helium.
C-N-O Cycle
A fusion process present in larger stars, converting helium into heavier elements.
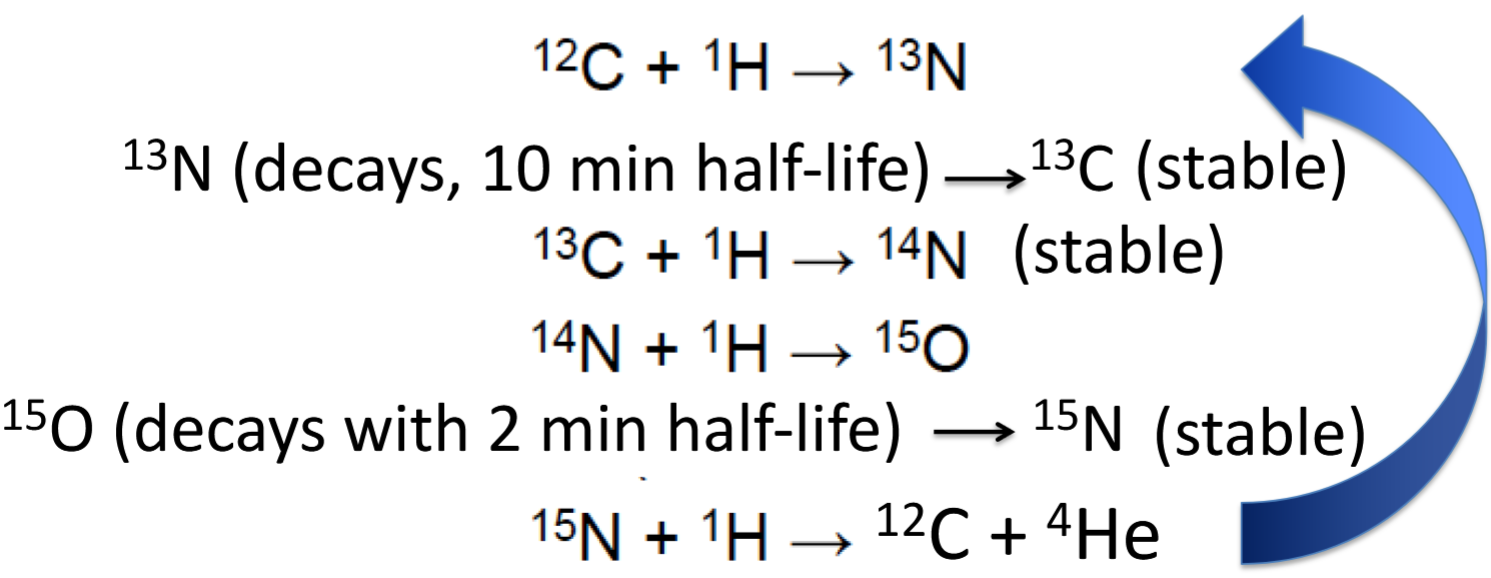
Red Giant Stage
A phase in a star's life when it expands after exhausting its hydrogen supply.
Solar Nebula
The cloud of gas and dust from which the solar system formed.
Accretion Process
The gradual accumulation of particles to form larger astronomical bodies, such as planets.
Role of Comets
Celestial bodies that deliver water and volatiles to forming terrestrial planets.
Differentiation of Earth
The process of the Earth forming distinct layers, including the core, mantle, and crust.
Siderophiles
Elements that prefer metallic phases, commonly found in Earth's core.
Chalcophiles
Elements that prefer to bond with sulfur and often form sulfide minerals.
Lithophiles
Elements that bond with oxygen and are incorporated into silicate minerals.
Atmophiles
Elements that prefer vapor phases and avoid solid phases.
Earth's Inner Core
The solid, dense center of Earth, primarily composed of iron and nickel.
Earth's Outer Core
The liquid layer surrounding the inner core, contributing to the Earth's magnetic field.
Mantle
The layer between the Earth's crust and core, composed of silicate minerals.
Oceanic Crust
The thinner, younger part of Earth's crust primarily composed of basalt.
Continental Crust
The thicker, older part of Earth's crust composed primarily of granitic rocks.
Ophiolites
Sections of oceanic crust exposed on land, providing insights into tectonic processes.
Xenoliths
Fragments of mantle material brought to the surface by volcanic activity.
Partial Melting
The process where some minerals melt while others remain solid, leading to differentiated compositions.
Refractory Elements
Elements that condense at high temperatures and are integral to the solidification of planets.
Heat-Producing Elements
Elements like potassium, uranium, and thorium that contribute to Earth's internal heat.
Giant Impact Hypothesis
The theory that the Moon formed from debris ejected during a massive collision between Earth and a Mars-sized body.
Lunar Basalts
Volcanic rocks formed from magma on the Moon, providing insights into its geological history.
Chondrites
Primitive meteorites containing chondrules, important for understanding the early solar system.
Carbonaceous Chondrites
A specific type of chondrite that contains organic compounds and water, relating to the origins of life.
Asteroid Belt
The region between Mars and Jupiter containing remnants from the early solar system.
Meteorite Impacts
Events where meteorites collide with Earth, creating craters and impacting the surface.
Classification of Meteorites
A system grouping meteorites based on their composition and origins.
Iron Meteorites
Meteorites composed mainly of iron and nickel, remnants from differentiated asteroids.
Stony-Irons
A combination of silicate materials and metal found in some meteorites.
Planetary Formation
The process by which planets develop from material in a protoplanetary disk.
Giant Planets
Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune, which are primarily composed of gases.
Snow Line
The distance from the Sun in the solar system where water ice can condense.
Kuiper Belt
A region beyond Neptune populated with icy bodies, including short-period comets.
Oort Cloud
A hypothetical spherical region surrounding the solar system, believed to be the source of long-period comets.
Comet Tails
The glowing trails formed when a comet approaches the Sun, releasing gas and dust.
Earth Differentiation
The process where Earth formed distinct layers during its cooling and solidification.
Trace Elements
Elements present in small amounts, important for understanding geological processes.
Astrobiology
The study of the potential for life beyond Earth, examining environmental factors and elemental compositions.
Habitable Zone
The region around a star where conditions are appropriate for liquid water to exist.
Terrestrial Planets
Rocky planets that include Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars, characterized by solid surfaces.
Exoplanets
Planets located outside our solar system, whose study helps understand planetary formation.
Atmospheric Dynamics
The study of movement and changes in a planet's atmosphere affecting climate and weather.
Geological Processes
Natural events such as erosion, volcanism, and tectonics that shape planetary surfaces.
Planet Definition Criteria
Guidelines used to classify celestial bodies as planets based on specific attributes.
Volatile Elements
Elements that easily vaporize; their composition changes in various planetary environments.
Seismic Data
Information derived from earthquake waves used to understand Earth's interior structure.
Density Profiles
Measurements that help infer the composition and layers of Earth's interior.
Magma Composition
The chemical makeup of molten rock, essential for understanding volcanic activity.
Differentiation Mechanisms
Processes responsible for the separation of materials based on their physical and chemical properties.
Angular Momentum
The rotational momentum of bodies, crucial during the formation and evolution of solar systems.
Geochemical Processes
Chemical interactions that occur within Earth affecting the distribution of elements.
Solar Nebula Theory
The model explaining the formation of the solar system from a rotating cloud of gas and dust.
Condensation Temperatures
The specific temperatures at which materials transition from gas to solid.
Planetary Recycling
The continuous process of reshaping the surface and materials of a planet over geological time.
Chemical Weathering
The breakdown of rocks through chemical reactions, influencing surface composition.
Volcanic Activity
Processes associated with the movement of magma and the eruption of material from the Earth's interior.
Impact Cratering
The process of formation of craters on surfaces due to collisions with meteoroids.
Erosion
The wearing away of Earth's surface materials due to various natural forces.
Thermal Contraction
The shrinking of materials as they cool, leading to geological changes.
Geological Time Scale
A timeline used by geologists to describe the timing and relationships of events in Earth's history.
Surface Pressure
The pressure exerted by the weight of the atmosphere on the surface of a planetary body.
Isotope Ratios
Proportions of different isotopes of an element used to understand geological processes.
Cosmic Structure
Formation and arrangement of matter in the universe following nucleosynthesis.
Hydrostatic Equilibrium
Equilibrium state where the gravitational force pulls inward and pressure pushes outward in a planetary body.
Photosynthesis
The process by which plants use sunlight to synthesize food, reliant on the elements available in the environment.
Planetary Environments
The various conditions and characteristics of planets, influencing their development and potential for life.
Solar Composition
The elemental makeup of the sun, serving as a baseline for comparing celestial bodies.
Inert Atmospheres
Conditions where gases in the atmosphere do not react chemically, crucial for certain applications.
Earth's Geodynamics
The internal processes of Earth affecting its geological structure and surface features.
Planetary Migration
The movement of planets within a solar system, changing their distances from their star.
Extraterrestrial Life
Life forms that may exist beyond Earth, influenced by planetary conditions.
Gaseous Composition
The makeup of gases in a planetary atmosphere, impacting climate and weather.
Magnetosphere
The region around a planet dominated by its magnetic field, affecting its atmosphere.
Water Cycle
The process of water circulation, influencing geological and atmospheric conditions on a planet.
Crustal Features
Structural characteristics of a planet's crust, indicative of its geological history and activity.