Chemical Nomenclature
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What is a covalent bond?
Bond between nonmetals where the electrons are shared
How do you name a covalent bond?
First element keeps its full name + numerical prefix
Base of the second name + numerical prefix
Example:
Dinitrogen monoxide
(full name + prefix) + (base: oxide + numerical prefix)
What is an ionic bond?
Metal & nonmetal bond where the electrons are not shared but given up
What are the 3 types of ionic bonds?
Bonds between two monoatomic ions, polyatomic bonds, and bonds with transition metals + nonmetals
How do you name ionic monoatomic bonds?
Full name of first atom (NO NUMERICAL PREFIX)
Base of the second name + ide (NO NUMERICAL PREFIX)
Make sure the final charge of the atom balances to 0
Ex:
Sodium flouride (NaF), Aluminum Nitride (Li3N)
How do you name ionic polyatomic bonds?
Full name of first atom no numerical prefix
Base name of second atom (NO NUMERICAL PREFIX) + ate or ite
*If the first atom has given up all it’s valence electrons to try and balance the atom, use ate. Otherwise use ite
EX:
PO4-3 There are four oxygen atoms giving it a charge of -8 (each oxygen has gained 2 electrons to get 8). Phosphorus has given it’s 5 electrons to balance the charge to -3. Because it’s given away all it’s electrons, we use ate.
PO3-3 Same thing, but phosphorus has not given up all it’s electrons otherwise the charge would be -1, so we use ite.

How do you name polyatomic ions that contain halogens?
Charges of +7 use the prefix per_____ate
Charges of +5 use ____ate
Charges of +3 use ____ite
Charges of +1 use hypo____ite

How do you name ionic bonds with transition metals?
When pairing with transition metals (anything in the d block) you name it like a regular polyatomic ion, but you add roman numerals to indicate the charge of the individual atom.
EX:
Fe2O3 —> Iron (III) Oxide (Oxygen always has a negative charge of -2, so total it’s -6. The two irons have both given up three electrons, so they both have a charge of +3.
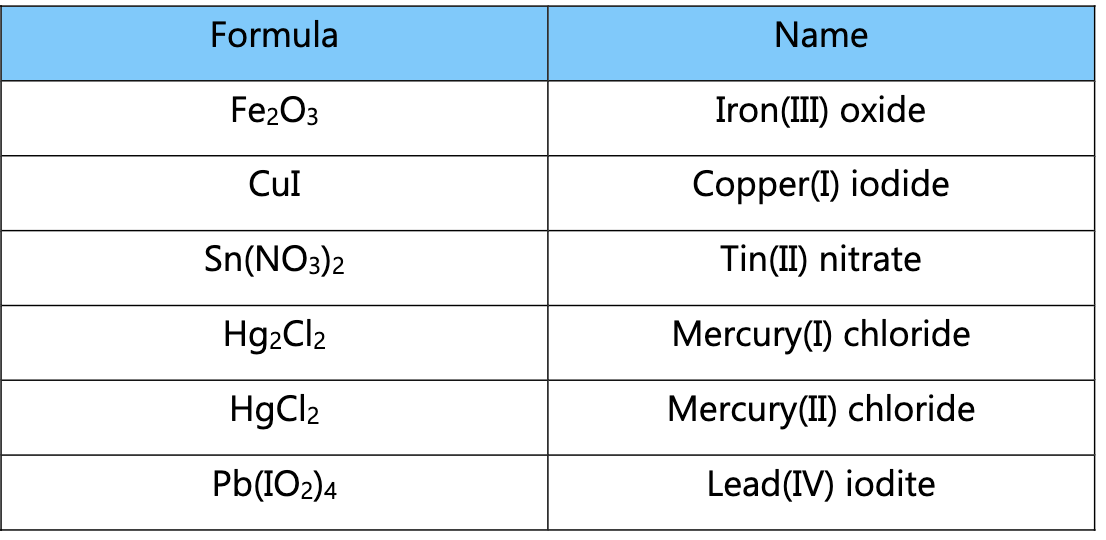
What four atoms are exceptions to the transition + nonmetal naming convention?
Silver, zinc, cadmium, and mercury.
Silver doesn’t use roman numerals and is always +1
Zinc & Cadmium also don’t use roman numerals and are usually +2
Mercury (I) doesn’t exist by itself.

What are hydrated compounds?
Compounds that crystallize in water.
What do you called hydrated compounds in their dry state?
Anahydrous
How do you name hydrated compounds?
You name the first element, then add a dot and add the number of water molecules + hydrate
EX:
Ba(OH)2 × 8H2O = Barium hydroxide octahydrate (8 water molecules)
Cadmium
Cd2+
Mercury (I)
Hg22+
Mercury (II)
Hg2+
Silver
Ag+
Zinc
Zn2+
Acetate
CH3COO-
Ammonium
NH4+
Bromate
BrO3-
Bromite
BrO2-
Carbonate
CO32-
Hydrogen carbonate
HCO3-
Chlorate
CIO3-
Chlorite
CIO2-
Chromate
CrO42-
Cyanide
CN-
Dichromate
Cr2O72-
Hydroxide
OH-
Hypobromite
BrO-
Hypochlorite
ClO-
Hypoiodite
IO-
Iodate
IO3-
Iodite
IO2-
Nitrate
NO3-
Nitrite
NO2-
Perbromate
BrO4-
Perchlorate
ClO4-
Periodate
IO4-
Permanganate
MnO4-
Peroxide
O22-
Phosphate
PO43-
Monohydrogen phosphate
HPO42-
Dihydrogen phosphate
H2PO4-
Phosphite
PO33-
Sulfate
SO42-
Hydrogen sulfate
HSO4-
Hydrogen sulfide
HS-
Sulfite
SO32-
Hydrogen sulfite
HSO3-