W9 star: Labor & Birth & Fetal Positions
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Define labor
regular uterine contractions that cause cervical change leading to birth
Pre term labor
onset of labor before <37 weeks gestational age
Dystocia
abnormally slow or protracted labor
Nulliparous (nullip or nullipara)
person who has never given birth to a child
Multiparous (multip or malutipara)
person who has given birth before
Birth
fetus, amniotic fluid, membranes, and placenta are separated and expelled from uterus
What are the things that happen before the onset of labor?
lightening (sensation of more space for the pregnant person to breathe because the baby is sinking down and going to pelvis (so not much pressure on diaphragm, lungs, heart) (2 - 3 weeks before term)
engagement (widest part of fetal head - or presenting part - that has passed through the pelvic inlet into the pelvis
cervix becomes soft & stretchy
increased vaginal secretions
bloody show
persistent back ache
possible spontaneous rupture of amniotic membranes
What are the stages of labor?
4 stages
First stage
Second Stage
Third Stage
Fourth Stage
The first stage of labor is from what to what?
onset of true progressive labor → complete dilation 10 cm
It’s Emily first time giving birth, how long is it expected to be in the first stage of labor?
6 - 18hrs for nullipara
It’s Emily 3rd time giving birth, how long is it expected to be in the first stage of labor?
2 - 10 hrs for multipara
What are the subcategories of the first stage of labor?
Latent (0 - 5cm) (irregular/regular contractions, mild → moderate, excitement)
Active (5 - 8cm) (effacement complete, contractions getting closer together)
Transition (8 - 10cm) (irritable, overwhelmed, nausea/vomit, shaky)
What happens in the second stage of labor? How long does it take?
complete dilation → birth of baby
30 min - 3hrs for nullipara
5 - 30min for multipara
What happens in the third stage of labor? How long does it take?
birth of baby → delivery of placenta
5 - 30 mins
What happens in the fourth stage of labor?
delivery of placenta → 1 hr postpartum
What are the maternal sensations in the second stage of labor?
urge to push
feeling excited & involved
contractions longer (90 second) and happen much quicker (1-2 mins)
What are the 5 P’s of Labor?
Passenger (fetus & placenta)
Passageway (birth canal - pelvis, cervix, vagina)
Power (power of uterine contractions)
Position (position of birthing person and fetus)
Psyche (mental & emotional factors)
What is included in the Passenger characteristic?
Presentation (which part is entering birth canal first)
Lie (which direction - relative to maternal axis - the fetal spine is)
Attitude (position of the fetal body part)
Position (where the baby is facing - the back of their skull, NOT their face)
What are the different presentations the fetus could have?
The part that enters the birth canal first
Head (occiput)
Shoulder (scapula)
Breech (sacrum / feet)
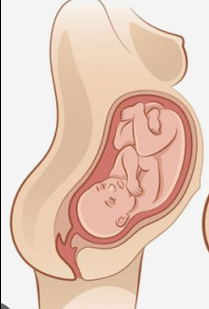
What presentation is the baby presenting?
occiput (head)
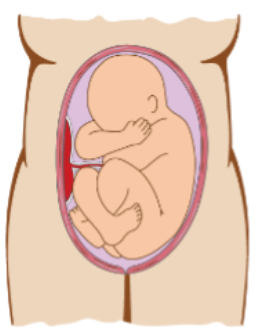
What presentation is the baby showing?
Breech (sacrum/feet)
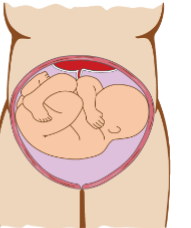
What presentation is the baby showing?
Shoulder (scapula)
What are the different lie the fetus could have?
Which direction the baby’s body is
Longitudinal (vertical)
Transverse (horizontal)
Oblique (diagonal..)
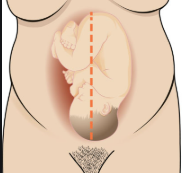
What fetal lie is this?
Longitudinal
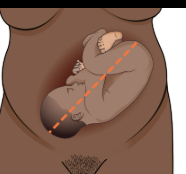
What fetal lie is this?
Oblique
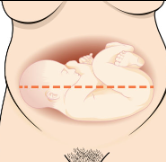
What fetal lie is this?
transverse
How to label positions?
maternal right (R) or left (L)
fetal presenting part
Occiput (O)
Sacrum (S)
Mentum - chin (M)
Breech (B)
fetal position (from the BACK of the baby’s head)

What position is this?
Right Occiput Posterior (ROP
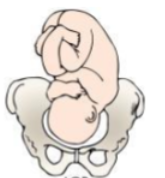
What position is this?
Left Occiput Posterior (LOP)
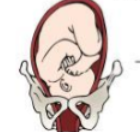
What position is this?
Right Occiput Transverse (ROT)
transverse (look their head is not facing the front or back, it’s like in the middle)
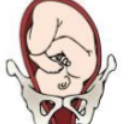
What position is this?
Left Occiput Transverse (LOT)
transverse (look their head is not facing the front or back, it’s like in the middle)
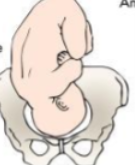
What position is this?
Right Occiput Anterior (ROA)
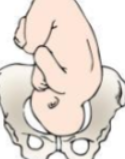
What position is this?
Left Occiput Anterior (LOA)

What position is this?
Occiput Anterior

What position is this?
Right Occiput Anterior (ROA)

What position is this?
Right Occiput Transverse (ROT)

What position is this?
Occiput Posterior

What position is this?
Left Occiput Posterior LOP

What position is this?
Right Occiput Posterior (ROP)

What position is this?
Left Occiput Anterior (LOA)

What position is this?
Left Occiput Transverse
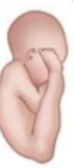
What position is this?
Right Sacrum Transverse (RST)
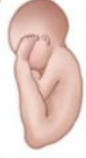
What position is this?
Left Sacrum Transverse (LST)
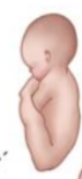
What position is this?
Left Sacrum Anterior (LSA)
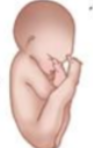
What position is this?
Right Sacrum Posterior (RSP)
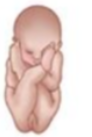
What position is this?
Sacrum Posterior
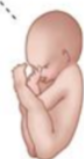
What position is this?
Left Sacrum Posterior (LSP)
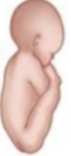
What position is this?
Right Sacrum Anterior (RSA)

What position is this?
Sacrum Anterior
Fetal station is what
where baby is in pelvis
11 station
A negative fetal station means the baby is above/below ischial spine? pick one
above ischial spine (further away from vaginal
A positive fetal stations means the baby is above/below the ischial spine? pick one
below the ischial spine (closer to vaginal opening)
What is effacement?
how thing the cervix is (describes it’s shortening)
100% effaced → cervix is completely thinned
Consider the 3 cervical exam finding of a laboring person below:
Patient A: 5 cm, 90%, +1, Fetus is LOP
Patient B: 7 cm, 80%, -1, Fetus is ROA
Patient C: 2 cm, 50%, -2, Fetus is LOA
In which scenario has the fetus descended the LOWEST into the maternal pelvis?
Patient A
Consider the 3 cervical exam finding of a laboring person below:
Patient A: 5 cm, 90%, +1, Fetus is LOP
Patient B: 7 cm, 80%, -1, Fetus is ROA
Patient C: 2 cm, 50%, -2, Fetus is LOA
Which birthing person’s cervix is most dilated?
Patient B
Consider the 3 cervical exam finding of a laboring person below:
Patient A: 5 cm, 90%, +1, Fetus is LOP
Patient B: 7 cm, 80%, -1, Fetus is ROA
Patient C: 2 cm, 50%, -2, Fetus is LOA
Which birthing person’s cervix is most effaced?
Patient A
Consider the 3 cervical exam finding of a laboring person below:
Patient A: 5 cm, 90%, +1, Fetus is LOP
Patient B: 7 cm, 80%, -1, Fetus is ROA
Patient C: 2 cm, 50%, -2, Fetus is LOA
Which fetus is in the most optimal position for vaginal birth?
Patient B
occiput anterior is best position for giving birth
most dilated and effaced and closer to pelvis than Patient C
What are pharmacologic pain management options during labor?
nitrous oxide gas (N2O)
sedatives (hydroxyzine (Vistaril))
opioids (morphine, fentanyl, Nubain)
pudendal nerve block (local anesthetic)
epidural analgesia (regional analgesic)
spinal anesthesia (regional anesthetic) (injection, time limited)
lidocaine local anesthetic)
What do sedatives help with in labor?
decrease anxiety & apprehension
induce sleep at higher doses
What do opioids help with in labor?
decrease pain
BUT if given too late might not get pain relief, result in drowsiness. risk of neonatal respiratory depression if given too late and doesn’t have time to leave the system by the time the baby is born. so baby has to battle it
keep narcan on hand
What is regional analgesia?
partial or complete loss of pain sensation below T8-T10 spinal level
What are advantages to regional analgesia
patient is awake and can participate in birth experience
airway reflex maintained
What are the types of regional analgesia?
epidural analgesia and spinal anesthesia
What are the limitations to regional analgesias?
immobility
Side effects: maternal hypotension, FHR changes, increased body temp, respiratory depression, N/V, itching, urinary retention
risk of spinal headache if spinal fluid leaks during placement (spinal injections)
How do epidurals work?
A continuous infusion of anesthetic plus opiate injected via a catheter into epidural space (between L4-L5)
blocks pain but still feels pressure
When is an epidural given?
once patient has entered active labor
How are spinal injections given?
injection of anesthetic directly into subarachnoid space (spinal fluid)
easier procedure than epidural and totally blocks sensation
How long do spinal injections last?
2-4 h
What should you assess for in the first stage of labor?
review prenatal hx & labs
culture, language, religion
labor status (contractions, membranes, cervix)
fetal status - FHR, amniotic fluid color/odor
brown, green, yellow color (indicated baby passed stool or could be sign of problem - baby stressed - so do assessments)
maternal status
birth plans
support, coping, comfort
nutrition, hydration
phase of labor (latent, active, transition)