MLP II Unit 4: Chemistry
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
POC tests in the medical office
Glucose
A1C
Cholesterol
Blood chemistry
Quantitative measurement of chemical substances in the plasma
POCT Chemistry Analyzers
Accu-Check glucometers
A1c Now (for HgA1c)
Cholestetech LDX Cholesterol System
Each machine has an operating manual, personnel for on-site training, and sometimes instructional DVDs to help the staff using them
It is important to learn your analyzers b/c improper use causes false results!
Quality Control
The goal of chem testing is to obtain ACCURATE results!
We can guarantee accuracy through QC
Two methods of QC: calibration and controls
Controls
A control is a solution similar to patient sample with a known result — usually an acceptable range
We use this to determine if reagents are performing properly
We also use to detect errors in technique by person performing test
Two levels:
Low/normal AKA level 1
High AKA level 2
When controls don’t work
Expired reagents/strips
Improper storage
Errors in technique used to perform test
Cannot run patient samples until controls work
According to CLIA, controls should be performed each day the test is done on a patient sample
Calibration
Used to check precision & accuracy of machine
Detects errors caused by lab equipment not working properly
Performed using a standard — usually a strip or cassette inserted in analyzer
Standards have EXACT known measurements — not an acceptable range like QC
If results are what we expect them to be, machine is in good condition
If not, patient samples shouldn’t be run until issue is fixed
Calibration frequency should be at least every 6 month according to CLIA
Usually at least when you use a new lot number
Glucose
Glucose is the end product of carb metabolism, required for energy
Ingested glucose not needed is stored as glycogen in muscle and liver
When no more tissue storage is possible, it is converted to triglycerides and stored as adipose tissue
Insulin is a hormone secreted in pancreas required for normal use of glucose in body
Needed to convert glucose to energy and also to glycogen
Normal glucose levels are necessary for homeostasis
Diabetes is the most common disease that affects glucose levels
Other diseases:
Pancreatitis
Endocrine disorders
Chronic renal failure
Type 1 Diabetes
AKA juvenile diabetes
Inherited disorder, usually presents before 18
Autoimmune disease — body attacks beta cells of the pancreas
When beta cells are 80% destroyed, pancreas does not secrete enough or any insulin to manage blood glucose levels
No way to prevent
Tx is insulin injections or insulin pump
Type 2 Diabetes
Adult-onset, lifestyle related
Insulin is available but not used correctly by the body
Treatments are lifestyle changes, oral medication, only insulin shots when other treatments don’t work
Both types of diabetes can cause serious complications with nerves, kidneys, eyes, circulation, and more
Diabetes S&S
Elevated fasting blood glucose (>140 mg/dL)
Polyuria
Polydipsia
Blurred vision
Positive glucose & ketones on UA dipstick
Fasting Blood Glucose
Normal FBG is 70-100 mg/dL
Fasting = 10-14 hours with nothing to eat or drink (only water)
This can be a POC test, done on glucometer with capillary blood (or venipuncture, analyze plasma)
As with all CLIA tests, you must perform normal and abnormal controls on each day of use & they must work!
Check lot numbers and expiration dates on strips & controls, make sure to use the same brand of strips as your glucometer
If FBG is elevated, provider can order a glucose tolerance test (GTT)
Provider usually makes diagnosis based on two or more elevated FBG results and results of GTT
3 Hour Glucose Tolerance Test
Draw FBG when patient arrives — if too high, physician may not continue test
Give patient oral glucose drink (usually contains 100 g of glucose)
Instruct patient they have 5 minutes to drink it, bring bottle up when finished
When the patient is finished with the drink, start timer for 1 hour
At 1 hour, draw patient’s blood then set timer for another hour
After 1 hr, blood glucose should be 139 mg/dL or less
At 2 hours, draw patient’s blood then set another 1 hour timer
At 3 hours, draw patient’s blood and let patient leave
During the test, patients cannot walk around, smoke, or eat
Provider will look at glucose results from all three draws to determine glucose tolerance
This is often done on pregnant women who fail the 1 hour GTT to diagnose gestational diabetes!
HgA1C
Used to monitor average glucose levels over a three month period — gives more in depth look rather than one FBG
Measuring the amount of sugar that has absorbed on the RBC membrane
Performed no more frequently than every 3 months — remember the average lifespan of an RBC is about 120 days
For diabetic patients, the goal is to have HgA1C below 7%
Non-diabetic should be 4-6%
CLIA-waived test uses capillary blood, quick and easy
Cholesterol
Waxy, fat (lipid) essential for body functions
Essential for cell membranes and production of hormones and bile
Most produced by liver, but some comes from diet
Amount of cholesterol affected by genetics and consumption of fat
Can cause atherosclerosis — build up of fatty plaque on walls of arteries
Can lead to heart attack, stroke, coronary artery disease
Hypothyroidism can also cause elevated cholesterol!
LDL
Picks up cholesterol from liver and ingested fats and deposits in blood vessels
This causes atherosclerosis
“Bad” or “Lousy” cholesterol
HDL
Removes excess cholesterol from cells/blood vessels and carries to liver to be removed
Lowers cholesterol buildup in arteries, reduces risk for CAD
“Good” or “Healthy” cholesterol
Ideal is greater than 60 mg/dL
Men - <40 and women - <50 = greater risk for heart disease
Cholesterol testing
All adults over 20 should have a total cholesterol tested once every 5 years
Cholesterol tests are screening tools to see if patient is at risk for CAD
Total cholesterol should be below 200 mg/dL
HDL is also measured, because low HDL increases risk for CAD
LDL is a calculation of HDL and total cholesterol
Patients do not need to fast for this test
Triglycerides
Fat in the blood related to caloric intake
Elevated levels typically stored in belly, associated with central obesity
Comes from two sources
Glucose
Diet
Normal range is below 150 mg/dL
If triglycerides are consistently elevated it suggests greater risk for CAD
Patients DO need to be fasting for this test!
Conditions with elevated triglycerides:
Obesity
Type 2 diabetes
Physical inactivity
Excessive alcohol consumption
Smoking
Hypothyroidism
Kidney disease
Liver disease
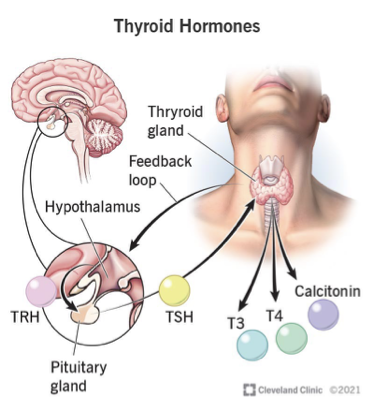
Thyroid testing
Thyroid located in anterior neck, produces T3 and T4
Primary hyper/hypothyroidism
Pituitary gland in brain controls thyroid by secreting thyroid stimulating hormone or TSH
Secondary hyper/hypothyroidism
Hypothalamus in brain controls this entire process by secreting thyroid regulating hormone or TRH
Tertiary hyper/hypothyroidism
Deficiencies in this process are called hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) or hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) and can be caused by genetics or autoimmune diseases
Hypothyroidism
Underactive thyroid
Genetics or autoimmune
Autoimmune = Hashimoto’s
S&S
Weight gain
Fatigue
Dry skin
MANY more!
Hyperthyroidism
Overactive thyroid
Genetics or autoimmune
Autoimmune = Graves disease
S&S
Weight loss
Exophthalmos
Cardiac arrhythmias
Menstrual irregularities
Sleep problems
MANY more!
Kidney function tests
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN)
Urea is the end product of protein metabolism
Normally present in blood and eventually excreted by kidneys
Problems with kidney usually = elevated urea (BUN)
Creatinine
A waste product of creatine phosphate (muscles)
Elevated in kidney problems
Commonly measured electrolytes
Sodium (Na) — conditions r/t = hypernatremia, hyponatremia
Potassium (K) — conditions r/t = hyperkalemia, hypokalemia
Falsely elevated in hemolyzed samples!!
Chloride
CO2
Panels
Physicians often order panels as part of physical or to diagnose disease:
Basic Metabolic Profile (BMP)
Comprehensive Metabolic Profile (CMP)
Renal Function Panel
Liver Function Panel
Lipid Panel
Basic Metabolic Profile (BMP)
Most common chemistry test ordered
Tests:
Glucose
Calcium
Electrolytes
Kidney function (BUN, Creatinine)
Used for screening or to monitor kidney function, diabetes management
Comprehensive Metabolic Profile (CMP)
Also commonly ordered
More in-depth than BMP because it measures protein and liver function
Tests:
Glucose
Calcium
Electrolytes
Protein
Kidney tests: BUN/Creatinine
Liver tests: ALT, AST, bilirubin, ALP
Renal Function Panel
BUN
Creatinine
Uric acid
Glucose
Liver Function Panel
ALP
GGT (liver specific enzyme, elevated in cirrhosis, severe liver damage)
AST
ALT
LDH
Bilirubin — can monitor separately in newborns
Helpful diagnosing and monitoring liver disease, more in-depth than CMP!
Thyroid Panel
T3
T4
TSH
Medication testing
Trough — medication level drawn before patient is to take his/her dose
Peak — medication level drawn 30 minutes after a dose of the medication
Specimen Collection Errors
Hemolysis
Exposure to light
Centrifugation
Drawing the wrong tube
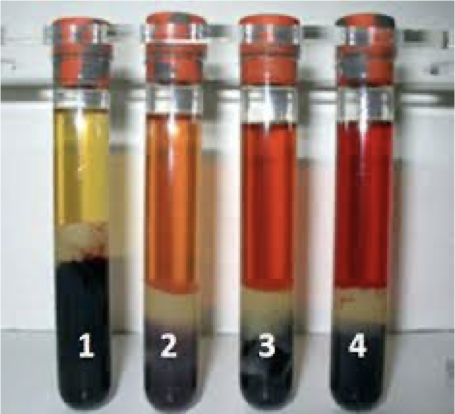

Hemolysis
Small needle, pulling too hard on syringe
Causes many errors in results, ESPECIALLY POTASSIUM (falsely increased)
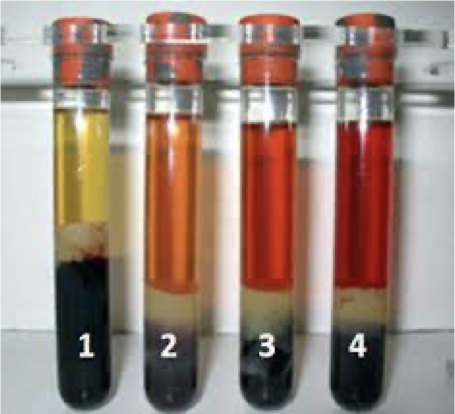

Exposure to light
Light breaks down bilirubin, causes falsely decreased bilirubin
Centrifugation
Not centrifuging promptly can cause intracellular RBC material to leach out into serum (falsely elevated potassium)
Drawing the wrong tube
Usually we draw a green tube for chemistry, but some tests require serum tubes or other special tubes