ARDMS SPI Practice Test - Forms A & B for Ultrasound Principles and Instrumentation
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
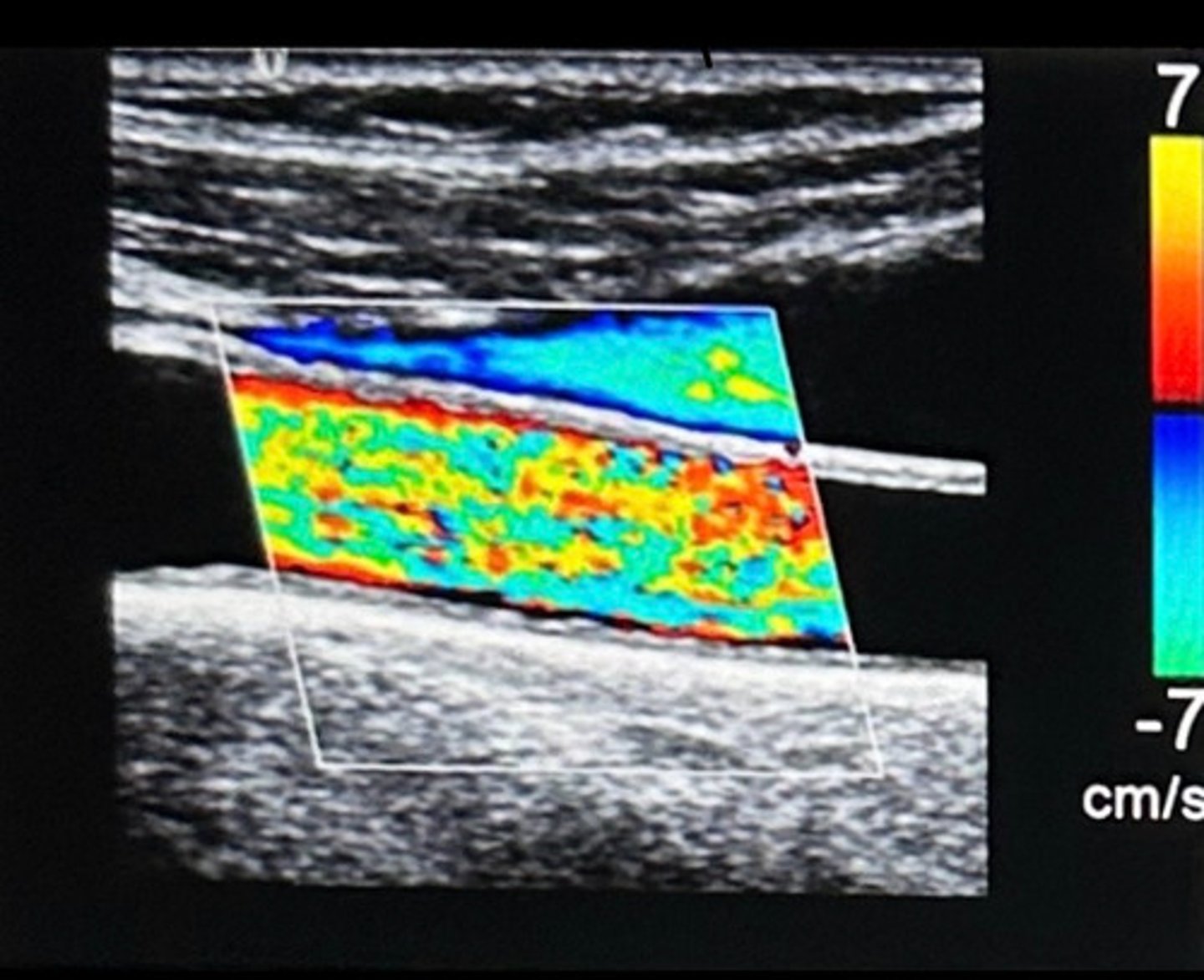
a. Change in vessel direction
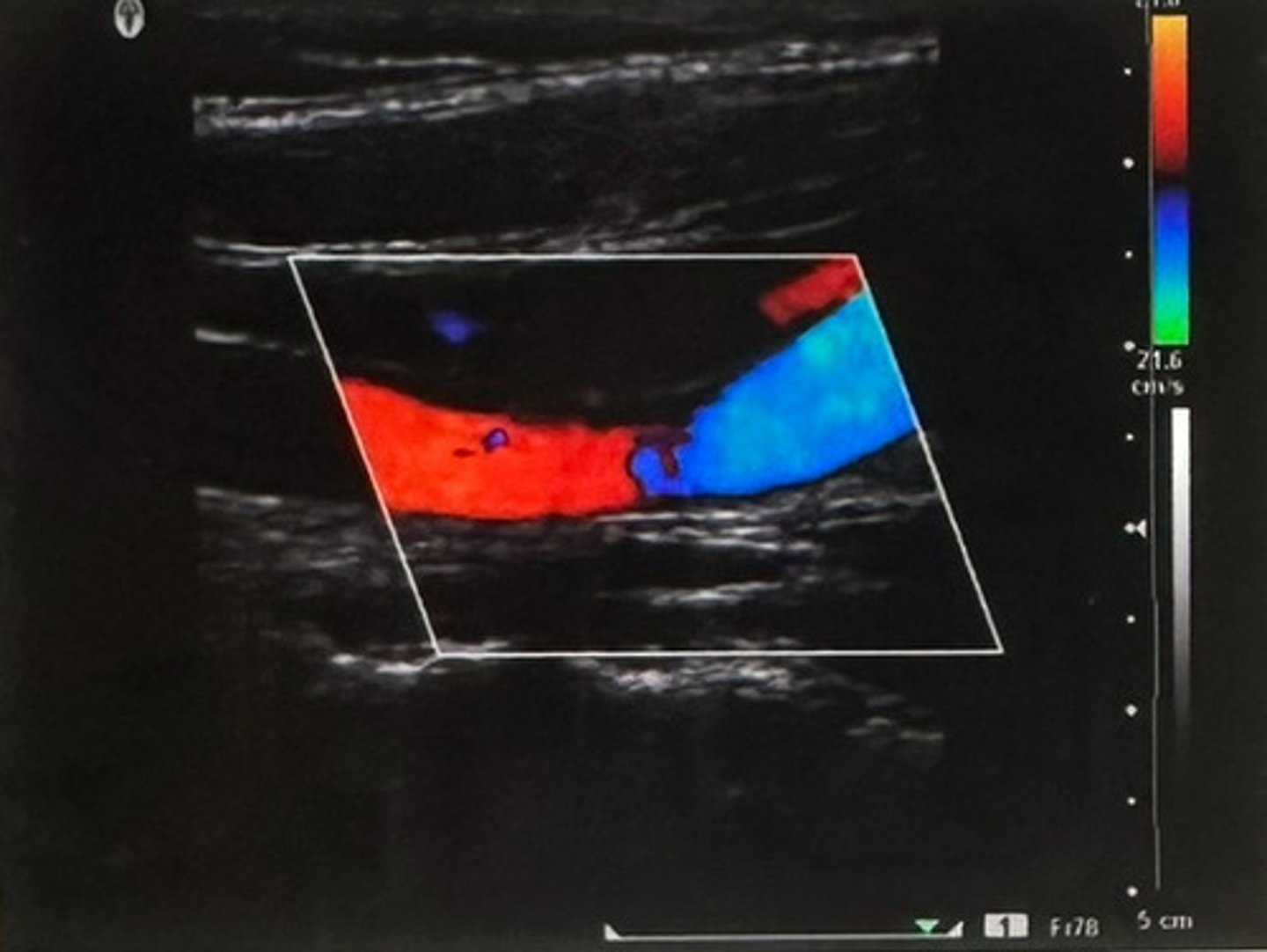
Which variable caused the color change from blue to red of the vessel in this image?
a. Change in vessel direction
b. Color scale set too low
c. Turbulent flow
d. Severe stenosis
C. Twice the transmitted frequency
With harmonic imaging, how does echo frequency relate to transmitted frequency?
A. Half the transmitted frequency
B. Equal to the transmitted frequency
C. Twice the transmitted frequency
D. Four times the transmitted frequency
A. Frequency
To which acoustic variable is penetration depth inversely related?
A. Frequency
B. Wavelength
C. Period
D. Propagation speed
D. Time-gain compensation
Which control improves the effects of attenuation?
A. Dynamic range
B. Pulse inversion
C. Multiple focal zones
D. Time-gain compensation
A. Phasic
Which term describes blood flow changes in response to respiration?
A. Phasic
B. Parabolic
C. Spontaneous
D. Pulsatile
D. Thickness
The center frequency of a transducer depends primarily upon which characteristic of the crystal?
A. Width
B. Length
C. Spacing
D. Thickness
B. Ability to sample depth
What is an advantage of using pulsed wave Doppler compared to continuous wave Doppler?
A. Higher echo sensitivity
B. Ability to sample depth
C. Decreased display of aliasing
D. Improved temporal resolution
A. 0 degrees
Which Doppler angle to flow results in the greatest absolute Doppler shift?
A. 0 degrees
B. 15 degrees
C. 45 degrees
D. 60 degrees
D. Spatial compounding
Which term describes the averaging together of scan lines from multiple angles to create one image?
A. Harmonic imaging
B. Real-time three-dimensional imaging
C. Elastography
D. Spatial compounding
B. B-mode
Which imaging modality can provide the most accurate measurement of tumor volume?
A. Color Doppler
B. B-mode
C. A-mode
D. m-mode
A. Transmit power
According to ALARA (as low as reasonably achievable) guidelines, which parameter should be minimized?
A. Transmit power
B. Frequency
C. Time gain compensation
D. Overall gain
A. By observing spaces between reflectors perpendicular to the beam
How is lateral resolution determined for pulsed-echo system using a tissue-mimicking test object?
A. By observing spaces between reflectors perpendicular to the beam
B. By observing spaces between reflectors along the beam path
C. By observing position of deepest visible reflector along the beam path
D. By observing position of deepest visible reflector perpendicular to the beam path
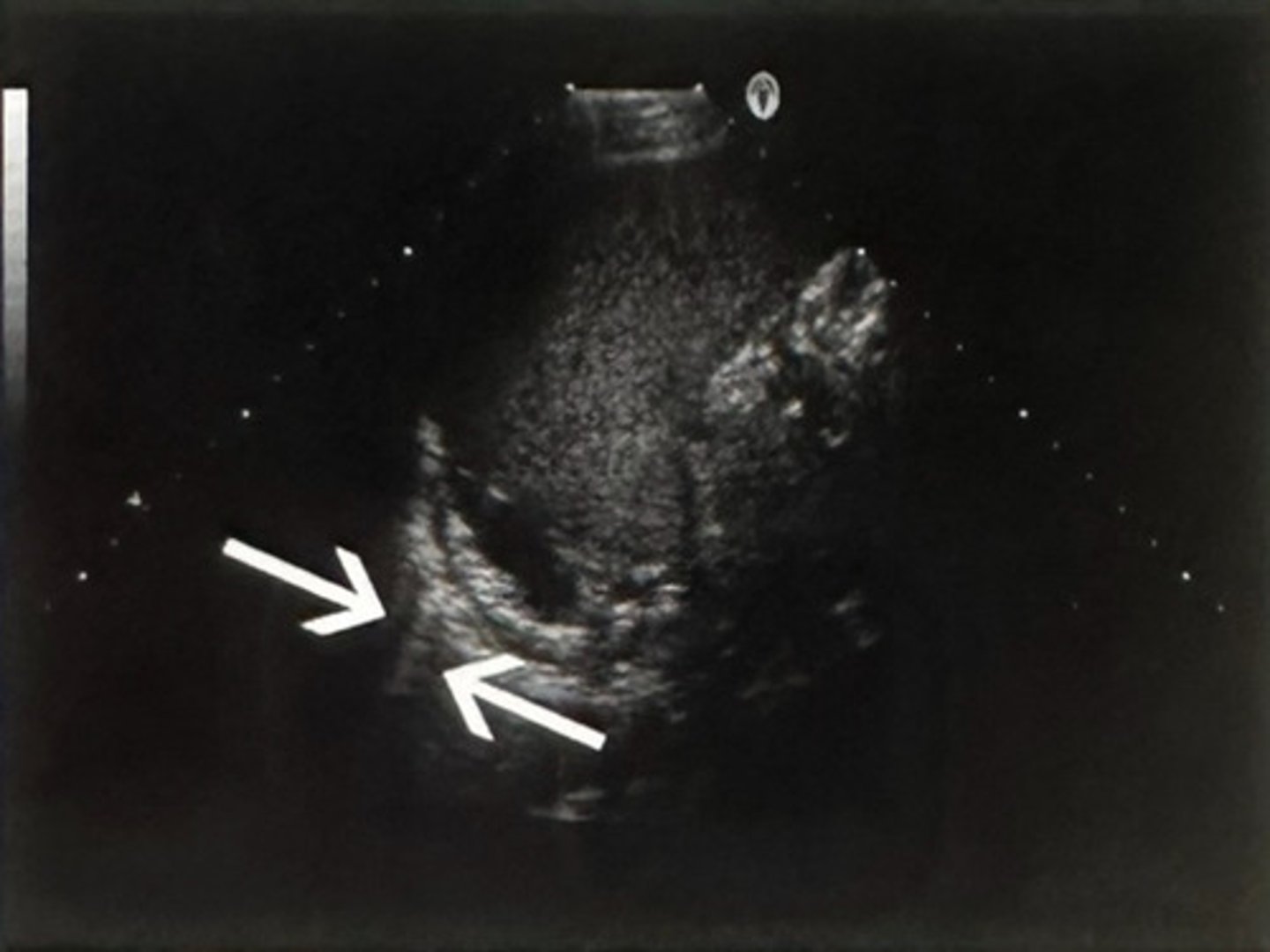
C. Comet tail
Which artifact is indicated by the arrows in this image?
A. Shadow produced by the diaphragm
B. Acoustic enhancement
C. Comet tail
D. Mirror image
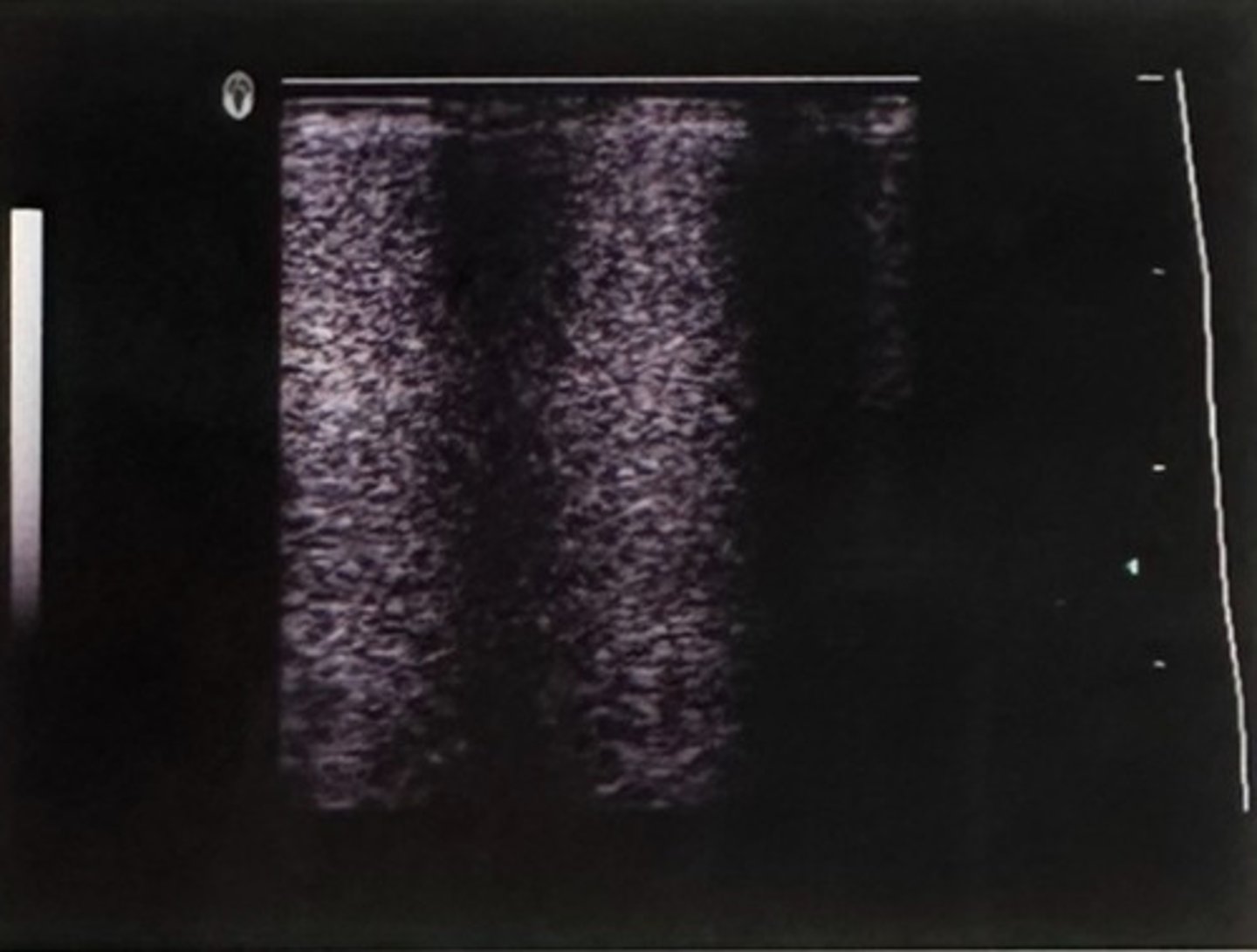
C. Transducer crystals are damaged
What is demonstrated in this image produced by a linear array transducer placed on a uniform tissue-mimicking phantom?
A. Time gain compensation not set correctly
B. System has low dynamic range
C. Transducer crystals are damaged
D. Focus control is malfunctioning
B. Minimizes effect of attenuation artifacts
Which statement is most accurate regarding surface rendering three-dimensional ultrasound imaging?
A. Improves accuracy of volume measurement
B. Minimizes effect of attenuation artifacts
C. Spatial resolution improve when using high resolution mesh
D. Feature-based reconstruction store full three-dimensional volume acquired
D. Depth of visualization
Which parameter is most likely to affect spatial resolution?
A. Dynamic range
B. Beam width
C. System sensitivity
D. Depth of visualization
A. Small acoustic impedance mismatch
Which variable can cause an acoustic shadow artifact?
A. Small acoustic impedance mismatch
B. Refraction
C. Perpendicular incidence
D. Low attenuation
D. Decreased penetration
What is the potential effect of increasing the pulse repetition frequency (PRF)?
A. Depth ambiguity
B. Decreased frame rate
C. Poor spatial resolution
D. Decreased penetration
D. Provides depth specificity
What is an advantage of using pulsed-wave Doppler versus continuous-wave Doppler?
A. Allows measurement of higher velocities
B. Increases range ambiguity
C. Reduces the potential for aliasing
D. Provides depth specificity
A. Lateral resolution
What does coded excitation improve in addition to penetration?
A. Lateral resolution
B. Signal-to-noise ratio
C. Frame rate
D. Dynamic range
A. Fat
When using a 5 MHz transducer, in which tissue is the ultrasound wavelength the shortest?
A. Fat
B. Blood
C. Bone
D. Muscle
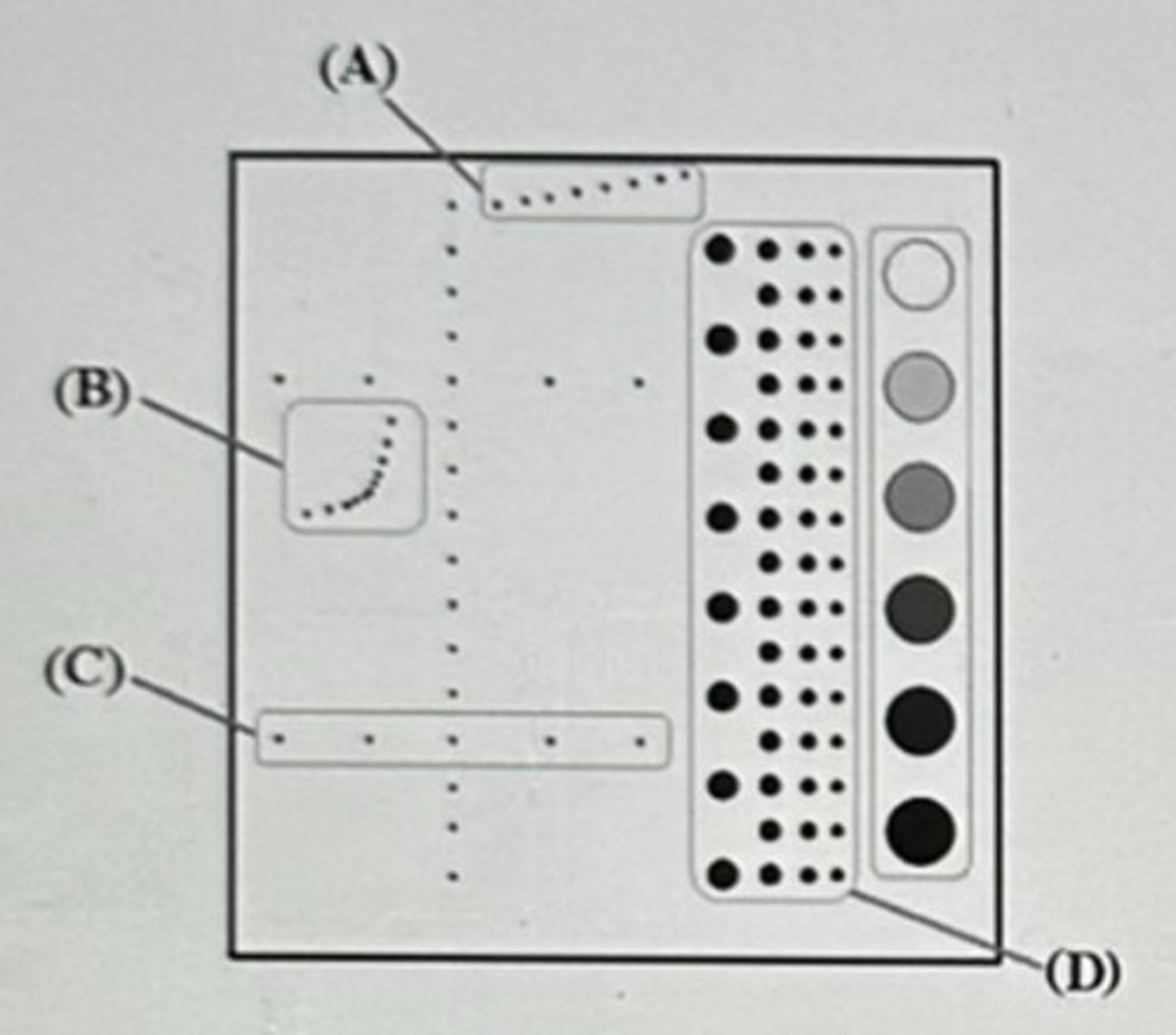
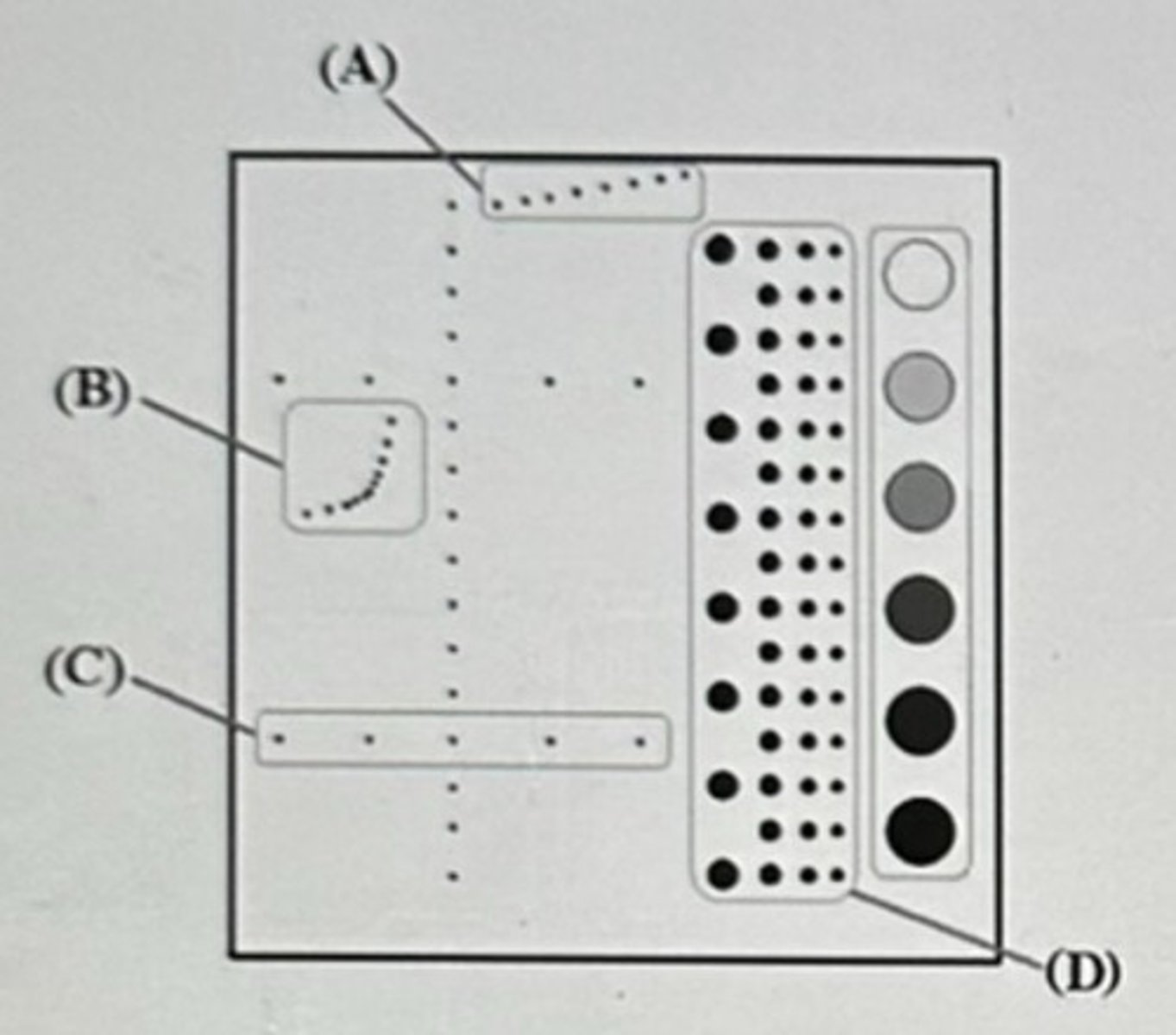
D. Horizontal distance accuracy
Which parameter is target group C evaluating based on this image?
A. Dead zone
B. Dynamic range
C. Axial resolution
D. Horizontal distance accuracy
C. Output power
Which ultrasound parameter directly affects an ultrasound beam's intensity?
A. Time gain compensation
B. Operating frequency
C. Output power
D. Frame rate
B. Packet size
An increase in which parameter will improve the accuracy of velocity measurements with autocorrelation?
A. Color field of view
B. Packet size
C. Wall filter setting
D. Transmitted frequency
D. Transducer aperture
Which affects the beam width in the near field?
A. Pulse repetition frequency
B. Pulse duration
C. Frame rate
D. Transducer aperture
B. Pulsed wave Doppler
Which imaging mode requires a broadband transducer?
A. Continuous wave Doppler
B. Pulsed wave Doppler
C. Color flow imaging
D. Harmonic imaging
C. Aperture that increases with increasing focal depth
What is a dynamic aperture?
A. Aperture that varies with transmit frequency
B. Aperture that decreases as a function of time
C. Aperture that increases with increasing focal depth
D. Aperture that changes as a function of frame rate
B. Adjusting the baseline
What change would minimize the artifact observed in this image, assuming the pulse repetition frequency is at its maximum limit?
A. Adjusting the sweep speed
B. Adjusting the baseline
C. Increasing the dynamic range
D. Increasing the transmitted frequency
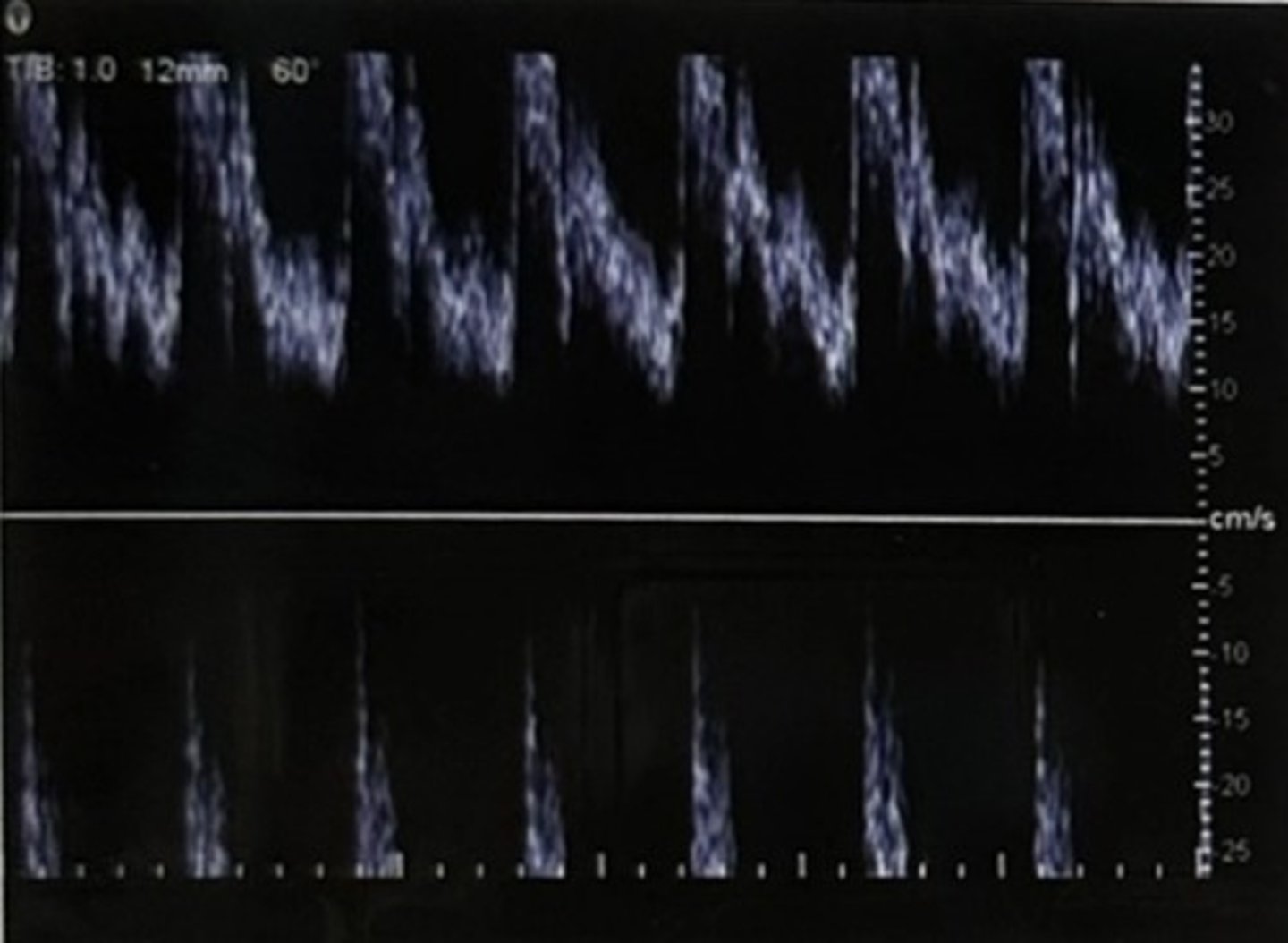
C. Speed of sound in tissue
Which factor limits image frame rate?
A. Transducer operating frequency
B. Sample volume size
C. Speed of sound in tissue
D. Spatial pulse length
B. Difference between the transmitted ultrasound frequency and the received ultrasound frequency
What is the Doppler Shift frequency?
A. Received ultrasound frequency multiplied by the transmitted ultrasound frequency
B. Difference between the transmitted ultrasound frequency and the received ultrasound frequency
C. Sum of the transmitted and received ultrasound frequency
D. Ratio of the transmitted ultrasound frequency to the received ultrasound frequency
D. Propagation speed of the medium
Which factor determines the displayed depth of a reflector?
A. Transducer frequency
B. Acoustic impedance
C. Pulse repetition frequency
D. Propagation speed of the medium
A. A
In this image, which target group is used to evaluate dead zone?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
C. Laminar
When a fluid is flowing at a slow and constant rate within a long tube having a uniform diameter, which is the nature of flow?
A. Disturbed
B. Turbulent
C. Laminar
D. Pulsatile
D. Continuous wave Doppler
Which imaging mode requires two elements mounted side by side?
A. M-mode
B. B-mode
C. Pulsed wave Doppler
D. Continuous wave Doppler
A. Edge enhancement
Which technique increases the sharpness of high contrast boundaries?
A. Edge enhancement
B. Interpolation
C. Smoothing
D. Frame averaging
D. 8 MHz
Which frequency is best to evaluate structures lying 1 to 2 cm from the transducer?
A. 2 MHz
B. 4 MHz
C. 6 MHz
D. 8 MHz
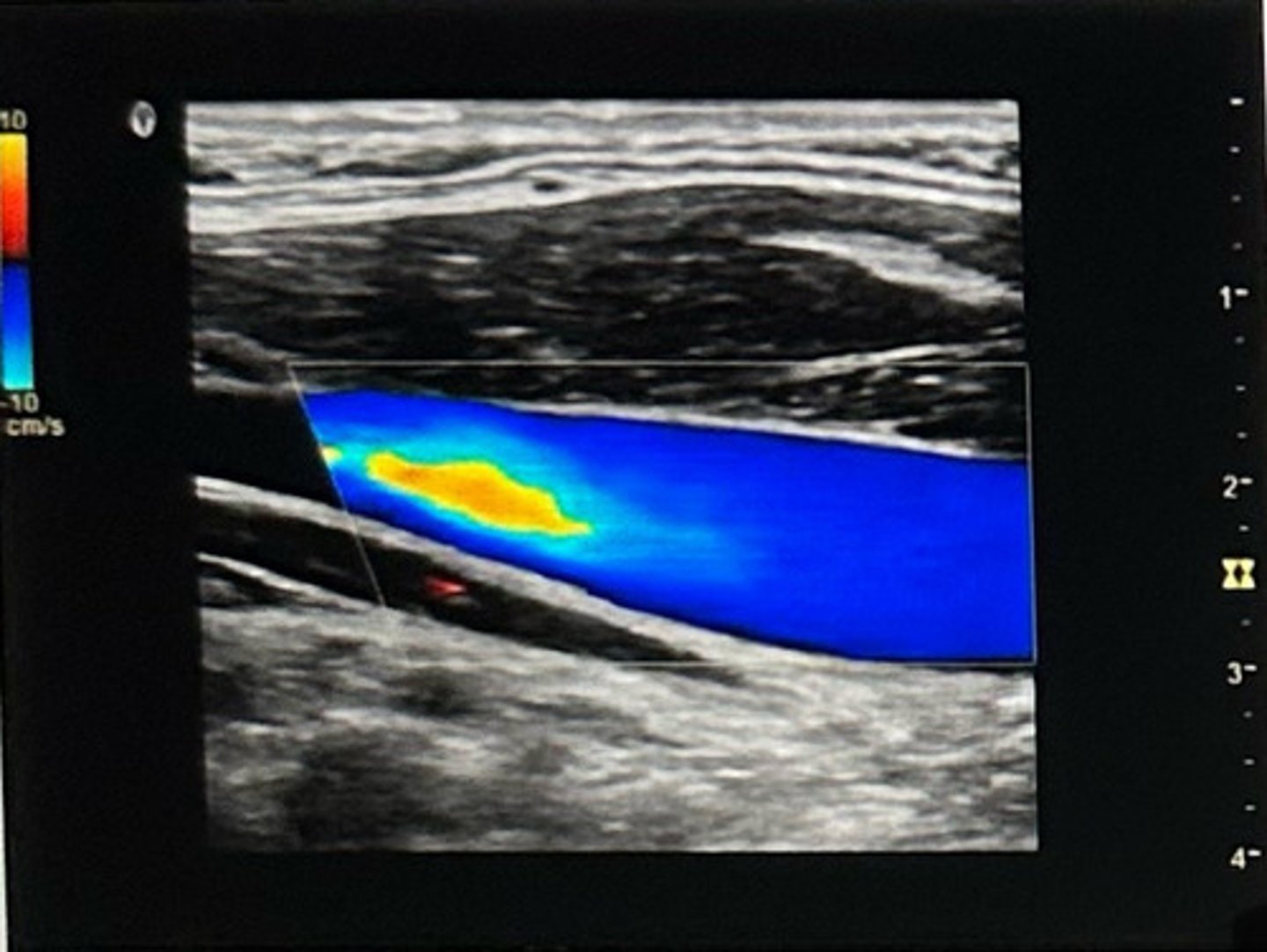
B. Left to right
In which direction is blood flowing in this image?
A. Right to left
B. Left to right
C. Bidirectional
D. Indeterminate
C. 8 kHz
What is the Nyquist limit if a pulsed-wave Doppler instrument has a pulse repetition frequency of 16 kHz?
A. 32 kHz
B. 10 kHz
C. 8 kHz
D. 5 kHz
C. Dynamic
When the focal point in a B-mode image is electronically changed, which type of focusing is in use?
A. Lens
B. Mechanical
C. Dynamic
D. Curved crystal
D. Increased Nyquist limit
Which factor reduces the likelihood of aliasing in pulsed wave spectral Doppler?
A. Increased sample volume depth
B. Increased frequency
C. Increased velocity
D. Increased Nyquist limit
A. 180 degrees
Which angle of isolation to blood flow produces the maximum Doppler shift?
A. 180 degrees
B. 150 degrees
C. 90 degrees
D. 45 degrees
A. Source and receiver moving at the same speed and direction
Which scenario will produce no Doppler shift to the receiver?
A. Source and receiver moving at the same speed and direction
B. Source moving toward receiver
C. Source moving away from receiver
D. Receiver moving toward source
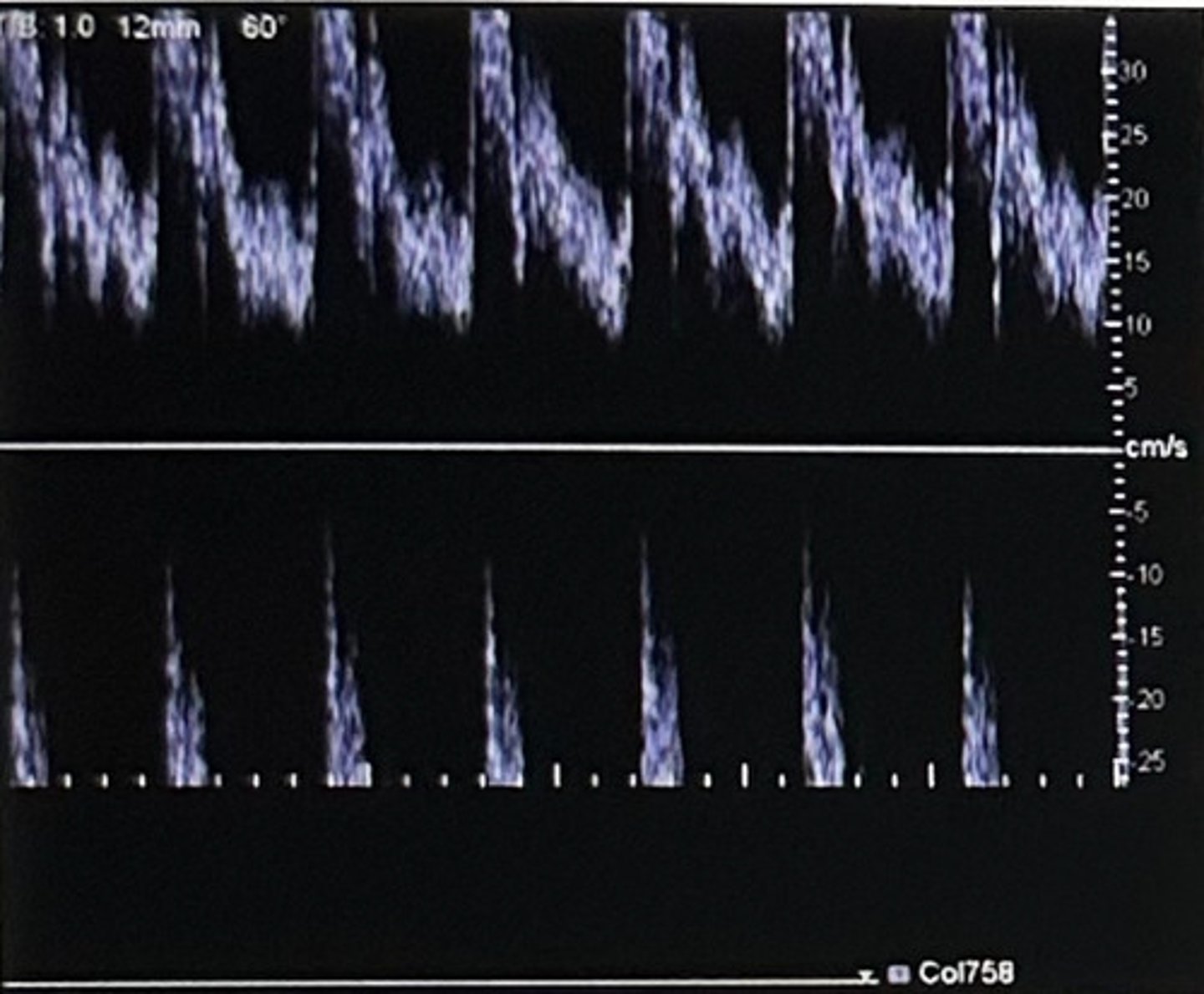
B. Aliasing
Which finding is demonstrated in this image?
A. Wall filter saturation
B. Aliasing
C. Range ambiguity
D. Reversal of flow
D. Surface rendering
Which technique results in a three-dimensional image?
A. Elastography
B. Harmonics
C. Spatial compounding
D. Surface rendering
A. Dynamic range
Which setting of an ultrasound system gives the sonographer the ability to display both strong and weak echoes?
A. Dynamic range
B. Resolution
C. Range calibration
D. Sensitivity
C. Increase color packet size
Which adjustment would eliminate the color artifact demonstrated in this image?
A.
B.
C.
D.
C. Coded excitation
Which technique utilizes frequency modulation of the transmitted pulse to improve signal-to-noise ratio?
A. Apodization
B. Panoramic imaging
C. Coded excitation
D. Spatial compounding
B. Absorption
Which type of interaction between sound and tissue is most affected by the thermal index (TI)?
A. Reflection
B. Absorption
C. Scattering
D. Refraction
A. Improper time gain compensation
What is the most common cause of localized vertical nonuniformity in a real-time B mode image?
A. Improper time gain compensation
B. Defective transducer elements
C. Faulty preamplifier
D. Malfunctioning scan converter
D. Thickness
What determines the center frequency of a transducer?
A. Diameter
B. Shape
C. Matching layer
D. Thickness
A. Bone
A sound wave propagates fastest through which substance?
A. Bone
B. Muscle
C. Fat
D. Gas
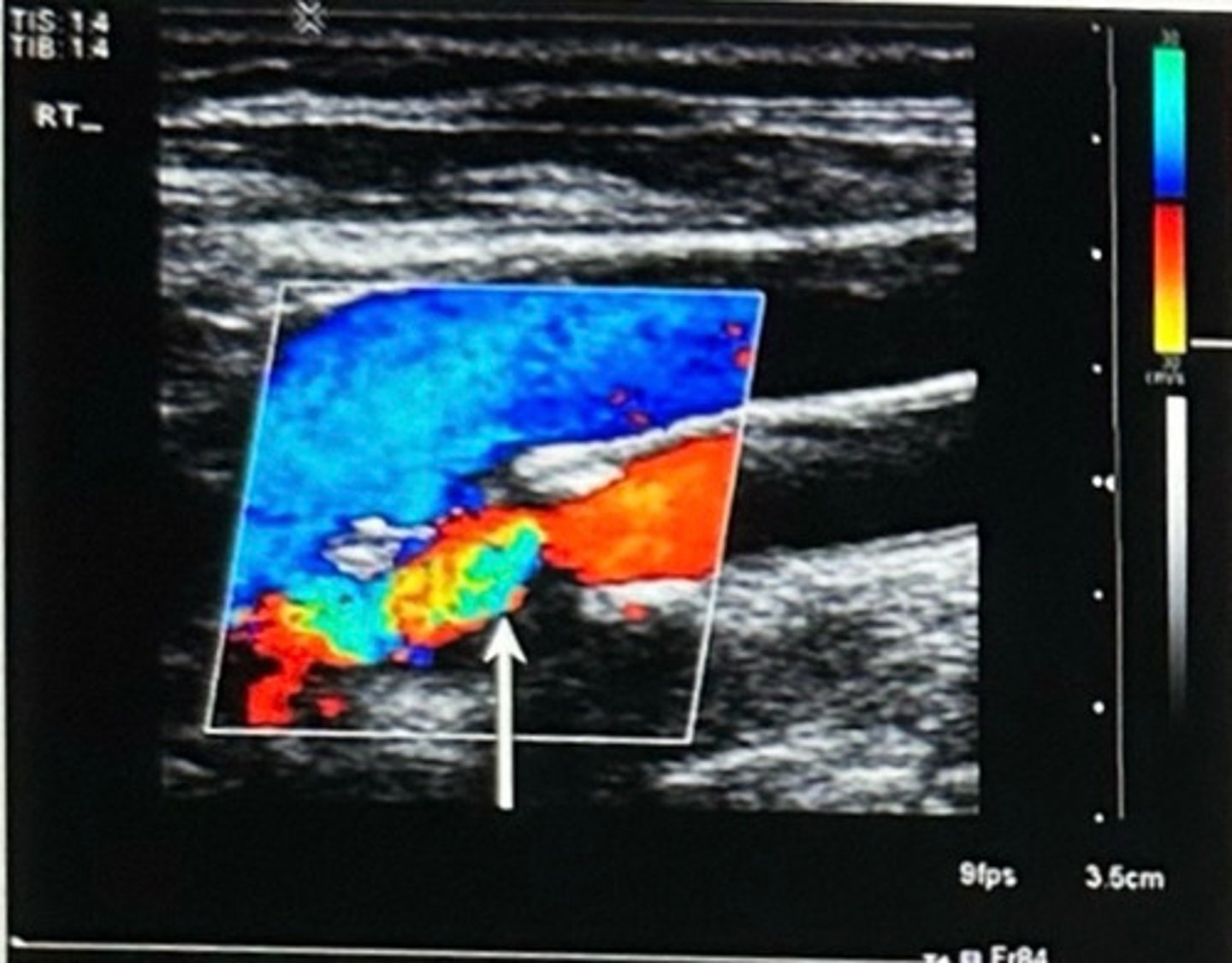
B. Aliasing
What caused the color pattern demonstrated in the artery indicated by the arrow in this image?
A. Superimposed venous flow
B. Aliasing
C. Flow reversal
D. Color side lobe artifact
D. Increasing the transducer frequency
Which action can improve axial resolution of a displayed image?
A. Increasing the pulse repetition frequency
B. Reducing the receiver gain
C. Changing the gray-scale map
D. Increasing the transducer frequency
C. A difference in tissue propagation speeds
Which condition must be present for refraction to occur?
A. The presence of a strong specular reflector
B. The presence of several small reflectors
C. A difference in tissue propagation speeds
D. A change in the angle of reflection
A. Time gain compensation
Which control allows adjustment for attenuation at specific depths?
A. Time gain compensation
B. Depth
C. Output power
D. Dynamic range
B. Improves dynamic range
How does frequency compounding improve image quality?
A. Increases frame rate
B. Improves dynamic range
C. Reduces speckle
D. Reduces overall gain
C. Near field
In an unfocused transducer, which term defines the region between the transducer face and the point where the beam diverges?
A. Side lobe
B. Focal zone
C. Near field
D. Far field
B. Frame rate
Which variable decreases when the number of acoustic lines per frame is increased without changing the maximum depth?
A. Spatial pulse length
B. Frame rate
C. Pulse repetition frequency
D. Receiver dynamic range
C. Reverberation
Which artifact is illustrated by this image?
A. Shadowing
B. Side lobe
C. Reverberation
D. Mirroring
B. Increased amplitude of the returning Doppler signals
Which of the following is a benefit of using contrast agents?
A. Output power can be increased after contrast administration to improve visualization
B. Increased amplitude of the returning Doppler signals
C. Harmonic signals produced by contrast agents are weaker than those produced by soft tissue
D. Frame rate is improved when interrogating contrast with power Doppler imaging