Brain & Cognition 1
1/117
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Mostly brain anatomy terminology, feels important to know those off the top of your head (aka the..... parietal lobe (💀))
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
Glial cells
Cells that assist neurons
Ependymal cells
produce cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Astrocytes
Glial cells providing structural support and involved in nutrient transfer and maintaining the blood-brain barrier.
Oligodendroglia
glial cells that myelinate axons in the central nervous system.
Schwann cells
Cells that myelinate axons in the peripheral nervous system.
Resting potential
The electrical potential across a neuron's membrane when it is not being stimulated.
Action potential
A rapid reversal of the membrane potential that propagates along the axon.
Excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSP)
Changes that depolarize the postsynaptic membrane and increase the likelihood of action potential.
Inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSP)
Changes that hyperpolarize the postsynaptic membrane and decrease the likelihood of action potential.
Neurotransmitters
Chemicals that transmit signals across a synapse from one neuron to another.
Ionotropic receptors
Receptors that allow ions to enter the postsynaptic neuron upon binding of neurotransmitters.
Metabotropic receptors
Receptors that activate G-proteins to influence other cellular processes upon neurotransmitter binding.
Diffusion (in neurotransmission)
The movement of neurotransmitters away from the synaptic cleft.
Cholinergic neurons
Neurons that secrete acetylcholine.
Adrenergic neurons
Neurons that secrete epinephrine (adrenaline).
Peptide
Chains of amino acids
Psychoactive drugs
Substances that alter mood, thought, and behavior.
Wanting-and-liking theory
The notion that wanting (craving) and liking (pleasure) are different processes in drug use.
Neuroplasticity
The nervous system’s ability to change in response to the environment
3 systems that peripheral nervous system controls
Somatic nervous system
Autonomic nervous system
Enteric nervous system
2 parts that central nervous system controls
Brain stem
Spinal cord
Somatic nervous system (SNS)
Carries somatic information to CNS from muscles and skin, and carries info TO them to produce movement
Autonomic nervous system (ANS)
Sympathetic (flight or flight) and parasympathetic (rest and digest) responses.
Enteric nervous system (ENS)
Controls the gut, occasionally gets commends from CNS via ANS, but mostly autonomous
Afferent flow of neural information
Incoming information into the CNS
Efferent flow of neural information
Outgoing information away from the CNS
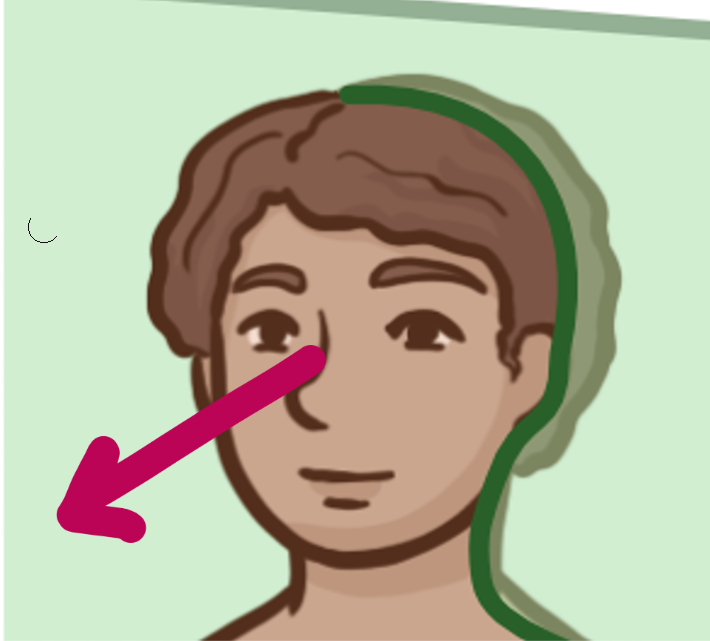
Which brain-body orientation is this
Anterior
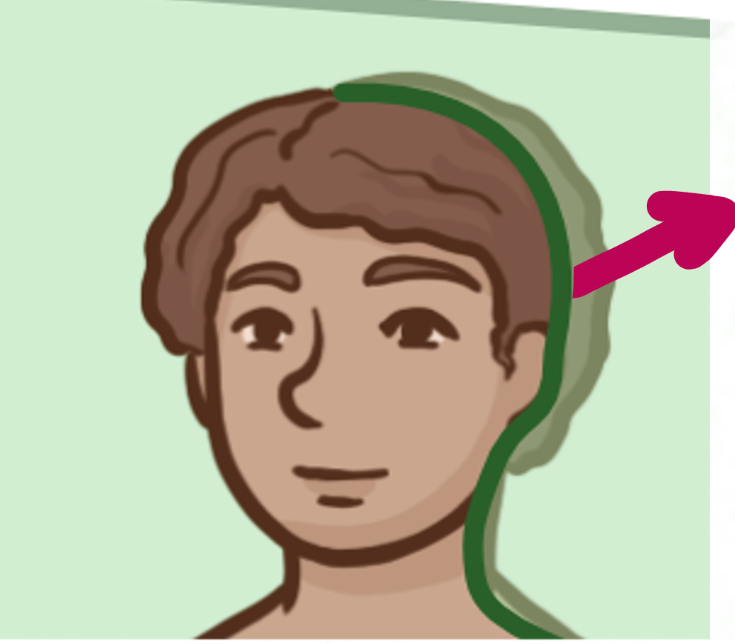

Which brain-body orientation is this
Posterior
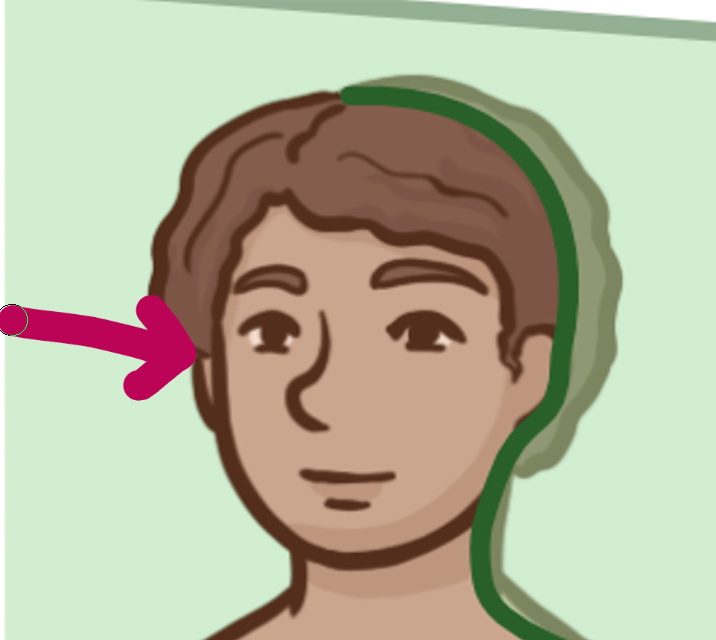

Which brain-body orientation is this
Medial
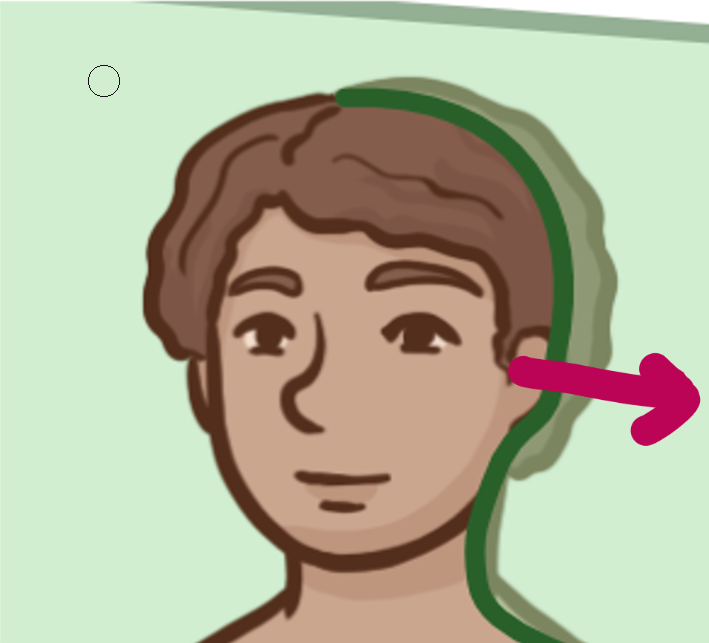
Which brain-body orientation is this
Lateral
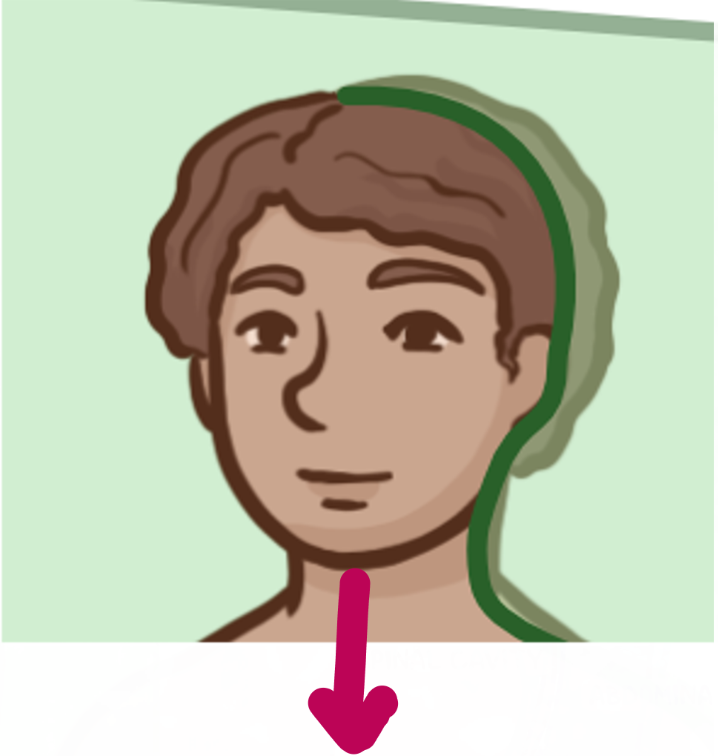
Which brain-body orientation is this
Ventral
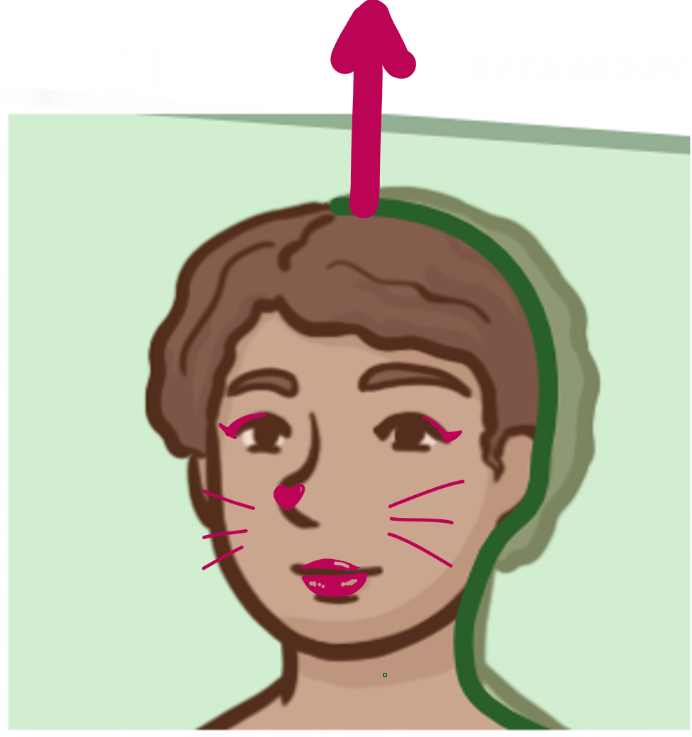
Which brain-body orientation is this
Dorsal
Coronal section of brain
Vertical plane (stubby slice, like when cutting a cucumber)
Sagittal section of brain
Long slice (side profile of head w/ brain)
Horizontal section of brain
Top-down view of brain (egg-shaped)
Caudal/ posterior
Towards tail of animal/ human backside

“Inferior”
(Scar has nothing to do with this acc)
Below
Superior
Above
Meninges (and what are the layers)
Protective tissue over brain
Dura mater - hard outer layer
Arachnoid layer - delicate spiderweb layer
Pia mater - moderately tough inner layer on brain itself
The 4 lobes in either hemisphere
Frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital
Which of the 4 lobes is most anterior?
Frontal lobe
Which of the 5 lobes is most dorsal?
Parietal lobe
Which of the 4 lobes is most posterior?
Occipital
Which of the 4 lobes is most ventral?
Temporal
Cerebrospinal fluid (where in meninges is it found, and what’s its purpose)
Between arachnoid layer and pia mater
Cushions the brain
Frontal lobe function
Brain’s executive functions like decision-making
Parietal lobe function
Directing movements

Temporal lobe function
Learning: Short-term memory, hearing, language, music, facial recognition, emotional processing (literally everything that makes us human it seems)
Occipital lobe function
Visual processing
(more on that later, as we all know :’))
Gyrus (or gyri plural)
Protrusion/ bump in brain
Sulcus (or sulci plural)
Groove in brain wrinkles
Fissure
DEEP groove in brain wrinkles
Cerebrum
Like most of the brain, both hemispheres go into this. Excl. cerebellum, and brainstem!!
What are the 3 cerebral arteries?
Anterior
Middle
Posterior
Gray matter
Composed of cell bodies and capillary blood vessels
White matter
Nerve fibers
What causes a stroke
Insufficient blood supply to the cerebrum from one or more of the cerebral arteries
Corpus callosum
Nerve fibers that join the 2 hemispheres
Function of glial cells
Hold neurons in place so they can do their thing
Tract vs nerves
A collection of nerve fibers inside CNS vs outside.
As an embryo, the part that becomes the forebrain is called…
Prosencephalon
As an embryo, the part that becomes the midbrain is called…
Mesencephalon
As an embryo, the part that becomes the hindbrain is called…
Rhombencephalon
What are the 3 components of the hindbrain
Cerebellum
Pons
Medulla
Pons
Nuclei in pons receive input from cerebellum
What are the tectum and tegmentum from (and which chapter is this told in)
Midbrain roof and floor
Chapter 2
What are the 2 colliculi and what do they do?
Superior colliculi: Processes visual info from optic nerve
Inferior colliculi: Processes auditory info
also prompt ‘orienting movements’ i.e. turn to see what you heard
What are the 3 brainstem structures
Midbrain
Pons
Medulla
2 diencephalon structures
Thalamus (1 per hemisphere)
Hypothalamus
2 forebrain structures
Cerebral cortex
Basal ganglia
Which chapter explores the path that the olfactory system takes (albeit briefly)?
Chapter 2
What is the neocortex and how is it special?
it covers all the lobes, and is responsible for sensation, motor movements, and cognition. It has 6 layers (diff thickness for sensation and motor regions).
Special: Very complex, a filter for how information is processed before it’s acc processed (see a smiley face in the wall)
What are 3 structures in basal ganglia
Caudate nucleus
Putamen
Globus pallidus
Cranial nerves
Nerves that control sensory and motor functions of head. neck. and internal organs
Dermatome
Body segment (like spinal cord segment) that has sensory nerves
segmented like a worm 🪱
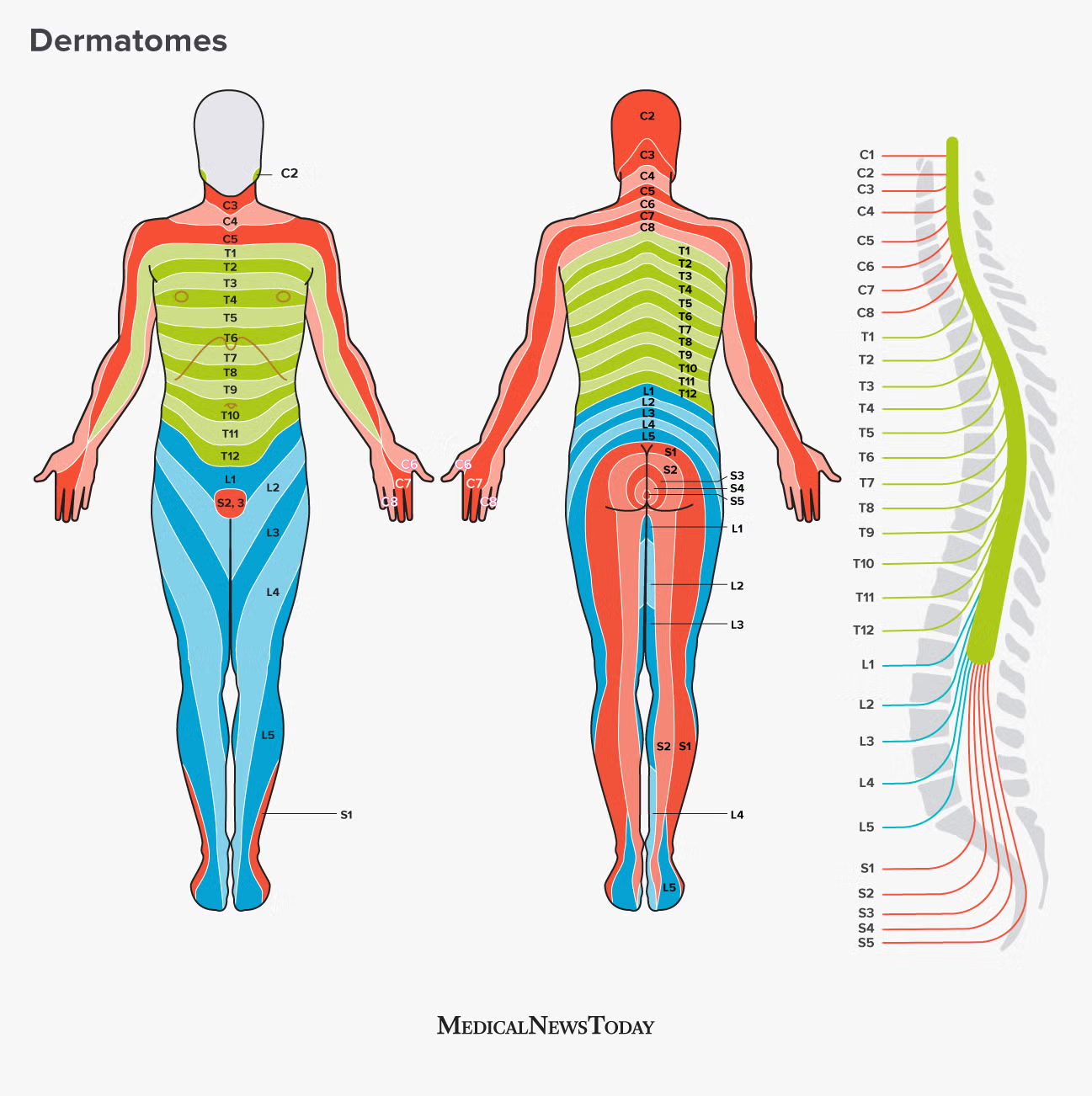
Are spinal nerves ipsilateral or contralateral
Ipsilateral
Where are the 10 principles of the nervous system listed?
Chapter 2 (at the end)
In which chapter are the MRI, CT scan, and those scanning methods explained?
Chapter 7
What are 3 structures that have layers (and a number in their abbreviation: primary ____s)
V1
S1
M1
What are the types of glial cells
Astrocytes
Oligodendrocytes - (you get points if you think you’d recognize this word among others, even if you can’t spell or pronounce it)

2 possible explanations for slow frontal lobe development
Aversive childhood experiences compromise the development
Decreased intelligence as you age = shitter frontal lobe
Basically it’s used less so it degenerates #brainrot
What are the 2 specialized functions of neurons
Sensory neurons - info from and to sensory receptors
Interneurons - Associate sensory and motor info in CNS
Motor neurons - Carry info from the brain and spinal cord to muscles
True or false: Glial cells repair the PNS and CNS
False. They only repair the PNS. The CNS is fked if it’s damaged.

In which chapter do you find the cell’s structure and anatomy?
Chapter 3
In which chapter do you find the details of protein synthesis?
Chapter 3
Where is the cingulate cortex
Above the corpus collosum

What sulcus separates the parietal and frontal lobes?
Central sulcus
What sulcus seperates the frontal and temporal lobes?
Lateral sulcus
Which lobe is Wernicke’s area in?
Temporal lobe
Which lobe is Broca’s area in?
Frontal lobe
Point all of these out for me rq
Good job!
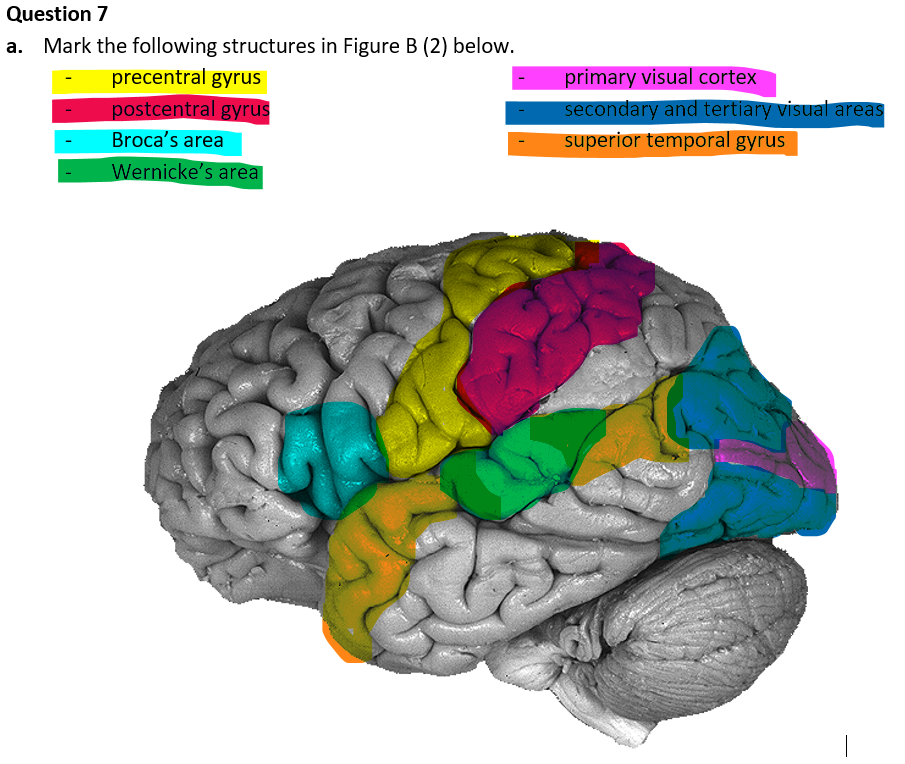
What does the precentral gyrus importantly include, and what’s its function?
Primary motor cortex (M1): voluntary movement

Broca’s area
Speech production

What does the postcentral gyrus importantly include, and what’s its function?
Primary somatosensory cortex (S1): Processing somatosensory info

What the superior temporal gyrus do?
Dibs on audio info
(First processing of auditory information")
What does Wernicke’s area do?
Language comprehension
What’s damaged if you can feel something, but can’t identify the object?
Superior parietal lobule
During embryogenesis, telencephalon becomes…
the whole cerebrum
During embryogenesis, diencephalon becomes…
the thalamus
During embryogenesis, metencephalon becomes…
the cerebellum + pons