Bacteriology final review
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
Which type of graph would best illustrate the timeline from pathogen exposure to onset of clinical signs?
Incubation graph
Which condition involves fungal infection of the guttural pouch and may lead to epistaxis in horses?
Guttural pouch mycosis
A gram-positive bacterial infection is most likely to be found in which group of animals due to their naive immune systems?
Piglets
What term describes organisms that can survive in both oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor environments?
Facultative anaerobe
What is the general term for a bacterial skin infection often seen in dogs?
Pyoderma
Which skin condition may be classified as surface, superficial, or deep depending on the layer of skin involved?
Pyoderma
Which of the following is a method of transmission that is not dependent on a pathogen's direct biology?
Blood transfusion, Vector
Which organism is most likely responsible for a yeast infection in a dog's ear?
[Awaiting correct organism—likely Malassezia pachydermatis]
What is the most common Staphylococcus species isolated from dogs?
Staphylococcus pseudintermedius
Which dermatophyte is most likely to be isolated from a cat with a fungal skin infection?
Microsporum canis
Which virulence factor enhances bacterial resistance to phagocytosis by forming clots around them?
Coagulase
Why do gram-positive bacteria retain the crystal violet stain during Gram staining?
They have a thick peptidoglycan layer
What species is most commonly associated with jaw infections in cattle?
Actinomyces bovis
A parakeet presents with budding yeast cells on cytology. What is the most likely diagnosis?
[Likely Candida species]
Which yeast species is commonly isolated from mucosal surfaces and can cause opportunistic infections?
Candida albicans
A dog presents with a pruritic lesion. Which fungal-like organism should be suspected?
Pythium insidiosum
What drug is commonly used to treat calf diphtheria caused by Fusobacterium necrophorum?
[Awaiting drug—common options include penicillin]
A goat is depressed and has "railroad track" Gram-positive rods on smear. What is the most likely diagnosis?
[Likely Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis or Arcanobacterium pyogenes]
What type of organism requires the absence of oxygen to survive and grow?
Obligate anaerobe
Which component of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is responsible for its endotoxic activity?
Lipid A
Which pathogen is associated with mucopurulent nasal discharge in horses?
Streptococcus equi (T. equi likely refers to S. equi subsp. equi)
Which condition represents the most severe form of cystitis?
C. cystitidis
A dog with a mottled liver and spiral-shaped, hooked bacteria is most likely infected with:
Leptospira interrogans
What is the most common outcome of campylobacteriosis in animals?
abortions
What organism is associated with conjunctivitis in guinea pigs?
Chlamydia caviae
Which gram-positive organism infects the brain stem and is associated with contaminated silage?
Listeria monocytogenes (not Lepto)
Which toxin prevents acetylcholine release at neuromuscular junctions?
Botulinum toxin
What is the most common cause of pinkeye in sheep?
Chlamydia pecorum
What is the common term for ulcerative posthitis in sheep, especially wethers?
Pizzle rot
What Listeria virulence factor allows it to escape from phagosomes?
Listeriolysin O
What is the causative agent of Thrombotic Meningoencephalitis (TME) in cattle?
Histophilus somni
Which pathogen grows over a wide temperature range and exhibits tumbling motility?
Listeria monocytogenes
Which bacterium causes facial dermatitis and nasal lesions in cats?
Cryptococcosis
Which species is the most resistant to tetanus?
Birds
Which pathogen is cultured in embryonated eggs and causes abortion in sheep?
[Likely Chlamydophila abortus]
What test differentiates Mycoplasma bovis from M. bovigenitalium?
[Awaiting test name—biochemical or PCR-based methods]
What is the significant single-titer cutoff point indicating Leptospira exposure or infection?
1:800
What confirmatory test is used for Brucella diagnosis?
Complement Fixation Test (CFT)
What is considered the gold standard diagnostic test for Leptospira?
Microscopic Agglutination Test (MAT)
What is the best method of urine collection for bacterial culture in small animals?
Cystocentesis
A sheep aborts at 42°C incubation. What is the most likely bacterial cause?
Campylobacter jejuni (tentative based on 42°C growth temp)
Which disease is characterized by muscle rigidity and spasms due to neurotoxin effects?
Tetanus
What is the most common cause of bovine infectious keratoconjunctivitis?
Moraxella bovis
What is a common bacterial cause of urinary tract infections in dogs?
Escherichia coli
What is a key pathogenic mechanism of Brucella species?
Intracellular survival and replication in macrophages
Joint fluid analysis can help diagnose which type of infections?
Septic arthritis or joint ill (pathogen varies)
Ewes with liver spots and comma-shaped bacteria are likely infected with:
Campylobacter fetus
What bacterial count in urine is considered diagnostic for a urinary tract infection?
>100,000 CFU/mL
What is the mechanism of ocular injury in equine recurrent uveitis (ERU)?
Immune-mediated inflammation
Which toxin is both hemolytic and necrotoxic?
Beta toxin
What is the correct classification for Shiga-toxin producing E. coli (STEC)?
STEC
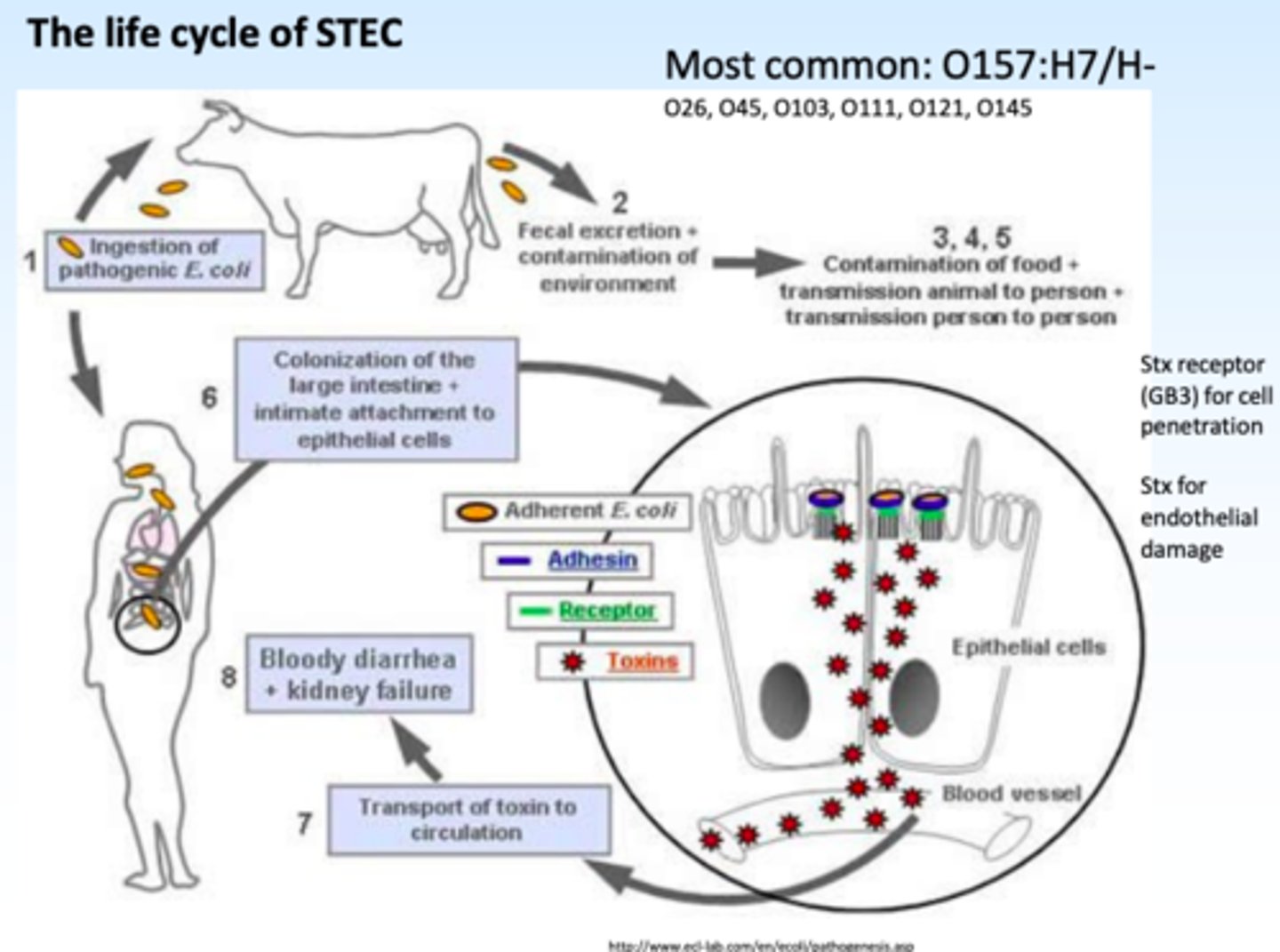
Which pathogen takes up to 16 weeks to grow in culture?
Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis
What are the two most common Salmonella serovars associated with disease?
Salmonella enteritidis
Salmonella typhimurium
What are key features of the agent that causes swine dysentery?
Anaerobic
Beta hemolysis
Which fimbrial antigen is most commonly associated with calf E. coli infections?
F5
Which Clostridium perfringens type is associated with necrotic enteritis and produces only alpha toxin?
Type A
Which toxins are produced by Clostridium perfringens Type C?
Alpha
Beta
What is the net physiological effect of Salmonella-induced diarrhea?
Malabsorption, exudation, hypersecretion
What is the most common cause of necrobacillosis?
Fusobacterium necrophorum subsp. necrophorum
Which Salmonella serovar is commonly associated with cattle but also affects other species?
Salmonella dublin
How does Trueperella pyogenes promote the growth of Fusobacterium necrophorum in necrobacillosis?
It provides oxygen and iron
Which organism requires mycobactin for growth in vitro?
Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis
A 5-year-old cow presents with chronic weight loss, diarrhea, thickened small intestine, and firm lymph nodes. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis (Johne's disease)
What is a key control strategy for necrobacillosis in cattle?
Feed management to avoid rumen acidosis
What is the likely diagnosis for a calf with watery diarrhea and no blood?
Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC)
Which toxins are produced by Clostridium perfringens Type B?
Alpha
Beta
Epsilon
What organism is responsible for causing black disease in sheep?
Clostridium novyi
What is the most likely cause of bloody diarrhea in 6-week-old pigs, with spirochetes seen on culture?
Brachyspira hyodysenteriae
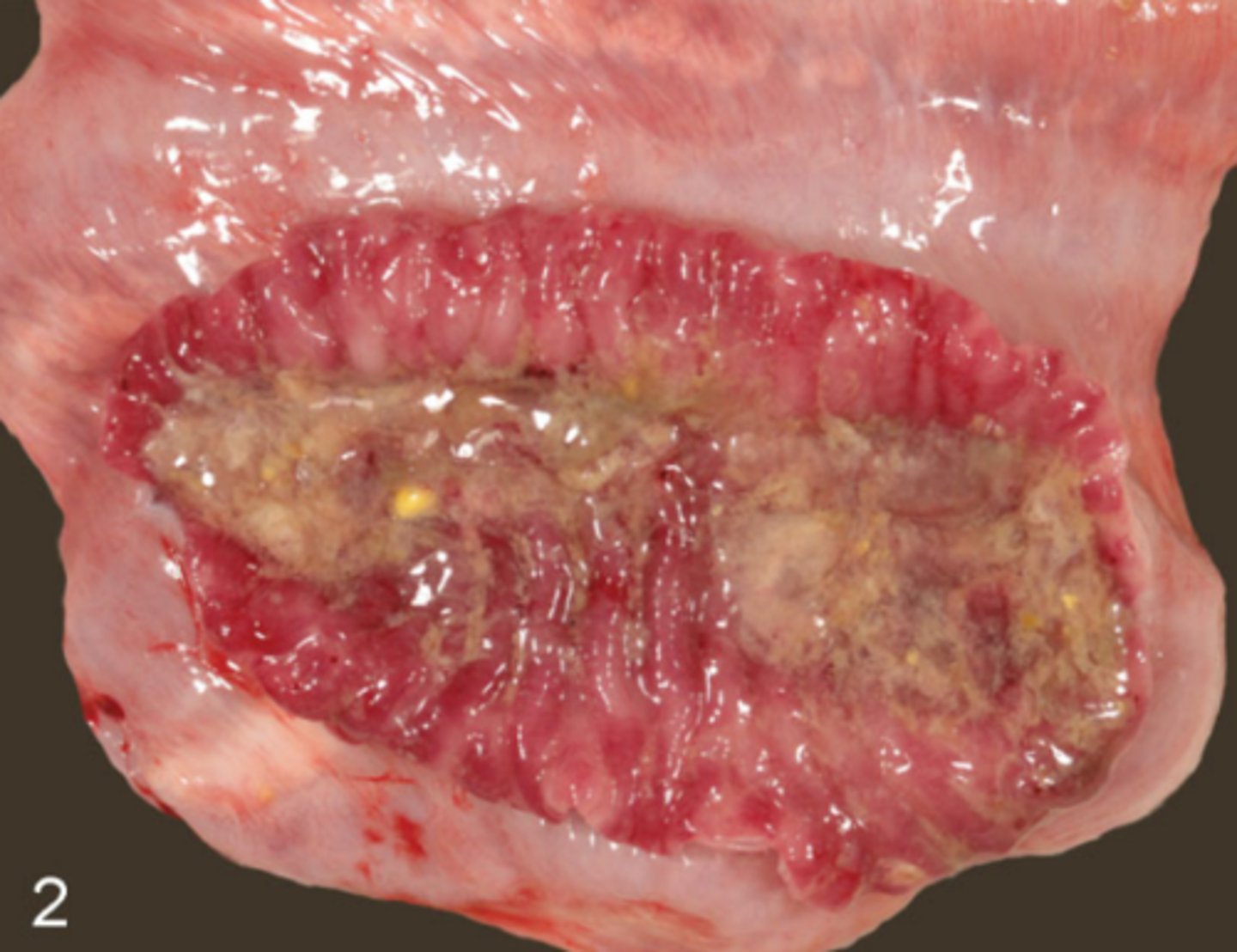
A 5-month-old foal presents with anorexia, lethargy, diarrhea, and thickened jejunum and ileum. What is the likely diagnosis?
Lawsonia intracellularis
How can necrotic hepatitis in young sheep, often secondary to liver fluke infection, be controlled?
Use of flukicides and vaccination against Clostridium novyi
What are the most common infectious agents associated with kennel cough in dogs?
Bordetella bronchiseptica, Canine Adenovirus-2 (CAV-2), Canine Parainfluenza virus (PI-2)
Scattered rice-like nodules in the lungs are indicative of infection with:
Mycobacterium bovis
Mannheimia haemolytica and Pasteurella multocida are commonly associated with which condition in pigs?
Atrophic rhinitis
Why are beta-lactam antibiotics ineffective against Mycoplasma?
They lack a cell wall
What is the vector for Borrelia species (e.g., Borrelia burgdorferi)?
Ticks
What is the best control method for blackleg and malignant edema in cattle?
Vaccination
A horse with limb edema and skin sloughing likely has:
Purpura hemorrhagica
What is the preliminary screening test for tuberculosis in cattle?
Caudal fold test
What is the primary cause of footrot in sheep?
Dichelobacter nodosus
A dog with chronic lower bowel diarrhea and lymph smear showing thin cell walls with a clear zone is likely infected with:
Histoplasma capsulatum
A coughing dog that remains alert and active most likely has:
Kennel cough (Bordetella bronchiseptica)
Fluke eggs found on fecal exam may indicate which rickettsial infection?
Neorickettsia helminthoeca
What does a Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) of 4 µg/mL represent?
The lowest drug concentration that visibly inhibits growth
To reduce the risk of tick-borne diseases, how quickly should ticks be removed?
Within 12 hours
What is the most effective way to prevent anthrax in livestock?
Vaccination
Which species is most susceptible to acute anthrax infection?
Cattle
What is the most common cause of bovine footrot?
Fusobacterium necrophorum
Which method is used to determine the MIC using a plastic strip with a gradient?
E-test
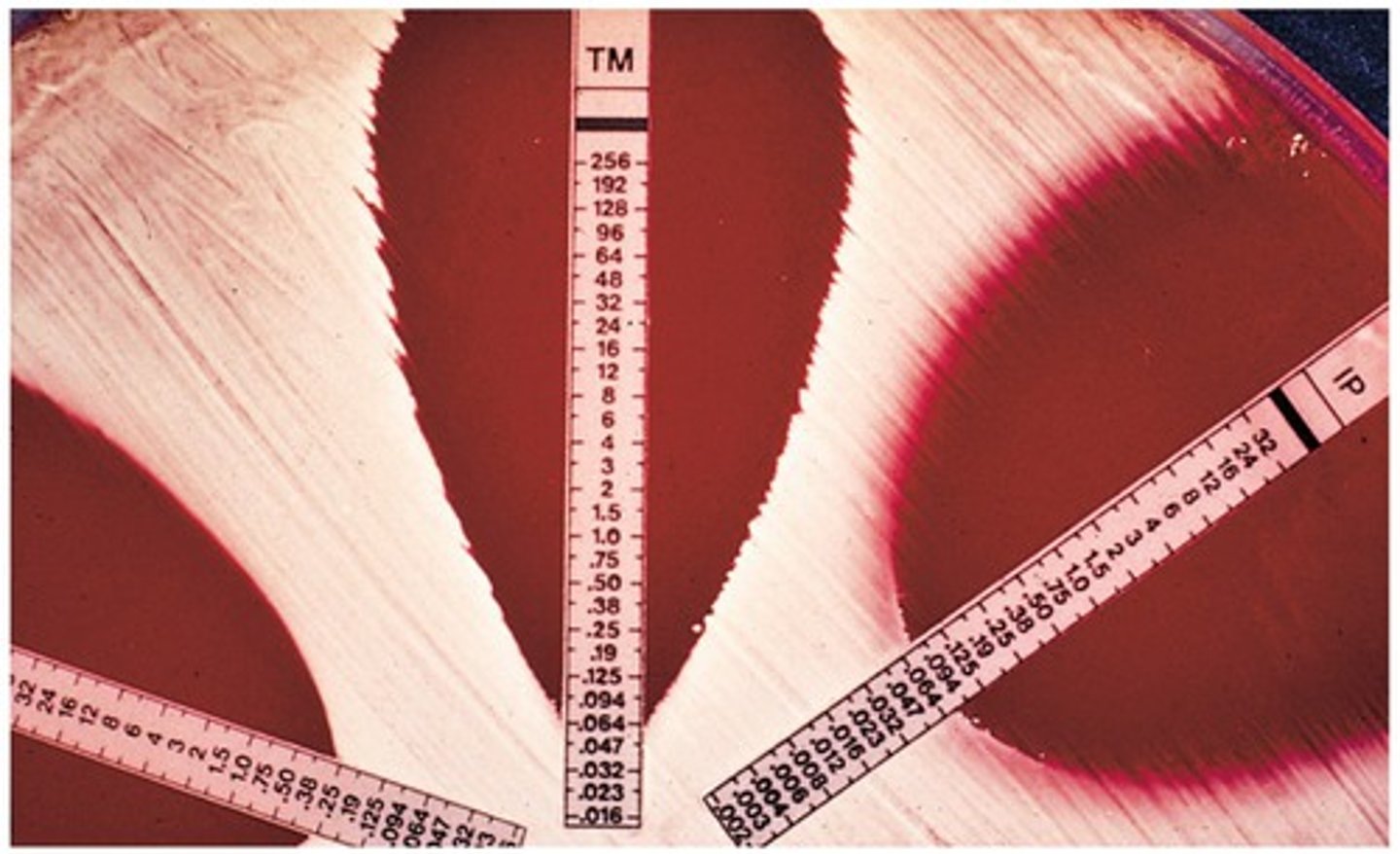
What pathogen causes canine monocytic ehrlichiosis?
Ehrlichia canis
Which organ is most fatally affected in canine Lyme disease?
Kidney
Pasteurella multocida types A and D cause what condition in pigs?
Atrophic rhinitis
What are the modes of transmission for Francisella tularensis?
Vectors, direct contact, ingestion, aerosol (not person-to-person)
What is the most common form of tularemia in humans?
Ulceroglandular
A goat with a caseous abscess is most likely infected with:
Non-nitrate-reducing Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis
What is the main virulence factor of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis in goats?
Phospholipase D
What is the primary virulence factor of Dichelobacter nodosus?
Type IV fimbriae
What is a classic colony morphology feature of Mycoplasma on agar?
Fried egg appearance
What pathogen forms large spherules in tissue?
Coccidioides immitis
What percentage of horses develop immunity after Streptococcus equi infection?
75%
What is the key virulence factor of Streptococcus equi?
M proteins