AP Psych | Unit 3 Part 2 | 3.7-3.9
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
learning (3.7)
process of acquiring through experience and enduring info or behaviours
habituation
An individual decreases their response to a repeated stimulus over time.
(A person working in a coffee shop stops noticing the background chatter after being there for a while.)
brain learns to ignore repeated stimuli
sensory adaption
A biological process where sensory receptors become less responsive to a constant stimulus.
After putting on perfume, you strongly smell it at first, but after a few minutes, you no longer notice it, even though others can still smell it.
ur senses adjust
classical conditioning
involuntary actions like salivation, blinking, sweating (stimuli are things we don’t control and we respond automatically.)
operant conditioning
voluntary actions (we operate on the environment to produce consequences)
associative learning
learning that certain events (positive and negative) occur together
can be two stimuli (classical conditioning) or a response and its consequence (operant conditioning)
stimulus
any event or situation that provokes a response
For popcorn eaters, the movie theater stimulates.
response
behaviour following the stimulus
for the popcorn eater, the voluntary behaviour was purchasing and eating the popcorn
how does classical conditioning occur
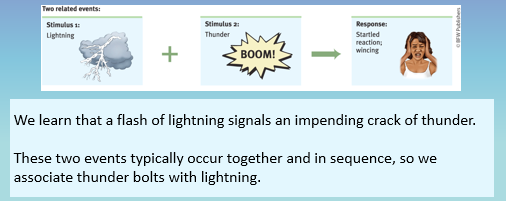
UCS
unconditioned stimulus
naturally occuring event (attractive female legs exiting the car)
UCR
unconditioned response
naturally occurring response (male arousal)
NS
neutral stimulus
tone (car)
CS
conditioned stimulus
after conditioning/training (the car)
CR
conditioned response
after training, the response that is gained (wanting to buy the car)
higher/second-order conditioning
the CS in one conditioning experience is paired with a new NS, creating a second (often weaker) CS
if the dog already knows that bell = food, and you add light after the bell, the dog will also start salivating even though the light was never associated with food in the first place.
acquisition
When learning begins and the response becomes stronger with repetition. where a response is established and strengthened.
extinction
in classical conditioning, the diminishing of a CR when an UCS does not follow a CS.
(when food no longer follows the bell)
spontaneous recovery
the reappearance (after a pause) of an extinguished conditioned response
generalization
the tendency for stimuli similar to the CS to produce similar responses
discrimination
in classical conditioning
when an organism learns to respond only to a specific stimulus and not to similar ones.
behaviourism
studying observable behaviors rather than internal mental processes
counter-conditioning
It’s when you change a bad reaction into a good one by pairing the bad thing with something nice.
preparedness
a biological predisposition to learn associations, like between taste and nausea (survival values)
one-trial conditioning
when a person or animal learns something after just one experience—usually because it was very strong or emotional.
operational conditioning (3.8)
learning type where a behaviour becomes more likely to reoccur if followed by reinforcer or less likely to reoccur if followed by punisher
we learn to associate a response (our behaviour) and its consequence, which causes operant behaviour
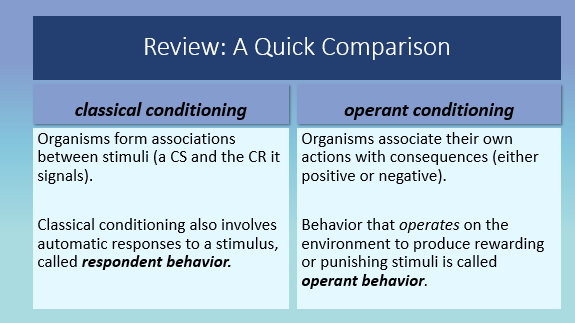
Classical Conditioning vs Operant Conditioning
CC: involuntary (respondent) behaviour
OC: voluntary (operant) behaviour
law of effect
behaviours followed by favourable consequences become more likely, behaviours followed by bad consequences less likely
reinforcement
any event that strengthens a response
shaping
an operant conditioning procedure
reinforcement guides behaviour toward closer approximations of desired behaviour (this is also called reward by successive approximations)
breaking down behaviours into smaller steps and giving + reinforcements help shape complex behaviours
discriminative stimulus
a signal that tells an organism that a particular behavior will get a reward.
dog sees its owner holding a treat → knows that sitting will earn the treat
instinctive drift
the tendency of learned behaviour to gradually revert to biologically predisposed patterns
positive reinforcement
INCREASING behaviours by presenting positive reinforcers.
studying hard on a test to receive a high grade
ADD GOOD
negative reinforcement
INCREASING behaviours by stopping or reducing annoying behaviour
hitting the snooze alarm to stop the annoying alarm
REMOVE BAD
primary reinforcer
innately reinforcing stimuli like satisfying a biological need
food, pain relief
conditioned (secondary) reinforcers
something that becomes rewarding because it is associated with a primary reinforcer (food, water, warmth)
money, good grade, pleasant voice tone
continuous reinforcement schedule
reinforcing the desired response every time it occurs
partial (intermittent) reinforcement schedule
reinforcing a response only part of the time
fixed ratio schedule
a partial reinforcement schedules
reinforcement occurs after a set number of responses
one free coffee after every 10 purchased
fixed interval schedules
a partial reinforcement schedules
reinforcement occurs after a set length of time
mail arriving at 2 pm everyday
variable ratio schedules
partial reinforcement schedules
reinforcement occurs after an unpredictable number of responses
payoff on slot machine after a varying number of plays
variable interval schedules
a partial reinforcement schedules
reinforcement occurs after an unpredictable length of time
checking our phone for a text from our friend
learned helplessness
the hopelessness and passive resignation an animal/person acquires when unable to avoid repeated bad events
punishment
an event that tends to decrease the behaviour it follows.
positive punishment
ADD BAD
Giving a traffic ticket for speeding
negative punishment
REMOVE GOOD
Removing misbehaving teen’s driving privileges
cognitive map
a mental representation of the layout of one’s environment
latent learning
learning that happens without any immediate visible sign of it and only becomes apparent when there is a reason to use it. This means someone (or an animal) can learn something but not show it until they need to.
insight learning
a sudden realization of a problem’s solution. learning that occurs with no environmental interaction
vicarious reinforcement/punishment
we learn to anticipate a behavior’s consequences in situations like those we are observing
mirror neurons
frontal lobe neurons
brain’s mirroring of another’s action may enable imitation and empathy
prosocial modeling
positive, constructive helpful behavior
antisocial modeling
negative, destructive behaviour