HAPP LEC Skeletal system
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
forms a collar around the opposing ends of the bone fragments. Osteochondral progenitor cells from the periosteum become osteoblasts, which produce bone, and chondroblasts, which produce cartilage.
external callus.
forms between the ends of the broken bone, as well as in the marrow cavity if the fracture occurs in the diaphysis of a long bone. Several days after the fracture, blood vessels grow into the clot.
internal callus
Bone remodeling involves a…..a temporary assembly of osteoclasts and osteoblasts that travels through or across the surface of bone, removing old bone matrix and replacing it with new bone matrix.
basic multicellular unit (BMU0
is also required for normal growth of all tissues, including cartilage; therefore, a decrease in this hormone can result in a smaller individual
Thyroid hormone
also influence bone growth. Estrogen (a class of female reproductive hormones) and testosterone (a male reproductive hormone) initially stimulate bone growth, which accounts for the burst of growth at puberty when production of these hormones increases
Reproductive hormones
is present on the posterior surface of the occipital bone. It can be felt through the scalp at the base of the head and varies considerably in size from person to person
external occipital protuberance
an elastic ligament that extends down the neck and helps keep the head erect by pulling on the occipital region of the skull
Ligamentum nuchae
a set of small ridges that extend laterally from the external occipital protuberance, are the points of attachment for several neck muscles.
Nuchal lines
The process can be seen and felt as a prominent lump just posterior to the ear. The process is not solid bone but is filled with cavities called…
mastoid air cells
, Anterior to the sphenoid bone is the…which can be easily seen and felt on the face
zygomatic bone
which consists of joined processes from the temporal and zygomatic bones, forms a bridge across the side
zygomatic arch
is anterior and inferior to the zygomatic bone to which it is joined
maxila
is inferior to the maxilla and attaches posteriorly to the temporal bone . The mandible consists of two main portions: the body, which extends both anteriorly and posteriorly, and the ramus (branch), which extends superiorly from the body toward the temporal bone.
mandible
The lateral wall of the nasal cavity has three bony shelves, called the …, which are directed inferiorly
nasal conchae
Several of the bones associated with the nasal cavity have large spaces, which open into the nasal cavity.
paranasal sinuses
has a pear-shaped opening anteriorly and is divided into right and left halves by a nasal septum
nasal cavity
is the hollow part of the skull occupied by the brain can be exposed by cutting away the calvaria, the upper, domelike portion of the skull
cranial cavity
is located in the center of the anterior fossa just superior to the nasal cavity is a point of attachment for one of the meninges, the dura mater, a thick connective tissue membrane that supports and protects the brain
crista galli
in the floor of the carotid canal, is an artifact of the dried skull. In life, it is filled with cartilage
foramen lacerum
protects the brain and houses our eyes, ears, nose, and mouth. When the skull is disassembled, the mandible is easily separated from the rest of the skull, which remains intact.
skull
The olfactory nerves extend from the cranial cavity into the roof of the nasal cavity through sievelike perfora tions in the cribriform plate called
olfactory foramina
of the temporal bone extends postero laterally from each side of the sella turcica. This thick, bony ridge (petrous, rocky) is hollow and contains the middle and inner ears
petrnous portio
smooth points of articulation between the skull and the vertebral column, lie on the lateral and anterior mar gins of the foramen magnum.
Occipital condyles
where the mandible articulates with the rest of the skull, is anterior to the mastoid process at the base of the zygomatic arch.
mandibular fossa
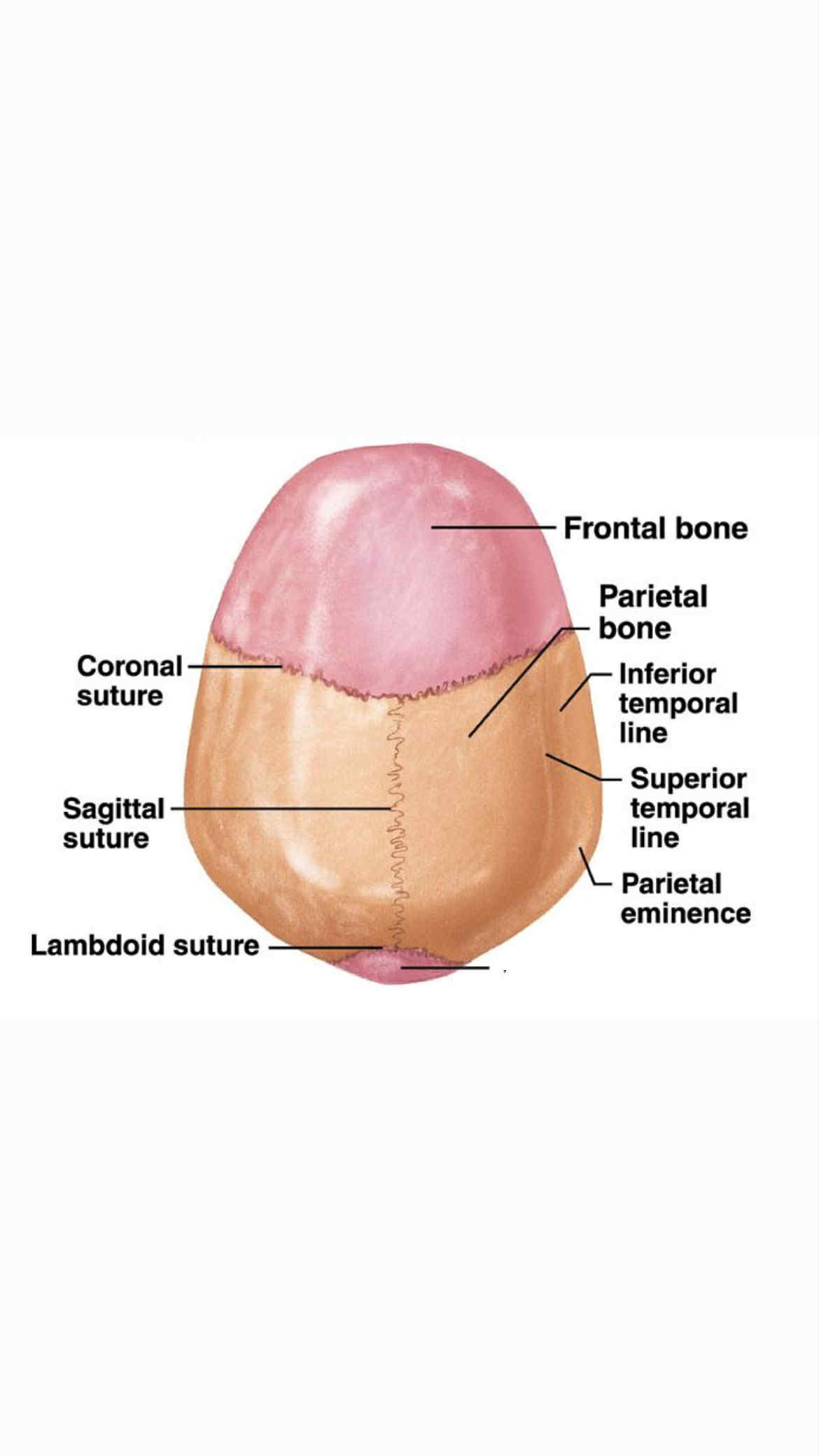
Occipital bones
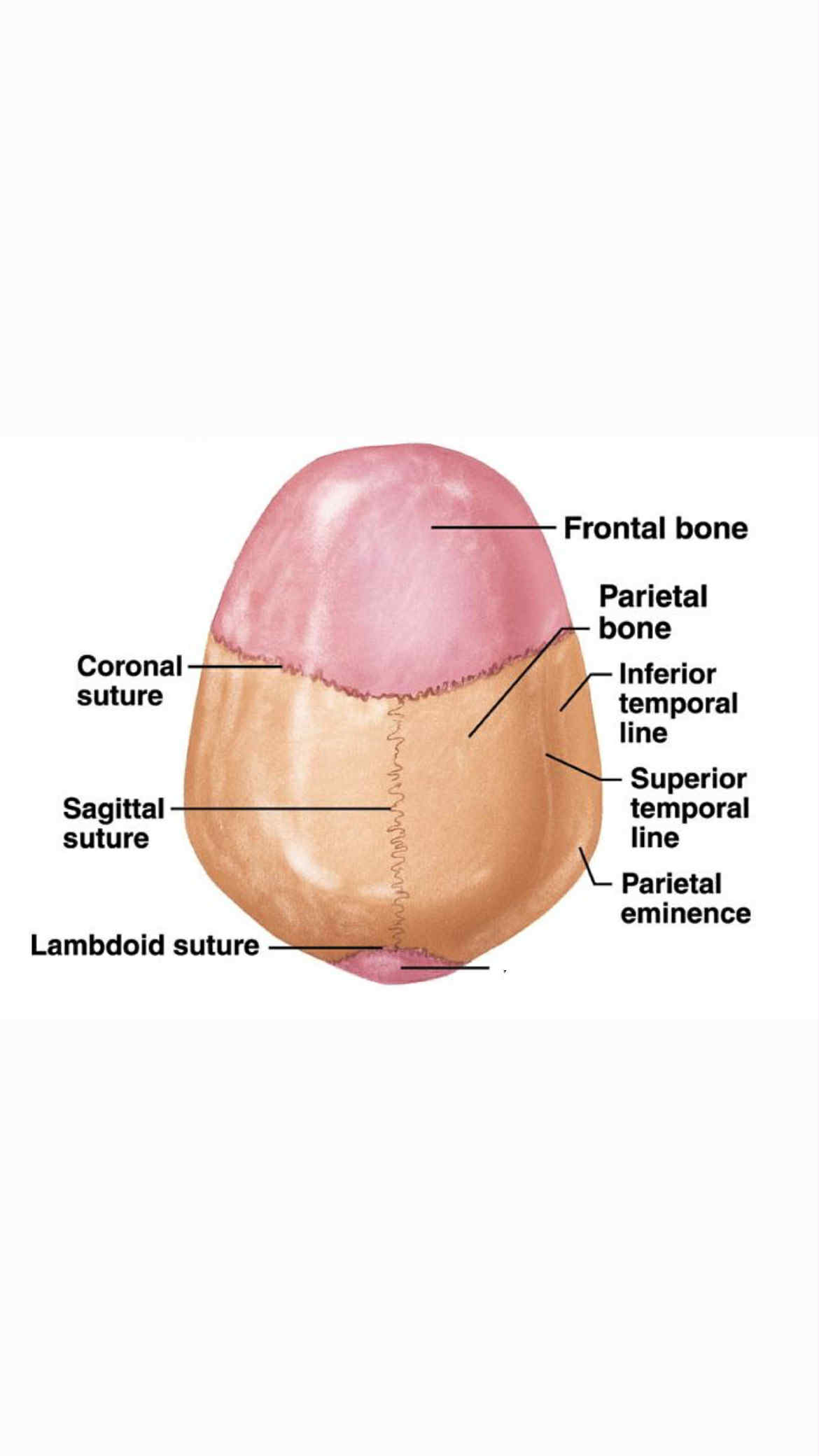
Inferior temporal line
forms the majority of the floor of the nasal cavity (and the roof of the mouth). Sutures join four bones to form the hard palate: The palatine processes of the two maxillary bones form the anterior two-thirds of the hard pal ate, and the horizontal plates of the two palatine bones form the posterior one-third of the hard palate
hard palate
which function in hearing. Each temporal bone holds one set of auditory ossicles, which con sists of the malleus, incus, and stapes. These bones cannot be observed unless the temporal bones are cut open
auditory ossicles
performs five major functions: (1) It supports the weight of the head and trunk, (2) it protects the spinal cord, (3) it allows spinal nerves to exit the spinal cord, (4) it provides a site for muscle attachment, and (5) it permits movement of the head and trunk
vertebral column
The vertebral column usually consists of 26 bones,
vertebrae
possess long, thin spinous processes directed inferiorly, and they have relatively long transverse processes
thoracic vertebrae
The right and left hipbones (ossa coxae or coxal bones) join each other anteriorly and the sacrum posteriorly to form a ring of bone called the
pelvic girdle
are attached to the carpal bones and constitute the bony framework of the hand. They are numbered one to five, starting with the most lateral metacarpal bone, at the base of the thumb
metacarpal bones
A ligament stretches across the wrist from the tubercle of the tra pezium to the hook of the hamate to form a tunnel on the anterior surface of the wrist called the
carpal tunnel
is a relatively short region between the forearm and the hand; it is composed of eight carpal (kar′păl) bones arranged into two rows of four each
wrist
is on the lateral surface, and the lesser tubercle is on the anterior surface of the proximal end of the humerus, where both are sites of muscle attachment.
greater tubercle
, consists of two pairs of bones that attach the upper limb to the body: Each pair is composed of a scapula, or shoulder blade , and a clavicle, or collarbone
Pectoral Girdle
is a large sesamoid bone located within the tendon of the quadriceps femoris muscle group, which is the major muscle group of the anterior thigh.articulates with the patellar groove of the femur to create a smooth articular surface over the anterior distal end of the femur.
patella
is the part of the lower limb between the knee and the ankle
legs
which is the attachment point for the quadriceps femoris muscle group, can easily be seen and felt just inferior to the patella
tibial tuberosity
navicular
which is boat-shaped, lies between the talus posteriorly and the cuneiforms anteriorly