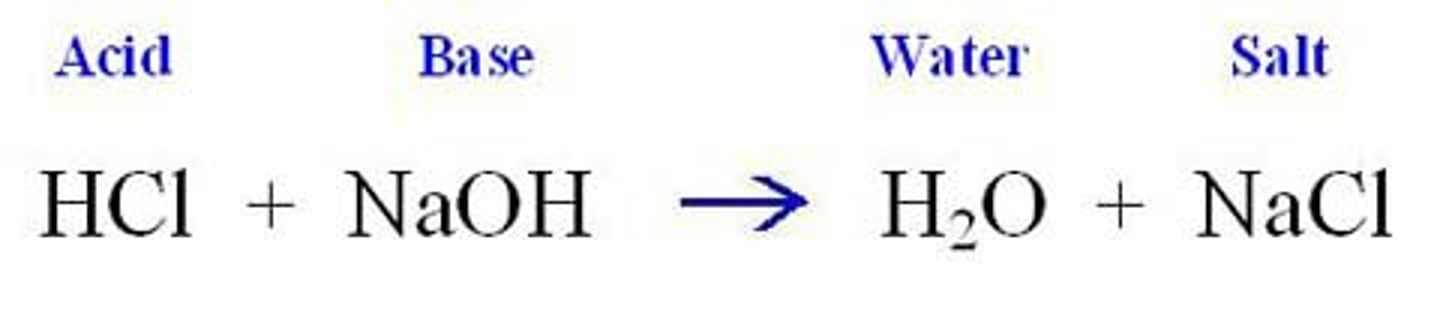SNC2DY-a Types of Reactions (Chapter 6)
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
synthesis
two reactants (elements or compounds) react to produce one new compound.
A + B = AB
metal oxide + water
metal hydroxide or base
nonmetal oxide + water
acid
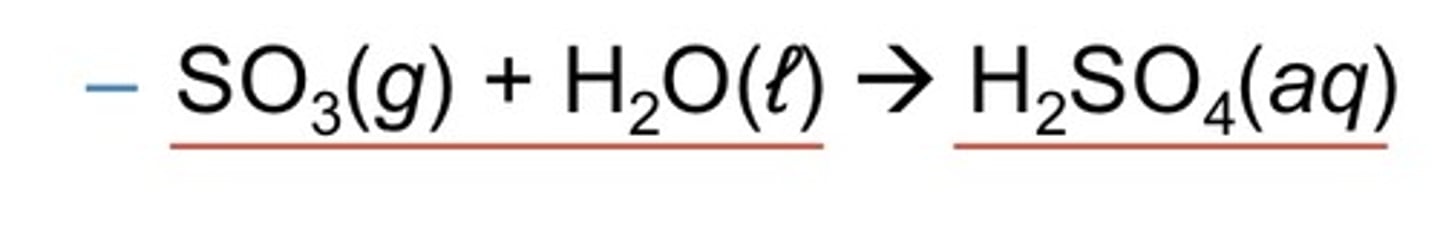
metal oxide + carbon dioxide
metal carbonate

metal halides + oxygen
metal halates
MgCl2(s) +3O2(g)---> Mg(ClO3)2(s)
decomposition
AB->A+B
Binary compounds (e.g. 𝐻𝑔𝐶𝑙2(𝑠) → 𝐻𝑔(𝑙) + 𝐶𝑙2(𝑔))
Metal carbonate -> Metal oxide + CO2 gas (e.g. 𝐶𝑎𝐶𝑂3(𝑠) → 𝐶𝑎𝑂 𝑠 + 𝐶𝑂2(𝑔))
Metal nitrate -> Metal nitrite + O2 gas (e.g. 2𝐾𝑁𝑂3(𝑠) → 2𝐾𝑁𝑂2(𝑠) + 𝑂2(𝑔))
Metal hydroxide -> Metal oxides + H2O (e.g. 𝐶𝑎(𝑂𝐻)2(𝑠)→ 𝐶𝑎𝑂(𝑠) + 𝐻2𝑂(𝑔))
Metal chlorate -> Metal chloride + O2 gas (e.g. 𝐾𝐶𝑙𝑂3(𝑠) → 𝐾𝐶𝑙(𝑠) + 3𝑂2(𝑔))
Certain acids -> Non-metal oxides + H2O (e.g. 𝐻2𝑆𝑂3(𝑎𝑞) → 𝑆𝑂2(𝑔) + 𝐻2𝑂(𝑙))
Hydrates -> H2O + anhydrous salt (e.g. 𝐶𝑢𝑆𝑂4 ⋅ 5𝐻2𝑂 𝑠 → 𝐶𝑢𝑆𝑂4 𝑠 + 5𝐻2𝑂 𝑔 )
complete combustion
hydrocarbon + oxygen --> carbon dioxide + water
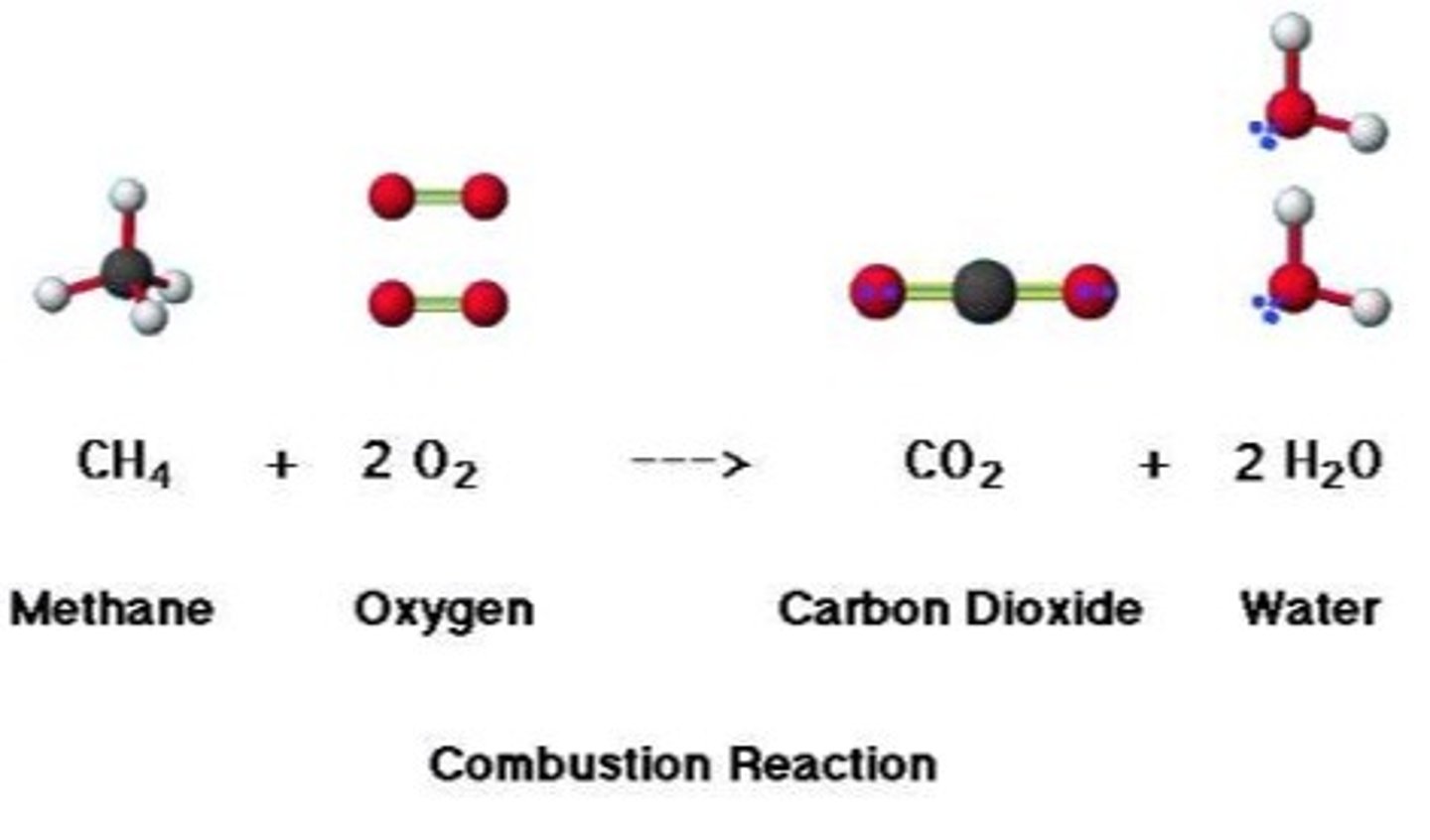
incomplete combustion
insufficent oxygen, produces: carbon monoxide, water and soot (solid carbon)

vehicles burn gasoline
incompletely (low engine temp)
CO binds w hemoglobin
metals + oxygen
metal oxide or peroxides

nonmetal + oxygen
nonmetal oxide
diatomic elements with states
HOFBrINCl
P4S8
all the solids: I2, P4, S8
liquid: Br2
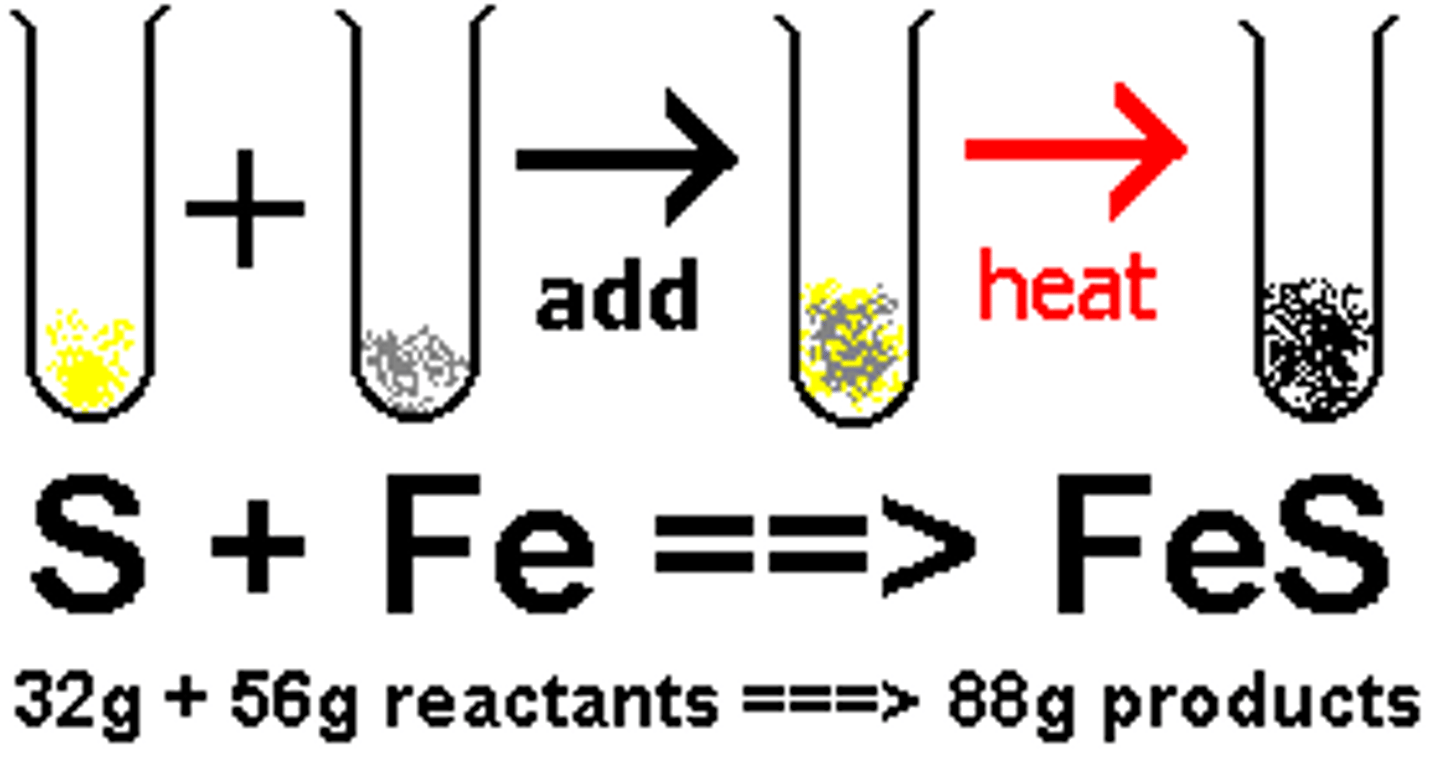
law of conservation of mass
Matter is neither created nor destroyed
single-displacement reaction
chemical reaction in which one element replaces another element in a compound
Metals replace another metal
A + BX → AX + B
Non-metals replace another non-metal
XA + B → XB + A
REMEMBER:
Metal Reacting with Water
(Eg. Reactive metals + water -> Base + H2 gas
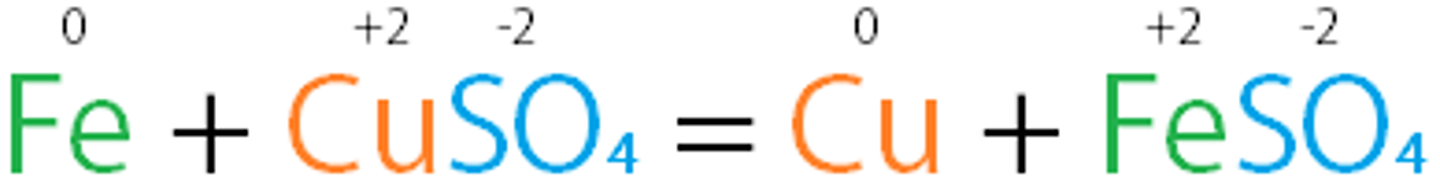
Metals from Li - Na
react w water to form metal hydroxide and hydrogen gas
Metals from Mg--->Cd
react w steam to form metal oxide n hydrogen gas
metals above hydrogen
react w acids to form ionic compound and hydrogen gas
NR meaning
non-reactive (cant dispace)
Metals from Li - Na w O2
forms metal peroxides and metal oxides
metals from Mg-Hg
reacts w oxygen to form metal oxide
what is corrosion
Corrosion is the destruction of materials by chemical reactions with substances in the environment.
metals that dont corrode
gold n platinum
where is corrosion beneficial
when reacting w oxygen aluminum oxide forms a protective layer coating the aluminum
and copper forms the green patina (weatherproof 75 years)
what is rust? diff between rust n corrosion
reddish brown flaky iron (III) oxide
rust doesnt stick to the metal unlike other metals
5 factors of rust
air, h20 electrolytes, acidity, mech.stress
more humid air=more rust
dry air=less rust
salt
speeds up rusting
protective coating for rust
cover metal w rust inhabiting paint, chrome or plastic
corrosion resistant materials
stainless steel (fe, ni, cr, c)
plastic
galvanizing
Coating steel with zinc to prevent corrosion forming ZnO sticking to steel n zinc
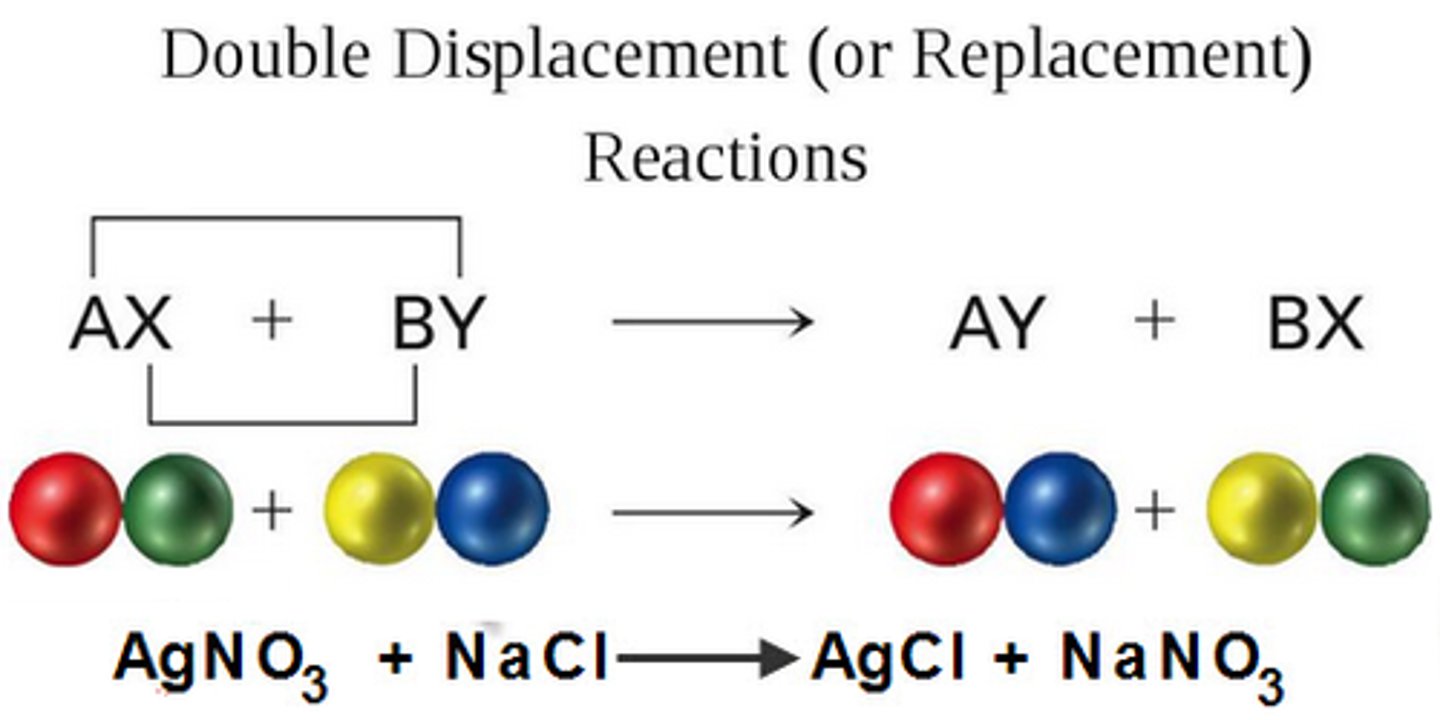
double-displacement reaction
AB + CD → AD + CB
A gas, a solid precipitate, or a molecular compound forms from the apparent exchange of atoms or ions between two compounds
1. Formation of a precipitate (s)
2. Production of a gas
3. Formation of water in neutralization - form water and a «salt»
4. Special Case: D.D. forming a carbonic acid
5. Special Case: D.D. forming ammonium
precipitation reactions
2 ionic= 2 new solids where 1 is precipitate (insol) and other is aq
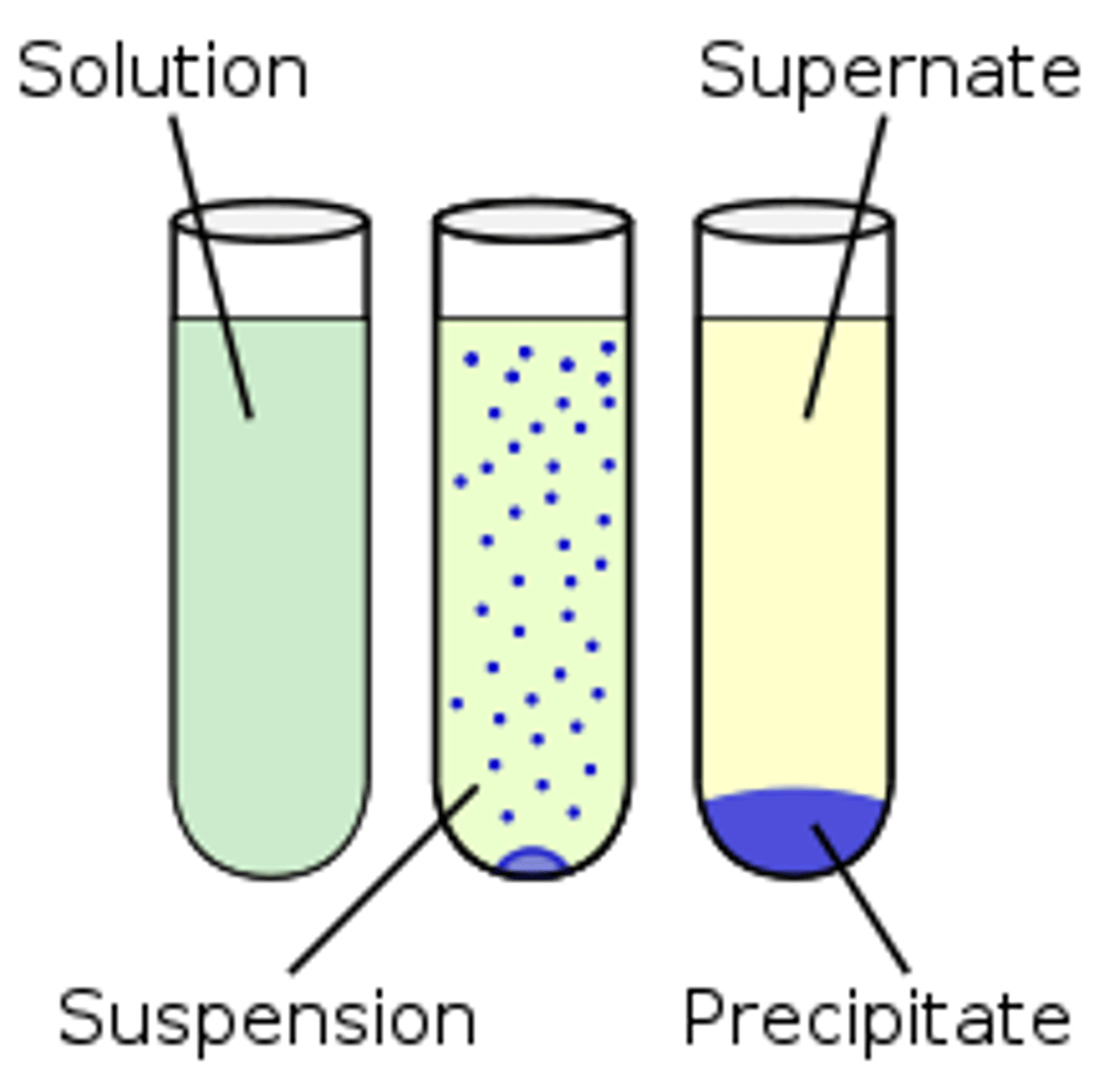
acid base reaction
a reaction where an acid reacts with a base to produce water and a salt (ionic compound)
when base is CO2 a carbonate also forms