BIS 2C Angiosperms
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms

What percent of plant diversity do angiosperms represent?
90%

What are the three synapomorphies of angiosperms?
flowers, double fertilization, vessel elements
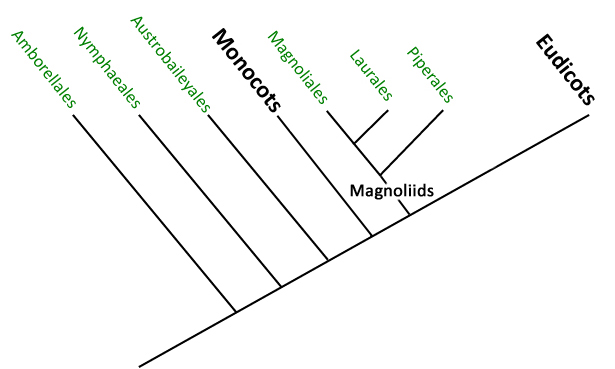
What are the three main angiosperm lineages?
basal angiosperms, monocots, and eudicots

Why did angiosperms become so diverse?
due to flowers, fruits, and coevolution with pollinators

What’s the main role of flowers?
to attract pollinators and enable sexual reproduction

Define perfect flowers
has stamens AND carpels

Define imperfect flowers
either has a stamen OR a carpel
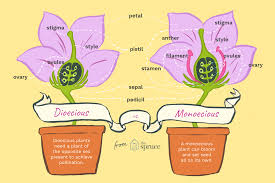
Define monoecious vs. dioecious plants
monoecious = both sexes on one plant; dioecious = separate plants

What are the four whorls of a flower?
sepals, petals, stamens, carpels (pistil)
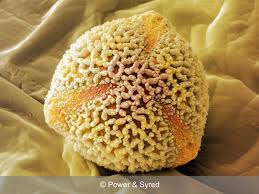
What does the anther do?
produces pollen (male gametes)
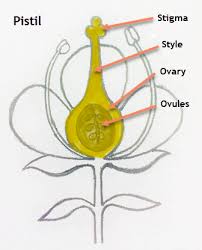
What’s the function of the carpel (pistil)?
receives pollen and contain ovules that become seeds
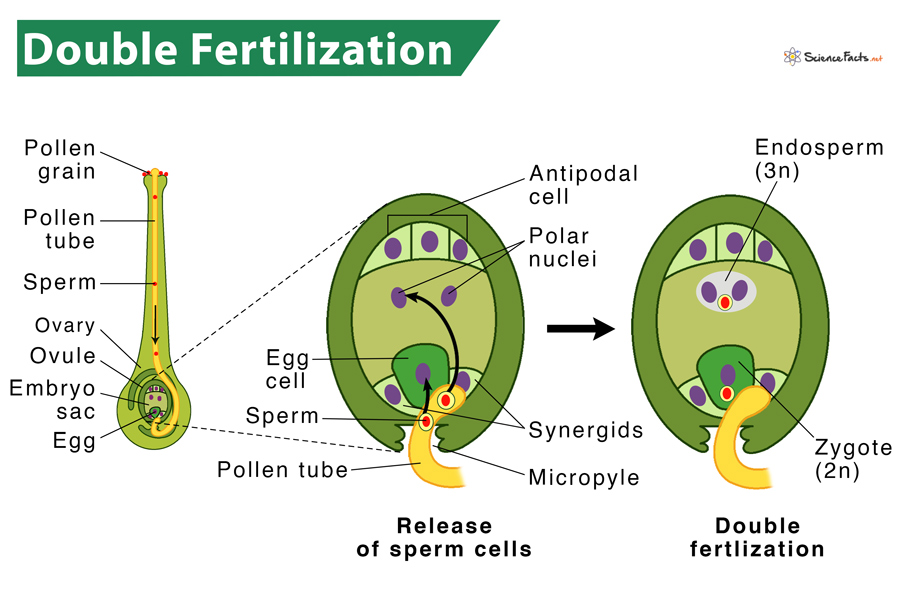
What happens in double fertilization?
one sperm = egg (zygote); another = central cell (endosperm, 3n)

why is double fertilization efficient?
nutrient tissue forms only when the egg is fertilized
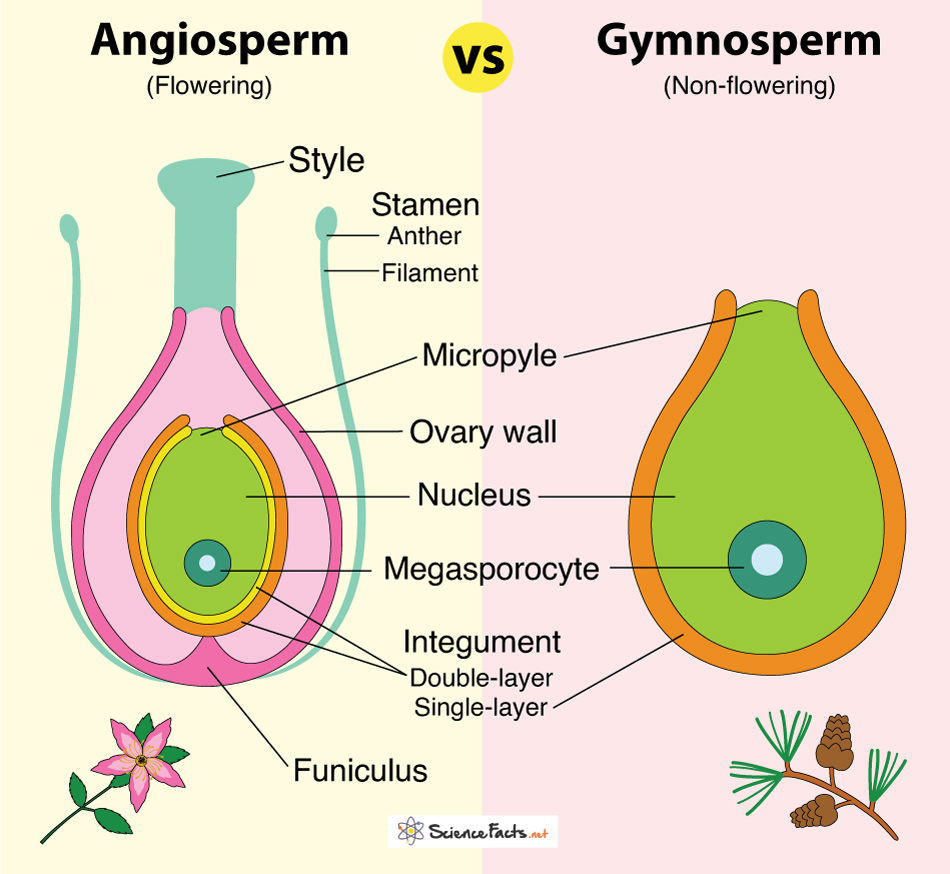
What’s the difference between gymnosperm and angiosperm seeds?
they differ in the origin and ploidy of nutritive tissue

What are the ecological roles of angiosperms?
primary producers, provide oxygen, store carbon, stabilize soil
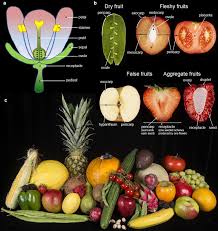
What is the function of fruit?
protects and disperses seeds
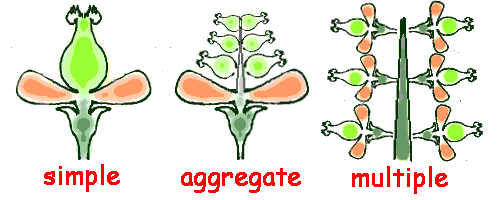
Define a simple fruit and give an example
from one ovary of one flower (e.g. cherry tomato)
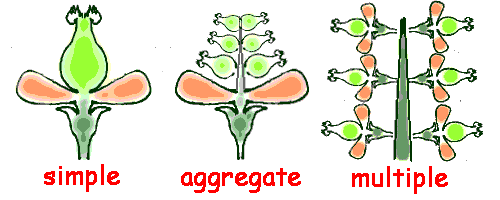
Define an aggregate fruit and give an example
from multiple ovaries of ONE flower (e.g. strawberry, raspberry)
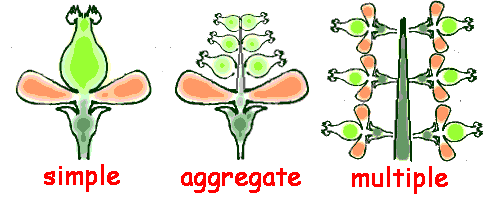
Define a multiple fruit and give an example
from fused flowers (e.g. pineapple)
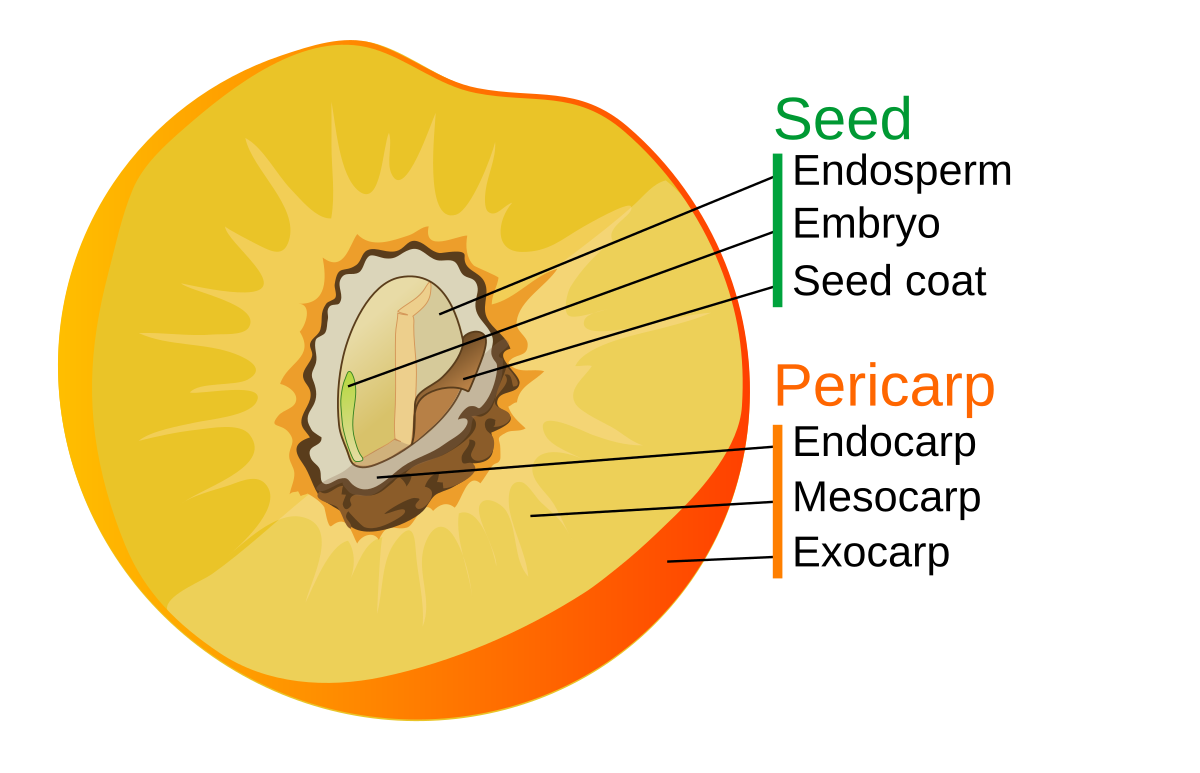
What’s a drupe?
a simple fruit with a stony pit (e.g. peach, cherry)

What’s a berry in botanical terms?
a fleshy ovary wall from one flower (e.g. tomato, grape)
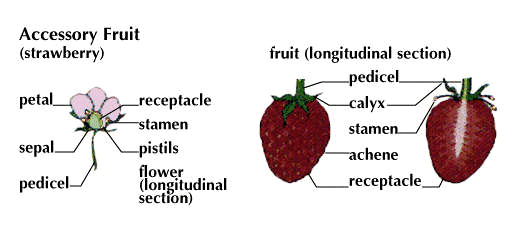
What’s an accessory fruit?
a fruit that includes non-ovary tissue (e.g. apple, strawberry)

What’s a true fruit?
formed only from the ovary (cherry or grape)
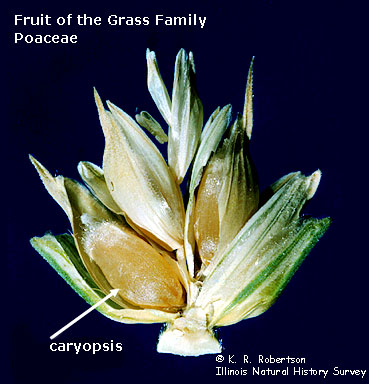
What’s a caryopsis?
a grain where the seed coat and ovary wall are fused
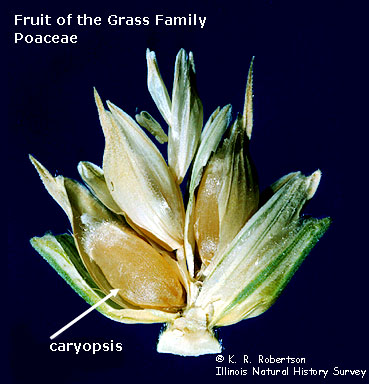
Examples of plants with caryopses?
wheat, rice, corn, barley

Function of trichomes on fruit and flower surfaces?
protection and reduced water loss

What do vessel elements do?
allow efficient water transport in angiosperms
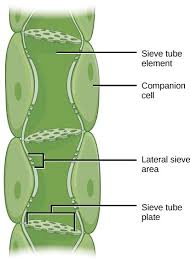
What do companion cells in phloem do?
support sugar transport by assisting sieve elements

What two hormones regulate primary growth?
auxin (roots) and cytokinin (shoots)