Demographic Transition Model and Migration Patterns
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Stage 1
Low NIR, high CBR, high CDR. Migration was usually high daily or seasonal mobility in search of food. Common cause of death was due to the inability to feed themselves because of inability to locate enough animals or vegetation.
Stage 2
High NIR, high CBR, rapidly falling CDR. High international emigration and interregional migration from rural to urban areas. Cause of death is still infectious diseases though it is on the decline due to improved healthcare.
Stage 3
Declining NIR, rapidly declining CBR, still declining CDR. High international immigration and intraregional migration from cities to suburbs. In this stage people are dying from chronic disorders and degenerative diseases associated with aging, specifically cardiovascular diseases and various forms of cancer.
Stage 4
Low NIR, low CBR, low CDR. Migration patterns are similar to stage 3. Common cause of death in this stage deals more with delayed degenerative diseases from stage 3, focused on lifestyle decisions that cause death.
Stage 5
Negative NIR, low CBR, increasing CDR. Cause of death is more age-related and diseases become more prevalent due to an aging population. Migration may occur from regions with declining populations to areas with more favorable economic conditions or higher birth rates.
Arithmetic Density
Total population/total land area = ?
Physiological Density
Total population/arable land area = ? Tells us the capacity of which a land is able to yield food for the needs of that population.
Agricultural Density
Farmer population/arable land.
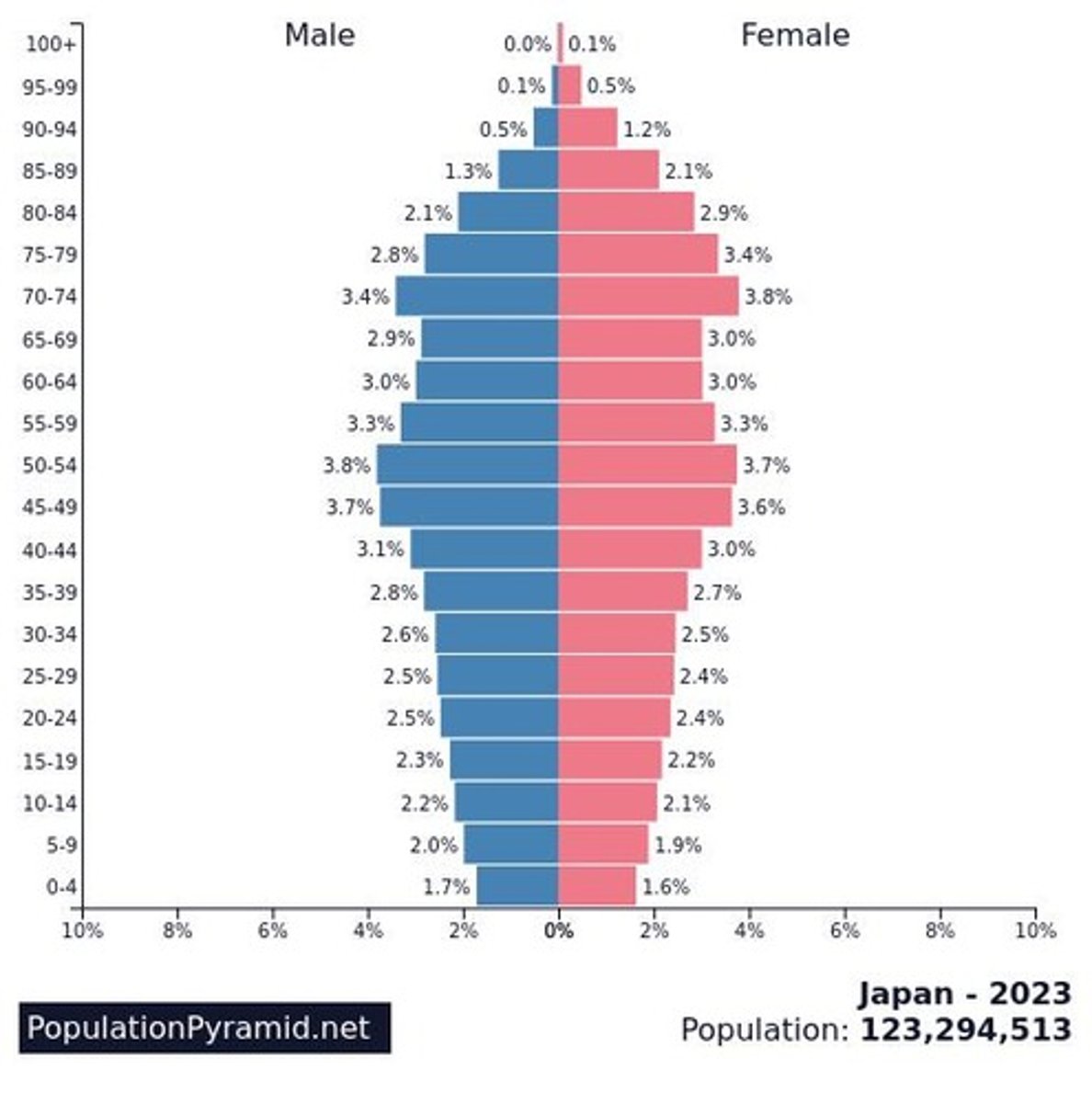
Population Pyramid Interpretation
Japan's demographic structure resembles more of a 'cup' shape. The child population constitutes only 11.5% of the total population, while the elderly population makes up a substantial 30.1%.
Net Migration
The difference between the number of immigrants and the number of emigrants. Equation: Immigrants - Emigrants = ?, if positive net in-migration, if negative net-out migration.
Emigration
Migration from a location.
Immigration
Migration to a location.
Remittance
Transfer of money by workers to people in the country from which they emigrated.
Intraregional Migration
Movement within one region of a country.
Interregional Migration
Movement from one region of a country to another in that same country.
International Migration
A permanent move from one country to another.
Push Factors
Events or conditions that cause people to emigrate from their present location.
Pull Factors
Events or conditions that cause people to immigrate to a location.
Urbanization
Migration from rural areas to urban areas. This happened in the 1800s and was due to the Industrial Revolution.
Suburbanization
Migration from cities to suburbs. This happened in the mid-twentieth century.
Natural Increase Rate (NIR)
Calculated by taking the total population, dividing it by 1000, multiplying the product by either the CBR or CDR, and then adding if it is the CBR and subtracting if it is the CDR.
Chronic Disorders
Diseases associated with aging, such as cardiovascular diseases and various forms of cancer.
Delayed Degenerative Diseases
Diseases that are more focused on lifestyle decisions that cause death, such as poor diets and substance use.
Aging Population
A demographic situation where the proportion of elderly individuals increases, leading to more age-related diseases.
Economic Conditions and Migration
Migration may occur from regions with declining populations to areas with more favorable economic conditions or higher birth rates.
California Gold Rush
A significant event that prompted migration to California during the period of 1850-1890.
Rust Belt
An area in the Northeast and Upper Midwest of the United States that experienced economic decline, leading to migration to the Sun Belt.
Suburban Life
A lifestyle choice that offers the opportunity to live in a detached house surrounded by a private yard.
Counter Urbanization
Net migration from urban to rural areas in developed countries, occurring in the late-twentieth century.
Language Family
A collection of languages related through a common ancestral language that existed long before recorded history.
Language Branch
A collection of languages within a family related through a common ancestral language that existed several thousand years ago.
Language Group
A collection of languages within a branch that share a common origin in the relatively recent past.
Dialect
Regional variation of a language distinguished by distinctive vocabulary, spelling, and pronunciation.
Lingua Franca
A language mutually understood and commonly used to communicate by people who have different native languages.
Multilingual State
A country where more than one language is spoken.
Sedentary Farmer Theory
Suggests the Indo-European language family diffused via peaceful spread of agricultural practices from Anatolia to Southwest Asia and Europe.
Nomadic Warrior Theory
Suggests the Indo-European language family diffused via conquest of Southwest Asia and Eastern Europe by skilled Kurgan horsemen.
Universal Religion
Attempts to be global, appealing to all people, regardless of culture or location.
Ethnic Religion
Appeals primarily to one group of people living in one place.
Christianity
A universal religion with three largest branches: Roman Catholic, Orthodox, and Protestant.
Islam
A universal religion with two largest branches: Sunni (88%) and Shiite (12%).
Buddhism
A universal religion with three largest branches: Theravada (56%), Mahayana (38%), and Vajrayana (6%).
Judaism
An ethnic religion.
Hinduism
An ethnic religion.
Christianity's Belief in God
Followers believe in one god.
Islam's Belief in God
Followers believe in one god, called Allah.
Buddhism's Belief in God
Followers do not believe in a single god or any god.
Hinduism's Belief in God
Followers believe in a supreme god consisting of multiple deities.
Judaism's Belief in God
Followers believe in one god.
Christianity's Teachings
Followers believe in the teachings of Jesus.
Islam's Teachings
Followers follow the teachings of the prophet Muhammed.
Buddhism's Teachings
Followers follow the teachings of Buddha.
Judaism's Teachings
Followers follow the teachings of Moses and Abraham.
Christianity's Text
Followers study the Holy Bible.
Islam's Text
Followers study the holy book called the Quran.
Buddhism's Text
Followers commonly cite the Tipitaka.
Hinduism's Text
Followers study the Vedas, a text comprised of several texts.
Judaism's Text
Followers follow the Torah, which is the Old Testament of the Bible.
Sacred Sites
Locations considered holy by religious followers.
Mecca
Islam's holiest city, located in Saudi Arabia.
Medina
Second holiest city in Islam, also in Saudi Arabia.
Bethlehem
Birthplace of Jesus, significant in Christianity.
Jerusalem
Sacred city for Judaism, Christianity, and Islam.
Tipitaka
Main scripture in Buddhism, containing teachings.
Vedas
Hindu scriptures consisting of multiple texts.
Race
Identity based on common biological ancestry.
Ethnicity
Identity based on cultural traditions of a homeland.
Nationalism
Allegiance to a specific country or nation.
Genocide
Mass killing to eliminate a specific group.
Ethnic Cleansing
Forcible removal of a less powerful ethnic group.
Blockbusting
Deceptive tactic to manipulate real estate prices.
White Flight
Emigration of Whites anticipating Black immigration.
African American Migration
Movements influenced by historical and social factors.
Forced Migration
Involuntary movement of people, often due to slavery.
Yugoslavia Ethnic Cleansing
Violence against Bosniaks during the 1990s conflict.
Hearth Area
Geographic origin of a particular religion.
Southeastern U.S.
Region with high concentration of African Americans.
Asian American Concentration
Predominantly found in California and the West.
Hispanic American Concentration
Mainly in the Southwestern U.S. due to migration.