216 General Survey, Vital Signs, Pain and Inclusivity terms
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
General Survey
study of the whole person, covering the general health state and any obvious physical characteristics such as posture dress, behavior, level of consciousness, mobility, distress
Temperature normal range
97.5-99.5 F or 36-37 C
hypothermia
body temperature below 95 F 35 C
fever, pyrexia, hyperthermia
temperature greater than 100 F 37.8 C
oral temperature
should not be used on a patient who cannot follow directions, has decreased mentation, is unable to keep mouth closed or breathes through mouth; standard for adult measurement of temperature
tympanic temperature
taken in the ear; should not be used on patient who is experiencing ear pain, ear drainage or has a large amount of wax
temporal temperature
Measurement of body temperature at the temporal artery on the forehead; usually 0.5 F (0.3 C) lower than oral temp
rectal temperature
temperature taken in the rectum; can stimulate the vagus nerve; contraindicated in rectal surgery, rectal disease, low WBC, blood clotting disorder, neurologic disorders, cardiac disease, diarrhea and hemorrhoids; 0.5 F (0.3 C) higher than oral temp
radial pulse
the pulse felt at the wrist; 60-100bpm expected
apical pulse
pulse taken with a stethoscope and near the apex of the heart
pulse deficit
the apical and the radial pulse rates.
bradycardia
slow heart rate (less than 60 bpm)
Tachycardia
rapid heart rate greater than 100 bpm
pulse volume scale
0 Absent pulse
1+ Weak and thready pulse, difficult to palpate
2+ Normal pulse, able to palpate with normal pressure
3+ Bounding pulse, may be able to see pulsation
Respiratory Rate (RR)
Number of breaths per minute; Adults = 12-20
Tachypnea
Increased breathing rate above 20 bpm
bradypnea
abnormally slow breathing (less than 12 breaths per minute)
depth of respiratory rate
shallow vs deep
rhythm of respiratory rate
regularly spaced or irregularly spaced
respiratory effort
Work of breathing-relaxed easy breaths expected
Dyspnea: labored breathing
Orthopnea: inability to breathe when horizontal
Systolic Blood Pressure (SBP)
The pressure in arteries and other blood vessels when the heart is contracting; the first (top) number recorded.
Diastolic Blood Pressure (DBP)
The pressure in arteries and other blood vessels when heart is at rest or between beats; the second (bottom) number recorded.
blood pressure levels in adults
normal: systolic <120, diastolic <80
elevated: systolic 120-129, diastolic <80
hypertension stage 1: systolic 130-139, diastolic 80-89
hypertension stage 2: systolic >140, diastolic >90
hypertensive crisis: systolic >180, diastolic >120
orthostatic vital signs
blood pressure & pulse taken lying, sitting, & standing and documented indicating the corresponding position
subjective data
things a person tells you about that you cannot observe through your senses; symptoms
objective data
information that is seen, heard, felt, or smelled by an observer; signs
Four key principles to inclusive assessment
1. treat every health assessment as an act of humanity
2. health assessments are not about "sameness"
3. examine your own personal biases
4. cultivate a safe environment of care
Cultural Sensitivity
recognizing and respecting the differences between cultures
cultural competency
the enabling of health care providers to deliver services that are respectful of and responsive to the health beliefs, practices, and cultural and linguistic needs of diverse patients
cultural humility
process that requires humility as individuals continually engage in self-reflection and self-critique as lifelong learners and reflective practitioners
Cultural safety
Culturally appropriate health services to disadvantaged groups while stressing dignity and avoiding institutional racism, assimilation (forcing people to adopt a dominant culture), and repressive practices.
Pain
is whatever the experiencing person says it is, existing whenever he/she says it does; should be accepted as such and respected
acute pain
short-term, self-limiting, often predictable trajectory; stops after injury heals
chronic pain
Enduring pain that does not decrease over time; may occur in muscles, joints, and the lower back, and may be caused by enlarged blood vessels or degenerating or cancerous tissue. Other significant factors are social and psychological.
intractable pain
severe pain that is extremely resistant to relief measures
intermittent pain
Pain that comes and goes at intervals
phantom limb pain
pain in a limb (or extremity) that has been amputated
radiating pain
starts at the origin but extends to other locations
referred pain
pain that is felt in a location other than where the pain originates
Quality of Pain Descriptors
stabbing, burning, itching, tingling, cramping, aching, dull, tender, shooting, sharp, pressure, crushing, throbbing, etc.
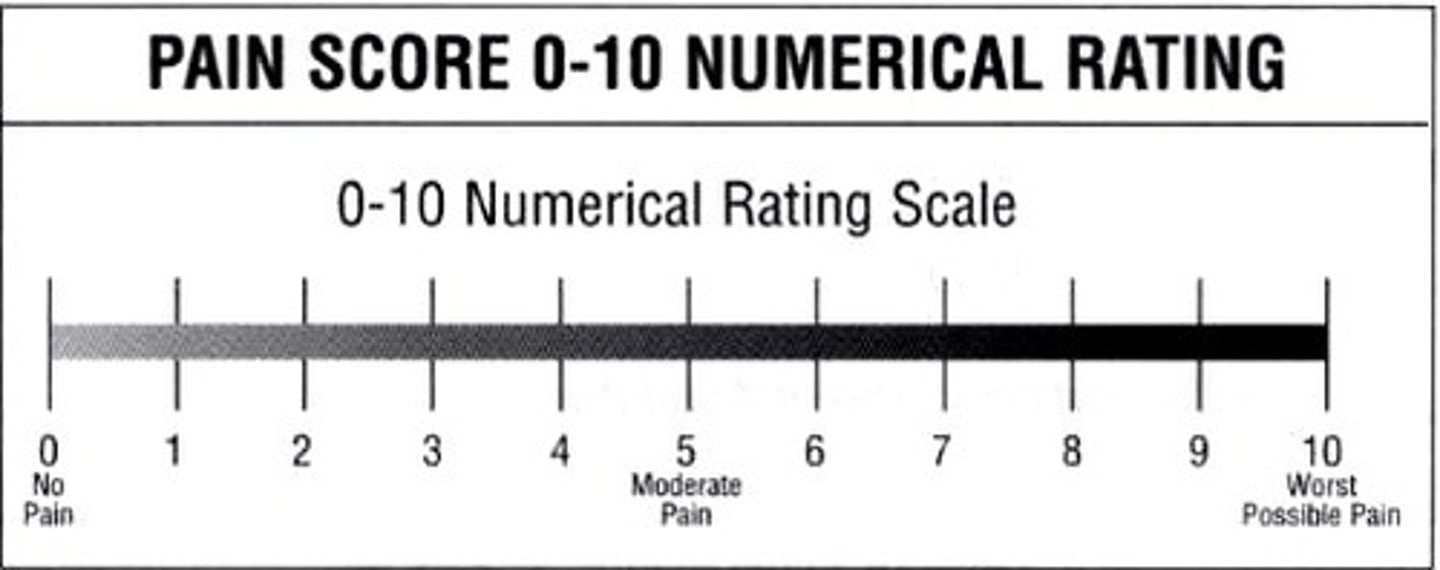
numeric rating scale
patient chooses level of pain for each site 0-10; most adults, but not old
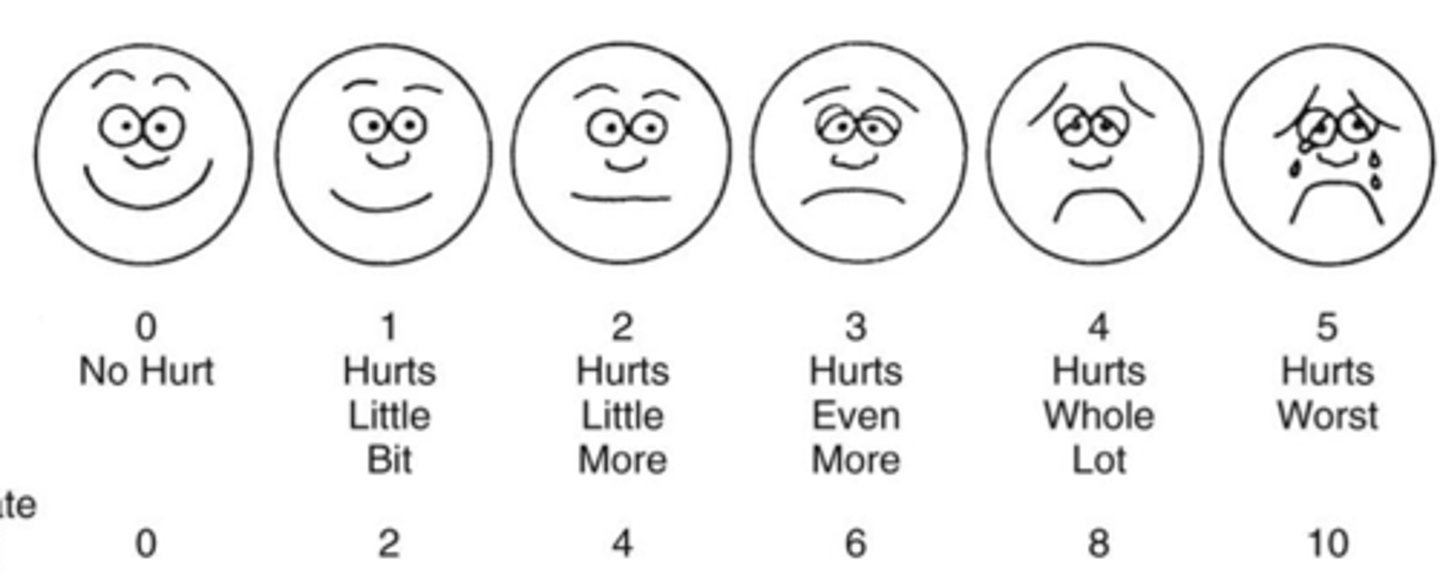
Wong-Baker FACES scale
a pain assessment tool that asks patients (often children) to select one of several faces indicating expressions that convey a range from no pain through the worst pain
PAINAD scale
assessment tool for pain used with dementia patients; assesses 5 common behaviors: breathing, vocalization, facial expression, body language, and consolability. A score of 4 or above indicates a need for pain management.
documentation of pain
Level of pain, description of pain, action taken, response to interventions
OPQRST (pain assessment)
Onset, Provocation, Quality, Region/Radiation, Severity, Timing.
OLDCARTS (pain)
Onset
Location
Duration
Character
Aggravating factors
Relieving factors
Timing
Severity