Chapter 16: Motivation
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/52
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
1
New cards
def 3 motivated beh
1. food
2. thirst
3. temperature
2
New cards
def 2 types of beh
1. Unconscious reflexes
2. voluntary movements
3
New cards
def motivation
the need or desire to do something
4
New cards
def 4 theories for motivation
1. evolutionary perspective
2. drive-reduction theory
3. optimal arousal
4. Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
5
New cards
analogy for motivation
ionic driving force - motivation depends on many factors
6
New cards
what 2 things vary with the driving force needed to perform the behavior
probability, direction
7
New cards
def Homeostasis
Maintains internal environment within a narrow physiological range
8
New cards
which part of the brain regulates homeostasis
hypothalamus
9
New cards
def 3 components of neuronal response
1. Humoral response
2. Visceromotor response
3. Somatic motor response
10
New cards
def humoral response
stimulating/inhibiting release of pituitary hormones
11
New cards
def visceromotor response
a reflex response to noxious stimulation of a visceral organ (the soft internal organs of the body)
12
New cards
def somatic motor response
voluntary muscle movement.
13
New cards
def 2 energy balance states
Prandial state—anabolism
Postabsorptive state—catabolism
Postabsorptive state—catabolism
14
New cards
funct: anabolism v catabolism
storing energy v using (breaking down) energy
15
New cards
Loading and Emptying the Body’s Energy Reserves
anabolism v catabolism
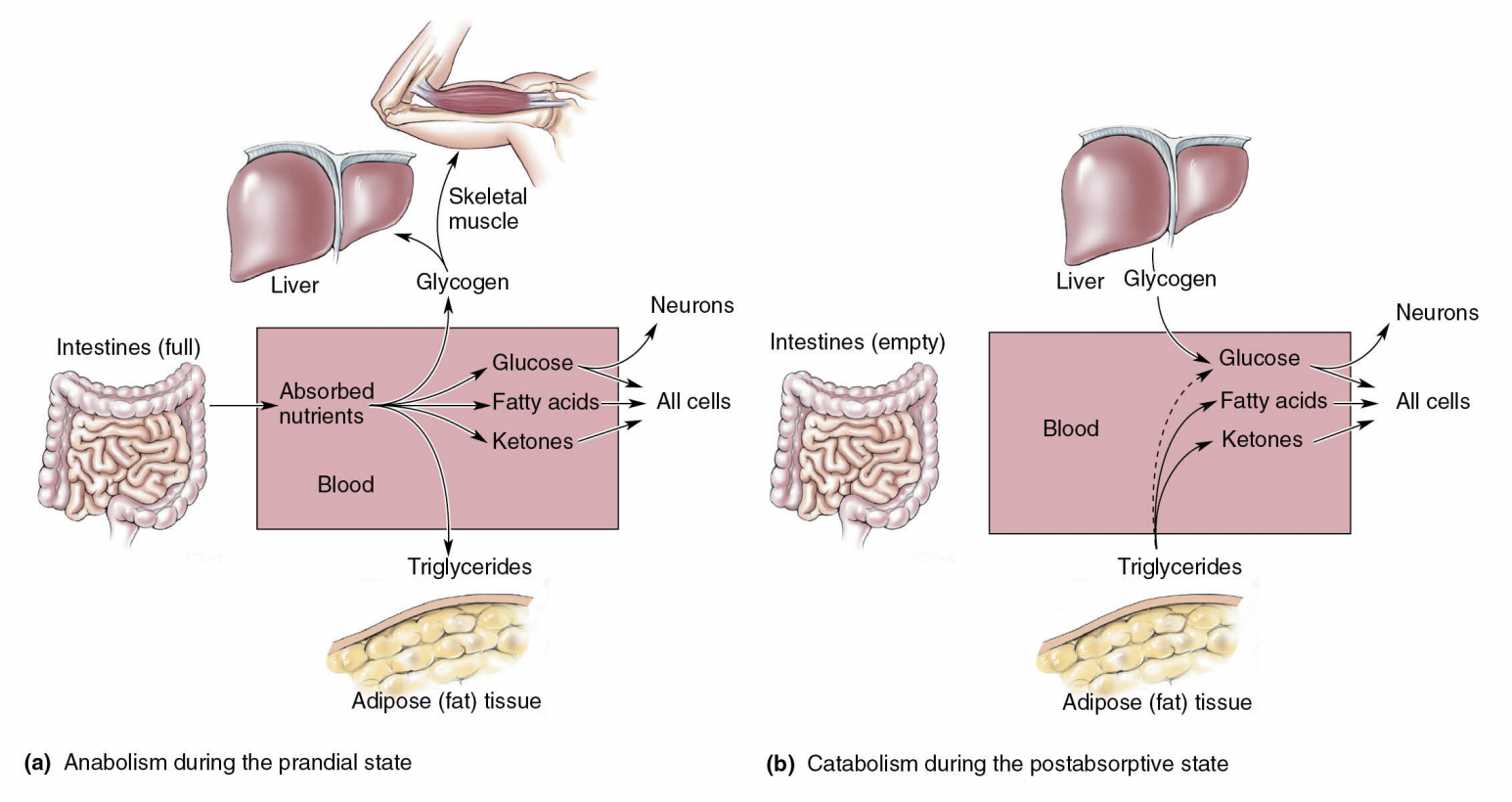
16
New cards
what hormone regulates body mass by decreasing what and increasing what
Leptin: Decreases appetite, Increases energy expenditure
17
New cards
what incites adaptive responses to fight starvation
leptin
18
New cards
what do experiments with parabiosis show (Lipostatic hypothesis)
our body has a set point of weight, we can adjust it with food, but usually regression to mean
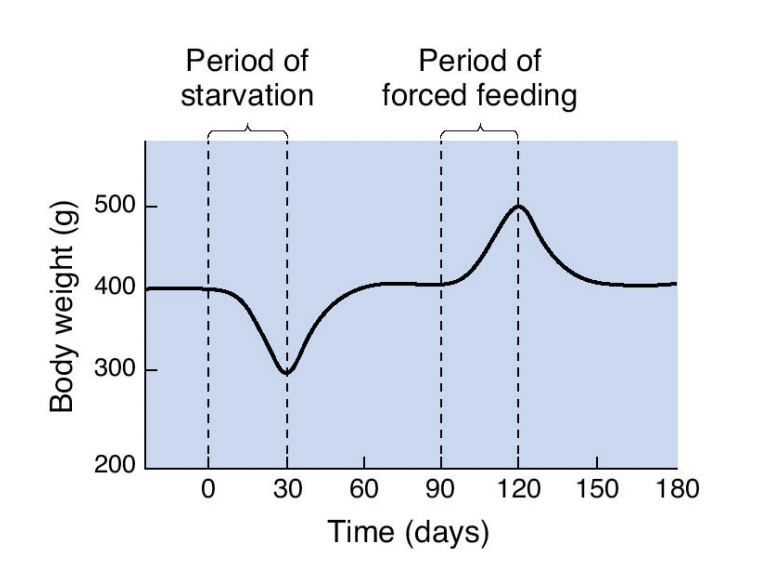
19
New cards
what disorder arises from lateral hypothalamic syndrome
anorexia
20
New cards
what disorder arises from ventromedial hypothalamic syndrome
obesity
21
New cards
what part of the hypothalamus controls feeding
Arcuate nucleus of hypothalamus
22
New cards
def 3 phases of regulation of Feeding
1. cephalic
2. gastric
3. substrate
23
New cards
def cephalic
hunger
24
New cards
what happens to Ghrelin during _____ phase
cephalic, it is released when the stomach is empty
25
New cards
what does ghrelin do once it is released in the cephalic phase
Activates **NPY/AgRP**-containing neurons in arcuate nucleus
26
New cards
Removal of ghrelin-secreting cells of stomach thought to cause…
loss of appetite
27
New cards
def gastric
feeling full
28
New cards
Gastric distension signals brain via during _____ phase
gastric, vagus nerve
29
New cards
Gastric distension works synergistically with ____ release
CCK
30
New cards
what peaks during eating a meal
insulin levels
31
New cards
insulin is released from β cells of the… and is important for…
pancreas, anabolism
32
New cards
both insulin and serotonin levels are highest during what phase
substrate phase
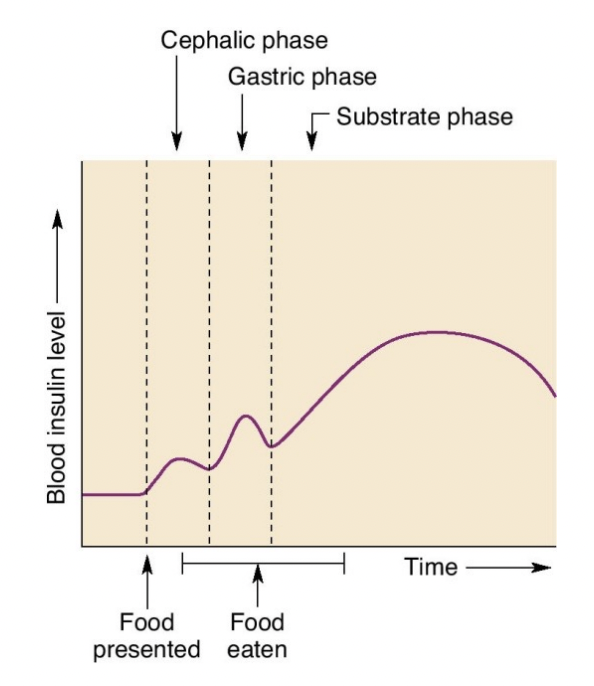
33
New cards
serotonin levels rise in… spike during… and are low during the… in what period of eating
* Rise in **anticipation of food**
* Spike **during meal**
* Low during the **postabsorptive period**
* Spike **during meal**
* Low during the **postabsorptive period**
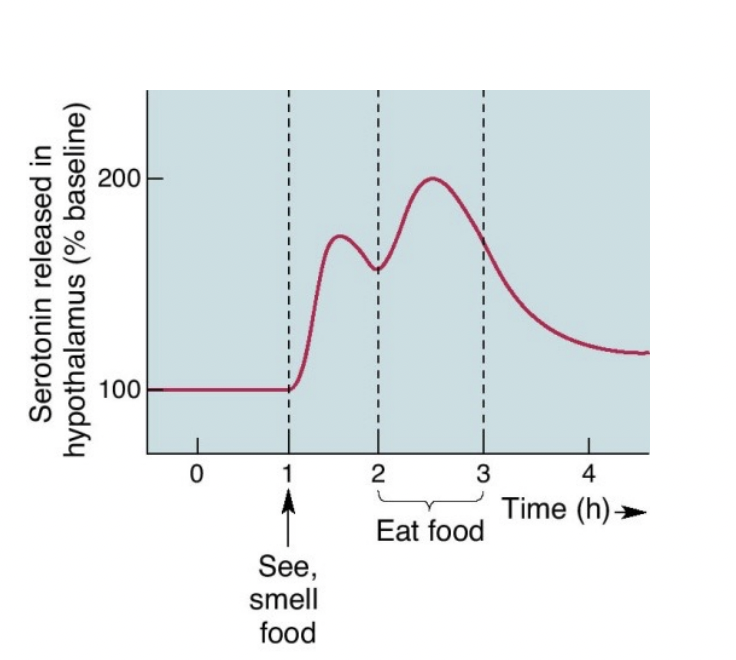
34
New cards
what NT is correlated with drive to eat
dopamine
* effective sites for self-stimulation: dopaminergic axons in the ventral tegmental area projecting to the forebrain
* drugs that block dopamine receptors: reduce self-stimulation
* Stimulation of the dopamine axons: Produces craving for food without increasing the hedonic impact
* effective sites for self-stimulation: dopaminergic axons in the ventral tegmental area projecting to the forebrain
* drugs that block dopamine receptors: reduce self-stimulation
* Stimulation of the dopamine axons: Produces craving for food without increasing the hedonic impact
35
New cards
eating: liking v wanting
hedonic v drive reduction
36
New cards
how do we identify brain sites of reinforcement
electrical self-stimulation experiments
37
New cards
Former belief of Role of Dopamine in Motivation
dopamine projection served **hedonic** (liking) reward
38
New cards
New understanding of Role of Dopamine in Motivation
* Dopamine-depleted animals “like” food but **do not “want” food.**
* **Lack motivation** to seek food but enjoy it when available
* **Lack motivation** to seek food but enjoy it when available
39
New cards
Disorders in which NT regulation results in anorexia nervosa or bulimia nervosa
serotonin
40
New cards
what is the automatic beh response when body is cold
mobilize: Body shivers, blood shunted away from the body surface, urine production inhibited, body fat reserves—mobilized
41
New cards
def Hypovolemia
pathway that decreases blood volume
42
New cards
what leads to volumetric drinking
hypovolemia
43
New cards
def hypertonicity
pathway that increased concentration of dissolved
substances in blood (solutes)
substances in blood (solutes)
44
New cards
what leads to osmotic drinking
hypertonicity
45
New cards
what hormone acts on the kidneys and increases water retention and inhibits urine production
vasopressin
46
New cards
vasopressin causes an inc or dec in drinking motivation
inc
47
New cards
when the temperature falls, what hormone is released
TSH
48
New cards
TSH is released by…
anterior pituitary
49
New cards
TSH stimulates release of…
thyroxin (from thyroid gland)
50
New cards
TSH leads to an inc in…
cellular metabolism
51
New cards
Food - Fat: location, blood leptin levels, aMSH/CART neurons, NYP/AgRP neurons, TSH/ACTH, sympathetic, parasympathetic, eat
hypothalamus arcuate nucleus, +, +, -, +, +, -, -
52
New cards
Drink - thirsty: humoral, visceromotor, somatic motor
inc vasopressin, inc sympathetic, drink
53
New cards
Temp - Cold: location, humoral, visceromotor, somatic motor
medial preoptic area, inc TSH, inc sympathetic (constricted blood vessels in the skin), shivering/seeking warmth