atoms, ions, compounds
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
isotope
atoms of the same element has the same amount of protons, but different amount of neutrons
relative atomic mass (Ar)
weighted mean mass of an atom of an element compared to an atom of carbon-12
relative formula mass
compares the mass of a formula unit with the mass of an atom of carbon-12
relative molecular mass (Mr)
compares the mass of a molecule with the mass of an atom of carbon-12
relative isotopic mass
the mass of an isotope relative to 1/12th mass of a carbon-12 atom
carbon-12
international standard measurement of atomic masses
mathematical expression for Ar
(isotope abundance x isotope mass number) / sum of abundances of all the isotopes
mass spectrometry
a technique that separates particles according to their mass
polyatomic ion
an ion made of two or more atoms
ammonium

hydroxide
OH⁻
nitrate
NO₃⁻
carbonate
CO₃²⁻
sulfate
SO₄²⁻
zinc ion
Zn²⁺
silver ion
Ag⁺
sulfide
S²⁻ (without oxygen)
sulfite
SO₃²⁻
hydrogen carbonate (bicarbonate)
HCO₃⁻
nitrite
NO₂⁻
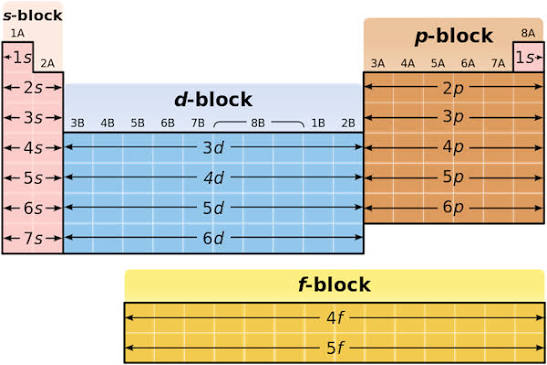
blocks on PT
S (metals) D (transition) P (nmetals) F
relative charge of
protons
electrons
neutrons
protons : 1+
electrons : 1-
neutrons : 0
relative mass of
protons
electrons
neutrons
protons 1
electrons 1/1836 of a proton
neutrons 1
cations and anions
cations : pawsitive ion (more E)
anions : negative ion (less E)
precipitate
an insoluble solid that forms from a solution during a chemical reaction, appearing as a solid cloud or settling to the bottom of the container